Types of runny nose in infants
A runny nose is a commonly diagnosed inflammation of the nasal mucosa in children. It affects teenagers, school-age children, and newborn babies. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish the following types of runny nose:
- Infectious. Occurs against the background of influenza, measles, acute respiratory viral infection.
- Catarrhal (chronic). The nose has been very stuffy for a long time, and the stuffiness does not go away either day or night.
- Allergic. All signs of a runny nose appear periodically and are most often associated with the seasons of the year - for example, grass blooms in the spring, poplar fluff flies in the summer, and ragweed blooms in the fall.
- Vasomotor. It is diagnosed in children with weakened immune systems, for whom even a small draft, provided they have warm clothes, threatens to develop into a runny nose.
Read this material on how to properly use aloe juice for a runny nose.
We also recommend that you read in more detail about how to treat thick snot in a child.
Symptoms of a runny nose
At 2.5 months, the baby’s nasopharyngeal mucosa is not yet ready to provide complete protection against pathogenic microorganisms penetrating through the nasal passage. It does not fully fulfill its functions. Sometimes the establishment of its functions occurs by 4 months. A runny nose begins to appear when a child gets sick. The newborn first sneezes, then secretory discharge appears from the nose, and a cough is possible. This reaction of the baby’s body may indicate an allergic reaction if previous causes have been excluded by the pediatrician.
The baby becomes capricious, disobedient, and cries constantly. Pay attention to how the child breathes. Breathing through the mouth means that the nose is clogged with mucus. The nasal mucosa swells, breathing is impaired, these symptoms indicate an infectious disease. How to cure snot and cough without fever?
For each stage of acute rhinitis (runny nose) there are symptoms:
- at the beginning of the disease (dry stage) – the nasal passages are dry, young patients experience unpleasant sensations (“itching”), sneeze, and a mild headache develops;
- wet stage - light-colored mucus begins to accumulate in the nasal passages, the mucous membrane swells significantly and there is complete nasal congestion;
- purulent - nasal discharge acquires a yellow-green tint, a stretchy and viscous structure.
At any stage of acute rhinitis, in addition to the above-described symptoms, headache, general weakness are added, children are capricious and require increased attention from adults. You may also be interested in learning about the treatment of yellow snot.
The causes of nasal swelling without a runny nose can be found at the provided link.
Runny nose in infants - features of the course
Newborns are characterized by the development of a physiological runny nose - a condition that is associated with the adaptation of the nasal mucosa to the outside world and independent breathing. In the womb, the child did not breathe through the mouth and nose - oxygen came through the blood through the umbilical cord.
After birth, the body must get used to/adapt (go through a period of adaptation) to new living conditions and the nasal mucosa simply “calculates” the required amount of mucus that should be produced. It is during this period that the baby may experience nasal congestion and the presence of mucus.
Read about the best nasal drops to use for a runny nose here.
Before you begin to treat a runny nose in a baby, an important rule is to immediately seek pediatric help. After the examination, the doctor will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
In newborns up to two months, the presence of a runny nose is not always the beginning of a respiratory disease. At this age, in babies, the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx cannot yet fully perform its functions, its work is not sufficiently regulated, so mucus can be released in quite large quantities, this is a physiological runny nose in an infant.
Of course, the main reason why a baby develops a runny nose is a common cold, as well as an acute viral infection or flu. During infections, a runny nose in children under one year of age is always accompanied by severe swelling of the mucous membrane, which significantly impairs the baby’s breathing.
The air in a metropolis or even in a small town, and indeed the whole modern life of a person, is full of the presence of various chemical irritants, to which a fragile baby may have an allergic reaction, which is manifested by a runny nose and sneezing, swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
In any case, especially if an infant gets sick for the first time, an examination by a pediatrician is required. If your baby has a fever, you should call a doctor at home; if there is no fever, you should come to the appointment. You especially shouldn’t put off calling a doctor if your child has a cough, watery eyes, refuses to breastfeed, or becomes lethargic or tearful.
It is easy to notice that a child has developed snot; there are no differences in the symptoms of a runny nose in a newborn and an adult - the baby sneezes, breathing through the nose becomes difficult, and mucous discharge appears from the nose. The child sniffles, sniffles, refuses to suck normally, and often throws away the breast or pacifier. But at this age, he still cannot blow his nose on his own.
Therefore, the nose must be cleaned using a special mucus sucker - an aspirator, which are sold in pharmacies or departments for infants. You can use a syringe with a soft spout, which should be boiled, cooled, pressed to pump out the air, inserted into the nasal passage, and released. All the mucus will be in the enema.
Do not use regular cotton swabs with a hard base, which can damage the baby’s delicate nose. You should also not use syringes, because at such an early age, mucus from the nose can easily enter the Eustachian tube under pressure, which can cause otitis media in the baby.
In case of lack of nasal breathing and shortness of breath, newborn children cannot always switch to mouth breathing. Medicine knows of cases where a prolonged runny nose in a child, blockage of the nasal passages with thick mucus, became the cause of death of the infant, since the child was suffocated. With a large accumulation of mucus and an unclean nose, it flows into the bronchi and provokes bronchitis, and if it enters the ear through the Eustachian tube, otitis media develops. Take this seemingly minor ailment in children under one year old, like a runny nose, very seriously.
How to treat a runny nose in a newborn? The first thing to do, as we have already said, is to clear the baby’s nasal passages of mucus using an aspirator. It is very convenient to use, you just need to get used to it. If there is not a lot of discharge, as happens with infants after birth, you can make a cotton swab and twirl it in the baby’s nose; after the procedure, the accumulated mucus will end up on the flagellum, and the nose will be cleared. Just don’t push it deep!
When a runny nose is accompanied by a fever, it is not recommended to walk with the child, especially in frosty weather; you should also not bathe the baby. When the temperature becomes normal, you can go for a walk, but in calm weather, you can bathe 4 days after the child’s condition has clearly improved.
As for nutrition, when a child has a runny nose, his appetite is reduced because it is difficult for him to suck with a stuffy nose. During sucking, he suffocates, and when she is forced to breathe through her mouth, the lips are not closed completely and sucking, especially the baby is unable to breastfeed. Also, against the background of ARVI, a decrease in appetite is natural, since the body is actively fighting a viral infection and there is an additional load on the digestive system; the liver is not needed in this case.
If a child refuses to eat, make every effort to ensure that the baby can breathe freely, clear the nose, do not be lazy, and instill vasoconstrictor drops. An infant, even during illness, should eat at least a third of a serving of milk, and the break between feedings should be shortened. If you are not breastfeeding, feed from a spoon, from a cup, from a syringe; it is important that the baby receives nutrition, since dehydration occurs very quickly in infants, which is life-threatening.
If the child is more than 8 months old and has already tried compotes, juices or herbal teas (see how to properly introduce complementary foods to a child up to one year old), then you can finish it with such drinks. If the child is older than one year, in this case the main thing is to give the baby a good drink; boiled water can be used as an additional liquid.
It is also worth regularly ventilating the room in which the baby is located, using a humidifier, carrying out wet cleaning daily or hanging wet diapers in the room on the radiator. When the air in the room is dry and dusty, the baby's recovery becomes protracted. If there is a high temperature in infants, it is recommended to knock it down at a temperature above 38C (see a detailed review of all antipyretic drugs for children in suspensions and suppositories).
The modern pharmaceutical industry is rich in various remedies for the common cold. In the absence of fever and other symptoms, treatment may be limited to the use of only local agents for instillation into the nose. For infants, it is more correct and safe to instill drops into the nose than to use various sprays.
What if it's all about a cold?
Another thing is a runny nose when you have a cold. If the baby starts coughing, has a fever and other symptoms appear, then it is necessary to treat the child’s runny nose. When you have a cold, a runny nose goes through the following stages:
- The mucous membrane swells and becomes dry, itching occurs in the nasal cavity, there is coughing and sneezing.
- Transparent discharge appears, breathing becomes difficult, the nose is constantly stuffy.
- The swelling subsides, the discharge turns yellow or green and becomes thicker. It becomes easier for the child to breathe. Dry crusts form.
If a child’s runny nose becomes prolonged at 3 months, his sleep is disturbed, he eats poorly, the temperature rises above +38ºС, you should immediately call a doctor. In addition, emergency care is needed if the child is 3 months old and has shortness of breath, if a runny nose occurs immediately after contact with an allergen, if the nasal discharge becomes purulent or bleeding comes from the nose.
How to treat a runny nose in a 3-month-old baby? Many medications are not intended for infants, so it is not recommended to treat a runny nose in an infant on your own, even with herbal remedies. You should consult your doctor before using anything.
What should parents do? The room in which the baby is located should be frequently ventilated; the air should not be too dry, dusty or overheated - these factors can be the causes of rhinitis in infants. If the child is on mixed or artificial feeding, then he should be given warm, clean boiled water. If the baby is capricious and refuses to eat, then there is no need to insist, but the drinking regime should be mandatory. Water will help thin mucus and remove toxins.

The floor in the room should be washed with a disinfectant, but if the child is prone to allergies, then just using water is enough. You can saturate the air in the room with natural phytoncides - from time to time place a saucer with chopped garlic or onions in the room.
A three-month-old baby's nose should be thoroughly cleaned of mucus. To do this, you can use cotton swabs or a nozzle extractor. If hard crusts appear in your nose, do not forcibly tear them off, soften them with a drop of olive or sea buckthorn oil and carefully remove.
The main remedy for a runny nose in a 3-month-old child is saline solution; vasoconstrictors are also prescribed. Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause of rhinitis itself, and all auxiliary means will help relieve symptoms and alleviate the child’s condition.
Some grandmothers advise putting mother's milk in the baby's nose. This is absolutely forbidden to do! Milk is a nutritious substance, and pathogenic bacteria will grow much faster on this basis.
Recommendations from Dr. Komarovsky
Dr. Komarovsky is a famous doctor, he helps to cope with many problems, talking in detail about the causes, symptoms and treatment in his videos. He also had a runny nose. What does Dr. Komarovsky recommend if snot appears without fever in a baby?
adhere to the correct daily routine (babies up to 4 months should sleep 2 times a day), rest is very important for the recovery of the body; proper and nutritious nutrition, the pediatrician should tell the mother how to start introducing complementary foods and that this should not be done before six months; daily exercises and air baths will help prevent the appearance of mucus; Walk with your child outside several times a day; fresh air is useful for rhinitis of any nature.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends removing mucus using nasal aspirators; they can be purchased at any pharmacy. Then rinse the nose and administer the medication.
Do not forget to give your child fluids so that the nasal mucosa does not dry out. In addition, Dr. Komarovsky advises burying the baby’s nose after 40–60 minutes with special moisturizing products. For example, saline solution or isotonic sodium chloride solution. The condition of the infant will improve 2-3 days after such procedures.
How can a mother treat thick snot in her child?
Colorless snot, as a sign of an incipient cold, is treated without the use of antibiotics. During this period, most of the treatment comes down to rinsing the nasal passages. It is impossible to blow a baby's nose, the sticky mass clogs the nasal passages and prevents full breathing, so you can get rid of thick snot using cotton wool wicks.
First, you need to drop a few drops of a saline solution (saline) into each nostril; the following drops will do:
- Marimer;
- Humer;
- Salin.
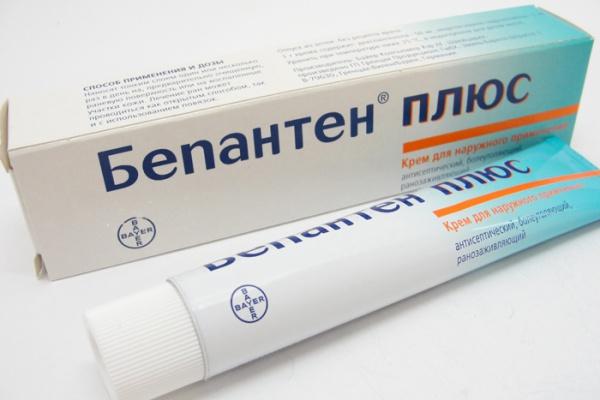
Moisten the wicks with vegetable oil and use them to remove the softened secretions from the baby’s nose. In infants, the skin around the nostrils may become irritated due to discharge. By applying Bepanten ointment, you can quickly deal with redness. Mothers can be advised to purchase devices for cleaning and rinsing the nose at the pharmacy:
- nasal aspirator.
- silicone tube;
- small rubber pear.
Inhalations for viscous snot
Inhalers are inexpensive devices that are easy to use. Having an inhaler at home is very convenient. The inhalation procedure is easy even for small children. An even more convenient device is a nebulizer.
The nebulizer comes with a mask; putting it on the child makes inhalation very easy. The solution for inhalation is recommended by the attending physician. Before consulting a doctor, you can use infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage).
You can use non-carbonated mineral water: Essentuki, Borjomi. A doctor may prescribe inhalation medications for viscous discharge: “Lazolvan”, “Fluimucil”. It is important to remember that if the baby’s temperature rises, inhalation should be stopped.
Acupressure
When the first symptoms of a cold appear, massage the active points located to the left and right of the child’s nostrils several times a day. Before starting the massage, rub your palms together vigorously. Hands should be warm. Massage for 2-3 seconds with your index finger. Make light rotational movements clockwise. Acupressure stimulates the child’s own immunity.
Removing snot with a nasal aspirator
An infant's snot cannot be blown out; pharmacies sell nasal aspirators to remove it. There are different types of nozzle ejectors for children:
- aspirators-syringes;
- mechanical;
- electronic;
- vacuum
See also
Symptoms and treatment of posterior rhinitis in adults and children
Read

Each model has its pros and cons, but it’s easy to suck out stubborn snot using any of them. It is better to get rid of secretions using a nozzle suction before meals and before going to bed at night. With a clean nose, a child eats and sleeps better.
After each use, the device must be disassembled and washed thoroughly.
Aspirators dry out the nasal mucosa. After cleaning them, you need to drip a saline solution into your nose, it will moisturize the inner surface.
When the snot does not go away for a long time, the doctor may prescribe nasal drops for the baby. In some cases, it is permissible to instill drops with a vasoconstrictor effect. Pediatricians prefer Otrivin and Nazol Baby.
Not every baby can treat a runny nose with an aspirator. It is contraindicated in the following children:
- with frequent nosebleeds;
- the presence of polyps in the nose;
- complete obstruction of the nasal canals.
When are antibiotics prescribed?
The doctor determines how to get rid of sticky snot if there is an infection. You cannot give pills to a sick baby without his or her prescription. Snot caused by a bacterial infection is treated with antibiotics. The main characteristics of infectious mucus: unpleasant odor, green (yellowish) color. Young children are prescribed:
- Isofr;
- Bioparox;
- Polydexa.
How to rid your baby of illness if the discharge is clear
viral infection; teething, in today's children this can be observed as early as 3 months; allergy; dry and hot air.
If the cause is ARVI, it is necessary to rinse the baby’s nasal passages with the help of pharmaceutical products. For example, Salin, AquaMaris, No Sol, Aqualor. Medicines such as Pinosol and Evamentol will help soften the mucous membrane and make breathing easier.
When clear discharge is associated with teething, there is no need to take medications or use vasoconstrictors. It is enough to rinse the baby’s nose with saline or the pharmaceutical products listed above. If rhinitis appears due to an allergy, the child will be prescribed Nazol Baby, Otrivin, Olint, Tizin, Farmazolin or Vibrocil.
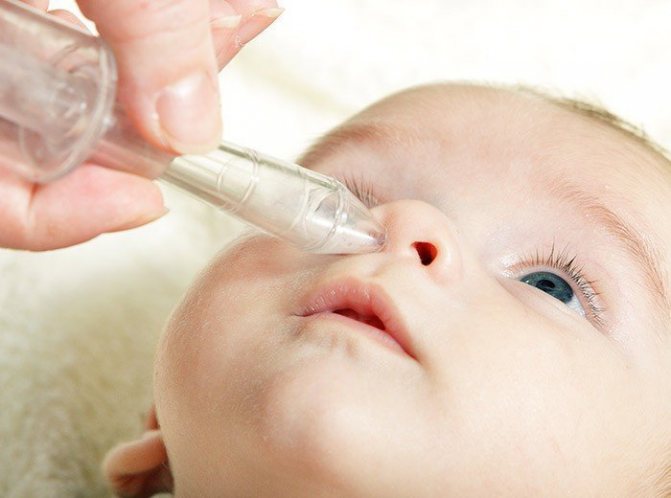
These drugs belong to the group of vasoconstrictor medications. If these medications are not effective for allergies and snot, the baby will be prescribed hormonal medications. They can only be used after visiting a doctor. Treatment is allowed with the following products that are safe for children: Avamis, Nasonex.
Diagnostic measures
A runny nose in an infant is diagnosed by a pediatrician already upon examination of the nasal passages - hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane, its swelling and the presence of mucus are noted. In some cases, instrumental methods of examining the child may be used. And more specialized specialists are invited for consultation - for example, an allergist, an infectious disease specialist.
Read about the treatment of green snot in children here.
The doctor must differentiate a common runny nose from infectious diseases in which the symptoms may be similar - for example, diphtheria, measles.
What medications to use for green and white snot
Dealing with green snot in a child is much more difficult. Their presence indicates bacterial infection of the body. Green snot is treated with antibacterial medications. Doctors often prescribe Protorgol, Polydex with phenylephrine, Isofra, Rinofluimucil. Protorgol has proven itself well; recently, pediatricians recommend using only it for the treatment of childhood rhinitis.
It is also recommended to use Nazivin, Sanorin, Naphthyzin against such a runny nose. Before using the drops, the child’s nose is washed with solutions containing sea salt, for example, Aqualor, Aquamaris.
White snot may appear due to complications during childbirth or poor adaptation of the newborn to the environment. You should definitely visit an otolaryngologist or pediatrician. What should you do if your baby suffers from copious white discharge that makes it difficult to breathe properly?
The treatment method consists of rinsing the nasal passages with saline or sea water-based products. Medicine But salt can be used from birth. Vasoconstrictor medications (Vibrocil, Nazivin Sensitive, Nazol Baby) are used no more than 2-3 times a day. The room should be constantly ventilated; it is not necessary to keep the window open for hours; ventilate the baby’s room every hour for 5 minutes.
What does a child's thick snot mean?
You can start treating thick snot in a child before visiting a doctor. Until the cause of their appearance is determined, limit yourself to rinsing the nasal passages with warm water and salt. The salt concentration is small - 0.5 tsp per 500 ml of water. The more often you wash your child’s nose, the better.
Salt water relieves nasal congestion, clears it of infection, and prevents it from penetrating into the paranasal sinuses. Attentive parents begin this procedure as soon as they notice clear, thick snot in their baby.
In some cases, rinsing the nose is enough and by 2-3 days the child’s clear snot becomes white and less abundant. The appearance of white discharge and a decrease in its intensity may indicate the attenuation of the inflammatory process in the nasopharynx.
In most cases, washing the nasal passages alone will not be able to cope with very thick snot in a child. There is no need to postpone visiting a doctor under any circumstances. By secreting thick nasal mucus, the body can signal the onset of a serious illness, which without proper treatment will become chronic and cannot be expected to go away on its own.

How the color of snot reflects the nature of the disease
When examining babies, the pediatrician analyzes the thickness and color of nasal mucus. Based on its thickness and color, it draws certain conclusions. Green snot in a child is the most unpleasant. Their appearance may be a symptom of a serious illness caused by a bacterial (viral) infection. They may be the result of an untreated cold. Possible diagnoses of an incipient disease:
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- rhinitis.
Infants are at greatest risk; their infection can spread to the ears and down into the bronchi.
Sticky snot of yellow or white-yellow color also does not bode well. It is highly likely that the child will develop inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. This color indicates that the disease lasts for a long time. The more intense the color of the mucus, the more acute the inflammatory process.
The least worrying thing is transparent viscous snot. They indicate the initial stage of inflammation. With proper treatment, a runny nose goes away within a week. The child has an infection, but it has not penetrated deeply, so such a runny nose in a child is often treated with traditional methods.
See also
Causes and treatment of nasal congestion without runny nose
Read
Due to physiological characteristics, infants produce thick transparent snot in the absence of a cold or infection (bacterial, fungal, viral). They are caused by hot and dry air in the room.
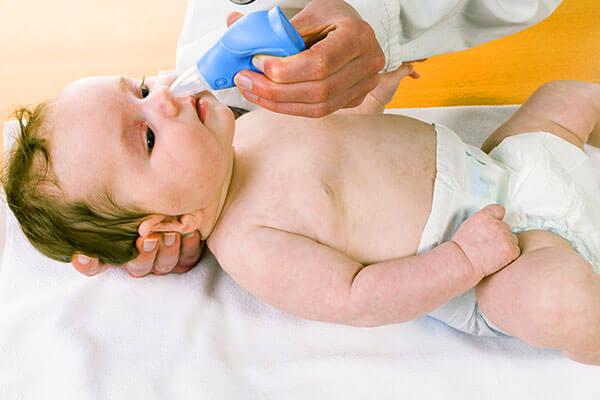
In some cases, a clear secretion is a sign of an allergy. The allergen, entering the baby’s body, causes irritation of the inner surface of the nose, mucus begins to be actively produced and flow out. In the chronic form of allergic rhinitis, the viscosity of the snot increases and it becomes more difficult to blow your nose.
A 5.5 month old child has a runny nose, how can you treat it please?
Inflammation of the nasal mucosa, accompanied by congestion, difficulty breathing, and sneezing, is called a runny nose. This simple and safe (misconception of many) disease can be isolated, or can be accompanied by other pathologies. Treatment of a runny nose should be carried out competently, especially in infants, since there is a risk of developing serious complications.
You can find out which children's drops for a runny nose are the most effective from this article.
Types of runny nose
A runny nose is a commonly diagnosed inflammation of the nasal mucosa in children. It affects teenagers, school-age children, and newborn babies. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish the following types of runny nose:
- Infectious. Occurs against the background of influenza, measles, acute respiratory viral infection.
- Catarrhal (chronic). It lasts for a long time and is characterized by nasal congestion, which bothers children both day and night.
- Allergic. All signs of a runny nose appear periodically and are most often associated with the seasons of the year - for example, grass blooms in the spring, poplar fluff flies in the summer, and ragweed blooms in the fall.
- Vasomotor. It is diagnosed in children with weakened immune systems, for whom even a small draft, provided they have warm clothes, threatens to develop into a runny nose.

You can learn how to properly use aloe juice for a runny nose in children under one year old from the contents of this article.
If a runny nose lasts more than 2 weeks, then you should consult a pediatrician - perhaps a physiological runny nose has developed into an infectious one.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4fIBnajW_Fc
Newborns are characterized by the development of a physiological runny nose - a condition that is associated with the adaptation of the nasal mucosa to the outside world and independent breathing. In the womb, the child did not breathe through the mouth and nose - oxygen came through the blood through the umbilical cord. After birth, the body must get used to/adapt (go through a period of adaptation) to new living conditions and the nasal mucosa simply “calculates” the required amount of mucus that should be produced. It is during this period that the baby may experience nasal congestion and the presence of mucus.
You can find out which drops for runny nose and nasal congestion are the best from the article.
Symptoms of a runny nose
- at the beginning of the disease (dry stage) - the nasal passages are dry, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations (“itching”), there is frequent sneezing, and a mild headache develops;
- wet stage - light-colored mucus begins to accumulate in the nasal passages, the mucous membrane swells significantly and there is complete nasal congestion;
- purulent - nasal discharge acquires a yellow-green tint, stretchy and viscous structure.
At any stage of acute rhinitis, in addition to the above-described symptoms, headache, general weakness are added, children are capricious and require increased attention from adults.
Acute rhinitis is highly treatable, and in some cases it goes away completely without the intervention of doctors or the use of medications. If a runny nose lasts more than 3 weeks, then the risk of the disease becoming chronic increases significantly.
What to do when your nose swells without a runny nose and how to deal with this problem, what medications and methods are indicated in the article.
Types of runny nose
The peculiarity of a runny nose in children under one year of age is a problem in its treatment. The fact is that the baby is not able to blow his nose and the release of mucus is difficult - it accumulates in the nasal passages, which can lead to the rapid development of chronic rhinitis.
If a child sneezes and has snot, it is necessary to treat comprehensively:
- provide the necessary humidity in the child’s room - you can use special humidifiers or place containers with water, hang wet rags over the radiators;
- Regularly clear mucus from the nose using cotton swabs for children under 9 months of age or an aspirator for older children.
How to treat if a child has snot and sneezes, read this article.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with cheap and effective means.
Treatment at the age of 1-12 months can last 3 or 4 days, but most often parents note final recovery a week after the start of the procedures. Albucid drops for infants are no less effective in treating a runny nose.
If an infant has a runny nose, then treatment should be extremely safe - in no case should drops and aerosols/sprays, such as Snoop, which are recommended for older children, be used to relieve symptoms!
For babies aged 3 months and older, you can use Nazivin drops - they have a vasoconstrictor effect. If the baby is already 5 months old, then you can dilute the accumulated mucus in the nasal passages with a physiological solution of sodium chloride and then carry out the procedure of sucking out the liquid (aspiration). Find out how to properly rinse your child’s nose from this article.
It is also possible to take homeopathic remedies agreed with your doctor. Aquamaris is an equally effective remedy in the fight against the runny nose.

According to the instructions, children can rinse their nose with Aquamaris from birth.
Good remedies for nasal congestion in babies aged 5-6 months include Otrivin, Xylen and Vibrocil. In the period from 7 months and older, you can safely drip Interferon - it has not only a therapeutic, but also a preventive effect.
Types of runny nose
Along with treatment with medications, you can use folk remedies. Therapy with home remedies allows you to quickly get rid of the disease. You cannot do home inhalations; use only the methods listed below to treat runny nose in infants.
Make beet juice; the vegetable can be ground in a meat grinder or blender and squeezed out the juice. Use as follows: drop 2 drops into each nostril after mixing with honey. Use the product 2 times a day. Mix equal amounts of aloe juice, honey and carrot juice. Take a pipette and drop 2 drops 3 times a day into each nostril.
Take 2 tbsp. l. viburnum flowers, 2.5 tbsp. l. calendula flowers, 1 tbsp. l. chicory. Pour one tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water. Give to a child from 6 months, take 2-3 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. Mix aloe with honey in proportions 1:1. Before going to bed, bury your baby's nose. Make carrot and beet juice.
Home remedies will not cause harm if used correctly. However, a medical consultation will not be superfluous.
Snot in a baby Komarovsky, a well-known children's doctor, whose recommendations are listened to not only by young parents, but also by experienced mothers and grandmothers, advises treating with the most gentle methods. Vasoconstrictor drops, and especially antibiotics, in his opinion, are often not needed by the child at all. And the situation can be corrected by adjusting the humidity level in the children's room, washing and other gentle home remedies.
Komarovsky wrote several books about snot, articles from them will be useful to all parents who care about the well-being and health of their child. Is it possible to go for a walk if you have snot and a cold, what remedies to use, what is the best treatment for snot - Dr. Komarovsky talks about all this clearly and impartially.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
The only remedy for phlegm that is truly effective and helps almost immediately
{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
In newborn children, the immune system is still very weak, so any symptom, even a harmless one, becomes very dangerous. A runny nose in a baby can lead to serious problems if proper treatment is not carried out in time. At the same time, this may be a normal process of adaptation of the body to external conditions (physiological runny nose). Therefore, you first need to understand the causes of this symptom, and only then carry out appropriate treatment.
A runny nose in infants is difficult: due to a clogged nose, they cannot breathe normally, and their sleep is disturbed. The baby becomes irritable and capricious, eats poorly. A runny nose can last up to two weeks, and in the first days it is accompanied by copious watery discharge from the nose.
If this is a symptom of a cold or a consequence of hypothermia, then the baby may experience an elevated temperature. If the runny nose is severe, the baby will experience irritation and swelling around the nose.
physiological; infectious or viral; allergic; vasomotor.
It does not require treatment. This is a characteristic symptom for babies aged 2 months and 3 months. The mucous membrane of a newborn is fully formed within 10 weeks after birth, so in this case you need to take care of comfortable conditions in the room and prevent drafts.
How to treat a runny nose in a child
There are many ways to get your child to stop running snot, using traditional and folk medicine methods. But without eliminating the main cause of inflammation of the nasal mucosa, the result will be short-lived. The underlying disease must be treated first.
To make it easier for the baby to breathe and drain secretions, raise the head of the bed. It is recommended to clear your nose of mucus 4-5 times a day; this should be done before feeding and before bed.
It is inconvenient to remove snot from a three-month-old baby with a handkerchief or napkin. In addition, you can injure the baby’s delicate skin around the nose. Snot getting on injured areas will cause irritation and pain. You can reduce discomfort with the help of ointments. Menthol products are not recommended for infants, but ointments with eucalyptus or rosemary oil provide a good additional effect for relieving puffiness and swelling of the skin.
You can clean the nose with thin cotton wool, a small syringe or an aspirator. You cannot use hard objects, as you can easily injure the narrow nasal passages.
To replenish moisture lost by the baby's body, it is useful to apply it to the breast more often. During illness, mother's milk will support the child's immunity. During this period between feedings, you should give the baby some water.
Green snot in a baby does not mean that you need to urgently use antibiotics. It is necessary to regularly thin and wash away mucus from the nose and increase the air humidity in the room. The underlying disease should be treated in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
It is not recommended to use vasoconstrictor drugs on your own to treat a three-month-old baby, as they are addictive. This can only be done after consulting a pediatrician with special children’s medications for no longer than 5 days.