After the birth of a child, a woman should pay special attention to her diet. It should be complete, but some foods will have to be excluded from the diet so as not to harm the health of the newborn.
How to eat kiwi while breastfeeding? If you follow simple rules, this exotic fruit is allowed for breastfeeding.
Vitamins and nutrients contained in kiwi
Kiwi contains many useful components:
- vitamin C is necessary to improve immunity;
- vitamin B6 helps fight dysbiosis;
- Vitamin E helps protect the body from toxins, improve the elasticity of blood vessels and the condition of nails, hair and skin;
- vitamins A, D, PP;
- folic acid is necessary for the formation of red blood cells in the blood, helps the female body recover after childbirth, and has a positive effect on the formation of the child’s nervous system;
- potassium is necessary for normal functioning of the heart muscle;
- calcium helps strengthen the musculoskeletal system and teeth;
- iodine is necessary to regulate metabolism;
- fiber has a positive effect on the digestive system and helps quickly remove toxins from the body;
- organic acids;
- pectins.

The berry is low-calorie, which allows the mother to lose excess weight gained during pregnancy. Kiwi also has a mild laxative effect, helping to relieve constipation, which many women suffer after childbirth.
It is useful to use as a prophylactic during colds.
Useful properties of kiwi
Kiwi is an overseas product originally from China. Eating one fruit a day covers the daily dose of vitamin C, which helps strengthen the body's defenses, correct absorption of iron and magnesium, and stabilizes the functioning of the vegetative-vascular system.
Kiwi contains vitamin E, a natural antioxidant, which is responsible for normalizing cholesterol levels in the blood, strengthening the human immune system, and helping to resist stress.
Kiwi contains components such as fiber, folic acid, potassium, iodine, pectin, vitamins A, B, C, E, PP. The product is low in calories - about 60 kcal per 100 g of product.
With moderate consumption of the fruit, the functioning of the digestive tract is normalized, and the risk of flatulence in mother and child is reduced. The product improves the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Due to the high water content, it prevents the development of urolithiasis. Cleanses the skin from rashes and inhibits the process of gray hair. This is one of the best remedies for heartburn.
Kiwi is a natural source of serotonin, which leads to improved memory and mood, normalizes appetite, improves sleep, and stabilizes blood pressure.
How can kiwi harm you while breastfeeding?
Kiwi does not always bring only benefits during breastfeeding. In some cases, it is harmful for a nursing mother to use. Use is contraindicated in the presence of an individual allergic reaction.
Breastfeeding women should be careful if they have gastritis, peptic ulcers, high acidity or kidney problems.
Having a laxative effect, it can cause diarrhea in a child, since the substances are transferred with milk.
Due to the high content of vitamin C, eating kiwi can lead to the destruction of tooth enamel. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to brush your teeth to neutralize the acidic environment in the oral cavity.
In what form can you eat kiwi while breastfeeding?
Of course, the raw fruit will bring the most benefit to the body: it can be used as a snack.
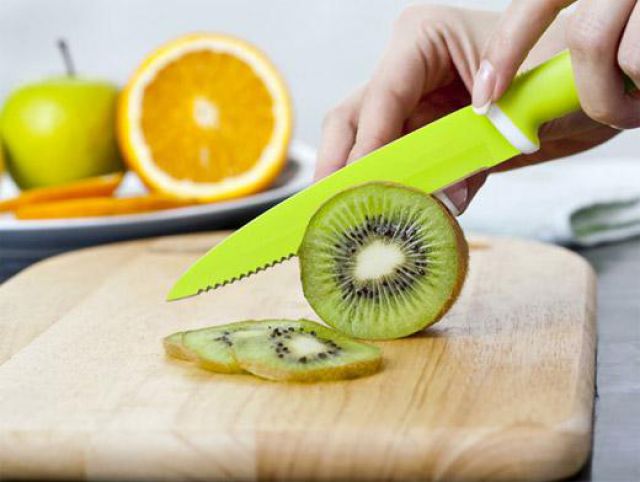

The aromatic berry can simply be eaten fresh.
As for freshly squeezed juice (such drinks are considered very healthy), it is very concentrated, and this is fraught with an allergic reaction. It is best to dilute the juice generously with water: in the ratio of 1 tablespoon of juice per glass of water.
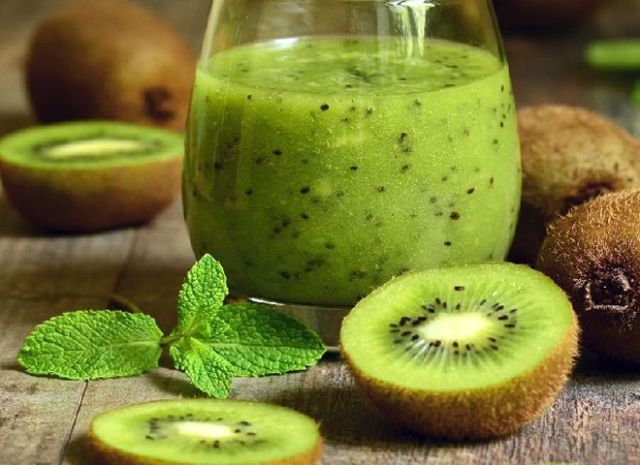

For a nursing mother, freshly squeezed kiwi juice is too concentrated and needs to be heavily diluted with water.
The peeled pulp is also good to add to berry compotes, which will not only enrich them with vitamins, but also add a piquant note.
Kiwi can be perfectly stored frozen - peeled and cut into pieces. This will allow a nursing mother to quickly prepare a drink.
The berry goes well with fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese. For example, to diversify her menu, a woman can prepare an unusual and very tasty casserole.
Cheese casserole
Ingredients:
- 400 g cottage cheese;
- 1 tbsp. spoon of flour;
- 1 tbsp. spoons of semolina;
- 0.5 cups low-fat kefir;
- 3 tbsp. spoons of sugar;
- 2 kiwis;
- 2 tbsp. spoons of sunflower oil;
- a pinch of salt and vanilla.
Preparation:
- Grind eggs, cottage cheese and sugar with a fork.
- Add dry ingredients and then kefir.
- Leave the mixture for 15 minutes for the semolina to swell.
- Pour the dough into the mold, decorate the top with kiwi slices and sprinkle with sugar.
- Bake in the oven for 40 minutes at 18 degrees.

Kiwi will add a piquant touch to a cottage cheese dish
Curd muffins with banana and kiwi
Ingredients:
- 150 g cottage cheese;
- 1 cup flour;
- 1 banana;
- 1 kiwi;
- 2 eggs;
- 4 tbsp. spoons of sugar;
- 50 g butter;
- 0.5 soda.
Preparation:
- Beat eggs with sugar until foamy.
- Separately mix cottage cheese with butter.
- Add the beaten eggs into the mixture and beat again with a mixer.
- Add flour and soda, mix everything well.
- Add banana and kiwi pieces.
- Fill silicone molds with dough.
- Bake the dessert in the oven for 30 minutes at 180 degrees.
- Sprinkle the finished dish with powdered sugar.
Video: airy curd dessert
An obligatory part of a nursing mother’s diet is vegetable salads. An interesting idea is to add kiwi there. So, the combination of sweet and sour berries with zucchini turns out to be interesting.
Vegetable salad with zucchini and kiwi
Ingredients:
- a small bunch of lettuce leaves;
- young zucchini (zucchini) - approximately 0.5 kg;
- 1 kiwi;
- 2 tbsp. spoons of low-fat cottage cheese;
- 20 g hard cheese;
- juice of half a lemon;
- olive oil for dressing.
- a pinch of salt.
Preparation:
- Tear the lettuce leaves with your hands. This method preserves the maximum of nutrients.
- Cut the kiwi and zucchini into small slices. Moreover, the berry pieces should be larger.
- Add cottage cheese (it should be crumbly).
- Prepare the sauce by mixing lemon juice with olive oil and season the salad with it.

Zucchini and kiwi - an unexpected but successful combination
How to correctly introduce kiwi into the menu
When breastfeeding, kiwi should be introduced into a woman's diet carefully so as not to cause a negative reaction in the baby. If a mother consumed this exotic berry during pregnancy, then when the child turns 3 months old, she can try to introduce it into her menu.
In the first months after childbirth, you should not eat kiwi.
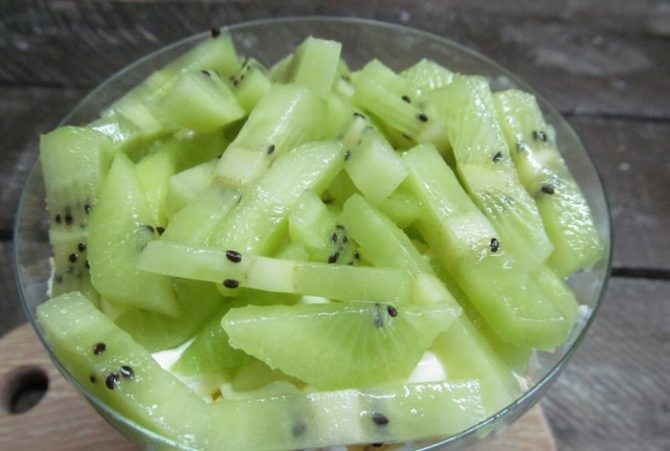

Kiwi salad is allowed during breastfeeding.
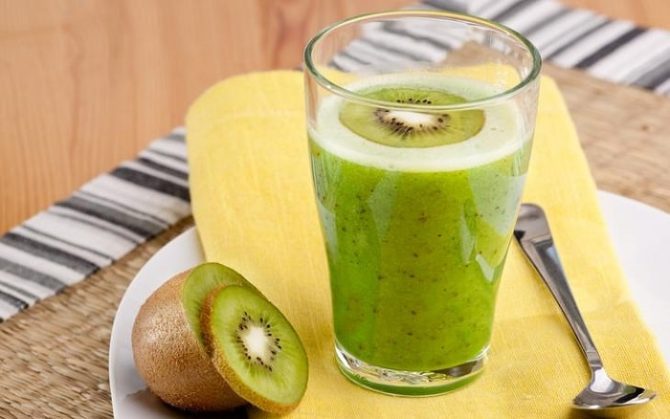

Kiwi pieces can be added to a smoothie.

Kiwi can be mixed with yogurt.
You need to start with a small piece (no more than 30 g) and monitor the child’s reaction throughout the day. If he is not allergic, then after 2 days you can eat another piece. But even if the child feels well, the mother is not recommended to eat more than 2 pieces per day.
The fruit can be consumed alone or in combination with other products, such as yogurt. Fermented milk drinks with kiwi pieces will diversify your mother's diet and bring her great benefits; they can be used as a snack.
You can add kiwi pieces to baked goods or fruit salads, cocktails and compotes.
The berry also goes well with vegetable salads with the addition of cottage cheese. By eating kiwi with peel, mom additionally saturates her body with healthy fiber. Before eating, you should wash it thoroughly, and if you eat it with the peel, it is advisable to scald it with boiling water.
Before eating kiwi, you should consult your doctor so as not to harm your child’s health.
It is better not to drink kiwi juice in its pure form; it must be diluted with water. It is enough to add 3 tbsp to a glass of water. l. freshly squeezed juice to get a drink rich in vitamins and other beneficial substances.
If a newborn has skin rashes or increased intestinal colic and behaves restlessly, then you will have to stop eating kiwi for several months.
At 6 months, the baby's digestive system will be stronger and mom will be able to try again if she likes kiwi.
Before eating the berries, it is recommended that the mother consult with a pediatrician so as not to harm the baby’s health. The doctor will help you calculate the optimal portion.
If a woman approaches her nutrition wisely during breastfeeding, she will not harm either herself or her newborn.
Nuances of use while breastfeeding
Due to the high allergenic properties of kiwi, this fruit can be tasted no earlier than when the baby is three months old. In the first months, the baby’s digestive system is not yet strong enough for such experiments.
You should start with a small piece (no more than 30 grams), which is best eaten in the morning, but not on an empty stomach. After this, the mother carefully evaluates the child’s condition for two days, paying attention to the manifestations of allergies and the functioning of the baby’s digestive system (there should be no colic or diarrhea). If the baby is fine, next time you can increase the portion of kiwi a little. However, the daily dose of the product should not exceed 100 grams (to avoid allergies due to an overdose of vitamins and minerals).

You can try a small piece for the first time
When introducing kiwi into your diet, you should not include other new foods at the same time.
How to choose quality kiwi
In order for an exotic berry to bring maximum benefits, you need to choose it correctly. It is recommended to choose individually, avoiding sealed packaging.
Fresh kiwi has a dark brown surface without cracks, dents, signs of rot or mold.

A ripe kiwi should be firm, fragrant, and free of dents.
The surface is covered with slightly harsh fibers, the area around the stalk is dry, without traces of secreted juice.
The smell should be aromatic and not contain sour notes from the fermentation process, which may indicate spoilage.
If you squeeze the berry with your fingers, it should press down slightly, but remain elastic. Fruit that is too soft and crumbly is not suitable for consumption.
You can buy unripe berries with a greenish tint to the skin. They will ripen at home in a warm place. And if you place kiwi in a bag next to a ripe apple or banana, the ripening process will speed up.
Breastfeeding period
Of course, after giving birth, a woman needs to restore her health. Taking vitamins, including in their natural form, will help cope with this task.
However, before introducing any product into the diet of a nursing mother, it is necessary to carefully weigh the pros and cons and only then make a final decision.
Despite the fact that a mother’s diet during lactation should be varied, most women still have to limit themselves in everything.
There is endless self-criticism and analysis of the likelihood of how the newly introduced product can affect the health of both mother and baby.
Pediatricians strongly recommend eliminating all foods that can cause an allergic reaction. This applies to both domestic fruits and vegetables and exotic ones.
Although the consumption of such a product as banana is even necessary during breastfeeding. But as for kiwi, it’s impossible to give a definite answer. But let’s still try to figure out whether a nursing mother can eat kiwi or not.
How does kiwi affect breastfeeding?
Domestic lactation consultants and pediatricians advise refraining from eating exotic fruits and berries, as they are completely chemically processed for better preservation during transportation. As for kiwi, it can also become an allergen for babies. Therefore, a young mother should not rush to introduce this berry. But at the same time, since kiwi is characterized by rich energy and vitamin value, its “reasonable” use will benefit not only the mother, but also the baby .
As you know, in order to eat this berry you need to peel it. But it will be much healthier to eat kiwi with the peel, since it is the peel that contains a large amount of vitamins and nutrients. But unfortunately, the quality of modern imported fruits and berries leaves much to be desired.
Basically, all vegetables, fruits and berries, both imported and domestic, are chemically treated to accelerate growth and ripening, as well as to increase their shelf life. Moreover, they are often coated with paraffin and wax. Therefore, I always wash purchased “vitamins” under warm running water and laundry soap, and most often I also use a sponge. Moreover, the child is already three years old, but I still peel the apples and give the baby only the pulp.
Harm to mother and baby from kiwi during breastfeeding
Reasons why you should limit your consumption of kiwi during lactation:
- The increased acidity of the berry due to the high concentration of vitamin C can cause destruction of tooth enamel in a young mother.
- The presence of fiber in kiwi determines its laxative effect, so it can provoke bowel problems in both mother and baby.
- The increased sensitivity of a fragile baby's body to the composition of the berry can cause allergic reactions in the form of skin rashes, redness and itching of the skin.
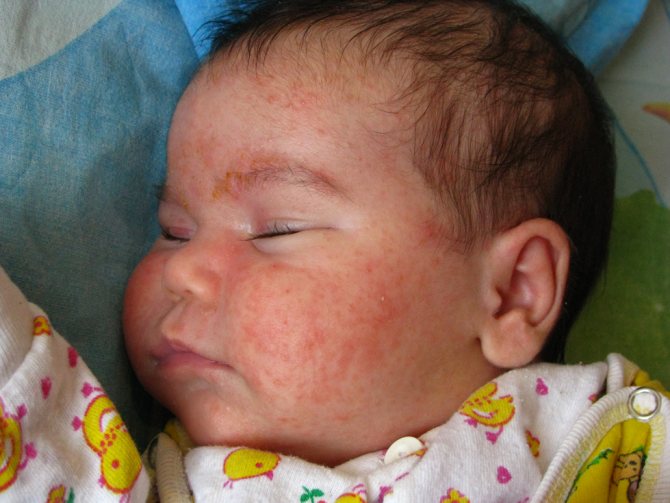
Eating kiwi by a mother during lactation can cause an allergic reaction.
Under no circumstances should kiwi be consumed together with dairy products, since the seeds contained in the pulp enter the intestines and interact with lactobacilli, causing fermentation processes. This can cause diarrhea, colic and bloating in the baby.
Kiwi juice, like the berry itself, is highly acidic, so the problem of early destruction of tooth enamel in children is becoming increasingly popular. Having personally studied the information about the benefits and harms of juice, I stopped giving my baby this not very healthy “water.” Of course, many children are attracted to colorful juice boxes with straws. But we mothers can be more cunning. As an option, you can cook homemade compotes yourself and let your baby drink them through a straw, either from a glass or from various colorful sippy cups.
Cases when a young mother is contraindicated to eat kiwi while breastfeeding
Kiwi is contraindicated for a nursing mother in the following cases:
- with impaired renal function;
- with increased acidity of gastric juice;
- for ulcers and gastritis of the stomach;
- in case of poisoning.










