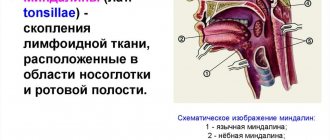
Description of the disease
Pharyngitis most often has a viral or bacterial origin and is not always an independent disease. In most cases, it is part of the general symptoms of influenza or a respiratory viral infection. The essence of pharyngitis is that the activity of a virus or other pathogen causes inflammation in the back wall of the pharynx and in the lymphoid tissue. The mucous membrane becomes swollen and acquires a reddish tint. In infants, the disease occurs frequently due to age-related looseness of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and fragile immunity. The course of the disease in young children can be complicated by rhinitis and inflammation in the nasopharynx.
Classification of childhood pharyngitis
The first classification is based on the place where the disease is localized; according to this criterion, the disease can be:
- Catarrhal or superficial, when the upper layer of the mucosa is affected
- Granular , when the inflammatory process spreads to an area located in the submucosal layer
Pharyngitis is of a limited and widespread type, respectively, when only the lateral structures or the entire pharyngeal surface from the back are affected.
The next classification of pathology is by form, distinguishing acute, subacute and chronic. The duration of acute pathology is up to 15 days , its main symptoms are the presence of cough, pain, and a very sore throat. Typically, the acute variety appears against the background of the development of an infectious-inflammatory lesion to which the trachea, nasopharynx and other elements of the respiratory system are exposed.
When the first symptoms appear, it is imperative to begin treatment of the child, otherwise there is a high risk of pharyngitis becoming chronic.
Most often, the disease is bacterial; it occurs when there is a local decrease in the body’s protective function. Often, simultaneously with the pharynx, the nasopharynx, the area of the paranasal sinuses and the auditory tube are also affected by the inflammatory process.
The appearance of subacute pharyngitis is usually caused by scarlet fever or rubella, while the disease in question is one of the symptoms of the main one.
Types of disease by duration
According to the duration of its course, pharyngitis can be acute (less than a month), protracted (lasts about a month) and chronic (occurs if the acute form has not received proper treatment). Also, a child can develop a chronic condition of inflammation of the pharynx as a result of frequent diseases of other respiratory organs, if the child had his tonsils removed before the age of 7, with diabetes, frequent allergies, or caries. Chronic pharyngitis in children can be catarrhal and granulosa. The catarrhal form is characterized by looseness of the walls of the pharynx, their redness, soreness and discomfort in the throat, and cough. The granular form is characterized by pain during swallowing, which radiates to the ear, soreness, dryness and redness in the throat, the appearance of viscous sputum and lymphoid granules.
Causes and forms of the disease
Pharyngitis in a child turns out to be a consequence of:
- Damage to weak mucous membranes by bacteria. Streptococci or pneumococci are more often activated as a result of a long course of rhinitis or sinusitis, more than 5-7 days.
- Impact of viruses. Children are susceptible to adenoviruses and all strains of influenza, cytomegalovirus. Herpetic pharyngitis in children occurs under the influence of the herpes virus and often begins with a visually visible vesicular rash on the mucous membrane of the tonsils and pharynx, which quickly turns into wound erosion.
- Active activity of fungal microorganisms. More often, these are varieties of candida fungus. Such pharyngomycosis is possible due to an imbalance of microflora. In children, it develops with weakened immune function or after irrational use of antibiotics.
- The presence of an allergic component. A series of tests are prescribed to determine the allergen. After treatment and then elimination of the irritant, such pharyngitis does not recur.
The time for pharyngitis to develop in preschool children is more than a week.
Children's pharyngitis appears after exposure to irritating factors: a chemical burn or inhalation of frosty or too hot air. Currently, doctors can recognize the underlying pathogen and promptly prescribe appropriate treatment. Therefore, there are fewer cases of the disease becoming chronic.
Should you see a doctor or treat your baby yourself? For many parents, such a disease does not seem serious. But pediatricians warn: only correctly and timely procedures will help you quickly get rid of irritating symptoms and prevent the mild form from becoming chronic.
Types of pharyngitis due to occurrence
Depending on the cause, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- The viral form is accompanied by hypermia and sore throat, hoarse voice, rhinitis, dry cough, and digestive disorders.
- Bacterial pharyngitis provokes headaches, a significant increase in temperature, enlarged lymph nodes and tonsils, and gastrointestinal disorders.
- The allergic type is notable for the absence of high body temperature and pain; it is characterized by a feeling of a lump in the throat and a dry cough
- The fungal form is characterized by the appearance of cracks in the corners of the mouth, its distinctive feature is a white cheesy coating on the back wall, the mucous membrane itself becomes loose and hyperemic.
- The herpetic type of the disease causes erosion on the tonsils, spreading to the tongue, cheeks and gums; fever with this pharyngitis lasts about 7 days, and the lymph nodes become enlarged.
- The atrophic form occurs along with bronchitis, tracheitis, rhinitis and laryngitis, accompanied by a dry cough. It rarely happens in children.
Symptoms
At first, the chronic form is characterized by the same symptoms as the acute form.
Attention! These include pain when swallowing, swelling of the palate and back of the throat and their redness, dryness, sore throat, and dry cough.
But over time, the symptoms expand and additional signs :
- burning in the throat;
- the feeling of dryness in the larynx is constant;
- in the morning (less often during the day), mucous discharge accumulates on the walls of the larynx ;
- The throat always remains red .
Sometimes such symptoms can disappear almost completely, but with the slightest hypothermia, vitamin deficiency or problems with immunity, the disease recurs.
Symptoms and treatment of pharyngitis in children
Symptoms
Pharyngitis in children has the following symptoms:
- Pain in the throat that becomes worse when swallowing;
- Dryness, discomfort, soreness, feeling of a lump in the throat;
- Low-grade fever (some forms of pharyngitis, such as viral, may not cause fever);
- Dry, shallow cough;
- Headache;
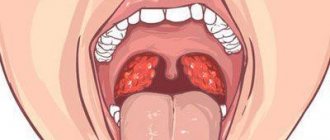
- Redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of plaques on the tonsils, enlarged lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of the disease
If parents notice signs of pharyngitis in their child, they should contact their pediatrician or ENT doctor for advice. The doctor makes a conclusion about the presence of the disease based on examination of the pharyngeal mucosa and the patient’s complaints. To clarify the diagnosis and identify the causative agent of pharyngitis, the doctor may take a swab from the throat for analysis. If the diagnosis is correct and appropriate therapy is prescribed, quick and effective treatment is possible. Pharyngitis is treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a local pediatrician or ENT doctor, following all his instructions.

Features of the course and therapy in infants
Symptoms of pharyngitis in young children have their own characteristics. Unlike older children, pharyngitis always causes an increase in body temperature in infants. Fever can reach 39 degrees, so parents need to stock up on antipyretics for children.
Important! If your body temperature remains above 39 degrees and does not drop, you should immediately go to the hospital due to the risk of developing a convulsive state.
Also, children under 2 years of age experience sleep and appetite disturbances. Babies may have difficulty sucking at the breast due to a sore and red throat. The amount of saliva increases. The swallowing reflex and the functioning of the digestive system are also disrupted. Rashes may appear on the skin of children, and conjunctivitis may appear on the eyes.
The difficulty of treating pharyngitis in infants is that, for the most part, medications in the form of lozenges and lozenges are not available to them; antiviral agents and antibiotics are also not age-appropriate. The most effective results are obtained by treatment using inhalations with special antiseptic solutions. When treating pharyngitis in such children, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
Treatment of pharyngitis
The treatment of this disease includes many medications, both medicinal and auxiliary, which can effectively treat pharyngitis in children. Auxiliary methods include humidifying the air in the room and drinking plenty of warm drinks. When choosing a drink, it is better to give preference to natural fruit drinks, compotes, and herbal teas. Food should have a soft consistency to facilitate swallowing and not injure the mucous membrane.
It is necessary to limit the physical activity of children, and it is better to organize bed rest. The air in the room should be fresh. If there is no fever, it is good to walk outside with children, this will speed up recovery.
Drug treatment
To successfully combat the disease, a complex of medications is used:
- An antibiotic or antiviral drug with complex action to combat the causative agent of the disease. It is selected depending on the type of pharyngitis and the factor that provoked it.
- Local medications. May be in the form of sprays, tablets or lozenges. They have an anti-inflammatory effect directly at the site of the disease. In addition, such medications reduce pain.
- Rinse solutions. Rinsing the mouth and throat is an important method in the treatment of inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract. Especially if the disease is accompanied by the release of copious amounts of sputum. For rinsing, you can use both ready-made pharmaceutical solutions, herbal decoctions, and table salt solutions.
- Physiotherapeutic agents. These include inhalations, which can be done at home or in a clinic. The doctor, if necessary, may prescribe light therapy or other methods available to the pediatric ENT department.
Important! When you find signs of pharyngitis in your child, you do not need to give him medicine yourself. All medications and their dosages are prescribed only by a doctor.
Traditional methods

Traditional medicine experts have their own answer to the question: how to treat pharyngitis? The range of such products includes various compresses and rinses, herbal decoctions. All folk remedies are good within reasonable limits and only in combination with traditional treatment.
Disease prevention

To protect your baby’s body from pharyngitis, you should strengthen the immune system, organize good nutrition, and include as many vitamins and minerals in the diet as possible.
Physical activity and walks in the fresh air also increase the protective functions of a small organism. You need to teach your child to follow hygiene rules: wash your hands after going outside, drink and eat from your own cutlery. Particular attention should be paid to the microclimate in the children's room: the air should be humid and the temperature should not exceed 25 degrees. Whenever possible, protect children from inhaling chemicals and tobacco smoke. It is also necessary to monitor the condition of your teeth, because caries is one of the causes of the development of the disease.
Prognosis and prevention
Prevention of pharyngitis in children includes:
- Good nutrition and vitamin intake;
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, first of all, frequent and thorough hand washing;
- Routine vaccination;
- Regular exposure to fresh air and hardening;
- Ventilation of the rooms of the house and regular wet cleaning using disinfectants;
- Limiting contact with infected people;
- The use of local means of prevention, for example, Oxolinic ointment for the nose;
- Strengthening the immune system.
The prognosis for pharyngitis is favorable, with the exception of the chronic atrophic form, in which there is a high risk of developing serious complications.
(Visited 22,914 times, 1 visits today)
- Author: Administrator
Rate this article:
(5 votes, average: 3.8 out of 5)
Children suffer from pharyngitis more often than adults - due to age-related weakness of general and local immunity. The main symptom of pharyngitis is a sore throat, which occurs on the first or second day from the onset of the disease. Knowing the signs of the disease will help you start treatment in a timely manner and protect your baby from possible complications.
Drugs: antibiotics
When a doctor suspects that pharyngitis has a bacterial component, he will immediately prescribe an antibiotic . The main symptoms of bacterial pharyngitis are:
- ineffectiveness of the antiviral agent within 3 days,
- a change in the general blood test, for example, an increase in the level of neutrophils.
Children under one year of age are prescribed antibacterial suspensions, and older children are prescribed antibiotics in tablets or capsules.
Carefully! Only bacterial pharyngitis requires the prescription of antibiotics; for the viral type they are useless, and for the allergic type they are dangerous. Taking antibiotics is often accompanied by taking antihistamines and probiotics.
Sumamed
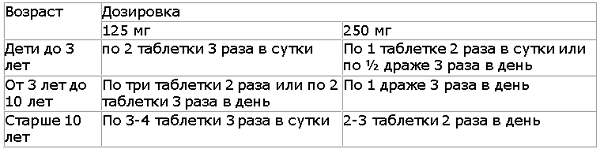
"Sumamed" is a new generation antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action. This is a macrolide, available in the form of tablets and suspension . In tablet form, the drug can be prescribed for pharyngitis in children over three years of age , but it will be more convenient to use a suspension.

To prepare it, you need to mix the powder with the required amount of water. The result is a jelly-like liquid with a pleasant taste and smell. At older ages, Sumamed tablets are recommended. It is important that the child can swallow the tablets , since chewing the medication is unacceptable. "Sumamed" in capsules is prescribed to children over 12 years of age.
The dosage regimen is based on the child’s weight.
| Form | Dosage |
| Pills | 20 mg per 1 kg of body weight 1 time per day for 3 days. The medicine is taken 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after it. |
| Suspension |
Flemoxin
"Flemoxin" is an amoxicillin antibiotic with rapid absorption. Available exclusively in tablet form . They can be chewed, swallowed whole, crushed, diluted with water. In this case, the drug does not lose its effectiveness.
Augmentin
"Augmentin" is approved for use in children from three months of age in a certain dosage. The doctor individually selects the dose for the child, taking into account his weight and age. There can be from 2 to 3 doses of medication per day. Drink the drug before or after meals one hour.
For children under 3-4 years of age, it is advisable to use a suspension . The tablet form is prescribed to children over 12 years of age.

Treatment
Therapy for acute pharyngitis should be comprehensive. In combination with medications, doctors recommend inhalation, applying compresses to the affected areas, lubricating the larynx with special products to moisturize the mucous membranes, and rinsing the mouth and larynx with solutions. Often children are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, with the help of which alarming symptoms recede.
It is important to strengthen the functions of the protective immune system during treatment. Children are recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits, which contain essential vitamins and minerals. Additionally, immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed.
Parents should monitor the baby's drinking regime. It is recommended to consume the required amount of herbal teas, berry compotes, juice, warm milk with honey and butter. For drinking therapy to be effective, it is recommended to alternate drinks.
The baby should get proper rest during the pathology. Coughing attacks and sore throat intensify during daytime or night sleep. So that the child can sleep peacefully, it is necessary to carry out the procedures prescribed by the doctor before resting.
Drops for oral administration
Drops for oral administration.
Medical practice shows that Tonsilgon-N drops help children with pharyngitis. They are allowed for babies up to one year old and have a minimum of contraindications. The medicine is intended for local treatment of the mucous membranes of the throat. The course of treatment and dosage is determined after examination by a specialist, depending on the patient’s age and the severity of the disease.
Medicinal aerosols
Medicinal aerosols.
Many drugs in the form of aerosols are approved for patients over 5 years of age. If the child is small, the use of funds, sprayed in the larynx, can reflexively cause respiratory arrest. Individual medications are prescribed to younger children in the absence of allergic manifestations.
Effective medications are Miramistin, Tamtun, Lugol, Bioparox. Medicines have a local antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect.
Rinse solutions
Rinse solutions.
At the first clinical manifestations of pharyngitis, it is recommended to rinse the mouth and throat with warm solutions at least 5 times a day. During the acute period, manipulation with liquids based on salt and alcohol is prohibited; these components irritate the oropharynx, dry out the mucous membranes, complicating the general condition of the patient. It is better to rinse the oropharynx with herbal tinctures and decoctions, after consulting with a doctor.
Patients under 5 years of age do not always understand how to perform the procedure correctly. Therefore, it is better for children to inhale or give medicinal lozenges to suck.
Prescribed rinses with solutions:
- furatsilin in the proportion of 1 tablet per glass of warm water;
- potassium permanganate (dilute the drug to a slightly pink color);
- hydrogen peroxide (1 tbsp per glass of water).
They practice manipulation with apple cider vinegar, a solution of calendula herb, Romazulan, Rotokan, Citrosept. Before use, you should familiarize yourself with the recipe for preparing the solution so as not to injure the oral cavity and pharynx, causing burns, drying out, and allergies.
In our time, recipes for decoctions of chamomile, sage, oregano, mint, and eucalyptus have come from traditional medicine. Herbal infusions relieve pain, stop inflammation and the migration of infection to healthy areas of the organs.
Preparations for resorption
Preparations for resorption.
Kids are interested in tablets and lozenges, as they have a sweet taste, reminiscent of candy. Medicines have a calming, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect on the respiratory system. Septolete, Faringosept, Imunod, Strepsils have proven themselves positively.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is recommended as a complement to drug treatment. Home remedies can help you improve your health.
Rinse
Sanitation of the pharynx with herbal decoctions is one of the simplest methods of treating pharyngitis. For a glass of water - a dessert spoon of chamomile. You need to rinse with warm broth, both before and after meals. Sage - quickly removes the inflammatory process, brew in the same proportions as chamomile, let it brew for one hour.
Mixtures
You will need 10% alcohol, glycerin or peach oil, mix, proportions: 1:2, lubricate the back wall of the throat with a cotton swab.
Propolis – small pieces, slowly chew well in the mouth, after eating, to naturally lubricate the throat.
Inhalations
Inhalations based on pine cones (20 gram cones are placed in boiling water, 250 ml.) will help get rid of the acute form.
Mix mother and stepmother (5g) with string (5g). Throw into a glass of boiling water, then leave for an hour, use for inhalation.
Compresses
Chamomile is useful not only for gargling, but also for compresses on the throat area. One tablespoon of herb is poured into two glasses of water, boiled, then strained and infused. Then soak gauze in the resulting product and apply it to the neck. Keep the compress until it cools.
How to treat
For the treatment of uncomplicated acute pharyngitis, a set of conservative measures is prescribed using local anti-inflammatory drugs . The effectiveness of this practice has been confirmed in pediatrics.
As a rule, after a diagnosis of “acute pharyngitis” is made, the child is prescribed :
- diet , exclude the consumption of spicy, salty, sour and solid foods;
- restorative therapy (massage, walks in the fresh air);
- vitamin therapy (ascorbic acid, combined vitamin complexes);
- antipyretics at elevated temperatures (paracetamol/ibuprofen);
- local antiseptics (chlorophyllipt, furacillin);
- lozenges, sprays (septolete, hexoral);
- immunostimulants (interferon);
- if a bacterial infection is suspected, antibiotic therapy (augmentin, amoxicillin).

- Rinse the oropharynx with a weak infusion of herbs: chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort. Boil for 5-10 minutes, leave for 2 hours, gargle 2-5 times a day.
- Inhalations based on essential oils , mint or eucalyptus. Inhalation should be carried out once a day.
- Tea with ginger, honey and lemon . Suitable for children over 3 years old. Grate the ginger root, mix with honey and lemon, pour boiling water. Give to the child 3-4 times a day.
- Tea based on linden and raspberries when the temperature rises.
At home

Therapy is carried out at home strictly as prescribed by the doctor. At home, treatment is based on a drinking regimen in which the child should receive the maximum amount of fluid. It is imperative to maintain air humidity in the room .
Among the procedures, the doctor may recommend :
- Rinse your nose daily with saline or saline,
- If the baby knows how to gargle on his own, it is necessary to carry out these procedures as often as possible using saline solution or herbal decoctions.
Concomitant treatment with traditional medicine recipes as a distraction therapy cannot be ruled out.
It is important for parents to ensure proper nutrition: food should not irritate the throat and provoke attacks of pain. The diet must include:
- light soups,
- puree,
- steamed dishes
- smoothie.
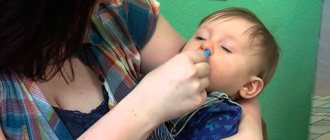
Of the medications, only those prescribed by the pediatrician are used. At home, you can carry out inhalations if you have a nebulizer .
Carefully! It is better to avoid steam inhalations, especially if the child is under 5 years old.
What features does chronic pharyngitis have?
The source of chronic pharyngitis is opportunistic bacteria of the oral cavity, which become more active when local and general immunity decreases. The main predisposing factor for chronic pharyngitis is untreated or inadequately treated acute pharyngitis. With chronic pharyngitis, one anatomical part of the pharynx is affected, and the neighboring ones are not included; the child’s well-being is almost never disturbed. There are no signs of intoxication, the temperature almost does not rise. The main symptoms are dry throat, lump in the throat, coughing. Due to daily itching, a dry, obsessive cough occurs, which becomes productive over time. Chronic streptococcal pharyngitis causes complications on the heart, kidneys, and thyroid gland.
Diagnostics
- To diagnose a child, doctors use a differential diagnostic method , which allows one to distinguish pharyngitis from other diseases that have similar symptoms. This is especially true for sore throat, which is so similar in nature.
- In addition to examining and identifying the most pronounced symptoms, the doctor, if necessary, may prescribe a smear from a sore throat for bacteriological or virological culture to identify the cause of the disease.
However, laboratory tests are prescribed quite rarely, in cases where there is a suspicion that the child is sick with a dangerous pathology, such as measles or scarlet fever.
What it is
In acute pharyngitis, the back wall of the pharynx becomes inflamed . The diagnosis is made based on examination of the child's larynx. As a rule, children complain of pain, soreness and/or itching in the throat.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished :
- Acute pharyngitis (up to 2 weeks).
- Chronic pharyngitis (more than 2 weeks).
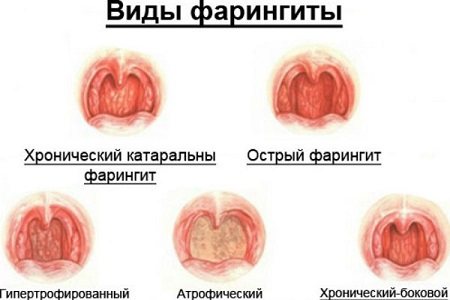
- Catarrhal pharyngitis is characterized by damage only to the mucous structure of the pharynx.
- In the granulosa form, the mucous layer and lymphoid tissue are involved.
- The atrophic form is observed in a chronic process. Thinning of the mucous membrane is characteristic.
Causes
The causes of pharyngitis are classified on different grounds. Depending on the cause, the disease is treated. So, the reasons could be:
- Viruses : corona viruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, influenza/parainfluenza virus, herpes virus, Epstein-Barr virus, etc.
- Bacteria : more often group A streptococcus, less often group C, diphtheria bacillus, meningococcus, anaerobes, mycoplasma.
- Fungi of the genus Candida.
- Allergic reaction.
- Traumatic injury (foreign body, burn of the oropharynx).
, the following contributing factors may also influence the development of the disease :
- child age from 4 to 14 years (get sick more often),
- contact with a carrier of infection,
- decreased immunity,
- prolonged nasal congestion,
- inhalation of dust particles from the air,
- damage to the mucous membrane by hot or hard food,
- spread of infection from another organ,
- crowd of people (schools, kindergartens, sports clubs).
Types of medications
Immunomodulatory
Prescribed to children with pharyngitis if they have a history of frequent respiratory diseases, or if the disease occurs against the background of ARVI. The most popular: Aflubin, Viferon, Immunoflazid, Laferobion, Kagocel. Immunomodulatory drugs are contraindicated only in case of individual intolerance to the drug.
Antibiotics
Prescribed only if you are sure of the bacterial nature of the disease. Before prescribing, it is necessary to take a throat swab from the child and conduct a sensitivity test to the antibiotic. Antibiotics of the penicillin and cephalosporin groups, such as Amoxicillin, Sumamed, Azithromycin, Suprax, Ceftriaxone, are usually prescribed.
Treatment without antibiotics is possible for viral and allergic pharyngitis without the addition of concomitant diseases of bacterial origin.
Antibiotics should not be used for viral pharyngitis because they are not effective and increase the risk of bacterial complications.
Antiviral
Prescribed in case of viral pharyngitis. Usually these are Arbidol, Cycloferon, Tsitovir. The antiviral drug Viferon is often prescribed in the form of rectal suppositories, which is indicated for children from birth.
Antihistamines
Used as a basis in the treatment of pharyngitis of an allergic nature. In case of acute situations, with severe swelling of the throat, Suprastin is used by injection. For the treatment of less acute forms, Alleron, Zyrtec, Cetrin are used.
It is not recommended to use hormonal antihistamines for a long time due to the risk of negative effects on the normal development of the child’s hormonal levels.
Antiseptics
Used to disinfect and reduce pain in the pharynx. Solutions of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Lugol and throat irrigation sprays Ingalipt, Hexoral are used.