Why do lumps appear behind the ear?
A lump behind a child's ear forms for various reasons. It is difficult to find the provoking factor on your own. It is better to visit a doctor, especially if the baby’s condition worsens.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes
There are many lymph nodes on the human body. They increase in size in response to inflammation or the spread of infection.
Lymph nodes behind the ears become noticeable in the following cases:
- Otitis;
- Sinusitis;
- Angina;
- Caries;
- Teething;
- Pharyngitis;
- ARVI and influenza;
- Infectious diseases, in particular measles, scarlet fever, chickenpox.
When palpated, the lymph nodes are painless, quite soft and do not move with the skin. Their size will return to the same size after recovery. The reason that caused their growth needs to be treated. In some cases, the increase is provoked by vaccination. Vaccine components are perceived by the immune system as a threat. This means that leukocytes begin to be intensively produced, which causes a temporary change in the size of the lymph nodes.
Skin disease
Lumps behind the ears appear in adolescents during puberty, when there are a lot of acne and pimples on the face. Acne, leading to inflammation, can form under the skin. In this case, the rashes do not turn red, but become painful to the touch. It is not recommended to squeeze them out yourself; there is a risk of scarring.
Birth injuries
In newborns, a lump is most likely the result of a birth injury. The baby develops a hematoma when blood accumulates.
For your information. A lump on the bone behind the ear may appear if the child hits himself. So, at one year old children are already trying to run and often fall unsuccessfully. Gradually, the consequences of the blow will disappear, but the child’s behavior must be monitored and be sure to inform the doctor about the noticed pathology.
Piggy
Mumps, or mumps, is a viral disease that can lead to serious complications. The lump behind the ear hurts, in addition, the soft tissues around it swell and the earlobe becomes enlarged.
Note! The disease affects the salivary glands located behind the ears, when they become enlarged and resemble a ball.
Mumps in a child
During mumps, the child's temperature rises, he becomes lethargic and capricious, and loses his appetite. In severe cases, inflammation can affect the pancreas, kidneys, and nervous system. In boys, the testicles are at risk; in some cases, mumps leads to infertility.
Ear fistula
Some pathologies are diagnosed in a child from birth. So, in the auricle there may be a small hole connected to the middle ear or oral cavity. Periodically, clear liquid flows out of it; if bacteria enter the fistula, inflammation will begin, accompanied by swelling. Then a lump may appear behind the child’s ear.
Atheroma and lipoma
A person of any age, including infants, can develop a subcutaneous formation of adipose tissue - a lipoma. It can only be benign and never grows into nearby cells and tissues. A lipoma can press on a nerve if it grows too large. They cut it out when it causes inconvenience.
Atheroma is formed when the sebaceous glands are blocked. It cannot resolve on its own. The formation is sebum covered with a membrane. If it is not removed, then you will not be able to get rid of the atheroma even if the contents are squeezed out. The only way out is surgery, otherwise an infection may enter the capsule, causing inflammation.
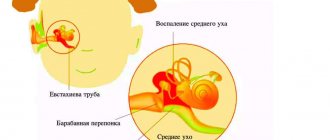
Inflammatory process in the ear
Otitis media sometimes results in a lump. This is typical for an advanced form of the disease, when there is a threat of hearing loss. You cannot put off visiting a doctor, especially if your child has a fever or complains of ear pain.
Note! A baby under one year old is not yet able to explain what is bothering him.
He will turn his head, start fiddling with his ears, and refuse to eat.
Treatment for a lump behind the ear
Enlarged lymph nodes do not require special treatment. A lump behind a child’s ear goes away on its own after 1-2 months. If inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs, then it is necessary to take antibacterial drugs to relieve pain from the group:
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides;
- penicillins.
The lump that appears as a result of inflammation of the lymph nodes will go away after the disease is eliminated. If the cause of the pathology is mumps, then to eliminate it it is necessary to limit contact with others for 9 days. There is no treatment for mumps; bed rest and a special diet are indicated. The lump will go away after recovery.
With chickenpox, the lymph nodes located behind the ears, on the neck and head are the first to be affected. The disease in children disappears after 10 days. After consultation with a doctor, the child may be prescribed drugs from the following pharmacological groups:
- immunomodulators (Viferon, Cycloferon);
- antiviral drugs (Miramistin, Acyclovir);
- solutions of essential oils (tea tree, calendula, celandine);
- antiallergenic agents (Fenistil, zinc ointment, Calamine and Tsindol).

Getting rid of a lump behind the ear caused by a tumor:
- Formations such as atheroma do not tolerate self-medication. This leads to tissue abscess in the child. Atheroma is removed by radio waves at the initial stage of development or by laser. The cyst can open on its own after suppuration if the baby has a strong immune system.
- Parents should be concerned if the lipoma begins to increase in size and the child complains of discomfort. Subsequently, the bump becomes a cosmetic problem, which is removed with a laser. Infected lipomas require emergency medical attention.
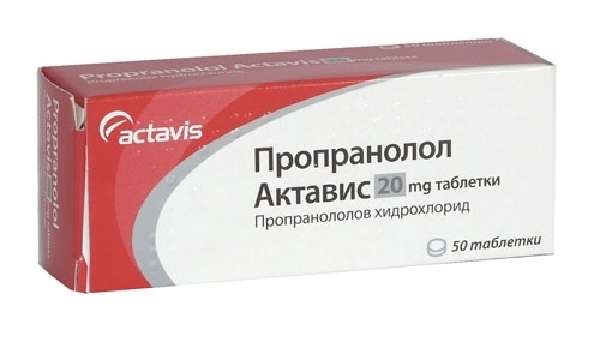
- Hemangioma is treated with Propranolol, a drug that acts as a beta-blocker. Before using the drug, you should read the list of contraindications for children.
Therapy for ear fistula
The doctor opens the ear fistula to release the accumulated pus. To alleviate the patient's condition, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Antiseptics: Furacilin, Miramistin.
- Antimicrobial ointments: Levomekol.
- Treatment solutions: Chlorhexidine.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
The discharge of pus is suspended until the next period of exacerbation. To avoid relapse, galvanocaustic surgery and laser treatment are performed.
Folk remedies
The most effective folk remedies for getting rid of a fistula behind the ear are:
- St. John's wort compresses . You need 2 tbsp. l of raw materials, pour 1.5 glasses of water and boil. Let it brew, then take a clean bandage or cotton wool, moisten it in the prepared broth and apply it to the fistula.
- Lotions made from mumiyo and aloe. You need to get juice from aloe, and soak the mummy in water until it darkens. Mix the resulting liquids. Soak a bandage in the solution and apply to the ear fistula.
- Ointment made from oil, pine resin, tar and aloe. Take the ingredients in equal proportions, mix and place in a water bath. Heat the product until smooth. The prepared ointment is applied to the affected area, wrapped in film and secured with a band-aid.
Diagnostics
Oxalates in the urine of a child under one year of age—causes of occurrence, calcium levels
To understand what kind of lump is behind a child’s ear, you need to visit a doctor. Usually a pediatrician and a surgeon are sufficient. You may need to consult an otolaryngologist if it turns out that the cause of inflammation is a disease of the ENT organs. Specialists examine the formation, assess how soft or hard, dense, and mobile it is.
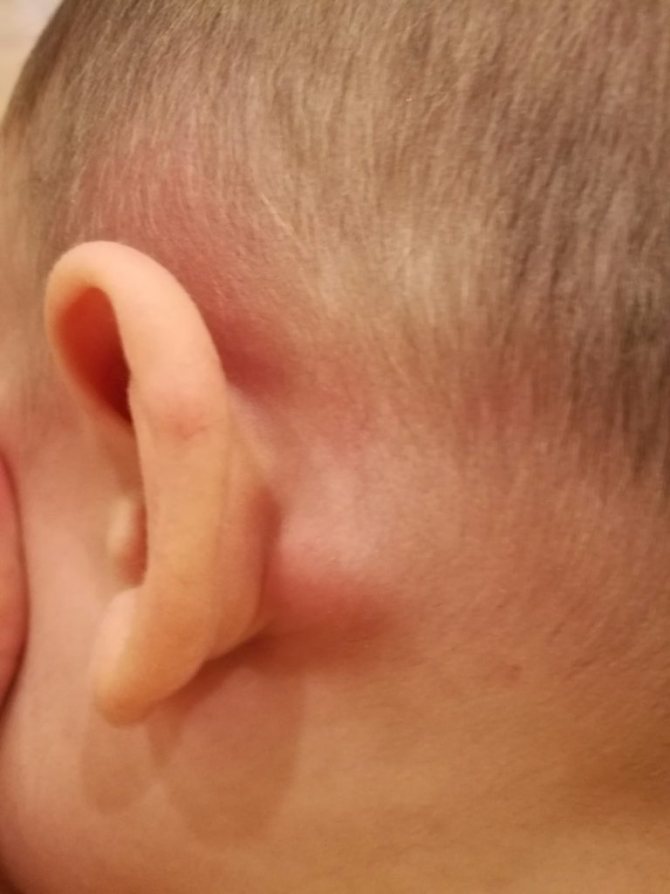
What does a lump behind the ear look like?
If necessary, examinations and procedures are prescribed:
- General blood analysis;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes;
- CT and MRI.
Causes of inflammation
Lymphadenitis is not a disease, but only a symptom indicating another dangerous condition or pathology. For example, inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes often indicates a sore throat. The cause may also be a disease such as mumps.
The lymph node enlarges due to the accumulation of microbes or the remains of their vital activity in it, which in turn causes an immune response and the accumulation of leukocytes.
If the situation becomes more complicated and the lymph nodes cannot cope with the load, inflammation develops. The skin swells, the nodes increase, and sometimes purulent processes develop. This condition is called lymphadenitis.
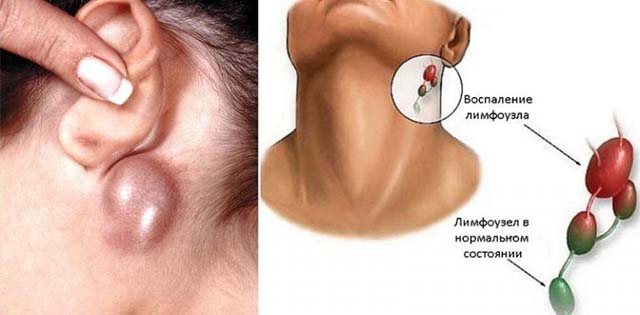
Lymphadenitis can act as a primary or secondary pathology. In the first case, the cause becomes the node itself when the integrity of the skin is violated and infection penetrates there, which leads to a purulent process.
A secondary cause is a cold or systemic disease, another option is a malignant formation (tissues affected due to leukemia, brain lymphoma, etc.). Often, the inflammation of nodular formations becomes a chronic process.
If the lymph nodes behind a child’s ear suddenly become inflamed, and the cause is unknown, you should definitely show him to a doctor to rule out dangerous causes of this phenomenon. Wrong actions can provoke further aggravation.
We recommend additional reading: How to relieve swelling of the throat in a child, first aid, symptoms and treatment
The reasons why the lymph node behind the ear in a child becomes inflamed are:
- ARVI;
- Furunculosis of the ear;
- viral or bacterial disease of the ENT organs, for example, pharyngitis or tonsillitis;
- pathologies of teeth and gums and other purulent processes, infected wounds in the mouth;
- infectious diseases: measles, mumps, mononucleosis or another option;
- reaction to otitis media or tonsillitis of bacterial origin, the first disease is characterized by inflammation of the middle ear;
- taking medications: quinidine, sulfonamides, captopril and some others.
After identifying the cause of an enlarged lymph node behind the ear, a course of treatment for the underlying viral or bacterial disease is prescribed, after which its condition returns to normal. Most of the listed pathologies also have other symptoms that may indicate the nature of the disorders.
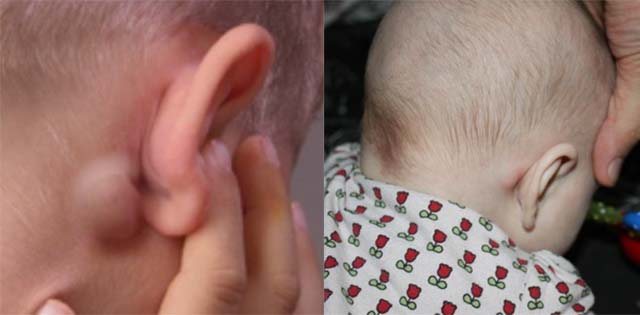
It happens that painful ear bumps are observed with chickenpox; lymph nodes with chickenpox in children become inflamed infrequently, but this does occur. The disease is characterized by the appearance of a vesicular rash on the body. This should not be ignored, but this does not pose a serious danger.
What should parents do?
Why does a child’s snot flow like a stream - the reasons for a runny nose
If a child has swelling behind the ear, the following actions should not be taken:
- press;
- lubricate;
- rub;
- warm;
- try to open it.
The only thing is that you can touch it slightly to understand whether the child is in pain and whether the swelling is moving relative to the skin. If the baby does not experience any discomfort, then you need to visit a pediatrician. Most likely, this is a lymph node; the doctor will help you find the reason for its enlargement. If the child is in pain, the lump turns red and festeres, it is necessary to urgently go to the surgeon.
Malignant tumor
A tumor that is malignant can be primary or secondary. Primary forms in one part of the ear, and secondary is characterized by germination into the ear itself or nearby organs. A malignant tumor tends to metastasize, which primarily appears in the regional lymph nodes in the neck, temporal part, zygomatic and other bones of the skull, as well as the salivary gland.
Surgical removal of hemangioma is particularly difficult, since during the operation there is a high probability of dangerous bleeding. Therefore, chemotherapy and radiation are used here. In most cases, many specialists use the method of ligation of afferent vessels and diathermocoagulation. Many people practice increasing blood clotting using injections with eighty-five percent alcohol.
If the tumor that has formed behind the ear has a solid structure, you should immediately contact an oncologist, as it may be a rather serious disease (lipoma or cyst). If it is a benign or malignant tumor, then it is mobile in nature and tends to move for some distance along with the skin.
Any neoplasm in the area behind a child’s ear should not be ignored. Timely consultation with a doctor is, above all, the key to a successful recovery.
- A lump behind the ear often appears in adults and children in the presence of chronic ENT diseases, hormonal disorders, and infections. It can be very dense, without inflammation of the surrounding tissues, or soft and mobile. A lump behind the ear can be the cause of an oncological process or maturing atheroma, which often occurs in young people due to hormonal disorders. Its appearance may be due to the inflammatory process that occurs in the lymph node located next to the source of infection.
To understand the reasons for the appearance of lumps behind the ears, you should seek advice from your local pediatrician, therapist or oncologist.
After examination, the doctor will make a conclusion and prescribe appropriate treatment. If necessary, an additional examination will be recommended, based on the results of which a medical report will be made and appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
Alarming symptoms
If the following signs are detected, the child should be seen by a doctor:
- The temperature has risen;
- The lump turned red;
- Swelling and itching appeared;
- There is pain when touched;
- There is liquid in the seal that can be felt by palpation;
- The baby refuses to eat, sleeps a lot and is capricious.
Self-medication and the use of traditional methods can worsen the situation. Delay poses a threat to the child's health.
Inflammation of the lymph node
Most often, the appearance of a dense lump behind the ear is caused by inflammation of the lymph node. The lymphatic system is very diverse in its structure. It includes capillaries, vessels, trunks, nodes and organs.
One of the organs of the lymphatic system is the tonsils, which exist in the body and function for up to 25 years and then, as unnecessary, turn into connective tissue and cease to function. In children, they often become inflamed, destroying pathogens of infectious diseases inside the folds. Pathological processes occurring in the tonsils can spread further, collecting in the nodes of the lymphatic system. This causes them to harden and become painful.
Lymph nodes behind the ear are needed to protect the ENT organs from infection and the development of pathological processes. Four such nodes are located behind the ear. With a chronic process that sluggishly flows in the oral cavity, one of them (or several at once) can turn into a lump, which will cause pain when pressed.
The postauricular lymph nodes cannot be palpated in healthy people. They perform drainage and protective functions. If the lymph nodes located behind the ear cannot cope with the aggressive environment, severe inflammation begins in them, ending in suppuration. With an active inflammatory process behind the ear, the entire lymph node hurts, painful sensations arise, and when you feel the painful area, a compaction is discovered, the size of which can be the size of a pea. Sometimes such seals can be larger.
Complications
Incorrect actions and attempts to get rid of the tumor on your own can lead to infection. Then healthy tissues will also suffer, and a purulent process will begin. If the lump appears as a result of otitis media, then without treatment the child’s hearing may be damaged if the eardrum ruptures.
Note! In advanced cases, inflammation can even affect the bones, then the problem can only be solved through surgery. You can avoid unpleasant consequences by carrying out therapy under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of a child
First of all, it is necessary to establish the main reason for the enlargement of the node in the child: consult a pediatrician, check the ENT organs, visit the dentist and make sure there is no helminthic infestation by taking stool for analysis.
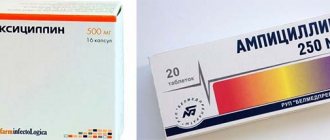
The doctor selects a treatment regimen based on the examinations performed. If the cause is the presence of worms, anthelmintic drugs are prescribed. If the dentist finds tooth decay, it is treated. Problems with ENT organs are also eliminated. Most often treatment is with antibiotics .
Unilateral purulent lymphadenitis in children is eliminated with antibacterial drugs. An enlarged lymph node caused by a cold is treated in combination with antibacterial and antiviral therapy.
During the recovery period, it is recommended to take immunomodulatory drugs and a complex of vitamins to improve the functioning of the immune system and help the body cope with foreign microorganisms.
Antiallergic therapy may be added to the treatment regimen if the child has a reaction to medications or ointments.
If the underlying causes are checked, eliminated, and the lymph nodes do not return to a healthy state in the next 2-3 weeks, the doctor performs a biopsy.
Komarovsky's advice
Children's doctor Komarovsky, voicing his opinion about a lump behind the ear in children, confirms that these are usually inflamed lymph nodes. In children they often increase after infectious diseases. They are noticeable near where viruses or bacteria are spreading. This is the body's response to the invasion of foreign microorganisms. This reaction should not be considered dangerous. If the lymph node in the neck or behind the ear does not begin to shrink within 5 days, it is better to show the child to the doctor.
Doctor examining baby's ear
A lump behind a child’s ear appears for a number of reasons. A doctor will help determine which factor provoked its formation. The doctor must examine and feel the lump. It is forbidden to press or crush it yourself.
How to treat a lymph node behind the ear in a child
What to do first of all, if the lymph node behind the ear is inflamed in a child, is to carry out a diagnosis. If the cause of lymphadenitis turns out to be an exacerbation of an ENT disease, then such a complication can only go away by eliminating the cause itself. After the underlying disease is cured, the lymph node behind the ear will also return to normal.
But such a situation can be harmful to health and have more serious consequences. In order for the treatment to be correct, you should go to the doctor; medications may be needed to boost immunity.
Drug treatment
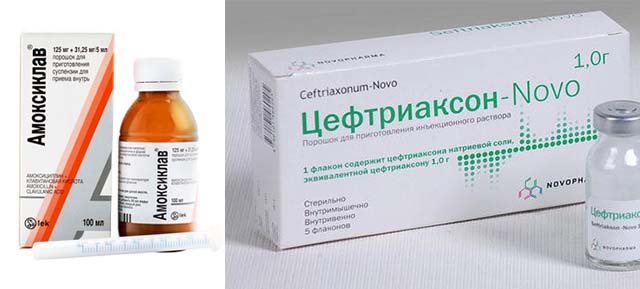
After an examination, the doctor determines the reason why the child’s lymph node is inflamed near the ear and prescribes appropriate therapy. For otitis media or tonsillitis, the patient is prescribed semisynthetic antibiotics (penicillins: Amoxiclav, Augmentin, cephalosporins: Ceftriaxone). General restorative medications may also be prescribed if indicated.
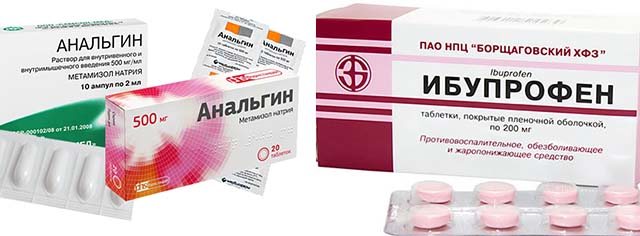
For pain, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal medications (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol) are most often prescribed. Analgesics and anesthetics (Analgin, Baralgin) are also prescribed to eliminate it. Some of them come in the form of creams that must be applied directly to the inflamed lymph node behind the ear.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated to relieve swelling. If there are signs of suppuration, treatment of lymph formation is carried out using surgical methods. The doctor prescribes surgical cleansing for diagnoses such as lymphadenitis, complicated by a nephrotic or phlegmatic process. After the intervention, treatment of an inflamed lymph node behind the ear in a child consists of providing careful care of the wound surface; drug therapy alone may not be enough.
Home care
Treatment of inflammation of the lymph node behind the ear in a child must be accompanied by proper and careful care, otherwise its effectiveness will be low. The result greatly depends on the correctness of the parents' actions. To get better, you need to strictly follow the pediatrician’s recommendations and undergo diagnostics; in such cases, therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
To quickly resolve the problem, you need to follow simple rules on how to treat an inflamed lymph node in a child behind the ear:
- Do not heat the cone. This can cause the spread of infection or a purulent process.
- Compresses can provoke a similar reaction, so their use is also prohibited.
- It is necessary to eat a balanced diet. Giving preference to healthy foods will help strengthen your immune system. They are most found in vegetables, fruits and herbs.
- Dress your baby according to the weather. It is important that he is not too cold, but he should not sweat either.
- While there is inflammation behind the ear, it is important to cover your head. When the child is healthy, walking without a hat in slightly cool weather will stimulate the immune system.
- Traditional methods of treatment can only be used if approved by the attending physician. Many of them can be harmful.
We recommend further reading: Causes and consequences of hydrocele in newborns
It is necessary to observe the dosage of medications and give them to the child on time, however, drug treatment may not be enough, in which case additional physiotherapy may be prescribed.

The task is to demonstrate the lump behind the ear to the doctor in a timely manner in order to exclude serious causes that could affect the process and prevent possible consequences. Parents should be sure to monitor changes in the child’s condition in order to act in time. Self-medication is unacceptable; in the event of complications, recovery becomes much more difficult.