Why flux develops in children - the main risk factors
In childhood, gumboil usually develops due to infection of the soft tissues in the oral cavity. Most often, the infection enters the peri-root area through a tooth affected by caries. Leukocytes concentrate within the lesion in order to resist harmful microorganisms, die, resulting in the formation of purulent exudate. Gradually, it accumulates in the resulting cavity, creating pressure on the surrounding tissues and provoking their inflammation. As a result, a painful lump appears on the gum and swelling develops.
As a rule, the following prerequisites lead to the occurrence of such a pathological process:
- advanced caries process and pulpitis,
- mechanical damage to the gums or cheeks,
- inflammatory process in gum pockets,
- low level of hygiene,
- failure to comply with the rules of asepsis during dental treatment,
- infectious diseases of ENT organs, etc.
Caries can cause the appearance of pathology
Flux in a child aged 5-7 years can appear as a reaction of the body to a sharp decrease in the immune system due to frequent colds1.
There is also confirmed evidence that a hereditary factor may become a secondary prerequisite for the development of the disease. If parents often suffer or suffered from a similar problem in childhood, the child is at risk.
What is baby tooth flux?
Periostitis is a purulent lesion of the periosteum.
It contributes to the formation of an abscess and the appearance of severe toothache. It can be acute or chronic. The acute form of the disease is difficult to miss - a lump appears on the child’s gum, filled with purulent masses. As a result, the cheek may “swell” and the cervical lymph nodes often become enlarged.
Chronic flux on a baby tooth often does not manifest itself at all. But at the same time, it has a destructive effect on the child’s jaw and causes negative changes in the functioning of his immune system. It is a consequence of incompletely cured acute periostitis, pulpitis, periodontitis or trauma.
ICD-10 code
K10.2 Inflammatory diseases of the jaws
How to recognize flux in baby teeth in children
Among the main symptoms of the disease are:
- the appearance of an abscess on the gum at the base of the tooth crown;
- the occurrence of aching pain from the inflammatory reaction;
- pronounced swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, lethargy;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- enlargement of the lymph node located on the side of inflammation.

The flux makes the child feel unwell. He becomes capricious, whiny, and refuses to eat.
Main symptoms and signs of periostitis
Flux in a child 6 years of age and younger occurs with pronounced symptoms. The main signs indicating the development of pathology include:
- Painful sensations in the oral cavity, intensified by eating food (at the beginning of the onset of the disease they are moderate, but as they progress they become intense).
- The appearance of a characteristic ball (accumulation of pus) in the gum area.
- Increased body temperature (up to 37.5-38°C).
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
- Redness and swelling in the gum area.
- The appearance of bad breath.
Young children aged 2-4 years with the development of flux may become capricious and refuse to eat. It is difficult for them to explain what the reason is; many parents mistakenly attribute this to bad behavior. Pay attention to other possible symptoms.
The main symptoms are pain and fever
If flux occurs on the upper jaw, then swelling may affect the cheek and parotid area. If all of the above symptoms are detected, you should not delay a visit to a specialist. Timely treatment guarantees the absence of negative complications.
Why does flux develop?
Various factors can lead to the disease. Among the most common:
- Trivial lack of oral hygiene. Many children refuse to brush their teeth and do not want to open their mouths at the dentist. If the health of their teeth is not carefully monitored, tooth decay will occur. As it progresses, the periosteum may become inflamed, leading to periostitis.
- Untreated caries. The enamel of baby teeth is destroyed very quickly, so the infection easily penetrates into deeper hard tissues.
- Gum injuries. If a child puts foreign objects in his mouth or chews something, he can damage the mucous membrane. The abrasion will become an entry point for infection.
- Pathologies of ENT organs. Sore throat, pharyngitis, adenoids, inflammation of the tonsils - all these are factors that can cause infection and provoke deepening of the gum pockets. This eventually leads to flux.
It is very important to understand why periostitis developed. Then it will be possible to eliminate the provoking factor, and therefore the disease will not return again.
Features of the pathological process
Periostitis can occur in acute or chronic form. In the first case, a small patient exhibits all the signs of gum suppuration, severe swelling and acute pain in the causative tooth, which intensifies with mechanical action. Often the characteristic symptoms are accompanied by high temperature.
If appropriate medical care is not provided in time, you may face the risk of the pathological process becoming chronic. In such a situation, the disease becomes even more dangerous, even though the acute symptoms usually subside.
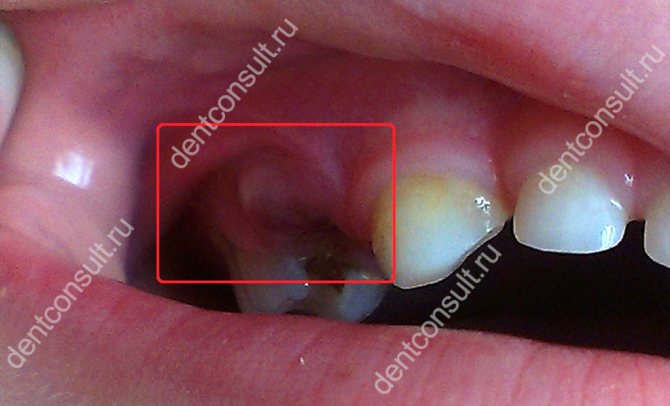
The mucous membrane turns red and swells within the pathological focus
In no case should they remain idle or try to correct the situation with improvised means without first visiting a doctor. The advice of traditional medicine really helps to relieve acute manifestations of the disease, but this does not mean that the pathology can be completely cured in this way. The infection will continue to spread through soft and even bone tissues, which can result in serious serious complications.
What is flux
Flux is a somewhat outdated name that is common only in everyday communication. In modern dentistry, this pathology is called periostitis, which reflects the essence of the disease.
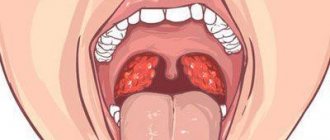
Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum that covers the bone of the upper or lower jaw. As the pathological process develops, the lesion ceases to be local in nature and spreads to other tissues - an abscess appears on the surface of the gum.
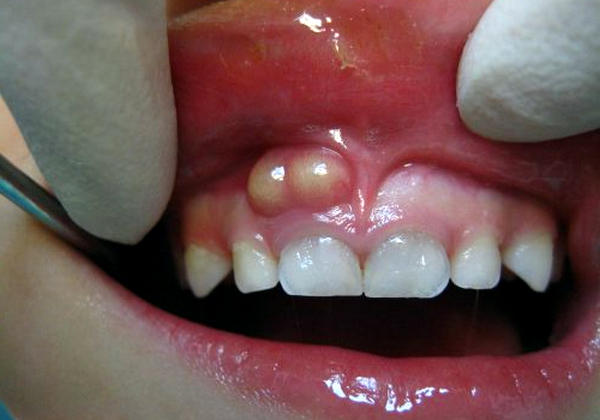
In the photo: gumboil in a 7 year old child
Clinical characteristics and diagnosis
The appearance of flux is difficult not to notice. The child becomes anxious because unpleasant sensations arise in the mouth, and the baby begins to experience obvious discomfort. In this case, visual signs of the pathological process are usually visible to the naked eye. The main symptoms of flux include the following:
- the appearance of a purulent lump on the gum,
- aching pain within the inflamed area,
- swelling of the face on one side,
- enlarged lymph nodes, pain when pressing,
- redness of the mucous membrane within the pathological focus,
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth,
- general weakness, fever.
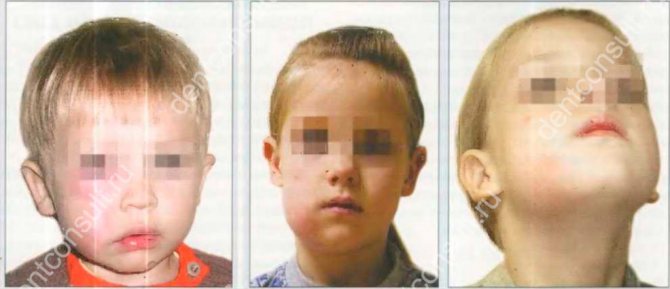
General weakness and swelling of the face appears on one side
“When my son was 5 years old, gumboil came out on his upper jaw. Of course, we went straight to the dentist. He opened his tooth and prescribed rinsing with soda, salt and iodine. By evening everything seemed to calm down, the child stopped crying and calmed down. The next day I saw that the balloon had inflated again. We went to the doctor, he cleaned everything there again and said we need to keep an eye on it. We stayed at home for a couple of days, then went back to the doctor. He looked carefully, everything seemed to be gone, and he put a filling. This is such an epic.”
MilaKar89, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
The further you go, the more acute the symptoms become. So, swelling can spread to the entire cheek, right up to the eyes. However, only a qualified dentist can correctly diagnose the disease. In the case of periostitis, it is important to begin treatment as soon as possible in order to prevent the development of serious consequences. In some situations, patients are sent for x-rays to differentiate the diagnosis and exclude other inflammatory pathologies, as well as check the condition of the bone tissue.
Causes
Parents should know what can lead to periostitis in a child. With this information, flux can be prevented by avoiding these conditions.
What are the causes of the disease?
- Mechanical damage to the cheek or gum itself.
- Formation of boils.
- Frequent caries.
- Lack of proper oral hygiene.
- Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during dental treatment.
- Inflammation of the gum pocket.
- Infectious processes in the body affecting the throat, for example, flu or sore throat.
- Incompletely treated teeth, for example, a canal that is not completely filled.
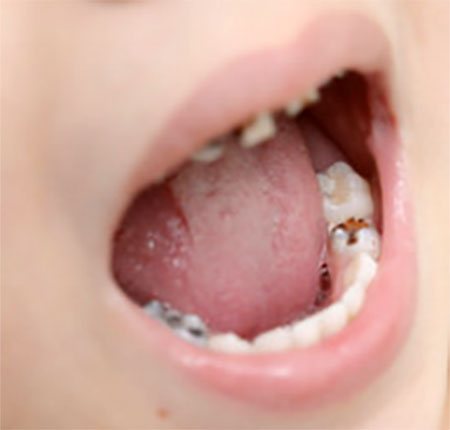
It is also worth considering that there are factors that place a child at risk, that is, increasing the risk of flux:
- hereditary predisposition;
- weakened immune system;
- ignoring stones formed on the teeth;
- excessive consumption of soda, as well as other sweets that provoke the development of caries;
- regular colds.
What you should never do - common mistakes
There are a number of important rules that parents should definitely follow when checking for signs of gumboil development in their child. Experts in the field of pediatric dentistry put forward the following categorical prohibitions in this regard:
- apply heat to the cheek from the side of the diseased tooth - such a compress can cause the infection to spread to the throat, ears and other parts of the body,
- giving a child antibiotics - the decision to prescribe such serious drug therapy can only be made by a professional doctor. Otherwise, potent drugs can negatively affect the health of the baby’s body,
- try to open the abscess yourself - again, only a doctor can do this correctly, in compliance with all the rules of asepsis, that is, without the risk of serious infection of internal organs and systems,
- overdo it with painkillers - if the child is really unwell, of course, before arriving at the dentist, you can give him half a painkiller tablet, but no more. Regarding the correct dosage and suitable remedy, you should consult your doctor, at least by phone.
During rinsing, make sure that the child does not swallow the solution - this can lead to infection entering the body. If after visiting the dentist the symptoms do not go away and the baby’s condition does not improve, it is better to consult a doctor again, and this should be done as soon as possible.
Flux treatment - how the dentist can help
As mentioned above, the disease should be treated by a professional dentist. Only after visiting a specialist and with his permission, you can use additional means at home as part of maintenance therapy, such as anti-inflammatory rinses and antibacterial agents for treating wounds.
If a purulent process develops, it will be necessary to perform surgical intervention - to open the cavity and, possibly, install a drainage system to ensure the outflow of purulent masses. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia with additional sedatives or even under general anesthesia, if necessary. If the causative tooth is severely damaged down to the root, it is removed.
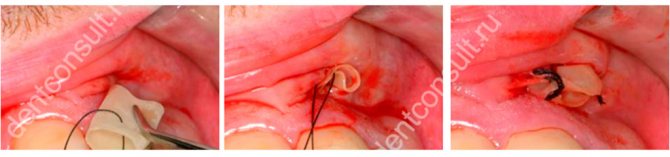
In difficult cases, drainage installation will be required
After the procedure, antibiotics are usually prescribed, as well as agents to relieve inflammation and antiseptic treatment. The medication course usually lasts about a week. In this case, the symptoms should gradually subside. If the swelling subsides and the pain becomes less severe, it means the child is recovering.
What to do with flux - treatment features
Attempts to open an abscess on your own can only aggravate the situation and lead to blood poisoning. The only thing is, if you can’t consult a doctor right away today, you can rinse the affected tooth with water and soda or salt. Also suitable for these purposes are pharmaceutical antiseptics designed specifically for treating the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The dentist always decides how best to deal with gumboil, taking into account the condition of the gums and the age of the patient. If the affected tooth is about to fall out, it is removed immediately. There is no point in stressing out a child by trying to save a unit that is about to leave the dentition anyway.
If we are talking about a tooth that the patient must live with for several more years, then conservative treatment is most often carried out. It is preferred to avoid crooked teeth in the future. Indeed, often when a tooth is pulled out prematurely, “neighbors” take its place. Because of this, the permanent unit then begins to erupt to the side, and it has to be put in place with the help of complex orthodontic treatment.
Conservative therapy involves opening a purulent neoplasm. The formed cavity is drained and washed with an antiseptic composition. If necessary, a drainage tube is installed in the gum for a while to avoid the re-formation of a purulent “bump”.
After such a procedure, special attention is paid to therapeutic rinses. The baby may even be prescribed antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Oral medications
To treat the disease, antibiotics are used to stop the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that cause gumboil. They are used when purulent foci appear, in cases where the inflammatory process is caused by the activity of streptococcal or staphylococcal bacteria, as well as to prevent complications. Antibiotics are also prescribed after surgery. The dosage and duration of administration are determined by the doctor. The average course of therapy is 5-7 days (sometimes more), interrupting it is not recommended.
Among the medications used in children, Lincomycin can be distinguished. It is effective and has a wide spectrum of action, can be used from 1 month. Ampiox is indicated for children from birth; up to 3 years of age, the drug is administered parenterally (bypassing the gastrointestinal tract).
From the age of 3, Biseptol can be used, which is well tolerated by the child's body and has a minimal number of side effects. If the situation is complicated by an increase in body temperature, then antipyretics based on ibuprofen or paracetamol are used - these drugs also provide an analgesic effect.
Treatment with antibiotics
Under no circumstances should you treat periostitis with antibiotics on your own. Only a specialist can choose the right medicine after a thorough examination of the patient. Antibiotics are selected on an individual basis. Along with them, medications for pain relief and elimination of the inflammatory process are necessarily prescribed. It is also worth taking medications that will reduce the harmful effects of antibiotics on internal organ systems. The dosage should also be prescribed by the attending physician, because in this situation it is important to take into account the general condition of the sick person and the severity of the pathology.
Periostitis is a very unpleasant disease that can have very serious consequences. Therefore, you should not endure toothache; it is better to immediately seek help from a specialist. It is also important to properly and regularly monitor the oral cavity in order to minimize factors that may affect the development of the inflammatory process in the periosteum. At the first symptoms of periostitis, you should consult a specialist to avoid surgical intervention.
Topical medications
For flux, rinses with an antiseptic effect are used, which are used 3-4 times a day after meals and before bed:
- aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin - used after reaching 5 years of age;
- Furacilin, ready-made solution or prepared independently - 1 tablet per 0.5 liters of water.
Surgical intervention
If the flux is accompanied by a deterioration in the condition and an increase in body temperature, the child should be urgently taken to the department of maxillofacial surgery. In other cases, surgical treatment of periostitis is carried out in a dental office. Local anesthesia is most often used, but general anesthesia is also used if necessary.
This is interesting: Should you go to the doctor if your frenulum ruptures?
The surgeon makes an incision in the area of the lump and installs a soft drainage tube, which prevents the edges of the wound from sticking together and allows the pus to drain freely until the inflammatory process stops. If this is not done, fluid will continue to accumulate in the tissues, which will worsen the inflammation. Typically, the drainage remains in the gum for about 3-5 days, after which the device is removed and the wound heals naturally.
When can you treat at home?
Flux is a disease so serious that even the best dentist in the world cannot cure it “in one fell swoop”. Even if everything goes according to plan, recovery will take several days. In the most severe cases, the child may require hospitalization, but this rarely happens.

Much more often, the doctor performs the necessary manipulations, and the child is sent home, where he must continue supportive treatment. At the same time, the doctor explains in detail to the parents what, how and when to do. Therapy is selected on an individual basis, and the more strictly parents adhere to the instructions issued, the greater the child’s chances of a full recovery.
In order to relieve a small patient of pain, the doctor will prescribe painkillers and explain how to take them.
Traditional methods
Often doctors, in addition to drug treatment, prescribe the use of traditional medicine.
- When flux is diagnosed in children, treatment at home can help reduce the severity of symptoms and alleviate associated symptoms. Sometimes it happens that periostitis is tolerated in a mild form; in such cases, traditional medicine methods are sufficient. But even then it is better to show the child to the dentist and be under his supervision.
- The use of an antiseptic - chlorophyllipt solution - will help to cope with the disease. To do this, you will need to add a tablespoon of the drug to 200 ml of water. Rinse your mouth with the prepared solution up to four times a day.
- Applying ice will help reduce pain. It is necessary to use specially designed pads filled with a salt solution or gel. As they heat up, you need to cool them in the refrigerator.
- If there is gumboil on a child’s gums, propolis tincture will help. It will quickly relieve inflammation and also disinfect the oral cavity. To prepare, add five drops of tincture to a glass of warm water. Rinse the mouth with this solution.
- You can make lotions. Cotton swabs are moistened in a solution of soda with the addition of iodine and sea salt.
- Garlic tincture has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- A decoction of sage, chamomile, oak bark, string and calendula has antiseptic properties. It is important to use freshly prepared products.
- Tincture of sage, St. John's wort, and eryngium has analgesic properties.
What not to do
Often parents do not know how to behave in such a situation. And there are times when they unknowingly harm a child. I present to your attention five points that are unacceptable in helping a child with gumboil:
- Use of antibiotics or analgesics. The use of any medications is permissible only after a doctor’s prescription. In addition, antibiotics can also kill beneficial oral microflora.
- Allow the baby to touch the bump. This can lead to infection, as well as to the fact that this swelling will burst and pus will begin to come out.
- Apply a heating pad or compress. The warming procedure negatively affects the inflamed area, in particular because it promotes the rapid proliferation of bacteria.
- Use aspirin after making an incision on the gum. This drug increases bleeding.
- You cannot be inactive and refuse to visit the dentist, especially if the lump has burst.
What can be done for prevention
It is important to understand that even with all the efforts on the part of parents, proper care and prevention cannot guarantee that the disease will bypass the child. Of course, in order to minimize the risk of developing any dental diseases, it is important to first ensure a high level of hygiene. Experts in the field of pediatric dentistry make the following recommendations in this regard:
- brush your teeth twice a day with a properly selected brush and toothpaste - it is better to consult your dentist individually about the choice of hygiene products. For baby teeth, it is usually recommended to choose a brush with soft bristles and a non-abrasive toothpaste that is appropriate for the child’s age.
- teach your child from an early age to rinse his mouth after every meal,
- promptly seek dental care if suspicious symptoms appear,
- visit a pediatric specialist every 3-6 months for a preventive examination,
- strengthen the immune system and accustom the baby to an active lifestyle,
- diversify the children's diet with fruits, vegetables and berries, as well as dairy products and fish - they contain all the necessary components for the proper growth and formation of dental tissues. Limit the consumption of sweets, flour and carbonated drinks, which contribute to the destruction of enamel and the development of caries.

Under no circumstances should you treat a child with flux at home - such arrogance on the part of parents risks leading to very disastrous and even life-threatening consequences. When the first symptoms appear, immediately go to the doctor and then, after the procedure of opening the abscess, strictly follow all his recommendations and instructions.
1Napolnikov L.B. Experience in preserving the causative tooth during periostitis on an outpatient basis, 2003.