Types of dropsy of the brain
The main functional variants of hydrocephalus include:
- obstructive hydrocephalus (so-called non-communicating): occurs when there is an obstruction to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid within the ventricular system of the brain;
- communicating hydrocephalus associated with a block in the normal absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
Special forms are also distinguished separately, for example, external hydrocephalus, which is characterized by enlargement of the ventricles as a result of a decrease in the amount of brain matter (brain atrophy). This condition is not true hydrocephalus and occurs as part of normal aging. Due to Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia, the process may be more pronounced.
Another type of hydrocephalus is called normal pressure hydrocephalus, or normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). It is characterized by the classic triad of symptoms (dementia, gait disturbances, urinary incontinence), as well as normal pressure during lumbar puncture. After bypass surgery, the condition improves.
Isolated IV ventricle is a type of hydrocephalus that occurs in the absence of communication with the III ventricle (through the aqueduct of Sylvius) and with the basal cisterns (through the foramina of Luschka and Magendie).
“Stalled” or compensated hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by the absence of progression or harmful consequences of hydrocephalus that would require the installation of a shunt. With this type of hydrocephalus, help is required only when symptoms of intracranial hypertension occur: headache, vomiting, impaired coordination of movements of various muscle groups, or visual disturbances.
Based on current rates, they are distinguished:
• Acute hydrocephalus, when no more than 3 days pass from the first symptoms of the disease to severe decompensation.
• Subacute progressive hydrocephalus, within a month from the onset of the disease.
• Chronic hydrocephalus, formed within a period of 3 weeks to 6 months or more.
Based on its origin, hydrocephalus is divided into congenital and acquired. In adults, the development of the acquired form is most often detected.
Types of disease
There are only three main forms of this pathology, in which fluid is observed in the head of a newborn:
- open hydrocephalus;
- closed, or occlusal form;
- hypersecretory form of pathology.
The closed type of the disease occurs in cases where there is a physical obstacle that interferes with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial container intended for it into the systemic bloodstream. This type is mainly caused by cysts along with tumors or hemorrhages.
The open type of the disease is usually observed when the mechanism of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the systemic circulation is disrupted. With this variant of the development of pathology, the cause of the disease is often previous infections. For example, meningitis or the presence of blood in the subarachnoid space.
Hypersecretory hydrocephalus is a relatively rare type of the disease in question and is observed in approximately five percent of cases. It usually occurs as a result of excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid. A similar situation can happen, for example, due to pathology of the choroid plexus.
Causes of hydrocephalus in adults
Causes of hydrocephalus in adulthood:
- CNS infections (meningitis, cysticercosis)
- hemorrhages (subarachnoid hemorrhages, intraventricular hemorrhages), in many cases temporary GCF occurs. In 20-50% of cases of extensive IVH, persistent HCF develops
- space-occupying formations of the brain (non-tumor, for example, vascular malformations and brain tumors). Types of tumors that can block the cerebrospinal fluid pathways: medulloblastoma, colloid cysts, pituitary tumors.
- hydrocephalus after surgery
- neurosarcoidosis
- “constitutional ventriculomegaly”: asymptomatic, does not require treatment
- spinal tumors.
Symptoms of the development of hydrocephalus in adults
The classic symptoms of the development of hydrocephalus are symptoms of increased intracranial pressure:
- papilledema;
- headache;
- nausea and/or vomiting;
- gait disturbances;
- oculomotor disorders (paresis of upward gaze and/or paresis of the abducens nerve).
Symptoms of axial dislocation of the brain may also be observed, which is a serious clinical condition and requires emergency medical care. However, slowly enlarging ventricles may not cause symptoms at first.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children over one year old
Parents should be alert to the following signs:
- The child began to complain of a headache, attacks of which at night or early in the morning caused vomiting;
- Vision problems, convulsions, urinary incontinence appeared;
- At times there is a disorder of consciousness;
- The child has developed insomnia, he does not show interest in outdoor games, general development has slowed down, and memory deterioration is pronounced;
- Nosebleeds occur quite often;
- Behavioral changes are noticed, coordination is sometimes lost, daytime sleepiness may appear, and the child will sleep for about a day.
All these changes most often occur against the background of increased growth and premature puberty, body weight increases rapidly and obesity manifests itself, despite dietary restrictions. Disruption of the endocrine system may be a sign of hydrocephalus.
Instrumental diagnosis of hydrocephalus
In most cases, the most informative studies on the basis of which doctors can diagnose hydrocephalus are computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. In some cases, to determine the advisability of shunt surgery in a patient with suspected hydrocephalus (non-obstructive), a Tap-test can be performed. The test involves removing 30 ml of cerebrospinal fluid through a lumbar puncture, after which the patient's cognitive functions are re-evaluated. Its improvement indicates a high probability of effectiveness of subsequent liquor shunt surgery.
Causes of brain hydrocephalus in children
Very often, parents of young children with a diagnosis of hydrocephalus turn to doctors. External hydrocephalus (water on the brain) is quite common among children, especially those born prematurely. In most cases, these children have normal psychomotor development, and often by the age of two years the size of the skull is normalized. The cause of this type of hydrocephalus in children may be immaturity of brain structures, hemorrhages and some other reasons.
Internal hydrocephalus in young children is congenital and is associated with the impact of pathological factors on the embryo and fetus. Such factors are various toxins, infections, medications, and abnormal formation of brain structures in the embryo.
Internal acquired hydrocephalus also occurs in children. The cause of acquired hydrocephalus in newborns is most often intraventricular hemorrhages that occur during childbirth. Acquired hydrocephalus can also occur as a result of brain injuries, infectious and parasitic diseases, neoplasms, etc.
Symptoms of hydrocele in children
Symptoms of hydrocele in children can appear at a very early age. With severe dropsy, pathological symptoms increase rapidly. With moderate dropsy, the symptoms are not so noticeable.
Main symptoms in young children:
- delayed physical and neuropsychic development
- lethargy, irritability
- decreased physical activity
- can't hold his head up well
- frequent regurgitation after eating
- increase in head circumference due to divergence of the cranial bones of the brain
- bulging and non-overgrowth of fontanelles
- expansion of the network of venous vessels in the head
- overhang of the brain skull over the facial skull, while the face appears very small
- deformation of the orbits, due to which the eyeballs turn downward.
In older children, fontanelles do not bulge; other symptoms predominate. Basically, this is a headache that is intense, often in the morning, and vomiting that does not bring relief. During the examination, specialists can detect stagnation phenomena on the retina, in particular, venous congestion and swelling. Over time, vision may deteriorate as optic nerve atrophy progresses.
Description of the disease
Today, almost every fifth newborn child can be diagnosed with increased intracranial pressure. Although in most situations it does not have any tragic consequences. But it is still worth checking the head for the presence of excess fluid in the head of a newborn. And if the diagnosis is confirmed, then you should definitely think about taking all the necessary measures for treatment.
Hydrocephalus of the newborn (or dropsy in other words) is the name of a complication due to which in the area of the brain in newborns there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, otherwise called cerebrospinal fluid. There are several variations of the disease, however, in children under two years of age, all its symptoms are very similar to each other.

The term "hydrocephalus" is derived from two Greek words that mean "water" and "head". In other words, this disease consists of excess fluid (water) in the head. This is where the second name of the pathology comes from, which sounds like dropsy of the brain. True, strictly speaking, this name is not entirely correct. The fact is that in the presence of hydrocephalus in the head of newborns, there is an excess not of water at all, but of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor is a liquid that is vital for the functioning of nerve tissues. It can be found in the spinal cord. We will consider the fluid levels in the head of a baby below.
In addition, it is also present in the brain. In it, a substance such as cerebrospinal fluid is concentrated in four ventricles, which are located in the center of the skull. The upper two are located in both hemispheres, and the lower ones are located along the central cerebral axis. The ventricles usually communicate with each other through a system of pipes called the cerebral aqueduct. In addition, cerebrospinal fluid can enter the subarachnoid space, which separates the meninges with special cisterns located at the base of the skull.
Complications of hydrocephalus
Untimely or erroneous diagnosis and treatment of patients with hydrocephalus can lead to the development of severe consequences that can lead to severe disability of the patient, such as: oculomotor and visual disturbances (up to blindness), disturbance of the shape and size of the skull, delayed intellectual/physical development, . In addition, in some cases, a dangerous complication of hydrocephalus can be displacement of brain structures and herniation of the brain, which leads to the rapid death of the patient.
Causes of fluid in the head of a baby
Dropsy in newborns can develop from simple prematurity. And in addition, from the presence or previous infectious diseases. For example, factors such as smoking, drinking alcohol and other bad habits of the mother, not just during pregnancy, but also in everyday life, can contribute to the development of this pathology in the newborn.
During the first few years of life, any head injury is very dangerous, as it can lead to an increase in the production of cerebrospinal fluid. A tumor that occurs in the brain can significantly interfere with the healthy flow of fluid in the head of a newborn baby. Which, in turn, will create excess pressure.
The importance of examination by a specialist
Considering the serious complications this disease can lead to, it is very important that from birth the child is under the supervision of competent specialists. First of all, a pediatrician, who, at the slightest suspicion of hydrocephalus, will prescribe a correct examination and refer you to the right specialists, first of all, to a neurosurgeon, who will prescribe a targeted diagnosis and select competent treatment, individually selected for the patient depending on the type and cause of the development of hydrocephalus.
As for adults, it is worth highlighting older people with symptoms of dementia and gait disturbances, which are often attributed to age. They also need examination by competent specialists, primarily neurologists and neurosurgeons, who, using diagnostic tests (TAP test) and instrumental examination (MRI with assessment of cerebrospinal fluid circulation, CT scan of the brain) can differentiate hydrocephalus from other causes of dementia. If you have hydrocephalus, most often normotensive in this situation, specialists can select a treatment that will significantly alleviate the situation.
Treatment
Surgery is one of the methods for treating hydrocephalus
A positive treatment result will depend on a number of factors:
- causes of the disease;
- the amount of liquor produced;
- dynamics of increasing head size;
- the extent of the disease at the time of its discovery.
This disease can be treated with both conservative and surgical methods. The patient should be under the strict supervision of a neurosurgeon or neurologist.
If we consider the initial stage of the disease, then medications will be prescribed first. The doctor’s actions will help reduce intracranial pressure; the specialist will also prescribe hormonal drugs to increase the accumulation of excess fluid and a diuretic. Diakarb is almost always prescribed; it perfectly lowers the pressure inside the skull and is also responsible for regulating the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
Surgical treatment is almost always prescribed for advanced conditions. The operation is performed in neurosurgery.
Parents should understand that delaying surgery may affect its outcome and lead to the development of more complications.
Initially, the doctor performs a puncture to pump out excess fluid.
If there is no positive effect, they proceed to bypass surgery. Shunts are inserted into the brain vessels, through which cerebrospinal fluid drains.
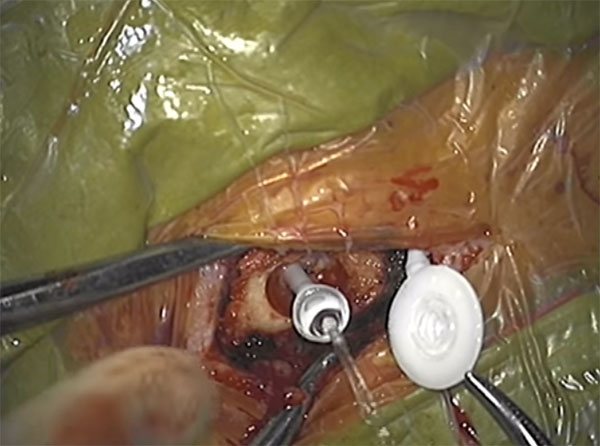
Bypass surgery