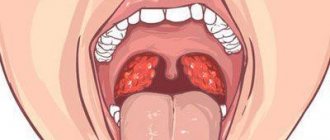
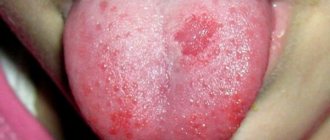
Description of white plaque on tonsils
As a rule, plaque is just a symptom of some disease, and is not a disease in itself. However, it can mean quite dangerous infections. Most often, plaque on the tonsils occurs in children of kindergarten age, less often in primary schoolchildren. And the older the child becomes, the less susceptible he is to the appearance of such a symptom.
A little about the tonsils themselves. These are paired organs located in the human throat. They act as a natural barrier to infections, but they perform this function only in children. In adults, immunity has already reached a new level, and the body does not need protection from the tonsils. Most often, in adults, these organs generally atrophy naturally.
The tonsils, or tonsils as they are popularly called, are very sensitive to weather conditions: cold weather and damp, frosty air can become a real disaster for them. But if the child has normal immunity, then the tonsils will react properly to any infection and cope with the disease. But if the level of immunity is reduced, then a white coating appears, which means that a virus has entered the child’s body.
If your throat and tonsils still hurt
As a rule, the appearance of plaque is accompanied by a sore throat, difficulty swallowing and other signs of a common sore throat. It is important to immediately show the baby to the doctor to make a reliable diagnosis in order to direct treatment in the right direction from the very beginning. The presence of plaque clearly indicates that an infection has entered the child’s body, and urgent treatment is necessary. As a rule, this symptom is visible in the recesses of the tonsils, in their most inaccessible places, where it is safest for bacteria and microbes to multiply and accumulate.
The sooner treatment begins, the better. If you do not respond properly to this alarming symptom, the infection from the tonsils can go “walking” through the body, leading to much more dangerous and severe complications.
Self-medication is not recommended: this is not the case when you can get by with gargling with weed or inhalations. Most likely, you will need therapy with antibiotics and other potent active drugs. For such treatment, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
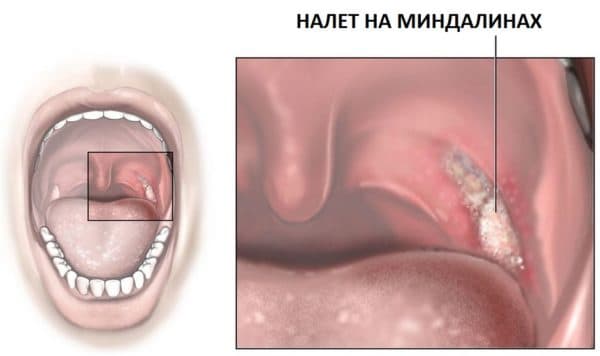
White plaque on the tonsils can mean not only a sore throat, but also other diseases.
Do not try to determine the color of plaque yourself: you will easily confuse gray and white, yellow and purulent. In addition, to an ignorant person they all look alike. Only a doctor with special tests and analyzes will be able to accurately determine what type of virus has affected the child. And as you understand, accurate diagnosis is the key to competent and effective treatment.
What should I do if I see white in a child’s throat?
The inflammatory process in the pharynx can take different forms. White pimples or spots, white plugs on the tonsils, pustules and white plaque on the mucous membrane may appear. The occurrence of such symptoms indicates the onset of one of the diseases of the ENT organs. In order to determine what kind of disease it is, a doctor must see the white spots in the child’s throat. After all diagnostic procedures, the doctor can prescribe adequate and effective treatment that will return the child’s tonsils and throat to normal.
What diseases can cause white plugs to appear in the lacunae of the tonsils?
Ulcers in a child’s throat can be a symptom of the following diseases:
- Sore throat or acute tonsillitis. This may be chronic tonsillitis, but the appearance of plugs is not typical for this form of the disease. With chronic tonsillitis, parents in most cases observe a white coating in the child’s throat.
- Chickenpox. Normally, this type of rash does not appear with this disease. Therefore, white pimples in a child’s throat may indicate severe chickenpox.
- Herpetic or follicular tonsillitis. In the first days of this disease, pimples appear on the throat, filled with serous fluid. Next, white balls appear because the serous fluid transforms into purulent fluid.
- A complication of otitis media, which is accompanied by the discharge of pus. In the case of this disease, inflammation spreads from the ear area to the inner surface of the nasopharynx, and white lumps appear in the throat.
- Diphtheria. This disease provokes the appearance of white areas on the mucous membrane in the larynx, which indicate the presence of pus. Gradually, such areas merge into a continuous purulent film, which cannot be removed without damaging the mucous membrane.
- Herpetic stomatitis. In this case, the infectious process affects not only the oral cavity, but also painful ulcers on the throat.
- Aphthous stomatitis. With this disease, the tonsils, inner surface of the cheeks and throat are covered with fairly large white pustules. The temperature does not rise.
- Scarlet fever. Abscesses cover the tonsils in unfavorable and severe cases of this disease. Sores appear in parallel on the child’s face, neck, elbow and knee bends, hands, and feet, but it does not look like a blister with pus, but rather like a bright red sore.
- Allergy. Blisters in a child’s throat may be part of a general allergic rash on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Peritonsillar abscess (complication of tonsillitis). This disease is also characterized by enlarged tonsils. The baby suffers from high fever and severe intoxication of the body.
- Thrush or candidiasis. This disease can manifest itself in the appearance of a white coating or small whitish rashes on the tonsils, side walls, and back wall of the throat.
- Pharyngitis of bacterial etiology. Pustules on the back of the throat in a child are one of the symptoms of this pathology.
- Injuries that damage the throat (its mucous membrane and soft tissues) - burns, mechanical damage - the so-called traumatic abscess. The addition of a bacterial infection provokes the appearance of rashes and purulent films.
- In some cases, white pimples appear as a consequence of colds (flu, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections) that the baby has already had.
What symptoms may accompany the appearance of ulcers?
White plugs can appear in the throat for various reasons. Only a qualified specialist can determine which disease caused such characteristic symptoms after studying the results of bacterial culture from the throat and carrying out other diagnostic measures. Typically, the appearance of traffic jams is accompanied by the same clinical manifestations, regardless of the type of disease:
- Signs of intoxication of the body with metabolites of pathogenic microorganisms and a decrease in the level of immune defense. This may include weakness, impotence, headache, reluctance to eat, vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature, aches in bones and joints, muscle pain, skin sensitivity.
- The mucous membrane of the throat is red, inflamed, swollen, with small hemorrhages.
- White rashes in the throat, tonsils and lymph nodes may be enlarged.
- The child has difficulty speaking and swallowing. The baby speaks in a whisper, his voice is hoarse or hoarse. Breastfed babies refuse to latch on to the breast, preferring an easier-to-suck bottle.
- The baby is capricious. White ulcers are very painful and prevent the child from sleeping.
- Mucus may appear on the back wall of the larynx and drain down. Mucus contains many pathogenic microorganisms, so its appearance stimulates the activation of the inflammatory process.
- The tonsils and mucous membrane of the throat may lose their smooth structure and become loose and porous.
- Congestion in the throat may be accompanied by swelling of the nasal mucosa and the appearance of snot. In this case, nasal breathing is greatly complicated.
- With purulent otitis media, pain in the ears and neck also appears.
- Indigestion, abdominal pain.
- Cough – non-productive dry or productive wet.
- Various skin lesions may appear - redness, swelling, rashes, itching, dryness and flaking of the skin.
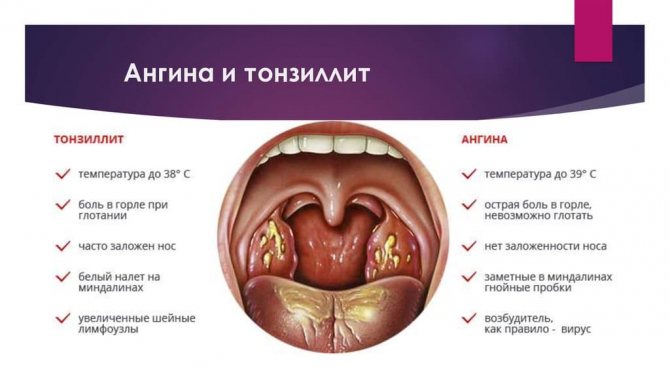
What does white plaque mean?
Let's find out what the most common type of plaque on the tonsils means - white.
So, white plaque on the tonsils can mean the following types of diseases:
- angina;
- scarlet fever;
- tonsillitis;
- stomatitis.
Diphtheria and some others. As you can see, the “range” of diseases is quite wide, and all these cases will require different treatment.
Thrush. Your child may develop this oral fungal infection if you give him antibiotics too often. You should be careful with these potent medications and not use them “every time you sneeze.”
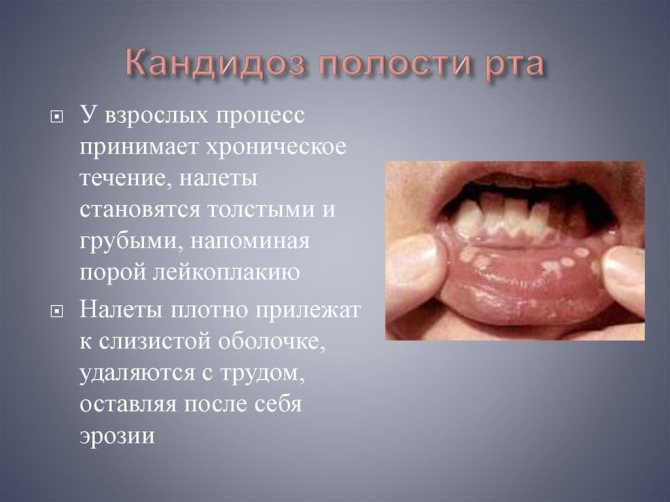
Often the cause of a whitish coating is a banal acute respiratory infection or pharyngitis. It should be clarified that in this case, not the entire surface of the tonsils will be covered with plaque, but only in spots.
To accurately determine the nature of the plaque, the doctor usually takes a scraping from the mucous membrane of the throat and sends it for laboratory testing.
If there is no increase in temperature
In some cases, it happens that a white coating is present on the baby’s tonsils, but there is no temperature. Don’t let the lack of fever reassure you: plaque is already a good enough reason to urgently consult a doctor; in itself, it can be a harbinger of dangerous diseases.
Plaque without fever most often occurs if the infection is fungal in nature. Various stomatitis and candidiasis appear as cheesy formations of a characteristic whitish color and are not accompanied by fever. Stomatitis is also very painful; the child will complain that it hurts to swallow and eat.

A sore throat may also be accompanied by plaque, and there will be no fever. But only at the beginning of the disease. Then the child will develop a fever anyway. And such a rare type of sore throat, such as syphilitic, occurs without fever at all. However, in this case, the tonsils become denser and become covered with a white film with subsequent lesions on it.
Sometimes purulent plugs can also be mistaken for plaque. They are not accompanied by fever, but are a rather alarming symptom.
With temperature
If a white coating is accompanied by a high temperature, then most likely the symptom is associated with a cold infection. This could be a sore throat, acute respiratory infections and other infections.
Treatment of white plaque in a child’s throat
White plaque in a child's throat
in most cases it appears in the tonsils and is a sign of normal immune function. That is, the formation of plaque in the throat means that the body’s immune system is trying to neutralize the pathogenic microflora that has entered the throat mucosa. If timely measures are not taken, pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate deeper and affect the respiratory tract.
If the child
there is no temperature, and the white plaque in the throat is localized in the recesses of the tonsils, then most likely this is a reaction of the immune system to minor inflammations in the body caused by the accumulation of food residues in the tissues of the throat, hypothermia or non-compliance with hygienic rules for caring for the oral cavity. A white coating without fever can also appear when the pharynx is injured or the larynx is burned from the inside.
When the child is sleeping peacefully
, eats well and plays, to treat white plaque in the throat, gargling with a solution of furatsilin, soda, chamomile and calendula may be enough. Rinsing with antiseptic solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs helps to painlessly and quickly remove plaque from the affected areas of the tonsils and pharynx, as well as relieve inflammation that led to its formation.
However, if the child has, in addition to white plaque in the throat
the temperature has risen, a sore throat has appeared, weakness and loss of appetite, you should urgently consult a doctor, since this condition may be an indicator of the onset of the development of the following dangerous diseases:
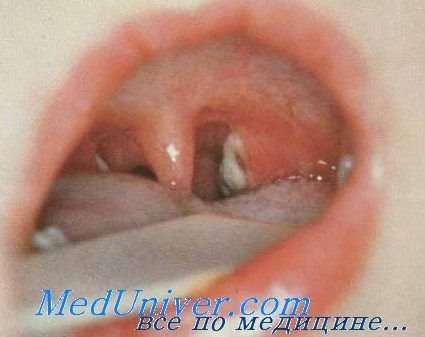
1. Diphtheria
. Thanks to the fact that vaccinations against diphtheria were introduced into health care practice in the 1920-1950s, this disease is rare these days, but it cannot be completely ruled out, especially if you are an ardent opponent of childhood vaccinations. Children are vaccinated against diphtheria 3 times, the first time at the age of 3 months, and the next two - with an interval of 1 month. Repeated vaccinations are carried out in the periods of 1.5-2 years, 6 and 11 years. In adults, to increase diphtheria immunity, vaccination should be done every 10 years.
Diphtheria is a very dangerous infectious disease caused by the diphtheria bacillus entering the body when air contaminated by a patient with this disease is inhaled through sneezing, coughing and talking. Most often, children aged 4-6 years suffer from diphtheria, and the disease is very severe due to inflammation of the membranes of the mouth, nasopharynx and larynx with the toxin secreted by the diphtheria bacillus at the site of its introduction. With diphtheria, a white, dense coating in the form of a film spreads not only over the tonsils and throat, but also covers the entire tongue. It is difficult to separate. Moreover, the more extensive and widespread the plaque, the stronger the intoxication of the whole body and the more severe the course of the disease.
In the absence of timely treatment with a special serum, the dose of which is calculated individually, diphtheria toxin spreads throughout the body through the blood and lymph, poisoning internal organs and causing life-threatening complications - damage to the heart, kidneys, nervous system and pneumonia. Symptoms of severe forms of diphtheria include double vision, high fever, sore throat, confusion and difficulty breathing. Drug treatment for diphtheria and quarantine are necessary not only for the child, but also for all family members and his immediate environment.
Purulent plaque
A similar symptom is known among the “people” as purulent tonsillitis. Most often, this disease is ordinary tonsillitis, but only in an advanced stage.
This symptom is in most cases accompanied by the following symptoms:
- fever;
- poor health, weakness, depression;
- headache;
- complete lack of appetite.
It should be noted that purulent tonsillitis takes a long time and is difficult to treat. Therefore, rather than dooming a child to this suffering, it is much better and more logical to cure tonsillitis in time.
In addition to the troubles caused in the form of painful symptoms, purulent tonsillitis very often also develops into a chronic form. In this case, the child, with the slightest cold, runs the risk of getting a sore throat again. Therefore, in this case, after recovery, it will be of great importance for the baby to prevent colds and strengthen the immune system in order to avoid a recurrence of the situation.
White plaque in an adult
A white formation in the throat without fever is a sign of the initial stage of a sore throat, the presence of a fungal infection, stomatitis, a burn or a common injury.
For stomatitis
White spots appear on the palate, tongue, and inside of the cheeks. With advanced disease, the white formation can spread to the throat area.
A white coating on the throat with fever in most cases indicates inflammation of the tonsils or pharyngitis.
If the separation of the gray-white plaque is difficult and is accompanied by bleeding, this is a sure sign of diphtheria.

The appearance of a white coating without pain may be one of the manifestations of thrush. Additionally, you can recognize it by bad breath. The process is not dangerous, but causes psychological discomfort.
Smokers often develop white plaques in the throat. They are not dangerous in themselves, but if ignored they can develop into cancer.
to the content?
Yellow plaque, how to remove
This type of plaque may indicate the same diseases as white plaque. However, in most cases, yellow plaque is just the initial stage of the formation of pus on the surface of the tonsils. Be careful with this type of plaque: if the disease that caused it is not treated, over time the plaque can develop into ulcers on the tonsils - extremely unpleasant, dangerous and painful.
Sometimes the cheesy coating that appears with thrush may also have a yellowish tint. But usually this is a characteristic sign of typical tonsillitis (tonsillitis).
This symptom is accompanied by the following signs:
- labored breathing;
- heat;
- cough;
- acute, severe pain in the throat.
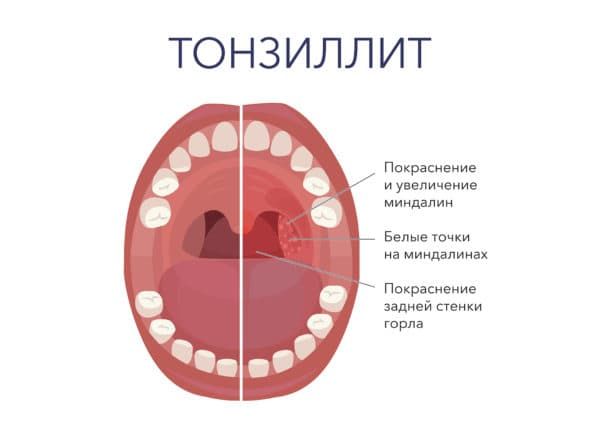
The main signs of tonsillitis.
It is necessary to get rid of yellow plaque with the help of antibiotics. Only these potent drugs can cope with a sore throat.
If you want to help treatment with traditional methods: rinses, infusions, inhalations, etc., then you must keep in mind that all these tricks can be used exclusively as additional therapy, and not as primary therapy. First of all, you should give your child antibiotics prescribed by the doctor.
What to do when a child has a white coating in the throat and what remedies should be used is described in the article.
How tonsils are removed during chronic tonsillitis in adults can be seen in the video in this article.
But how tonsils are removed with a laser for chronic tonsillitis can be seen in the contents of this article:
We recommend that you read about the removal of tonsils for chronic tonsillitis in this material.
Possible causes of white plaque in a child’s throat
The structure of human tonsils is not dense; they have small depressions called crypts. In these grooves, as a rule, not only food particles accumulate, but also all kinds of microorganisms, as well as their metabolic products.
For this reason, a white coating forms on the child’s tonsils. Such spots significantly reduce the body's defenses and can provoke the development of serious pathology.
If plaque is accompanied by fever
Based on the type and location of plaque in the baby’s mouth, the doctor can determine the cause of its occurrence. Diseases that cause white spots in the throat are described in the table:
| Name | Pathogen | Symptoms |
| Follicular tonsillitis | Streptococci, staphylococci, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses. | Sore throat, migraine, high temperature (up to 40 degrees), white dots (ulcers) against a red throat, weakness, poor appetite (we recommend reading: what to do if a child has an abscess on his gum?). |
| Lacunar tonsillitis | identically | Joint pain, hyperthermia, often vomiting, light spots on the tonsils, which eventually merge and completely cover the baby’s oral cavity. Possible cramps and loose stools. Submandibular lymph nodes may become enlarged. |
| Diphtheria | Diphtheria bacillus | A characteristic light coating on the tonsils and on the back walls of the larynx, hyperthermia, severe headache, aches, nausea, enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Causes severe intoxication of the body. Treatment is carried out exclusively by a doctor, since the disease can cause death. |
| Tonsillitis | Adenoviruses, pneumococci, moraxella, herpes, chlamydia, staphylococci, Epstein-Barr virus | Pain when swallowing, general malaise, swelling of the oral cavity (tonsils, soft palate), whitish lumps in the throat, possible purulent plugs and ulcers, hyperthermia (up to 40 degrees). |
| Infectious mononucleosis | Lymphotropic Epstein-Barr virus | Fever, damage to the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx and nose with a characteristic plaque; a blood test reveals atypical mononuclear cells. |
Plaque without fever
White or yellow spots in the baby's mouth may appear without an increase in body temperature. In this case, they are caused by fungal microorganisms, which include:
Treatment
If any type of plaque is detected, the first step is to show the child to the doctor. First, as usual, see your local pediatrician, and then, if necessary, you can visit an otolaryngologist.
Treatment recommendations for treating tonsils in a child
Of course, for a complete and rapid recovery of the child in this case, antibiotics will be required. They should be prescribed by a doctor after examining the baby and taking the necessary tests. The most widely used now is Flemoxin, as well as its cheaper analogue Amoxicillin. Find out how to take Amoxicillin correctly for a sore throat by following the link.
The antibiotic is selected by the doctor individually. Depending on what type of microbes caused the disease. If a sore throat is diagnosed, it is very important to drink the entire prescribed course of antibiotics. An untreated disease can result in serious complications: even heart problems may occur.
To relieve the unpleasant symptoms that accompany the appearance of plaque: fever, sore throat, weakness, you need to take antiviral drugs. For example, a medicine such as Amizon is suitable.
To relieve a sore throat, gargles are suitable. Solutions for these procedures can be prepared based on salt, iodine, and baking soda. These home remedies will relieve pain and help your child swallow.
If the plaque is caused by stomatitis, a remedy such as Stomatidine will help. This drug perfectly relieves inflammation of the tonsils.
Instructions for using Faringosept for children can be found here.
Rinse
This method is the simplest and most effective for removing plaque from the tonsils and providing the baby with the opportunity to swallow and eat normally.

How to gargle during plaque:
- Baking soda is a remedy available to everyone, and with regular use it leads to good results. You may also be interested in recipes for inhalation with soda in a nebulizer.
- Furacilin is a long-known antibacterial agent.
- Herbal infusions . A wide range of medicinal plants are available in pharmacies. The following are best suited for getting rid of plaque in the throat: chamomile, marigold, sage.
- Beetroot water is an ancient remedy that is good for sore throats. To prepare it, you need to boil small peeled beets, and after cooking, use the water drained from the saucepan for the procedure.
- Lemon juice can also be a great help in the fight for healthy tonsils. Only the juice must be diluted with water before use.
The following are used as medicinal rinses:
- Miramistin (read how to properly use Miramistin for sinusitis here);
- Iodinol;
- Lugol (we recommend that you read the instructions for use of Lugol).
These solutions perfectly remove microbes from the surface of the tonsils, preventing their further reproduction.
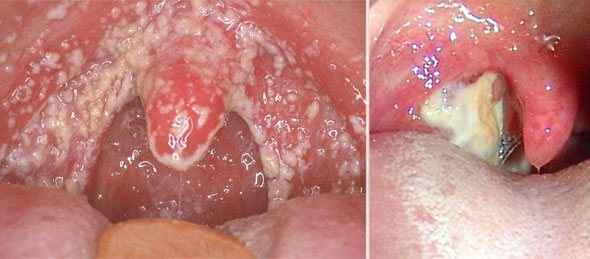
Yellow plaque on the throat
The yellow layer on the tonsils may be a sign of the same diseases as the white formation. In some cases, the formation of a yellow color may be the first manifestation of the appearance of pus. In the absence of proper treatment, the yellow formation develops into painful purulent abscesses.
In children, the causes of yellow plaque are the same as in adults. Often, a yellow layer on the mucous membranes of a child in the first year of life indicates candidiasis. This is a fungal disease caused by Candida fungi. Children are more susceptible to it than adults because they like to put things in their mouths.
to the content?