( 9 ratings, average: 4.56 out of 5)
Adenoids are immune tissue that produces immunoglobulins that are directly involved in the normal development of the child’s body.
Negative effects: colds, infections, allergies provoke the growth of adenoids and the inflammatory process. Such factors indicate that the body is exposed to allergens and there are malfunctions in the immune system.
Performing a protective function, adenoids neutralize the negative influence of the external environment on the child’s body. As a result, mucous discharge occurs and the adenoids swell, which interferes with nasal breathing.
Adenoids can have varying degrees of growth.
- I degree: during the daytime the child’s breathing is nasal, free and easy. At night, when the adenoids slightly increase in volume, breathing becomes difficult and snoring appears.
- II and III degrees: the child breathes through his mouth throughout the day. At night, snoring occurs due to an increase in the volume of the adenoids and obstruction of the posterior sections of the nose.
Symptoms of adenoids in a child 1-3 years old
The disease progresses sluggishly, without sharp and obvious symptoms, this can somewhat relax the parents’ vigilance and may even give the impression that the child is healthy. However, you should not be superficial about adenoids and their manifestations.
- The first warning sign is frequent colds.
- The child complains of frequent runny noses, which over time can transform into chronic rhinitis.
- The child experiences restless sleep, accompanied by snoring and even attacks of suffocation. As a result of poor sleep, the child does not regain strength and is lethargic and inactive during the day.
- Due to the limited mobility of the soft palate, the sound is formed incorrectly, and the child’s speech turns into an illegible set of sounds.
- If the disease has become chronic, changes in the facial skeleton may be observed, as the jaw is in a constantly sagging position. As a result, the lower jaw acquires a narrow and elongated shape, the bite is also formed in an incorrect way, and the hard palate in the upper jaw becomes high; in medicine, this phenomenon is called a “Gothic” palate.
- The chest is formed incorrectly, since the child breathes for a long time through the mouth and not through the nose.
- The child develops a morning cough and hearing deteriorates.
Adenoid growths in children 3 years of age: symptoms of general pathology/distinctive manifestations
In order to clearly see the difference in the external and visceral picture of adenoid pathogenesis, let's do this. Let's divide the sheet into 2 halves: on the left side the symptomatic signs of adenoid vegetation, which are characteristic in most cases of the disease, will be indicated. On the right side there are unusual clinical manifestations, which immediately indicate a threatening situation for the further normal development of the child’s body.
| 1). Adenoids in children become inflamed due to frequent respiratory intoxication. The primary manifestations are standard – a thin, light runny nose. An increase in temperature characteristic of colds is a stable graph, from 36.6 to 37.5 (38.2). The temperature brings chills, a feverish state. Headache, general malaise. Children find it difficult to breathe, as a profuse runny nose causes rapid swelling of the visceral nasal mucosa. 2). The adenoid parenchyma remains within physiological parameters for quite a long time. Despite intensive respiration. 3). Laboratory blood tests indicate an incipient inflammatory process in the child’s body - an increase in the percentage of leukocytes, a change in ROE and ESR. Leukocyte and protein compounds are present in the urine. The color of the urine changes from a light straw color to a dark (rusty) color. | 1).Unlike the first category of children, in some three-year-old children, the inflammatory generation of adenoids can begin without the usual symptoms. In children with clearly weakened immunity to respiratory invasion, adenoid hyperplasia begins suddenly, immediately with headaches and general malaise. The child complains of dizziness and tinnitus. But there is no runny nose as a severe manifestation of a cold. Nasal discharge is insignificant; on the contrary, dried crusts are observed in the nasal passages. The mucous membrane of the nasal epidermis is pasty, but not so much as to interfere with free nasal breathing. A distinctive biomarker of the state of homeostasis of the body is temperature, in these cases subfebrile. An unstable increase/decrease in temperature is recorded (from 36.6 to 37.8). 2). Endoscopy and rhinodiagnostics confirm the unusualness inflammation of the adenoids in children, symptoms adenoid pathogenesis. The diffuse density of lymphoid tissue is uneven, darkening boundaries are noted in the parenchyma of the organ, which indicates spreading adenoviral intoxication. But, the incubation period of adenoid inflammation began quite recently and is not fully “developed.” The peak of adenoid vegetation (in time) is still far away, and the pathology demonstrates dangerous visceral changes in the nasal tonsil glands. 3). In addition to routine laboratory tests, it is necessary to undergo detailed microbiological laboratory tests - histology, biopsy, labeling with synthetic genes by strains (identification of the main causative agents of the disease). |
Articles on the topic Cough and adenoids in children: what unites two different painful manifestations
Important information! The distinctive adenoid symptoms have a variable clinical appearance. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the strains of viral-bacterial microflora, which are the primary sources of influenza, ARVI, acute respiratory infections (Asian virus, influenza type “A”, “B”, atypical infection), change every year. It is these modems of viral, bacillus - microbial intervention that primarily provoke inflammation of the adenoids in children!
To explain more clearly: additional painful sensations are possible:
- Aches in the joints;
- Ascites – bluishness of the paranasal areas (blue discoloration of lips, nails);
- Dysfunction of the epigastric gastrointestinal tract - diarrhea, dyskinesia, dysbacteriosis;
- Yellowness of the skin, combined with heartburn, pain in the right hypochondrium (liver).
Virologists repeatedly emphasize the fact that antiviral vaccinations, on the threshold of seasonal epidemic outbreaks of influenza (ARVI, acute respiratory infections), reduce the risk of severe forms of adenoid pathogenesis in children in the first 3 years of life by hundreds of times. Moreover, they manifest themselves in previously unfamiliar signs that are unusual for the typical course of adenoid disease of the nasopharyngeal organs in young children.
Adenoid removal – pros and cons
The nasopharyngeal tonsils actively participate in immune reactions and the formation of the body's defense against viruses, which is why most doctors practice the use of conservative treatment methods.
In addition, it is difficult to completely remove the adenoids of a small child. And given the ability of the adenoids to recover, after surgery, after some time, the situation may repeat. There are cases where a child had to undergo repeated surgery three or even four times.
However, surgical treatment of adenoids cannot be avoided in cases where conservative treatment has exhausted itself and has not led to the desired result - recovery.
It is important to remember that the period of functioning of the adenoids occurs before the age of 11-14 years. Subsequently, having completed the appropriate amount of work for them, the nasopharyngeal tonsils disappear.
In any case, you should not agree to remove the adenoids. It is necessary to consult additionally with several doctors. If the diagnosis is confirmed, you should undergo several courses of conservative treatment, and if the symptoms of enlarged adenoids do not disappear, use the last resort method - surgery.
Komarovsky’s point of view on the treatment of adenoids in a child
The outrageous doctor assures that the best treatment is prevention. Proper nutrition, walks in the fresh air, daily routine and hygiene can do more than the most modern methods of treatment. This makes common sense.
Komarovsky believes that children “earn” the chronic form of adenoiditis due to acute diseases that are not fully cured . Against this background, a new infection enters the body, and the adenoids become inflamed again. The whole problem is that parents believe that the child is healthy when his temperature subsides. In fact, this is just the beginning of recovery. At this time, you need to take the child outside, walk with him, and communicate with other children.
Find out how to do the “cuckoo” correctly for sinusitis here.
According to the doctor, the increase in complaints about chronic adenoiditis is influenced by the social factor. Children who live closer to nature get sick much less often. In the city, the situation is different: parents are more worried about good grades at school than about the health of the child. Even untreated children are sent to study, and not to go out into the streets.
If prevention does not produce results, and there is a need for surgery, then you need to undergo the necessary studies. If the growth of adenoids is associated with an allergic reaction of the body, then there is no point in surgical intervention. It’s better to get rid of the dusty carpet and start hardening.
Conservative methods of treating adenoids only make the doctor smile. He is sure that they do not give the desired effect. In case of serious complications, surgery cannot be avoided. But this can be avoided.
How to treat adenoids in children under one year, 2 or 3 years old
Treatment of adenoids is carried out in several stages. Before prescribing the necessary course of treatment, you should consult an otolaryngologist who can correctly assess the situation.
Modern medicine offers several possible treatment options for adenoids, however, each of them involves eliminating the source of infection, stopping inflammation and stopping the focus of bacteria causing the disease.
Regarding treatment methods:
- Drug therapy. Saline solutions are used to rinse the nose and remove mucus. Drugs that have antiseptic properties are used to dry out the nasal mucosa. In addition, drugs are needed to eliminate swelling and inflammation.
- Laser therapy. This method is aimed at eliminating swelling and inflammation of the adenoid tissue. The nasal mucosa dries out and the number of pathogenic microbes decreases. For a full course of treatment, 10 procedures are required.
- Homeopathy. This method is based exclusively on natural preparations, however, its disadvantage is the duration of the course of treatment - several months.
- Nasal rinsing
Traditional treatment of adenoids in children
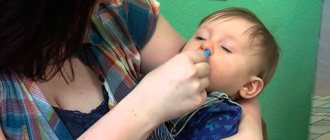
1.Nasal rinsing
Before starting the procedure, you should clear your nose of mucus. It is necessary to free the nose in stages, each half separately. Rinsing the nose will help eliminate secretions accumulated on the adenoids.
Procedure diagram:
- place the child on his tummy, with his head slightly tilted forward;
- the syringe must be inserted into one half of the nose perpendicular to the face to a depth of no more than 1 cm;
- the solution should be administered in small portions, gradually increasing the jet pressure.
To reduce adenoids and eliminate the inflammatory process, you can use:
- infusion of horsetail. Pour 1 teaspoon of herb with a glass of boiling water and leave for no more than five minutes. Cool and rinse your nose.
- herbal decoction: oak bark, eucalyptus, St. John's wort. Proportion: 5-6 grams of collection per 200 ml of water. Boil for five minutes, cool and apply.
- sea salt solution. Proportion: for 1 glass of water, 0.5 teaspoon of sea salt.
- Chamomile decoction with honey. Proportion: for 1 glass of water 5-6 grams of chamomile, 0.5 teaspoon of honey. Add honey to the prepared and not hot decoction.
- green tea. Proportion: for 1 glass of hot water, 1 teaspoon of tea. Leave for 15-20 minutes, rinse your nose.
2. Nasal drops
- fresh beet juice. The number of drops depends on the age of the child: from 4 to 8 drops. Instill after rinsing the nose.
- decoction of duckweed. Proportion: 2 tablespoons of herb per 0.5 glass of water, boil for five minutes, strain, drop in nose after rinsing.
- infusion of green walnut skin. Proportion: for 1 glass of water, 2 tablespoons of chopped nut peel. Pour in water, bring to a boil and leave for an hour. Strain, instill 3-4 drops no more than 4 times a day.
You can also use a plastic inhaler and breathe in the vapors of eucalyptus, calendula and soda. The ingredients can be mixed or used separately. One inhalation requires 0.5 teaspoon of the mixture. The duration of the procedure is from 5 to 10 minutes, frequency – 1-2 times a day.
Before using traditional methods of treatment, it is important to check whether the child is allergic to the components, and also consult a doctor.
The reasons for such differences in adenoid vegetation at the three-year mark of development of the child’s body

For what reason does such a dividing course of adenoid hyperplasia occur in children? And why does such a pathogenic picture with adenoids occur precisely in the 3rd year of a child’s life?
The origins of the answer lie far from the age we are considering (3 years). The laying of the future homeostasis (health) of a person begins at the genetic-molecular (cellular) level (with the division of female and male cells, which give the start to future life). The hereditary factor plays a big role here. Not perception (strong immunity) or, conversely, a tendency to adenomicrobial, viral, bacterial invasion.
And in the first trimester of pregnancy, which is especially important for the baby. In this phase of the formation of organic systems, nature “pays increased attention” to the immune system and the proper creation of nasopharyngeal lymphoid glands. After all, these are the primary, natural barriers against that same harmful and evil adenoid hyperplasia that lies in wait for older children.
Related articles: Symptoms of facial deformation due to adenoids in children: description
But the three-year age limit, unfortunately, and for still unclear evidentiary morphological and physiological reasons, is assessed by pediatrics as the most vulnerable age for adenoviral intoxication. Children 1, 2 years of age, after the third year (4-10 years) suffer much less from adenoid growths. Perhaps the stumbling block, according to leading experts in otolaryngology and pediatrics, is still in the incomplete process of formation of the immune system, its peripheral organic sectors, which include the lymphoid glands of the nasopharynx.
In conclusion of the discussion of topics of interest to parents of 3-year-old children with adenoids, the topics “ Symptoms of adenoids in a 3-year-old child” and “ Inflammation of the adenoids in children, symptoms”, we emphasize the main leitmotifs.
The difference in the manifestation of inflammation of the adenoids in children (3 years old) is an established fact in the practice of pediatric visceral otolaryngology and pediatrics. Such cases are observed everywhere. And such circumstances depend on the child’s innate immunity, on the tendency to acquired pathologies (the formation of strong or weak resistance) to colds and infectious infestations.
Take this indisputable advice! Preventive measures, preventive washing and rinsing with healing solutions are considered effective resistance. Timely instillation, on the recommendation of the supervising ENT doctor, with anthranasal drops, lubrication of the nasal cavities with medicinal ointments.
Regularly carry out warming wellness procedures - ultraviolet and LED irradiation, halotherapy (visiting salt rooms). Intensively use climatic therapy (water procedures with sea water, air “baths”, hardening in the summer in mountain children's sanatoriums).
For parents, the 3rd year of their children’s life bears increased responsibility and concern for the baby’s health. Especially if the child already shows weakness in respiration, often catches colds, and is weak by nature. Be extremely careful and careful, and the 3-year period will pass without pathogenic adenoids!
Cost of surgery to remove adenoids in children
If there is a need for surgery, it is important to remember that there are certain favorable periods for removing adenoids. It is better not to perform the operation during the child’s growth period, when the nasopharynx is growing and developing. The optimal period for adenotomy is the period when the child’s growth slows down, namely from 5 to 6 years, from 9 to 10 years and after 13-14 years.
Many people have fresh memories of having their adenoids removed without anesthesia. However, modern medicine, which uses endoscopic equipment, offers a completely painless method of performing surgery under general anesthesia.
The cost of such an operation will be slightly higher than adenotomy under local anesthesia. This is explained by the fact that not only the surgeon, but also the operating nurse and anesthesiologist take part in the operation. Also, the operation requires the use of modern equipment.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
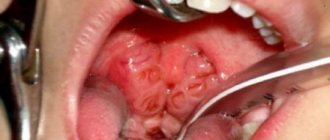
Adenoids are enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsils that serve as a barrier to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. Their attacks intensify the vegetation of the tonsils, which, after the inflammation is relieved, acquire their previous appearance. If the child’s body is often subjected to such attacks, then they can increase so much that they cause various kinds of complications.
Adenoids are formed by the end of the first year of life, for some this process is completed at two years, from about 12 years they begin to decrease in size, and by 17 years they can completely atrophy.
They are located at the top of the pharynx. This disease has 3 stages:
- The first, enlarged tonsil covers the third part of the nose.
- Second, half of the nasal passage.
- The third is characterized by either complete closure or 2/3 of the nasal opening.
Adenoids in children most often grow for the following reasons:

decreased thyroid function,- birth injury,
- intrauterine hypoxia,
- frequent consumption of sweet foods,
- scarlet fever,
- frequent ARVI,
- flu,
- allergic occurrences,
- artificial feeding of infants,
- living in unfavorable living conditions,
- hereditary predisposition to lymphaticism,
- viral diseases of the mother in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Parents may suspect grade 2 adenoids in children based on the following signs:
- Cough is a symptom of stage 2 of the disease. It occurs due to irritation of the nerve endings of the nasopharynx. Cough with adenoids does not develop into pneumonia and bronchitis.
- The child breathes through his mouth not only during sleep, but also during the day.

Snoring during sleep.- Change in voice, appearance of nasality.
- Decreased appetite.
- Frequent colds.
- Frequent ear problems.
- History of pharyngitis, laryngitis.
- Inability to concentrate.
Grade 2 adenoids in a child may subsequently occur with a slight rise in temperature and purulent discharge from the sinuses. Also, children may develop an adenoid type of face. Due to constant nasal congestion, babies are forced to breathe through their mouths, while trying to capture as much air as possible. In this case, the lower jaw remains in a lowered position, leading to a change in the face. This defect is not only cosmetic, it also leads to malocclusion and narrowing of the nasal passages.