About the sucking reflex: weak or absent sucking reflex
A weak sucking reflex or its absence in a newborn is determined by a simple method - feeding the baby. If the baby is healthy, then he immediately takes the breast and sucks greedily. Newborns who experience a decrease in this important reflex for life suck sluggishly, rarely swallow, periodically refuse the breast, and may fall asleep during feeding. A decrease in this unconditioned reflex occurs for various reasons:
- hypoxia during childbirth or pregnancy;
- neuralgic syndromes (eg, weakening of the facial nerves);
- severe somatic diseases;
- rhinitis, stomatitis, ARVI;
- flat shape of the mother's nipples.
With a reduced sucking reaction, the child is malnourished, which means he does not receive the norm of nutrients, which affects his development. The solution to the problem may be to feed the baby with a spoon or bottle every two hours. This should only be done on the recommendation of a doctor.
Why is there no sucking reflex in a newborn, what is the reason for this? The absence of such an important reflex for survival indicates a serious pathology. The diagnosis can only be made by a doctor, but if a newborn has a lack of sucking reflex, then the reasons for this usually lie in the neuralgic plane.
Such a symptom may indicate damage to the central nervous system, which will affect the further development of the baby. The reason for the absence of a reflex may be weakness of the muscles of the mouth and tongue, chewing muscles. In the complete absence of the sucking reflex, the newborn is fed through a tube. Inferiority of basic reflexes is often observed in premature infants.
The sucking reflex may be absent when:
- Paresis of the facial nerves.
- Severe somatic illness of the child.
- High degree of mental retardation.
- Hypoxia during pregnancy or childbirth, causing damage to the central nervous system.
- Weakening of the muscles responsible for chewing, the muscles of the tongue and mouth.
- Deep prematurity.
- Birth injuries of the spinal cord.
Diseases such as acute respiratory viral infections, stomatitis or a runny nose can lead to a decrease in the sucking reflex. Also, its weakened degree can be provoked by flat nipples in the mother.
Weakness or complete absence of the sucking reflex can be determined during feeding. Healthy babies immediately energetically grab their mother's breast and suck it greedily. But newborns who have a reduced reflex fall asleep during feeding, they are constantly lethargic, rarely swallow and often refuse to breastfeed altogether. Premature and weakened babies are discharged from the hospital only when they can suck on their own.
When does a premature baby develop a sucking reflex? In a baby who is developing normally, the swallowing reflex appears at approximately 10-11 weeks of development inside the womb, and the sucking reflex appears at 29 weeks. The sucking reflex in premature babies develops later and manifests itself worse, and sometimes is completely absent. Therefore, such children need to be fed through a catheter, using a pipette or spoon.
You can check a weakened sucking reflex in this way: put your finger in the child’s mouth, if he has no deviations, then the baby will begin to instinctively suck his finger. The main reasons why this reflex decreases:
- severe somatic conditions;
- hypoxia during pregnancy and during the birth process;
- paresis of the facial nerves;
- mental retardation;
- in some cases - acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections and stomatitis.
The absence of a swallowing reflex in a newborn indicates damage to the central nervous system (brain), and this is an extremely negative neurological sign. If a baby lacks these reflexes, he simply cannot survive. These children are fed through a tube. Sometimes difficulty sucking or its absence can be a consequence of birth trauma. Also among the main reasons is neurological pathology, such as weakness of the tongue, orbicularis oris muscle and masticatory muscles.
Due to injuries to the neck or cervico-occipital zone, the medulla oblongata is damaged, resulting in a decrease in the sucking reflex. Due to such injuries, the overall development of the baby slows down. By the presence of natural reflexes, one can judge the baby’s health and the state of his central nervous system.
The content of the article
The sucking reflex in newborns is a vital reflex that triggers many important processes in the baby’s body, and most importantly, allows him to get food, because in the near future the baby will be able to eat only breast milk or formula from a bottle.
Somewhere between the third and fourth year of life, the baby's sucking reflex disappears. This is why many people believe that it is necessary to breastfeed a child up to 4 years of age, as this is inherent in nature.
Unfortunately, it happens that for some reason in some newborns this reflex is very weakly expressed or absent altogether. It is quite simple to check this - just put your finger in the baby’s mouth, and if he does not have any developmental abnormalities, he will instinctively begin to suck his finger.
The sucking reflex is a very complex physiological act, which involves five pairs of cranial nerves that are located in the brain.
The main causes of impaired sucking reflex in newborns are paresis of the facial nerves, mental retardation, severe somatic conditions, and other abnormalities in the central nervous system.
Most often, the risk group includes babies who have suffered hypoxia during pregnancy or childbirth.
In more rare cases, the causes of a decrease in the sucking reflex may be ARVI, acute respiratory infections, stomatitis and other viral diseases.
As soon as you notice any abnormalities, be sure to contact a neurologist or therapist. It is very important to remember that such states are very important to observe in dynamics, i.e. visit the doctor regularly, tracking the trend.
The vital sucking reflex that allows a newborn to survive may be weakened for several reasons:
- paralysis of facial and cerebral nerves;
- severe somatic disorders that weaken the body;
- mental retardation;
- intrauterine oxygen starvation, causing damage to the nervous system.
We suggest you read: How long do newborns lie with jaundice?
Viral and infectious ailments, acute stomatitis, and a severe runny nose can reduce the sucking reaction. Since the baby is regularly malnourished, he has to be fed with expressed milk from a spoon, syringe, pipette or bottle. The baby may suck poorly due to the mother's flat, inverted nipples. But these cases are rare, and they can be dealt with using special silicone nipple covers.
When it turns out that the reflex is weakened, mommy should take immediate action. After all, this threatens a newborn with malnutrition, underweight, mental and neurological disorders, leading to developmental delays.
The subsidence of the sucking reflex requires an immediate visit to a neurologist and constant medical supervision of the child.
- birth injuries leading to damage to the medulla oblongata;
- deep prematurity;
- weakened facial muscles
cause the complete disappearance of the sucking reflex. The neurologist should examine the baby and evaluate his other unconditioned reflexes. After which observation will be carried out. Therapeutic treatment may be required.
The sucking reflex in premature babies is always weakened or completely absent. So that the child can develop normally, after birth he is fed through a tube or special nutritional solutions are administered intravenously. This method of feeding lasts until the sucking reflex appears to a pronounced degree and the nervous regulation mechanisms responsible for the baby’s reactions develop.
When a baby is reluctant to suck, the question of how to restore the reflex becomes paramount. This is where pacifiers and feeding the toddler with milk from a bottle come to the rescue. The doctor recommends a facial massage before each feeding. To restore the reaction, you should know the cause of the weak reflex, and, if possible, work to eliminate it. Without consulting experienced specialists, you cannot deal with the problem on your own. This is dangerous for the baby.
The vital activity of the body of every person, including a newborn, is determined by reflexes.
Reflexes of a newborn are a response to stimuli from the internal and external environment of the body. Innate reflexes are embedded in the nervous system even before the birth of a child.
The sucking reflex in a newborn is the ability to suck on the mother's breast or the nipple on a bottle of artificial nutrition placed in the mouth. Nobody teaches a baby to suck. This is not a habit, but one of the important reflexes. It is formed during the intrauterine development process. And in the future it has an impact on the formation of the psyche in early childhood. With the help of the sucking reflex, the newborn satisfies its hunger.
It occurs for the first time in life and is one of the innate reflexes that ensures the baby’s survival. This is the very first and most important unconditioned reflex. During feeding, when the palate touches, the baby begins to suck milk from the mother's breast or from a bottle and sucks it in. The severity of the sucking reflex in newborns is determined by whether the child is hungry or full. After eating, the sucking reflex weakens. But within an hour it makes itself felt again. Rhythmic sucking calms the baby very well.
Responsible for the sucking reflex are 5 pairs of cranial nerves. For the baby, it is a pleasure to suck on a pacifier and a very hard job to suck milk from the mother's breast.
By 12 months, the sucking reflex weakens, and by 3-4 years it disappears.
It is very easy to check the sucking reflex in a child: you need to stroke the cheek or touch the lips. The baby will open his mouth and move his tongue as if he wants to suck.
Weakness or absence of the sucking reflex is determined by the feeding method. Healthy babies immediately and vigorously latch onto their mother's breasts and suck greedily. Unlike healthy babies, newborns with a reduced sucking reflex fall asleep during feeding, are lethargic, swallow very rarely, and often refuse the breast altogether. Weakened and premature babies are discharged from the hospital when the baby can suck on his own.
How to determine if the sucking reflex is normal
In order to awaken the sucking reflex, a bent finger is inserted 2-3 cm into the baby's mouth. A healthy full-term baby begins to suckle immediately. If the reaction is well developed, touching the lips and stroking the cheek is enough. The baby will open his mouth and begin to move his tongue intensively, as if sucking.
When assessing the sucking reflex, test feeding is used. They give the baby breastfeeding or a bottle of formula and see how he copes. With a weak reflex, the baby sluggishly sucks food. He quickly loses strength, rarely swallows and falls asleep. Subsequently, interest in the breast is lost, and the baby is even able to refuse it.
What to do if it is absent or weakly expressed
The absence or pronounced weakness of the sucking reflex should be responded to immediately, because this threatens the baby with malnutrition, as a result of which the baby may lag behind in development. If your mother notices such a weakening, you should immediately consult a doctor. The neurologist will check it and other innate reflexes of the baby, after which he will monitor the baby or prescribe the necessary treatment.
In a situation where he is not present immediately after birth, the baby begins to be fed either through a tube or parenterally (nutrient solutions are administered through a vein). This is especially common in babies who were born prematurely. They are not discharged home until the reflex is sufficiently restored.
Reasons for absence or weakening
The sucking reflex may be absent when:
- Paresis of the facial nerves.
- Severe somatic illness of the child.
- High degree of mental retardation.
- Hypoxia during pregnancy or childbirth, causing damage to the central nervous system.
- Weakening of the muscles responsible for chewing, the muscles of the tongue and mouth.
- Deep prematurity.
- Birth injuries of the spinal cord.
Diseases such as acute respiratory viral infections, stomatitis or a runny nose can lead to a decrease in the sucking reflex. Also, its weakened degree can be provoked by flat nipples in the mother.
Restoring the reflex
The identified weak reflex at birth will not allow the mother and baby to get home on time, as doctors will eliminate the causes of the weakened habit. Discharge will be possible only after restoration of function.
If the sucking reflex has been weakened already during the life of the baby, then the first action of the mother is to contact a pediatrician and neurologist. Only after their consultations and recommendations should the cause be eliminated.
Weakening of sucking function occurs against the background of one of the above reasons. The reflex can be improved if you approach it responsibly and systematically. In most cases, weakened function is restored by organizing more frequent feedings. If you are breastfeeding, you may need to express milk and bottle feed your baby.
An additional method of developing the reflex can be a prescribed massage of the facial muscles. The doctor must teach the mother the correct massage movements, which she will regularly perform on the baby’s face.
We suggest you read: Massage of the lacrimal canal in newborns with dacryocystitis
It is important not only to teach the baby a new skill, but also to monitor the dynamics of development. Self-medication in this case is strictly prohibited, and during the restoration of function, be sure to regularly consult with a doctor until the problem ends.
An unsatisfied sucking reflex can lead to atrophy of function, so it is very important to feed the baby, if he is breastfed, on demand. Formula-fed newborns should be fed from a bottle with a small hole so that they eat for at least 15-20 minutes. The pacifier has a positive effect on maintaining and developing the sucking reflex.
A child’s health is formed by a number of reasons, both external and internal. Maintaining the necessary balance falls entirely on the shoulders of the parents; it depends on them how the child will grow and develop, how healthy and fulfilling his future will be.
If the baby sucks very weakly, the question of how to develop it is extremely important for his health. Organizing feedings, using a pacifier and bottle feeding helps with this. The doctor will also recommend performing a special facial massage before feeding. Of course, for successful recovery it is important to take into account the reason for its weakening, so no action should be taken without consultation and advice from a doctor.
You can learn about the benefits of a pacifier in its development by watching the following video.
How long does this phenomenon last?
Until what age does a newborn develop a sucking reflex?
As already noted, a born baby begins to suck after 2-3 hours, and the formation and emergence of this reflex occurs long before birth. A few hours after birth, the baby begins an active search for the mother's breast in order to realize its natural instinct.
The duration during which the sucking reflex in infants is most pronounced is the first 12 months of life. Then, closer to a year, it begins to weaken. And by about 3-4 years it disappears completely.
For this reason, many experts agree that breastfeeding is necessary until the sucking reflex completely disappears in accordance with the norms inherent in nature.

The weakness of the touch instinct can be determined during the feeding process. Healthy babies immediately and greedily take their mother’s breasts and suck on them quite actively. And newborns, in whom this reflex is reduced, fall asleep during feeding, they rarely swallow, are lethargic, often completely refusing the mother's breast.
The main reasons for a decrease in the sucking reflex in a newborn include:
- hypoxia during pregnancy or childbirth;
- severe somatic conditions;
- mental retardation;
- paresis of the facial nerves;
- sometimes ARVI, stomatitis.
The reason may also be improper attachment of the baby to the mother's breast:
1. First, make sure that the baby is completely awake and wants to eat. To do this, run your finger along the corner of your mouth. If the baby is hungry, he will try to grab your finger, confusing it with the nipple.
- the baby's chin is pressed to the chest;
- his mouth is wide open;
- the lower lip is pushed down;
- the distance between the baby's upper sponge and the nipple should be greater than under the lower one.
3. If the baby has difficulty breathing (due to a cold or runny nose), this is also an obstacle to the full implementation of the reflex. At the same time, the baby will suck sluggishly and take breaks.
4. Also, the reason for the weakening of the instinct may be the incorrect shape of the nipples (inverted) - use special pads.
If you cannot cope with the problem, it would be more advisable to contact a breastfeeding specialist, since this trouble may hide serious disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.
If the sucking reflex is absent, this is the first sign that the functioning of the central nervous system, specifically the brain stem, is disrupted and this is a dangerous neurological symptom. In the complete absence of this reflex, the baby has practically no chance of survival.
The reason for the absence of the sucking reflex is usually a neurological pathology:
- weakness of the chewing muscles;
- language;
- orbicularis oris muscle.
Any self-medication on the part of parents in this case is unacceptable. At first, you will need to feed your baby with a spoon. But consultation with a specialist is necessary.
The presence of reflexes indicates the full state of his central nervous system. In the process of their formation, the child’s gradual, full development occurs.

The vital functions of the body largely depend on reflexes. For newborns they are also extremely important. The baby’s body reacts in a certain way to various stimuli. Innate reflexes in the baby’s nervous system are formed in the womb.
Every newborn baby must develop a sucking reflex. When a bottle of food is placed in his mouth or his mother gives him breast, he begins to actively suck on it. Nobody teaches this to a child. And this is not a habit, but an important reflex that ensures normal functioning. The sucking reflex is formed in the womb and affects the development of the newborn. This reflex allows the child to satisfy his hunger.
Already in the very first hours after birth, the sucking reflex is triggered to ensure survival. At this stage of life, it is the most important thing for a child. When the breast or nipple touches the roof of the mouth during feeding, the baby automatically begins to suck on it. If the child is hungry, the reflex will be more pronounced, but if the child is full, it will be weaker. An hour after the baby is fed, the reflex becomes stronger again. Rhythmic sucking perfectly calms the baby.
The cranial nerves are responsible for this innate reflex. Sucking at the breast is a difficult task for a baby, but he enjoys sucking on a pacifier.
When a child reaches the age of 12 months, the sucking reflex becomes much weaker and disappears completely at about 3-4 years.
To check for a sucking reflex in a newborn, you need to lightly stroke his cheek or touch his lips. He should open his mouth slightly and start moving his tongue.
How many months does the sucking reflex last in a child, why can it be weak or absent?

Detailed article on the basic reflexes of newborns
The sucking reflex in a newborn is the ability to suck on the mother's breast or the nipple on a bottle of artificial nutrition placed in the mouth. Nobody teaches a baby to suck.
This is not a habit, but one of the important reflexes. It is formed during the intrauterine development process. And in the future it has an impact on the formation of the psyche in early childhood.
With the help of the sucking reflex, the newborn satisfies its hunger.
It occurs for the first time in life and is one of the innate reflexes that ensures the baby’s survival. This is the very first and most important unconditioned reflex.
During feeding, when the palate touches, the baby begins to suck milk from the mother's breast or from a bottle and sucks it in. The severity of the sucking reflex in newborns is determined by whether the child is hungry or full. After eating, the sucking reflex weakens.
But within an hour it makes itself felt again. Rhythmic sucking calms the baby very well.
It is very easy to check the sucking reflex in a child: you need to stroke the cheek or touch the lips. The baby will open his mouth and move his tongue as if he wants to suck.
Children are born with certain basic skills that help them survive, thrive, and thrive. The sucking reflex in newborns is one of the most important instincts inherent in nature. It is the presence or absence of the sucking reflex that is responsible for the timely and complete development of the newborn.
The lack of sucking skill in children does not allow them to eat. Even if you pour milk into the baby's mouth, he will not be able to swallow it. Such children are fed by tube or intravenously and their lives depend on whether this habit can develop in the future or not.
The presence of a reflex indicates the health of the baby and his central nervous system. A weakening of the skill is usually associated with improper actions of the mother or acquired diseases. We will talk in more detail in this article about how to check the presence of the instinct to satisfy hunger, how to develop it and why it is absent or weakened.
The formation of the sucking reflex in a newborn occurs in utero. A newborn baby is ready to suck on his mother’s breast or bottle; this process not only saturates him, but also calms him.
By the way, this is why many babies suck their fingers, fists or pacifiers. If a child lacks this natural skill completely, then, unfortunately, it is impossible to develop it.
Exceptions are premature babies, who, due to being born too early, could simply not have developed this habit.
In a healthy newborn, this skill is clearly expressed at birth and remains highly active for up to a year. The extinction of the sucking reflex occurs by 3-4 years.
At birth, doctors first assess the presence and extent of this innate habit. To do this, you just need to touch the child’s cheek or lips. If the reflex is increased, the baby will immediately begin to smack his lips, as if imitating sucking.
If there is no reaction to such a stimulus, a finger is inserted into the child’s mouth to evaluate sucking skills.
If the baby reacts sluggishly and inactively, then this indicates a weak skill, which will interfere with the necessary absorption of food and weight gain, all this will lead to general underdevelopment of both physical and psychosomatic indicators. If sucking is weak, a number of measures are taken to develop the skill.
An absent or weak sucking reflex is a serious cause for concern for adults. In both the first and second cases, medical assistance is needed.
The sucking reflex in premature infants may be completely absent or weakly expressed. When the lack of a formed habit is due only to the child’s prematurity associated with his early birth, then it can be acquired by gaining the required weight and growing the baby a little.
All this time, the newborn will be in the hospital, and nutrition will be delivered to him by a tube directly into the esophagus or intravenously through injections. If the habit is absent due to damage to the central nervous system, then, unfortunately, it is very difficult, and sometimes simply impossible, to help the baby.
- Stiffness of the facial nerves, which does not allow the baby to make sucking and swallowing movements.
- Somatic diseases.
- Mental retardation to a high degree.
- Underdeveloped or very weak muscle system around the mouth that moves the tongue.
- Acquired colds, leading to a runny nose and swelling, as well as stomatitis, which causes extremely painful sensations in the child when sucking.
Nipples that are uncomfortable to grasp and suck on can also weaken your baby's sucking reflex. If he has to make a lot of effort to extract milk from his mother’s breast, then he may simply fall asleep from fatigue during feeding, and gradually develop the habit of constant malnutrition, which will affect weight gain, the formation of the muscular system and the overall development of the child.
During the neonatal period, unconditioned reflexes begin to work in the child. This is a natural reaction to certain external stimuli. Some of them gradually fade away, being replaced by acquired ones.
We invite you to read: Winter strollers for newborns: how to choose a stroller for the winter
The sucking reflex in newborns awakens from the first hours of life, persisting throughout the year. The baby grabs the nipple with his lips and sucks rhythmically. This unconditioned reflex is necessary for the formation of a conditioned reflex - food.
No one teaches a child to suck - this is laid down by nature in the womb.
What it is
The unconditioned sucking reflex has a huge impact on the formation of the baby’s psyche from early childhood. With its help, the baby satisfies hunger.
Sucking reflex test. How can I check (Photo)
When feeding, the nipple or teat on the bottle touches the palate, the reflex is triggered - and the baby actively begins to suck out the food. The severity of the sucking reflex determines how hungry the baby is. After saturation, the reflex weakens, but soon awakens again. Rhythmic sucking has a calming effect on the newborn.
There are 5 brain nerves responsible for sucking: the vagus (the shortest), ternary, sublingual, facial and glossopharyngeal. Their interaction is strictly coordinated by the sucking reflex. If the central nervous system or one of these nerves is damaged, the response weakens or disappears completely.
In order to awaken the sucking reflex, a bent finger is inserted 2-3 cm into the baby's mouth. A healthy full-term baby begins to suckle immediately. If the reaction is well developed, touching the lips and stroking the cheek is enough. The baby will open his mouth and begin to move his tongue intensively, as if sucking.
When assessing the sucking reflex, test feeding is used. They give the baby breastfeeding or a bottle of formula and see how he copes. With a weak reflex, the baby sluggishly sucks food. He quickly loses strength, rarely swallows and falls asleep. Subsequently, interest in the breast is lost, and the baby is even able to refuse it.
A baby’s reflexes are skills without which he simply cannot live fully. These include the sucking reflex. It is thanks to him that the baby develops harmoniously, receiving with mother’s milk all the necessary substances for full development and growth. If a newborn receives the breast on demand, he will begin to feel protected and loved.
Sucking is a very complex process. 5 pairs of nerves in the cranium are responsible for its implementation. It’s easy to check this reflex in a child - just stroke his cheek or touch his lips. The baby will open his mouth slightly and begin to move his tongue, as if he wants to suck.
The sucking reflex in a newborn is the ability to suck on the mother's breast or the nipple on a bottle with a mixture placed in the mouth.
No one specifically teaches a child to suck, since it is not a skill, but one of the most important reflexes (it is formed during the process of intrauterine development).
It occurs in the first hours and belongs to the group of innate reflexes that ensure the survival of the newborn. During the feeding process, when the palate touches, the baby begins to suck milk from the breast or from the bottle. The severity of the sucking reflex in a baby determines whether the baby is hungry or full.
The instinct weakens after eating, however, an hour later it reminds itself again. Rhythmic sucking has a good calming effect on the baby. During the sucking process, the baby may even fall asleep, because he feels under reliable mother’s protection, he is calm and comfortable.
Until what age does a newborn develop a sucking reflex?
As already noted, a born baby begins to suck after 2-3 hours, and the formation and emergence of this reflex occurs long before birth. A few hours after birth, the baby begins an active search for the mother's breast in order to realize its natural instinct.
The duration during which the sucking reflex in infants is most pronounced is the first 12 months of life. Then, closer to a year, it begins to weaken. And by about 3-4 years it disappears completely.
For this reason, many experts agree that breastfeeding is necessary until the sucking reflex completely disappears in accordance with the norms inherent in nature.
Weak sucking reflex in a newborn photo A weak sucking reflex in a newborn is detected during feeding, but sometimes mothers are not able to independently determine the presence of a problem. The sucking reflex is manifested in children by the ability to suck on the mother's breast or a pacifier placed in the mouth.
How to restore the swallowing reflex in a newborn
Hello! Help me please! On March 3, my daughter was born. The birth was difficult, I pushed for more than an hour. When the baby was born, she was all blue and not breathing. My heart beat weakly. The pregnancy was going well. The child was admitted to intensive care.
She was on a ventilator for 10 days, was in a coma, did not move, her eyes were closed, and there was periodic tremor. Doctors said that the condition was extremely serious. At birth, the Apgar score was 1. They did an ultrasound of the brain. Brain edema was discovered.
Now the child is also in intensive care, she is breathing on her own, her eyes are slightly open, and she is moving a little. Doctors say that the swelling may have subsided, but hemorrhage of the ventricles of the brain has occurred. They are fed through a tube because there are no sucking or swallowing reflexes.
Please tell me what forecasts there might be? And further. If there is no sucking and swallowing reflex, are they somehow restored?
Sucking reflex: absent, no, threat of cerebral palsy. Swallowing reflex - disorder
Unfortunately, an Apgar score of 1 point, the child being in intensive care for more than 3 weeks, cerebral edema, hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain, absence of a swallowing reflex, absence of a sucking reflex indicate an extremely serious condition of the child. After such conditions, perinatal encephalopathy of mixed origin of the 3rd degree often develops, which is prognostically quite severe. The child has a high risk of developing cerebral palsy (high risk of cerebral palsy).
Sarklinik previously treated children who had no sucking and swallowing reflexes (no sucking reflex in a child, no sucking reflex in a newborn) at 7, 9 and even 12 months. The treatment was difficult. The forecast depends on how further events will occur.
Treatment of the consequences of birth injuries, encephalopathy, cerebral palsy in Saratov, Russia
Sarklinik wishes you fortitude, courage and patience.
Nature took care of the newborn child, endowing him with protective reactions that help the baby adapt to new conditions. Some innate reflexes are observed in children only in the first months of life, others remain forever.
As the baby grows and develops, many unconditioned reflexes turn into conscious actions.
It is by innate reactions and the degree of their severity that doctors judge whether the baby is developing correctly, whether there are any deviations in its development that signal health problems.
Moro reflex
All full-term newborns normally exhibit the Moro reflex, or as it is often called the startle reaction. It is expressed by abducting the arms to the sides (throwing up), extending the fingers, extending the legs, followed by flexion of the hips, and then returning the limbs to their original position when the baby is scared.
The presence of this innate reaction is checked by patting the child on the thigh/buttock, or by hitting the table on which the baby is lying (at a distance of at least fifteen centimeters from the head). The reflex appears almost immediately after birth, and fades away by five months.
The presence of such a protective reaction indicates the correct development of the nervous system, while the absence or distortion of the reflex is a signal indicating problems.
You need to pay attention not only to the presence/absence of the Moro reflex, but also to the duration of its manifestation. If the fear reaction persists after five months, then this is an alarming signal.
Babkin reflex (hand-mouth reflex)
In newborns who do not have health problems, the Babkin reflex is observed. The reaction appears when light pressure is applied to the baby's palm. The baby moves its head and opens its mouth.
In the first two months, the unconditioned reaction is well expressed, and then it weakens, it completely disappears at three months. The unconditioned hand-mouth reflex is responsible for subsequent hand-mouth reactions in newborns.
Sluggishness of the reflex should alert you, as this may indicate damage to the central nervous system.
Robinson reflex (grasp reflex)
The Robinson reflex is one of those innate reflexes that do not fade away, but change to a conscious action. It manifests itself from birth: if you put a finger in the baby’s palm, he will grab it tightly, sometimes the grip is so strong that the child can be lifted without difficulty.
A newborn with muscle hypotonicity may have a weak grasp reflex, which will need to be developed. For this purpose, dynamic gymnastics and massage are used, however, any measures should be used only after consultation with a pediatrician. If the newborn’s grasping reflex is completely absent, then consultation with a doctor is necessary immediately.
In such cases, as a rule, timely treatment ensures the further development of the child in accordance with age standards.
Swallowing reflex in a newborn
One of the most important innate reflexes that ensures the life of a child is the swallowing reflex. It is often considered in conjunction with the sucking reflex.
Such unconditioned reactions appear immediately after birth: if the baby’s palate is stimulated, he will immediately begin to suck milk and then swallow it. If the sucking reflex subsides, then the swallowing reflex remains forever, taking the form of deliberate actions.
If a newborn has a lack of a swallowing reflex, this indicates a central nervous system disorder. This pathology often occurs if fetal hypoxia has been diagnosed. In a newborn with such problems, the absence of a sucking reflex is recorded.
Your doctor will tell you how to restore the swallowing and sucking reflex. Rehabilitation in the complete absence of these basic reflexes takes place in hospital treatment, since it is necessary to constantly monitor the child’s condition.
Babinski reflex
The Babinski reflex, which manifests itself in all healthy babies, helps determine whether there are problems with the nervous system in newborn babies. To check the reaction, you need to run a hammer from bottom to top along the sole.
Normally, there should be involuntary extension of the thumb while the rest are immobile or fan-shaped. The reflex should appear symmetrically. Its absence indicates neuralgic pathologies and may be a sign of cerebral palsy. The reflex fades as you get older.
If the reaction is observed after three years, then it is worth contacting a neurologist - this is how motor neuron pathology may manifest itself.
Galant reflex
From about the fifth day of life, the Galant reflex can be detected in newborns; an unconditioned reaction is observed until the fourth month. The reflex is manifested by an arched bending of the back when exposed to stimuli.
If the nervous system is damaged, the reaction in a month-old baby is absent or weakly expressed. If the spinal cord is affected, the reaction does not appear for a long time.
Prolonged expression of the reflex also indicates deviations: if it is observed after six months, then this is an alarming signal.
Bauer reflex (crawling reflex)
On the third or fourth day of life, newborns develop the Bauer reflex (crawling). Lying on his stomach, the baby makes characteristic crawling movements.
They intensify if you place your palm on the child’s soles - he will reflexively push away from it. This reaction is physiological for up to four months; it precedes future locomotor actions.
With spinal cord injuries, this unconditioned reflex is completely absent; with asphyxia, it can be partially observed.
Breath holding reflex
All newborns have a breath-holding reflex, which performs an important function - it contributes to the successful passage of the birth canal. It is thanks to the ability to hold your breath that the baby does not swallow amniotic fluid during birth. It is recommended to develop the reflex by immersing in water. The first dives should last no more than 6 seconds.
Before teaching your baby to swim, you should consult a specialist. You need to know how to conduct classes, since staying a baby under water longer than normal can have consequences.
Perez reflex
In the first decade of life, the Perez reflex can be observed in newborns, with the help of which the reaction of nerve endings is checked. The reflex occurs when a finger is passed along the baby's spine. In response, the baby, who has no pathologies, should bend his limbs, raise his pelvis and head.
The reaction is usually accompanied by screaming, since such actions cause discomfort to the child. Normally, the reflex is observed until about four months. If it is suppressed or absent, then this indicates a pathology of the central nervous system. The reflex should not be caused independently; it must be checked by a neurologist.
Landau reflex
In newborns, various straightening reactions can be observed, the main one of which is the Landau reflex. It consists of two phases. The first phase appears between 4 and 6 months. In a position on the stomach, the baby stretches his arms forward, raises his chest and head, and straightens his torso.
The second phase of the reflex is pronounced from 6 to 8 months. To check the reaction, you need to lay the child on his back. In this position, the baby will raise his legs up, while simultaneously pulling them to the level of the body.
The tone of this pose indicates that the child is ready to master more complex movements.
Vomiting reflex
The gag reflex is one of the vital unconditioned reactions of an infant. A baby can easily choke on milk. To protect it, nature provided a gag reflex.
When it is triggered, the baby sticks his tongue forward, after which the food he choked on comes out back.
If a newborn's gag reflex is partially or completely absent, then you should consult a doctor and carefully monitor the child during and after feeding in order to provide assistance if he chokes.
Walking reflex (support reflex)
In newborns, the automatic walking (support) reflex can be observed. It is pronounced up to 1.5 months, and then fades away and disappears at three months. The baby will acquire the ability to independently perform walking actions only by the age of one year.
In newborns, the unconditioned support reflex is normally manifested as follows: if the baby is lifted by the armpits, he begins to bend his legs, and upon subsequent contact with the surface, the baby stands on half-bent legs. If you tilt it slightly forward, characteristic stepping movements appear.
A poor walking reflex can be observed in diseases of the neuromuscular type in a newborn, intracranial injuries, and birth asphyxia.
Source: https://rody-beremennost.ru/voprosy/kak-vosstanovit-glotatelnyj-refleks-u-novorozhdennogo
Newborn reflexes
When a tiny baby is born, it seems that he is completely defenseless in front of a new world for him. However, nature took care of his protection, rewarding him with a certain set of abilities important for his life, instincts that are responsible for successful adaptation and development. We are talking about conditioned and unconditioned reflexes, thanks to which the baby is able to survive.
The unconditioned reflexes of a newborn are what are primarily assessed by neonatologists in the maternity hospital, and then pediatricians use these reactions to “read” how developed he is, and whether there are any pathologies or abnormalities.
Conditioned reflexes are those “developments” of the baby that will remain with him for the rest of his life, what he acquired in the course of development and experience. Simply put, this is what a little person does consciously, understanding the goals and reasons for his actions.
What are they needed for?
The innate reflexes of newborns are triggered automatically as soon as the child comes into this world. These are peculiar small programs that begin to be executed immediately. Even the first breath is considered reflective, because no one taught the baby to breathe.
There are several dozen of them (about 75), but in pediatrics, 15 clinically important unconditioned reflexes of newborns are distinguished, the tasks of which are very different: some disappear instantly after the birth of the baby, since they are programmed only to facilitate this very birth, others are needed to stimulate the development of new ones, and There are those that stay with a person for life.
The life of a newborn depends entirely on the adults who care for him. He is not able to independently obtain food, drink or warm himself. The well-being of the little man depends only on the guardians; only they can make sure that he is not cold and hungry.
But at the same time, the child’s ability to accept this care will depend on the innate reflexes of newborns, on their activity. What does this mean? Let's take feeding a baby as an example. In order to feed him, you will need breast milk or a bottle of formula. But the baby will have to suck on the breast or bottle! The outcome of feeding will depend on the severity of his sucking reflex: the more active this reflex is, the more likely the baby will get to the hind milk - the fattest and most nutritious one. So this skill ensures his survival.
Unconditioned (innate) reflexes
In the supine position
Kussmaul search reflex
If you touch or stroke lightly the corner of the child’s mouth next to the cheek, he will turn his head towards the stimulus, lift it slightly and open his mouth slightly. This is how the baby looks for food. The reaction will fade away by 3 months, since by this age he will see food with his eyes - a breast or a bottle. In infants with damage to the facial nerve, this reflex is weak or completely absent.
Sucking
This is a vital mechanism that allows the baby to survive. Thanks to him, he takes food - sucks milk from the breast or formula from a bottle. Essentially we are talking about the normal feeding process.
After the baby is satisfied, the sucking reflex fades away. But after half an hour or an hour it resumes again. It remains in the baby for up to a year.
Remember: the absence or weakening of sucking and swallowing reflexes may be due to the fact that the baby is not yet hungry. They are most pronounced only before feeding.
But if there is no sucking reflex, if the baby sucks poorly, grasps the nipple incorrectly, fluid leaks from the corner of his mouth, he takes in a lot of milk, but cannot swallow, then all this is cause for concern.
Vomiting reflex
It is necessary for the baby if he chokes. Immediately after birth, babies, although able to suck, still cannot eat “like clockwork,” which is why they often choke and choke. The gag reflex helps him spit out the milk he choked on.
Babkin's palmo-oral reflex
If you put your fingers into the palms of a month-old baby and press a little on them, he will immediately grab them and raise his head along the midline. Some children can open their mouths and even stick out their tongues. This reaction is especially pronounced during the newborn period, lasts up to 2 months, and disappears by the third month.
Prehensile
If you put your fingers into your baby's palms and press lightly on them, he will reflexively grab them, and very tightly. The grasping reflex, which exists up to 3-4 months, gradually transforms into a conditioned one, when the child no longer unconsciously grabs the toy, but purposefully.
Robinson reflex
The baby is able to squeeze the fingers of an adult with such force that he can lift himself up. The Robinson reflex is similar to the grasping reflex and has all its features.
Inferior prehensile (plantar)
If you press on the baby's feet closer to the toes, he will respond by squeezing those toes. Disappears by the age of one year.
Moro reflex (grasping)
If you slap your palm on the place where the baby is lying, 20-30 cm from him, the response should be to spread your arms to the sides and unclench your fingers (first phase) and bring them together with an attempt to hug or hug yourself (second phase). Often, in the first week after the baby is born, only the first phase appears. The absence of the second does not indicate a deviation. This is a more stable reflex, it lasts up to almost 5 months, and its individual elements can be seen at 6 months.
Babinski reflex
If you irritate the outer edges of the child's soles from the heel to the toes, the response will be a pronounced extension of the big toe, and the remaining toes will open like a fan. May occur in children under 12 months of age.
Standing
Automatic walking or step reflex
The stepper is checked as follows: the doctor puts the baby on his feet, while he stands either on a full foot or can stand on his toes. If you rock him and tilt him forward, he will make stepping movements. This is reflexive automatic walking, inherent in infants in the first month of life. This is how the baby prepares to verticalize the body in space. However, this skill will disappear at 2 months; this reflex is the fastest to fade.
Support reflex
There are two phases:
- The child bends his legs at the knee and hip joints when an adult takes him under the arms.
- The child straightens his legs and stands with his full foot on a hard surface, for example, a changing table.
He will retain this skill for no longer than 2 months.
Reflexes on the stomach
Protective
If a newborn is placed on his tummy, he will slightly raise his head and turn it to the side. He protects himself so as not to suffocate. He appears one of the first, literally in the delivery room. The baby is placed on his mother's stomach in the first minutes after his birth, and he turns his head to the side.
Spinal
We recommend reading: Why does a baby throw his head back?
With the help of spinal reflexes, a pediatrician will be able to check the set of reactions that are responsible for the functioning of the muscular system of an infant.
Galant reflex. For example, a child lies on his stomach, his arms and legs are bent, and if you pass some stimulus along the child’s spine (parallel to it), his body will arch and his leg will straighten towards the stimulus.
Perez reflex. If you run your finger along the spine from bottom to top, from the butt to the neck, the baby will simultaneously bend his legs and bring them to his tummy, and his back will arch. An opening of the anal sphincter is often observed, and the baby may wet himself. This reaction is the last to be tested, as it causes discomfort in the child, and the baby begins to scream loudly. Therefore, it is not recommended to check it yourself. The Perez reflex manifests itself up to 4 months.
Bauer's crawling reflex
An adult's hands are placed under the baby's legs. The baby will begin to make crawling movements. Sometimes it is necessary to push the baby to provoke these movements. It is observed in newborns from birth and is recorded up to 4 months.
The absence of reflexes in a newborn requires immediate resuscitation
Weak or not at all
In some newborns they are very weak, do not appear clearly or appear a little later. This may be due to birth injuries, certain diseases, etc. In premature babies and babies who have experienced mild asphyxia, oral and spinal reactions are weakly manifested.
But if they are not there at all, then the baby must be immediately provided with resuscitation care, which is carried out only by specialists. The absence of reactions can indicate the most unpleasant things - from intrauterine defects and severe birth injuries to severe asphyxia or strangulation by the umbilical cord. The faster the problem is fixed, the less unpleasant the consequences will be. True, the child’s body is very flexible, the reserves that nature has endowed it with are enormous. Therefore, in most cases everything works out well, and the body recovers quickly.
mladeni.ru
What it is
The unconditioned sucking reflex has a huge impact on the formation of the baby’s psyche from early childhood. With its help, the baby satisfies hunger.
Sucking reflex test. How can I check (Photo)
When feeding, the nipple or teat on the bottle touches the palate, the reflex is triggered - and the baby actively begins to suck out the food. The severity of the sucking reflex determines how hungry the baby is. After saturation, the reflex weakens, but soon awakens again. Rhythmic sucking has a calming effect on the newborn.
There are 5 brain nerves responsible for sucking: the vagus (the shortest), ternary, sublingual, facial and glossopharyngeal. Their interaction is strictly coordinated by the sucking reflex. If the central nervous system or one of these nerves is damaged, the response weakens or disappears completely.
weak and until what age is it present?
The vital functions of any person’s body are ensured by the implementation of a set of reflexes. As for newborn children, they also have a certain set of natural reflexes, which are a unique manifestation of their body’s response to external and internal stimuli. All movements are laid down long before the birth of a newborn, during intrauterine development.
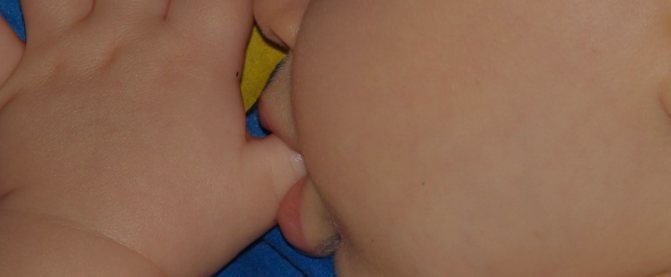
One of the first to appear is the sucking reflex, but many do not know until what age it is present and when it should fade away. Often, parents are able to see in ultrasound images how, while still inside the mother’s womb, the baby can suck his own finger. After birth, this reflex begins to be honed and improved, as soon as the nipple or mother’s breast touches the newborn’s lips. Thanks to this action, the baby eats.
What is natural instinct
5 nerve pairs located in the child’s skull are responsible for movement. A newborn baby is able to suck everything that falls into his mouth, be it his mother’s breast or a nipple during artificial feeding. The ability to suck is not a habit, as it is formed during the period of intrauterine development. This reflex is formed long before the birth of a newborn, after about 15 weeks of development, and has a significant impact on the early formation of the child’s psyche. Also, thanks to the possession of this reflex, the newborn has the opportunity to satisfy his own hunger, which, without exaggeration, ensures his survival.
Studies show that children who had the opportunity to be breastfed for a long time or were not deprived of pacifiers until they were old enough, in later life are less susceptible to various bad habits, they are calmer and more balanced.
Every mother can be sure that as soon as the pacifier or its nipple touches the palate in the baby’s mouth, he immediately begins to suck. Already in the first hours of his life, the baby is ready to take his mother's breast. The reflex is implemented in practice by rhythmic sucking movements that calm an irritated child. In the process of sucking a pacifier, about 4 muscles are involved, and when sucking on a mother's breast - about 40. While sucking, the baby can even fall asleep, as he feels protected, comfortable and calm.
More > What to do if your newborn sleeps restlessly?
After satisfying the feeling of hunger, the reflex begins to weaken and, conversely, intensifies as soon as the feeling of satiety disappears. Thus, periodically repeating, the sucking reflex in newborns makes itself felt.
The signal for the implementation of this phenomenon will be a simple touch to the child’s cheek or lips. As soon as the mother touches the nipple or pacifier on her cheek, the baby will immediately turn his head in her direction and open his mouth slightly. This signal indicates that the baby is ready to suckle and the mother should provide him with this opportunity.
How long does this phenomenon last?
As already noted, a newborn baby begins to suck after a couple of hours of his life, and the formation and appearance of this reflex generally occurs long before birth. A few hours after birth, the baby begins to actively seek the mother’s breast in order to support and realize its natural instinct.

In this regard, many experts point to the need to breastfeed the child until the sucking reflex completely subsides in accordance with the norms laid down by nature.
Additionally > What can a child do to please his parents at 10 months?
Weakened or absent sucking reflex
In practice, there are cases when the sucking reflex manifests itself to a lesser extent, it is weakened or absent altogether. The following symptoms will indicate an underdeveloped skill:
- the baby rarely swallows during feeding;
- the baby will be lethargic by itself;
- during feeding, the baby may suck very weakly and even fall asleep;
- in rare cases, the baby cannot take the mother's breast at all.
The main causes of weak sucking are considered to be paresis of the facial nerves, severe somatic conditions, mental retardation and other deviations in the development of the central nervous system. Such conditions can be observed in newborns as a result of hypoxia during childbirth or during pregnancy. Other, more rare cases that provoke deviations can be colds and viral diseases or stomatitis.
Rate this article
Loading…
Features of the sucking reflex in premature babies
Babies born prematurely with low birth weight have many different health problems and their own developmental and nursing characteristics. In particular, the sucking reflex in premature babies, as well as the swallowing reflex, is often absent, especially with a body weight of less than one and a half kilograms, when there is underdevelopment of many organs, their small volume, impaired thermoregulation, difficulty breathing, etc.
Inferiority of reflexes is associated with insufficient development of nervous regulation mechanisms and incomplete formation of sucking muscles. Such children cannot be immediately put to the breast, but a long delay is also scary because of the possible large loss of body weight.

A long delay is given in case of severe injury or suspected cerebral hemorrhage. If the child has not been fed for more than 12 hours, he is transferred to parenteral nutrition with a glucose solution. Tube feeding of premature babies is practiced with a significant reduction in sucking and swallowing, while the volume of each feeding is dosed with a special syringe. They switch to bottle feeding after the baby develops good reflexes.
The issue of breastfeeding is decided separately for each child, taking into account his condition and the stability of reflex signs. Usually they start with once or twice a day, if the child gets tired, then they feed him from a bottle; in total, such children are fed up to 10 times a day. The main thing in the process of nursing premature babies is not to force things.
The process can be lengthy, but success is ensured with the competent approach of doctors and the baby’s mother; such children catch up with their peers by the end of the first or maximum third year of life.
Thus, the sucking reflex is one of the most important innate reflexes that human nature has endowed to provide the most comfortable conditions for survival and further development. Its complete absence is an irreparable problem, incompatible with life, and a decrease is a menacing signal about a serious neurological problem, which must immediately begin to be looked for and eliminated in all possible ways with the involvement of neurologists and other specialists.