Reasons for appearance
A red throat in a child (the photo helps determine the severity of the symptom) is a sign that indicates natural processes.
Namely:
- Allergic reaction. The throat may turn red upon contact with a food irritant. For example, honey, orange, raspberry. The child may also be allergic to animal fur, dust, or pollen. The severity of symptoms varies. One child has a slight redness of the throat, while the other has severe coughing and sneezing. Most often, with allergies, the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx swells, breathing becomes difficult, and the eyes turn red. Additionally, rashes appear on the skin, the child sneezes.
- Eruption of baby teeth in infants. During this period, various symptoms are observed. In addition to redness of the throat, the child may have a runny nose. Additionally, there is an aversion to food, as pain in the gums causes discomfort.
- Injury to the pharynx and throat. If the mucous membrane is scratched, a symptom may appear. This happens when swallowing small bones or improper oral care. Redness of the throat also develops in case of a burn (too hot food).
- Deviation of the nasal septum. In children with this disorder, one side of the nose is wider than the other. As a result, the airflow in the cavity sometimes changes. But most often it comes evenly. The deformity may not be accompanied by symptoms. But difficulty breathing and nasal congestion are possible. The child constantly breathes through the mouth, as a result the throat may become red.
There are factors that increase the likelihood of a red throat.
These include the following points:
- frequent hypothermia - the child spends a long time outside in the cold season, dressed inappropriately for the season;
- weakened immunity – the infection enters through the nasal and oral cavity, the body cannot defend itself;
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- contact with a sick (angina, ARVI) child.
Features of the clinical picture in various diseases
Redness of the throat can occur both in children 2-3 years old and in older children, for example, 7-10, 12-15 years old. Various diseases can cause this symptom. In this case, the patient’s clinical picture will have some common features. These include:
- Pain when swallowing.
- The baby may lose his appetite, the baby will be capricious and refuse to breastfeed.
- The throat feels sore and dry.
- A dry cough often appears.
- Some children complain of difficulty breathing.
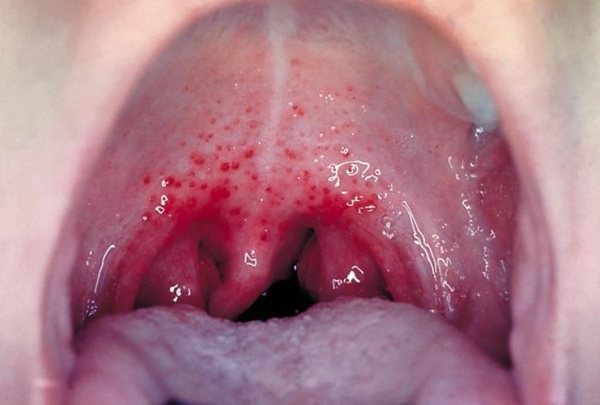
If parents notice such signs in their child, it is important to conduct an initial examination of the throat. In this case, you can see swelling, redness, and enlargement of the tonsils.

When palpating the cervical lymph nodes, they are observed to increase in size. More detailed symptoms will depend on the cause that provoked the disease in a particular case.
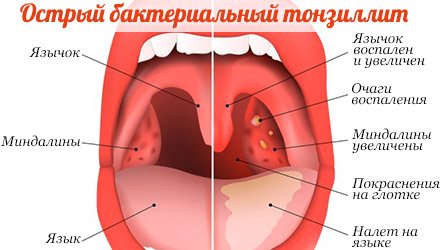
Clinical picture of angina
Infection of the throat with streptococci causes such a dangerous infectious disease as sore throat. At the same time, the child’s body temperature rapidly rises to 39-40°C, is difficult to knock down and can persist for 5-7 days. High temperature is very dangerous for babies in the first three years of life. If you suspect a disease in your baby, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-treatment at home is not allowed.
You may be interested in: Signs and treatment of pneumonia in a child
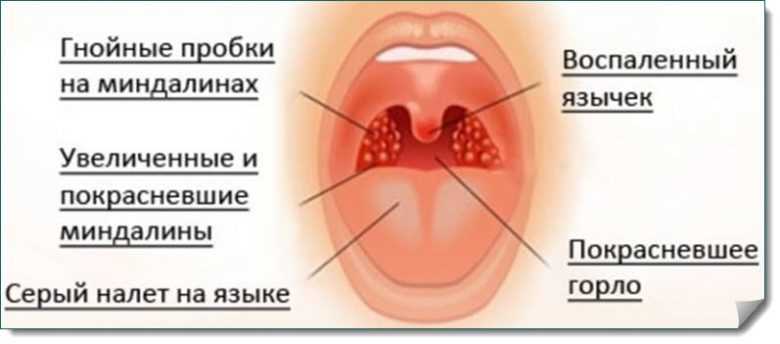
Symptoms of sore throat in children:
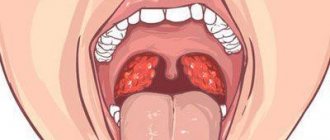
- Loose throat and tonsils.
- Redness.
- Enlarged tonsils. They often increase so much that breathing difficulties are observed, especially in infants.
- The newborn has constant drooling and snot may appear, although this sign is not typical for a sore throat.
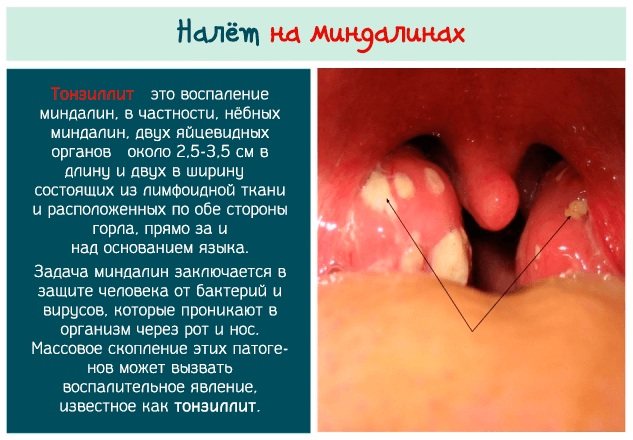
- High body temperature, as a rule, occurs simultaneously with the appearance of white plaque on the tonsils.
- Purulent formations (plugs) appear in the lacunae of the tonsils.
- The child complains that his throat hurts. The posterior wall is swollen and mucus may drain along it.
In addition, children with sore throat lose their appetite, become lethargic, moody, and generally lose strength. Often there are signs of intoxication of the body. The little patient suffers from diarrhea, body aches, headache, and pain in the abdomen.
Sore throat is a disease that is often accompanied by complications. It is recommended to treat the disease in children in a hospital setting under close medical supervision.
Symptoms in children with pharyngitis
In children in the first months of life or in children after a year, an infectious disease such as pharyngitis can provoke redness of the throat. In its primary manifestations, pharyngitis is a bit like a sore throat, but later the pathology is not so acute. The body temperature of a small patient rises to 37-38°C. Higher levels can be observed in babies 6-8 months old with weakened immune systems.
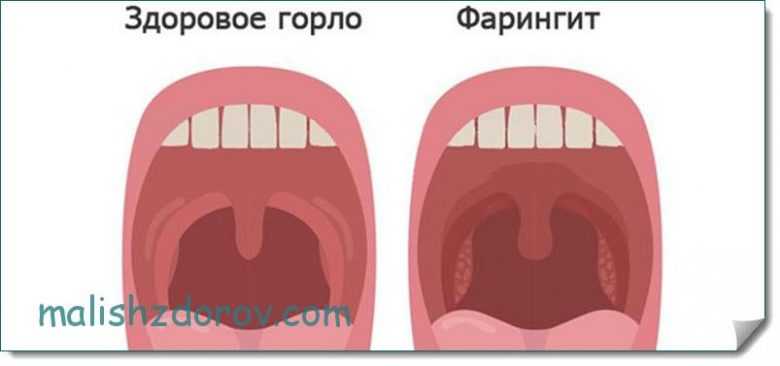
The general well-being of the patient, as a rule, is not disturbed. The child eats well, plays and sleeps normally. The situation worsens if medical assistance is not provided in the early stages. In this case, the inflammatory process is often transferred to the lower parts of the respiratory system, and the disease becomes chronic.
Manifestations of an allergic reaction
Redness of the throat and swelling are often observed in children with the development of an allergic reaction. A swollen throat is not considered the only symptom. The clinical picture of the disease has the following manifestations:
- Allergies, as a rule, occur without fever.
- The child has swelling in the nasopharynx area.
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing often develop.
- The mucous membrane of the eyes turns red and swells.
- A small patient suffers from a dry cough, nasal congestion, and sneezing.
- There is increased lacrimation.
- There is moderate soreness and soreness in the throat.
Allergies in a one-year-old baby or older children can be triggered by a variety of factors.

These include food, dust, pet hair, pollen, insect bites, the use of certain medications, etc. To prevent complications, it is important to detect and eliminate the allergen. Otherwise, any treatment will be ineffective.
Mechanical damage to the throat
Hyperemia and swelling in children in the larynx area often occurs due to accidental damage to the mucous membrane of the throat. The baby can be injured by swallowing solid food, while brushing his teeth, or by swallowing a small object with sharp edges. If this happens, you should immediately seek help from a hospital. It is especially dangerous if, for example, there is a fish bone stuck in your throat. Trying to get it out at home can only cause a foreign object to dig deeper into the soft tissue and cause more severe injury to the throat.

To prevent such situations, you should carefully monitor the food that the child takes and do not leave children without adult supervision.
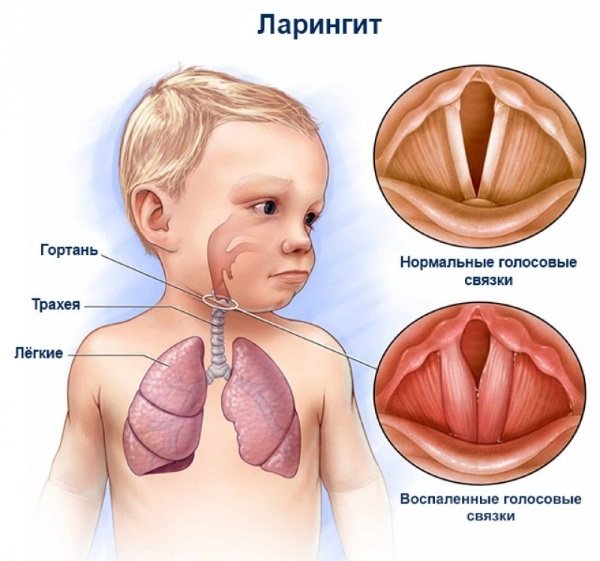
Clinical picture of laryngitis
By this concept, doctors mean an acute infectious disease, accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process in the larynx. Laryngitis can be caused by both viral and bacterial pathogenic agents. Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Redness of the throat.
- Swelling of the laryngeal tissues.
- Dry barking cough.
- Pain when swallowing.
You may be interested in: Treatment of allergic rhinitis in a child
The danger of the disease for children is that the pathology can provoke laryngospasm and an attack of suffocation. If you suspect laryngitis in your child, you should immediately consult a doctor. Children with weakened immune systems and prone to allergic reactions are at risk.
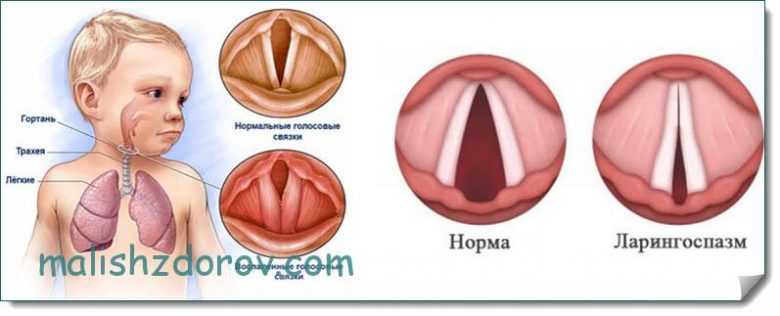
You can read more information about the symptoms and treatment of laryngitis in children in one of our articles.
Features of the course of fungal infection in the mouth
Redness and soreness in the larynx may not always indicate tissue damage by a viral or bacterial infection. Sometimes the problem develops against the background of infection of soft tissues by pathogenic fungi. In this case, the child has the following clinical picture:
- Redness and swelling.
- Baby's refusal to eat.
- Moodiness, irritability.
- Formation of white papules in the throat and entire oral cavity.
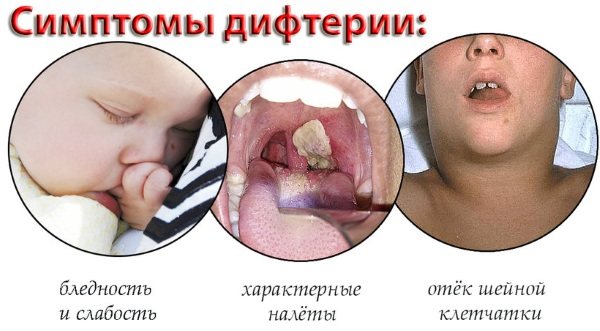
It is important to know that white formations can appear with such a dangerous disease as diphtheria.
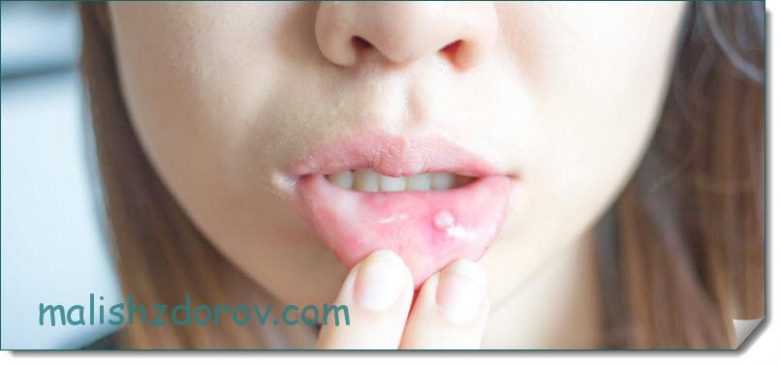
A fungal infection differs in that the white plaques are easily removed. If you try to remove plaque with cotton wool during diphtheria, a bleeding wound will remain at the site of formation.
Expert opinion
Ksenia Dunaeva
User experience expert and comment moderator. Higher medical education and more than 5 years of actual practice.
Ask Ksenia
Another pathology that can cause redness, pain and swelling in the throat is scarlet fever. The disease is caused by streptococcus bacteria. Scarlet fever is transmitted by airborne droplets and often provokes complications in children and adults. You can read more about the symptoms and treatment of scarlet fever on our information portal.
Possible diseases
Redness of the throat may indicate illness. They are listed in the table.
| Name of pathology | Description |
| Angina | The disease is characterized by inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the pharyngeal tonsils. Sore throat appears when exposed to pathogenic microorganisms - streptococcus and staphylococcus. Another name for the disease is acute tonsillitis. Symptoms of a sore throat in a child:
The child does not want to eat and complains of a sore throat. If you examine the tonsils, you can see plaque, as well as redness.
The disease is contagious to others. Therefore, it is necessary to isolate the child in a separate room, provide him with hygiene supplies (towel, soap, etc.), and dishes. |
| Pharyngitis | With pathology, the mucous membrane of the pharynx becomes inflamed. Symptoms of the disease:
The disease is divided into acute and chronic. In the first case, the symptoms are pronounced, but they begin to appear 2–3 days after the virus enters the body. Chronic pharyngitis is characterized by mild symptoms and develops in the absence of therapy for the acute form. |
| Tonsillitis | The disease affects the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils. Tonsillitis can be acute (tonsillitis) or chronic. The second type has a sluggish course. Chronic tonsillitis appears when angina is not treated in a timely manner or when there is no treatment at all. The main difference between the form and the acute form is the severity of symptoms. Chronic tonsillitis develops slowly, and tonsillitis develops quickly and with clear signs.
|
| Retropharyngeal abscess | Another name is retropharyngeal. The disease is characterized by suppuration and inflammation of the tissue in the retropharyngeal space (the area behind the pharynx) and lymph nodes. An abscess most often develops in the absence of treatment for infectious diseases (measles, ARVI, tonsillitis). Pathology is always accompanied by symptoms. Common signs:
|
| ARVI | Acute respiratory viral infection. Abbreviated as ARVI. The disease is an acute inflammatory lesion of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. The causative agents of ARVI are viruses. There are a total of 300 agents that can cause infection. A group of pathologies occurs in each child up to 10 times a year. ARVI symptoms:
|
| Laryngitis | Pathology involves inflammation of the vocal cords. Symptoms of laryngitis in a child:
Laryngitis is dangerous due to the development of an obstructive form (croup). The larynx narrows sharply, and there is a lack of oxygen. At the same time, the child’s body begins to turn blue. Parents need to closely monitor the condition and call an ambulance. Before the team arrives, it is necessary to set the child to a calm breathing rhythm.
|
| Stomatitis | Lesions appear on the oral mucosa. Ulcers and erosions can be single or multiple. Symptoms depend on the type of stomatitis: 1. Viral. The most important symptom is a rash in the form of blisters. It quickly opens and erosions form on the mucous membrane. While eating, a person feels pain, lymph nodes become enlarged, and appetite decreases. Sometimes you may notice redness of the throat. 2. Fungal. Most often, the variety occurs in children of the first year of life. Symptoms include tightness and dryness of the oral mucosa. Additionally, an unpleasant odor appears from the cavity. Infants may behave restlessly and refuse to eat. 3. Bacterial. The mucous membrane of the mouth turns red and swells. You can also notice yellow erosions. Additionally, salivation increases and the temperature rises. 4. Aphthous. The child’s well-being worsens, and there is dryness and pain in the mouth. Next, the mucous membrane becomes covered with ulcers with a fibrous film. |
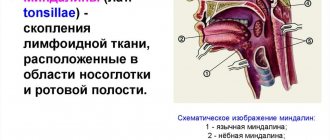
| Adenoids | The pathology consists of enlarged tonsils, which are located in the nasopharynx. Symptoms:
Adenoids are dangerous because nasal breathing is impaired, then problems with the central nervous system appear, and the child lags behind in development. Additionally, there is a focus of inflammation; the infection can spread to other organs. |
| Diphtheria | An infectious disease that affects the nasopharynx. But pathology can also affect other organs - bronchi, larynx. Without timely treatment, the disease is fatal. The causative agent of diphtheria is a rod-shaped bacterium. It is tenacious and can withstand low temperatures. When the pathogen enters the body, the production of a dangerous poison begins.
Symptoms of diphtheria:
After some time, the temperature drops. The parents think it’s a cold and calm down. But the disease develops and affects the body. After a few days the following symptoms appear:
|
| Chicken pox | The abbreviated name is chickenpox. The disease is infectious in nature. Chickenpox most often occurs in children under 12 years of age. Symptoms:
|
| Scarlet fever | An infectious disease caused by streptococci. Symptoms:
|
| Rotavirus infection | An infectious disease that develops under the influence of rotaviruses. Another name for the pathology is intestinal flu. Symptoms in children:
|
| Rubella | Acute viral disease. Symptoms:
|
| Respiratory system diseases | With bronchitis or pneumonia, the throat may become red. Diseases are rarely accompanied by this symptom, but the symptom cannot be excluded. |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | Contents from the stomach move back into the esophagus. Symptoms in children:
|
Symptoms of a red throat in a child
Common clinical signs of red throat in children are:
- complaints of pain when swallowing;
- refusal to eat (the baby may refuse the mother’s breast);
- sore throat;
- coughing;
- dry throat.
When examining a child’s pharynx, you may notice slight swelling and severe tissue hyperemia. When palpating the cervical lymph nodes, their pain and increase in size are noted.
Depending on the specific cause of the red throat, the child may experience despair and symptoms.
Red throat with sore throat: symptoms
Sore throat is an infectious disease caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. The disease is extremely dangerous due to its rapid progression and possible complications, so parents should not self-medicate and try to cope with the disease at home, especially if the child is under 3 years old.
To the clinical symptoms described above are added:
- the appearance of a sharp swelling in the area of the tonsils - sometimes their enlargement is so strong that the child cannot breathe normally;
- pain even when swallowing saliva - this is why, with a sore throat, infants experience constant drooling, and older children spit out saliva to avoid pain;
- the appearance of white or gray plaque on the surface of the tonsils - in severe cases, yellow purulent plugs form in the lacunae of the tonsils;
- coated tongue with a gray or yellowish coating;
- high body temperature – rises rapidly and reaches 39.0-40.0 degrees.
A child with a sore throat is lethargic, apathetic, cries, and cannot open his mouth normally. In the absence of timely treatment, signs of intoxication of the body quickly appear - muscle pain, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and sometimes vomiting.
Important! a child with a sore throat must be treated strictly in a hospital, especially if he is less than 3 years old, since the progression of a sore throat and swelling of the throat tissue can lead to laryngeal stenosis and suffocation.
Red throat in a child with pharyngitis: symptoms
Most often, redness of the throat in children is caused by pharyngitis, a viral infection that affects the mucous membrane of the pharynx. At the initial stage of development of the disease, pharyngitis resembles a sore throat, only the clinical picture is not so acute and the child’s condition is not so severe.
Body temperature may remain within normal limits or rise to 38 degrees; the child’s condition is generally not impaired. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, complications may arise in the form of the disease becoming chronic, the spread of inflammation to the upper and lower respiratory tract, and the development of sore throat.
Laryngitis as a cause of red throat in children
Laryngitis is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx, characterized by a cough and a change in the timbre of the voice.
The main clinical signs of laryngitis in children are:
- redness of the throat;
- swelling of the tissues of the pharynx and enlargement of the tonsils;
- the appearance of a dry cough reminiscent of a dog barking (called a “barking” cough);
- sore throat and complaints of pain when swallowing.
Laryngitis can be complicated by laryngeal stenosis and asthma attacks in a child, so it is better to be under the supervision of a doctor, especially if the disease occurs for the first time in a child.
Attention! The risk group for the development of laryngeal stenosis includes children prone to allergic reactions and babies under 3 years of age. In the absence of timely assistance from medical personnel during stenosis, the child may suffocate and die!
Fungal infection in the mouth
A red throat can be the cause of the multiplication and growth of a fungal infection in the mouth. The disease is characterized by the appearance of white spots in the mouth and on the surface of the mucous membranes of the oropharynx, which are easily removed with a gauze swab soaked in a soda solution.
Clinically, fungus of the oral cavity and pharynx is manifested by the following symptoms:
- baby crying;
- severe anxiety;
- refusal to eat, and the baby refuses mother's milk;
- the formation of white plaques of varying sizes throughout the oral cavity.
The main distinguishing feature of this disease from diphtheria is that white spots are easily removed with a gauze swab, whereas with diphtheria, white plaques are difficult to remove and bleeding wound surfaces remain in their place.
Allergic reaction
A red throat in a child may be caused by an allergic reaction. In addition to this symptom, signs of allergies are:
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- labored breathing;
- discharge of large amounts of mucus from the nose;
- swelling and redness of the eyes;
- skin rashes;
- sneezing, nasal congestion;
- lacrimation;
- sore throat, cough.
An allergic reaction can be caused by various factors, the most common of which are:
- house dust;
- contact with household chemicals (child’s things can be washed with low-quality powder);
- inhalation of mold fumes;
- contact with pet hair;
- flowering of herbs and plants;
- allergic reaction to certain foods (nuts, honey, citruses, salmon caviar);
- use of high-risk medications (antibiotics, throat sprays).
Throat injuries
A child's red throat may be the result of injury to the delicate mucous membrane by small foreign objects - a fish bone, a toothbrush, toys, small parts. If such a situation occurs, the child must be immediately taken to the hospital and under no circumstances try to remove the stuck object on their own. With incorrect movements, you can push a foreign body deeper into the respiratory tract, which will lead to blocking the access of oxygen and asphyxia of the child (suffocation).
To avoid developing throat injuries, it is recommended not to leave young children unattended.
Diagnostics
A red throat in a child is a sign that requires examination. It is carried out before treatment is prescribed. A photo of the sign and a study of the symptoms allows you to make a preliminary diagnosis. But to get complete information about your health, you need to undergo an examination.
It includes the following procedures:
- Blood and urine tests. The procedures allow you to determine the value of important indicators (red blood cells, hemoglobin, etc.).
- Rhinoscopy of the nose. The procedure is carried out with a special instrument. It's called a rhinoscope. The modern device is equipped with a video camera through which the doctor examines the nasal cavity. The image is displayed on the monitor. If the child is small, the mucous membrane may be numbed with anesthesia (spray) before the procedure.
- Pharyngoscopy. Method of examination of the pharynx. First, the mouth is treated with an anesthetic spray to eliminate discomfort. The root of the tongue is pressed with a spatula, a mirror is inserted into the cavity, and the condition of the mucous membranes is assessed.

- Throat swab. The procedure is carried out to determine the type of pathogenic microorganisms. The nurse collects plaque and mucus in the mouth with a cotton swab. The biomaterial is placed in a test tube with a nutrient solution and sent to the laboratory.
- X-ray. A diagnostic method is prescribed if there is a suspicion of nasal pathology.
The cost of diagnostics varies, it all depends on the list of procedures, city, and clinic. Therefore, you need to find out the specific price from the organization.
When to see a doctor
A red throat in a child (photos and videos help make a preliminary diagnosis) is within the competence of the pediatrician. The doctor conducts a survey; parents need to describe the child’s well-being. The next step is inspection. It involves measuring temperature and pressure and listening to the heart. They also count breathing and pulse rates, examine the oral cavity and skin.
It is possible that you will additionally need to consult a surgeon (if surgery is necessary), or an otolaryngologist (who treats diseases of the ears, nose and throat).
Symptoms that require calling your doctor or an ambulance:
- the temperature is high (more than 39 degrees) and does not subside with the use of antipyretics;
- the sore throat is severe, the child cannot swallow;
- severe vomiting with blood;
- breathing is impaired;
- The child’s well-being deteriorates sharply.
Throat examination
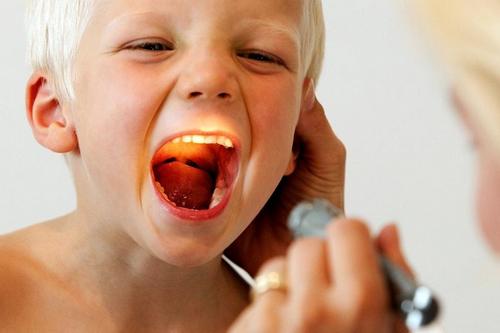
The hardest time is for those parents who need to examine the throats of young children. To assess the condition of the pharyngeal region, you need to know several rules.
- There will be little sunlight to examine the throat. Therefore, you need to use additional lighting in the form of a flashlight or lamp.
- To examine the throat, you need to take a wooden stick and a spoon. Pressure with these objects should not cause the patient to feel vomiting. Therefore, you should press not on the root of the tongue, but on its middle or tip.
- If a person needs to see the condition of the tonsils, it is not necessary to use a spoon or stick. It is enough to stick out your tongue well and shine it with a flashlight.
- While examining the pharynx, you need to breathe through the oral cavity. At this moment, the tongue itself goes down, and the palate, on the contrary, rises.
If all measures are followed, the procedure will be painless.
Prevention
A red throat in a child (photos and descriptions of symptoms allow a preliminary diagnosis to be made) is a sign that can be avoided. To do this, it is recommended to follow preventive measures.
They include the following rules:
- absence of hypothermia - selection of clothes according to the weather;
- draft prevention;
- washing hands before eating, after going outside and going to the toilet;

- nail frequency control;
- purchasing hand sanitizer or disinfectant wipes;
- proper lifestyle - balanced nutrition, physical activity;
- frequent walks in the fresh air;
- preventive examination by a pediatrician once every 6 months;
- examination of the body once every 12 months.
Prevention of throat diseases in children
To prevent various viral, bacterial and fungal diseases, parents should teach their child to adhere to simple preventive methods.

The following tips should be taken into account:
- Humidity and temperature in the room. In the children's room, the temperature should be between 18-23 degrees and the humidity should be 40-60%.
- The baby should eat properly and drink enough fluids. It helps in the prevention and treatment of various diseases.
- Drinks and food should be warm. They should not be allowed to be too hot or, conversely, cold.
- The children's room should be wet cleaned daily.
- It is necessary to ventilate the room frequently.
- It is important to wash your hands thoroughly after visiting the street and crowded places, especially during the cold season.
- It is important to eliminate allergens if your baby is prone to allergic reactions.
- You need to walk in the fresh air every day.
- Children should not be left unattended. This will help prevent situations where small objects may be swallowed.
These simple recommendations will help keep your little ones healthy. If negative symptoms do arise, you should not let the situation take its course, look for treatment methods on various forums, or self-medicate. The child should definitely be shown to a doctor. Only timely and competent medical care gives every chance of a quick recovery and prevention of dangerous complications.

All information in this article is provided to readers for informational purposes and cannot be regarded as a call for self-medication.
Treatment methods
Redness in the throat needs treatment.
Treatment involves the use of:
- medicines;
- folk remedies;
- other methods.
Additionally, it is necessary to follow the general rules of treatment:
- periodically ventilate the room to reduce dry air;
- the child should drink plenty of water - clean still water, tea with raspberries or lemon;
- food should be warm, but not hot;
- exclude spicy, fried, salty foods;
- carry out wet cleaning every day;
- remove all flowers that may cause allergies;
- feed 5 – 6 times a day, but you cannot force the child;
- games should be calm, according to the child’s wishes;
- walks are allowed, but if there is no high temperature.
Medications
Medicines help eliminate symptoms and make the child feel better. Medicines are prescribed depending on the cause of the symptom. Detailed information is shown in the table.
| Cause of red throat | Method of drug therapy |
| Allergic reaction | The child must take antiallergic medications. Namely:
|
| Teething | To reduce pain and redness in the mouth, the following medications should be used:
|
| Angina | Treatment of the disease includes the use of the following groups of medications: 1. Antibiotics. Medicines destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Prescribed only when the disease is bacterial in nature. The group includes Sumamed, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav. 2. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The drugs eliminate pain and fever. Representatives of the group are Nurofen, Ibuprofen. 3. Antiseptics. The preparations are intended for rinsing the mouth. After use, the number of bacteria decreases. The group includes Miramistin, Chlorhexidine. 4. Antitussives. Medicines can eliminate cough. The group includes Gerbion, Rengalin, Lazolvan. The choice of drug depends on the type of cough (dry or wet). 5. Immunomodulators. The drugs improve the body's protective functions. The group includes Echinacea, Immunal. 6. Vasoconstrictors. The drugs are intended to relieve runny nose and nasal congestion. Representatives of the group are Nazivin, Otrivin. Before using the drops, the nasal cavity must be rinsed with sea water (Aquamaris, Aqualor, Dolphin). Then the effect of vasoconstrictors will increase. 7. Vitamin complexes. The drugs restore the deficiency of nutrients in the body. The group includes Complivit, Multi-Tabs. Additionally, it is recommended to purchase medications for sore throat (Strepsils, Grammidin, Faringosept). There are also medications in spray form (Tantum Verde, Hexoral, Ingalipt). |
| Retropharyngeal abscess | As a medical treatment, antibiotics, immunomodulators, and NSAIDs are prescribed in the initial stages of the disease. |
| ARVI | For the treatment of a group of diseases, NSAIDs, antitussives, and vasoconstrictors are prescribed. Additionally, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes, immunomodulators, and remedies for sore throat. Antiviral drugs are also prescribed for ARVI. Medicines effectively fight pathogenic microorganisms. Antiviral drugs include Arbidol, Anaferon, Viferon.
Additionally, it is possible to use drugs that are intended for the symptomatic treatment of acute respiratory infections. They struggle with fever, fever and pain. The group includes Fervex, Theraflu, Maxicold. |
| Laryngitis | The following groups of drugs are used to treat the disease:
|
Medicines should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account individual characteristics, the cause of the symptom, and age category. When purchasing medications, you must study the instructions.
Traditional methods
A red throat in a child (the photo will help the doctor monitor the effectiveness of treatment) is a symptom that can be reduced by using folk remedies.
Herbal recipes have a low likelihood of side effects. Folk remedies must be used as part of complex therapy, together with medications and other methods. If you neglect this point, the effectiveness of using recipes will not be maximum.
Folk remedies that can be used for redness of the throat:
- Soda solution. To prepare, you need to take 1 tsp. component and 250 ml of boiled water. Mix thoroughly and use this solution to rinse 2 – 3 times a day.
- Chamomile decoction. To prepare the recipe, you need to take 1 tsp. crushed flowers and 1 glass of hot water. Cook over low heat for 5 – 10 minutes. Leave covered for 10 minutes. Filter through cheesecloth. Gargle 2 – 3 times a day.

- Calendula. To prepare, you need to take 1 tsp. component and 250 ml of hot water. Leave for 5 – 10 minutes, filter through gauze. Gargle 2 – 3 times a day.
- Cabbage leaf. To prepare, you need to omit 1 - 2 pcs. product in boiling water for 2 - 3 minutes. Wait for the sheet to cool and apply it to your throat. To enhance the effect, wrap your neck with a plastic bag and a towel on top.
Other methods
In addition to medications and folk remedies, other methods can be used for redness of the throat.
Namely:
- Surgical intervention. If other methods of therapy do not help, the disease has reached the last stage, surgery may be used. The type of intervention and method of implementation are determined by the doctor based on the patient’s age, individual characteristics, and specific disease. For example, with a retropharyngeal abscess, it is opened. And if pus has formed, the fluid must be suctioned out. Additionally, the intervention can be used for a deviated nasal septum.
- Inhalations. Thanks to the method, you can reduce redness in the throat. Inhalations are also recommended for ARVI and sore throat.

The method is divided into 2 types. The first type includes the use of plants (chamomile, sage, etc.). An inhaler is used for this. For example, Chamomile. Inhalations are also performed using a nebulizer using medications (in the form of a solution) intended to eliminate cough (ACC, Lazolvan, Ambrobene).
Possible complications
A red throat in a child can be characterized by complications. Most often they appear due to untimely therapy or its absence. For example, if a red throat indicates a disease, the pathology may enter the chronic phase. As a result, therapy takes longer.
Additional complications:
- decreased immunity;
- dental diseases;
- oncology;
- pathology of the hematopoietic system.
A symptom such as a red throat can appear in every child. The sign indicates physiological causes (allergy, hypothermia) or pathology (sore throat, ARVI).
Judging by the photo, we can tell about the severity of the symptom. After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed, which includes the use of medications, folk remedies and other methods (surgery, inhalations). To reduce the likelihood of complications, timely therapy is necessary.
Article design: Vladimir the Great