Immediately after birth, obstetricians or neonatologists, in addition to the mandatory general examination, check the newborn for a series of unconditioned congenital reflexes.
Their presence not only provides the baby with adaptive functions from the first minutes of life, but also speaks about his health.
The Moro reflex, along with the others, has been included in the list of mandatory checks for a child after birth for many years.
The essence of the reflex in children
The Moro reflex - in simple words, the fear reflex - is one of the innate unconditioned reflexes in a child in the first months of life. Normally, the reflex reaction to a potential threat is completely replaced by a conscious response by the age of six months.
The essence of the reflex is the baby’s response to a loud sound that is unexpected for him in the form of throwing up and spreading his arms wide to the sides. At the same time, the fingers of the hand are extended, and the pose is maintained for several seconds. After this, the hands return to their original position, the fists clench again, and the child tries to assume the fetal position.
Note! Such testing often provokes the baby to cry, which is completely normal.
Moro reflex in a baby - what is it, how long does it last and how does it manifest itself?
A baby is born with a whole set of natural reflexes, with the help of which he survives in a new world. Unfortunately, the child does not have instructions, and therefore many young parents begin to panic when faced with some phenomenon that was previously unfamiliar to them. As a rule, most parents get scared when their baby throws up his arms. A similar phenomenon was called the Moro reflex.
This phenomenon is also commonly called the startle reflex. New parents, not aware of its existence, turn to the pediatrician with the question of why their baby throws up his arms for no reason. And some even grab the baby and run with him to the neurologist. The Moro reflex is present in newborns, but it quickly fades away over the course of several months. The presence of this reflex is checked by a neonatologist. He lays the baby on his back and removes his hand from under it. In addition, the Moro reflex occurs with an unexpected, loud sound, for example, with a sharp clap near the crib where the newborn is lying.
Parents, who know that this phenomenon is quite normal, even consider such a reaction of the baby funny, and therefore occasionally cause it on purpose, for example, to amuse their friends. Doing this is strictly prohibited! Despite the fact that the Moro reflex in itself is not dangerous, the baby does not throw up his arms because he is happy. This action is provoked by tremendous fear, since the baby is sure that he is falling, and therefore strives to grab onto his mother. We can say that he is actually saving his life. A newborn cannot yet understand that he is safe. That is, every time the Moro reflex is triggered, it is a real stress for the child’s body.
Parents may not notice, but every time this reflex occurs, the baby’s breathing and heartbeat quicken, and an increased dose of adrenaline is produced. Often, after throwing up the arms, the baby begins to cry. We can say that for a newborn the Moro reflex is a strong fear.
It goes without saying that it will not be possible to completely avoid the manifestation of the reflex. In particular, if there are pets in the house, the family lives on a noisy street, or the baby has young brothers and sisters. Throwing up the arms can be triggered by a loud sound, a sudden movement of a parent with a baby in their arms, an excessively fast movement of putting them into a crib, etc. In addition, the Moro reflex in the same newborn can manifest itself even with minor factors, but, on the contrary, it cannot be observed with loud sounds. For parents, this situation should not cause concern.
As a rule, the Moro reflex completely disappears after 9–12 weeks of the baby’s life. However, if the reflex persists for a longer period and does not fade even after 5 months of age, then the baby should be shown to a specialist. In addition, the absence of this reflex or its distortion indicates problems with children's health. You must always carefully monitor what is happening to the baby, how he reacts to the environment.
How is the reaction in a newborn checked?

The most optimal time is the first half of the day, 1.5-2 hours after feeding .
The reflex is tested in several ways:
- Clap your hands loudly in front of the baby's face.
- The child is picked up, lifted up, and then sharply lowered down.
- The newborn lies on his back. The child's legs are straightened and sharply raised upward along with the pelvis. The response should manifest itself in a similar way if you press the baby’s arms tightly to his chest and then abruptly release them.
- At a distance of approximately 20 cm from the head of the lying child, make a sharp clap on the surface of the mattress.
During any of the listed test options, the child opens his arms wide to the sides with open palms, and then returns them to their original position. The mechanism of action is very similar to the fact that the baby is urgently trying to grab onto someone or something at this moment of perceived danger.
It is best to conduct dynamic testing during a massage or playing with a child. It is definitely worth taking into account the peculiarities of the child’s nervous activity. How bright the reflex is will depend on this. For example, an easily excitable baby will have an active reaction, while a phlegmatic baby may react rather sluggishly, but this is still not a reason to talk about deviations from the norm.
It is advisable to repeat the test periodically for as long as the reflex should be present: until the baby is 6 months old. The best option is once every 14 days.
Reference. The initial purpose of testing is to check the full functioning of the child’s central and peripheral nervous system. The manifested reflex causes a high degree of stress in the baby with the release of adrenaline, rapid breathing and heartbeat.
No matter how comical the child may look, it is strongly not recommended for young parents to use such a test for fun.
The essence of the reflex
The Moro reflex can be observed immediately after birth. Thus, obstetricians and neonatologists test the baby for various reactions, which, in turn, can show the state of the nervous system and whether there are any abnormalities in brain activity.
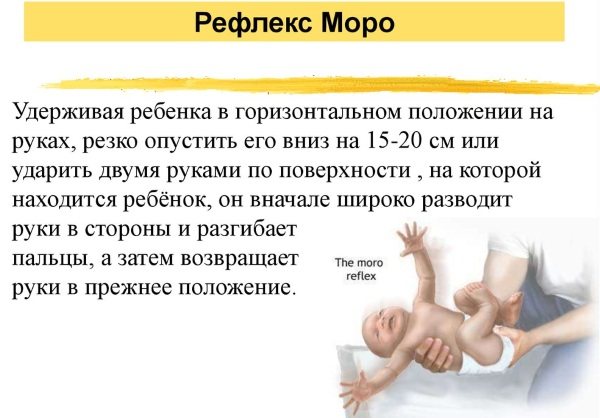
The essence of the test is as follows: the baby is placed on a flat, hard surface on his back. Then the doctor hits the surface with his hand at a palm distance (about 15 cm) from the baby’s head or makes a loud bang. As a response, the baby's arms sharply throw back, he moves them symmetrically to the sides, straightening his fists. This is the so-called first phase of the reflex, lasting several seconds. In the second phase, the handles slowly return to their original position, the cams are compressed.
When testing the Moro reflex, a baby's crying is normal.
Similar symptoms are also observed if a baby is held in your arms, lifted up, and then sharply lowered down. Another check is this: the legs of a baby lying on his back are straightened and they are lifted together with the pelvis, as if upward. The reaction with handles will be the same.
When does the reflex go away? Complete extinction occurs at approximately 6 months. Up to 4 months it is quite well expressed, and from 4 to 6 only its individual fragments can be observed.
What should be the conditions for assessing the Moro reaction? It is very important that at the time of the test the baby is calm, moderately full (recommended in the morning - 2 hours after feeding) and healthy.
Manifestation in a dream in a baby

Involuntary sudden movements can appear at any, even the deepest, phase of the baby’s sleep.
The reflex can be triggered by loud sounds made by pets, any noise, or a careless sudden movement of one of the parents.
Over time, the baby's violent reaction to external stimuli will fade away more and more, and the reflex will manifest itself only selectively.
Other reasons for a child to startle in his sleep
The causes of startles during sleep can be the baby's transition from one phase of sleep to another. Typically, muscle twitches, eye movements and sounds occur during REM sleep. Babies dream, and their body reacts to this with motor acts. This is typical for children in the first months of life, until the routine is definitely established. After three years, such problems usually disappear.
Restlessness and shaking during sleep are typical of colic or teething. Thus, children react to pain impulses. It is important to eliminate any irritants to normalize sleep.
Loud sounds and noise can frighten a child, so it is important to create a calm environment, but do not teach your child to sleep in perfect silence. Excessive heat and uncomfortable posture, as well as a feeling of insecurity, may have an effect.
Pathological manifestations
The Moro reflex is also characterized by spontaneous manifestations. Even if any external irritant could not cause such a reaction, the baby can throw up his arms and spread them to the sides. In some cases, this indicates increased intracranial pressure in the infant and requires consultation with a neurologist.
An incomplete reflex reaction is also considered a deviation from the norm: the child only slightly spreads his arms. As a rule, this indicates hypertension. If the baby holds his arms apart for a long time with his fingers open, this is a sign of damage to the central nervous system to one degree or another. And the lower the threshold for the manifestation of the reflex, the higher the likelihood of problems with the central nervous system.
An asymmetric reaction, when the baby moves to the side, for example, only the right arm and right leg, may be a symptom of Erb's palsy or cerebral palsy.
In premature babies or those who have experienced asphyxia during childbirth, the reflex may appear late. With timely treatment measures, proper care and nutrition, the reaction will manifest itself over time.
Symptoms
Moro syndrome allows the baby to take its first breath when leaving the birth canal.
Subsequently, the correct symptoms can be checked as follows:
- Lightly and unexpectedly hit the pillow on which the newborn's head rests. At the same time, the child’s arms, which were previously in a half-bent position, move apart and the fingers spread out.
- If you suddenly slightly stretch the child's legs, he creates a movement of his arms similar to the first situation. The arms move to the side, the fingers expand, and then everything returns to its original position.
- You can check it in another way. Slam the changing table on which the baby is lying. In response, he will spread his arms and straighten his bent legs. After 2-3 seconds. will return to its original position. You can also take the child by the hind legs and slightly stretch them out and lift them. The reaction will be the same.
This is a normal reactive state, on the basis of which it is concluded that the child’s reflexes are fine. This syndrome should normally be present for up to 4–5 months.
Moro reflex
In the future, you should carefully monitor the baby's involuntary movements. If a child often spreads his arms for no reason, and his movements are asymmetrical, then you should pay attention to this and seek advice from a pediatrician.
In infancy, the syndrome is triggered by the sensory system, but if it does not go away later in life, it causes problems. The adrenal glands begin to work in increased mode, which leads to hyperactivity and subsequently problems with attention.
Once the adrenal glands become tired from overstimulation, the child typically develops chronic allergies, asthma, autoimmune and other health problems associated with adrenal fatigue. In addition, when the body is constantly in "crisis mode", the brain is in an excited state and cannot store or perceive information. This leads to further problems in learning.
In subsequent years, one can observe clinical manifestations of the pathological activity of the reflex, which was not completed in infancy:
- aggressiveness;
- isolation;
- increased sensitivity;
- difficulty communicating with others;
- immature emotions;
- increased imagination.
Changes also occur at the hormonal level:
- decreased cortisol production;
- excess norepinephrine;
- blood deposition (its accumulation in venous vessels).
If missing

As a rule, in this case, a number of reflexes are suppressed and the Apgar score is low.
This is a widespread phenomenon in acute oxygen starvation of the fetus, extreme prematurity, or due to severe problematic labor.
The absence of a reflex indicates one of these problems:
- pathologies of the cervical vertebrae;
- brain stem damage;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- cerebral edema.
Attention! All of the listed possible pathologies are serious cerebral lesions that require immediate and adequate treatment.
The child should be under systematic supervision of a pediatrician and neurologist. All kinds of testing for reflexes in infants are indicators of the health of their nervous system. And this is a good reason to begin eliminating the existing problem immediately in order to avoid even more severe complications in the near future.
How to get adequate results?
When conducting diagnostics and determining the level of development of the baby’s reflexes, it is necessary to take into account the following factors and basic positions:
- physiological, general condition of the baby - he should be well-fed, rested and not overexcited in any way, the general state of health must also be taken into account, whether he is tired or not, healthy or sick, and if he is not feeling well, it is recommended to postpone the study;
- the Moro reaction is checked in the dynamics of its manifestation, not limited to a single test - it is best if this is done in the morning, 1.5-2 hours after feeding;
- The characteristics of nervous activity and the level of excitability of the child are taken into account.
When assessing the results, the main thing to pay attention to is how pronounced the fear reaction is, the timing of the first and second phases.
The characteristics of the reaction give an idea of how adapted the child is to the world around him.
Sometimes parents can observe a spontaneous Moro reflex in a baby - this means that the baby can throw his arms to the sides, opening and closing his fingers even in the absence of both internal and external stimuli. It is recommended to show the child to a neurologist and pediatrician, as this may indicate numerous health problems.
Pathological causes of flinching
Periodic, repeated shuddering and jumping up with crying and impaired muscle tone are signs of pathologies. With such complaints you should consult a doctor. The causes may be metabolic disorders and metabolic disorders of the nervous system with the formation of convulsions and muscle spasms. This is possible with irrational feeding with a deficiency or excess of certain substances - lack of calcium and vitamin D with the development of rickets, disruption of the parathyroid glands with the provocation of spasmophilia.
Poor sleep and trembling are possible with increased intracranial pressure, which is formed due to birth injuries or congenital abnormalities of the brain structure.
Sharp shudders are typical of increased nervous excitability. This happens with hypoxia during childbirth or in utero, after an injury.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
1, total, today
( 53 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
How to reduce your breast milk supply
Is it possible to give a newborn water, feeding infants: pros and cons