Role of plasma cells
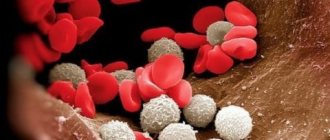
Plasma cells are among the leukocytes - white blood cells responsible for immunity. Their main task is the production of immunoglobulins or antibodies. They are formed when the body is attacked by bacteria, viruses, toxins, everything that poses a danger to children and adults. Such foreign substances are called antigens.
Note! Antibodies produced by plasma cells are the body's immune response to the danger that has arisen. They attach to antigens and prevent them from harming the body, and also contribute to the destruction of foreign agents.
Most often, plasma cells are found in lymph nodes, concentrated in the spleen, and fixed in the red bone marrow. In the latter case, they influence the formation of stable, most often lifelong, immunity to certain diseases. Cells remember a dangerous substance; the next time they encounter it, they won’t have to recognize it, so it can be destroyed much faster and easier.
What are plasma cells
Every hour a person lives under the “protection” of his immunity. That's why they often talk about improving health. Plasma cells belong to the group of white blood cells (leukocytes). Unique in structure and purpose: capable of synthesizing specific proteins, immunoglobulins, adapting to the type of pathogen, thereby accelerating recovery. They have a “memory”, which, when encountering infections again, helps to cope with them.
Attention! High indicators generated in the analyzes should not be ignored. The cause may be serious diseases that quickly progress and weaken the immune system.
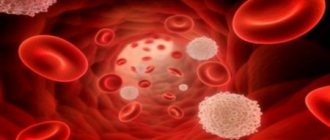
The location of the cells is predominantly lymphatic tissue; they are also found in the bone marrow and spleen. Unlike other components of immunity, they are not constantly present in the blood. The functionality includes the production of antibodies for resistance. The appearance procedure occurs as follows: when attacked by viruses or bacteria, immune cells send a signal to the center of the nervous system.
Next, the brain signals the B cells which specific infection is attacking. B lymphocytes move to the lymphatic tissue, where they transform into lymphocytic plasma cells. In this state they are ready to fight diseases. To fight, they produce an immune system response. Thousands of antibodies appear in a short time. If the infection factor is absent, the body does not need these cells.
The appearance of plasma cells in the child’s blood
Lymphocytes are converted into plasma cells if the body is under threat. When an antigen penetrates it, a signal is sent to the brain warning of danger. Group B lymphocytes, essential for the formation of immunity, are concentrated in the lymph nodes, activated, and later converted into plasma cells.
It turns out that plasma cells are transformed B-lymphocytes, some of which become active, which is a necessary condition for eliminating the threat to health:
- Some produce antibodies that fight the harmful agent;
- Others turn into memory cells. They are necessary if the same antigen enters the body again. Then they give a signal, and the fight against the dangerous substance begins. Immune memory works for months or many years. Sometimes it persists until the end of life. The plasma cells themselves die quite quickly; after 2-3 days they are not detected in the blood.
Plasma cells in the blood
Cells of the human immune system are not only the first to help the body in the fight against pathogens and toxic substances, but also play an irreplaceable role in the diagnosis of various diseases.
Therefore, the presence of plasma cells in a blood test is considered an indisputable sign of a recent infection or a currently developing inflammatory process. Such information is quite easy to obtain and does not require any complex diagnostic techniques.
The presence or absence of plasma cells can be determined during a general blood test, thanks to which an experienced specialist can easily find out the reason that provoked the appearance of these formed blood components, which are atypical for a healthy person.
What are plasma cells?
Plasmocytes, or plasma cells, have an oval or round shape, a diameter of 16–19 microns and belong to the class that provides the protective function of the body - leukocytes. They are formed from group B lymphocytes, and their main function is aimed at producing specific immunoglobulins or, simply put, antibodies (AT).
After receiving a signal from the brain that an antigen (AG) has entered the body, the B-lymphocyte settles in the lymph nodes, and then the process of its transformation into a plasma cell begins. That is, it turns out that a plasma cell is the final stage of the formation of a B-lymphocyte, which has become active and is capable of producing antibodies suitable for one specific antigen.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YHzwv9imDaE
This type of white blood cell is usually concentrated in the red bone marrow, lymph nodes and spleen. Most plasma cells live no more than 3–4 days, after which they die. But some are transformed into the waiting phase and remain in the red bone marrow for a certain time.
As soon as antigens of a similar type enter the body, these cells are activated and perform their main function - they fight against harmful agents. In parallel with plasma cells, immune memory cells are formed and develop, which are capable of signaling the re-introduction of harmful antigens after many months and even years.
They are characterized by a long life cycle, and it can last from several months to the end of a person’s life. It is these blood elements that provide long-term immunity to some infectious diseases suffered throughout life, thus preventing the re-development of pathology. Whereas the life of plasma cells is much shorter and lasts only a few days.
Interesting fact! Each plasma cell produces several thousand immunoglobulins in one second.
To conduct a plasma cell test, no additional preparation is required. The patient only needs to follow generally accepted recommendations, which must first be clarified with the medical staff. As mentioned above, the number of plasma cells is calculated when carrying out the total, or, as it is also called. clinical blood test.
Blood sampling from a child for testing should be done once every six months.
The basic rules that must be followed by those undergoing this procedure include the following:
- visit the laboratory to submit biomaterial in the morning or early afternoon;
- refrain from eating for breakfast, and dinner should be no later than 20.00 the evening before the analysis;
- try not to overwork physically and psycho-emotionally, as this may negatively affect the results of the study.
Reasons for the decrease in lymphocytes in the blood
The biomaterial is collected from a finger, that is, peripheral blood is taken for research. To take it, a puncture is performed with a sterile scarifier and a few drops are taken into a special test tube, which will be enough for diagnostics.
The sample is then labeled and sent for microscopic examination to the laboratory. The results will most often be known the next business day, but this may also depend on the workload of the laboratory.
In a situation where research materials are required as soon as possible, it is worth contacting a private clinic, where, for a fee, the analysis will be deciphered in 1–2 hours, and the patient will receive the necessary information as quickly as possible.
If plasma cells are detected in the blood of an adult, we can confidently say about a pathological process. In this case, the doctor needs to figure out whether the disease is in the active phase of development or whether it is residual effects of a previous pathology.
But in any case, a set of additional examinations will be required, since the normal level of plasma cells in the blood of adults is their absence! These cells in the peripheral blood of a healthy person are determined to be no more than 1–2 per thousand formed elements.
The only exception is children - in newborns, normal levels of plasma cells can fluctuate within 1-2% of the total number of other blood cells. And in older children and until adolescence, the content of these cells can vary from 0.25 to 0.5%.
Plasmocytes in a blood test
In an adult healthy person, the described cells are absent in the blood, but in some pathological processes they may appear in a general blood test, where they are considered as part of the leukocyte formula.
It should be noted that the peripheral biomaterial of a child may, in some situations, contain single representatives of this type of white cells, and this will be equated to the norm. But in other cases, plasma cells in a general blood test are determined in diseases or pathologies such as:
- viral infections – varicella (chickenpox), mononucleosis, rubella, measles;
- pathological processes characterized by the prolonged presence of antigen in the blood - septic conditions, serum sickness, tuberculosis, autoimmune diseases and others;
- plasmacytoma or Rustitsky-Kahler disease - a malignant tumor of plasma cells;
- oncological neoplasms of a malignant nature;
- streptococcal, staphylococcal, fungal and other infections;
- the harmful effects of ionizing rays;
- ARI, ARVI, influenza.
External signs of chickenpox in a child, in which plasma cell levels in the blood may increase
If plasma cells were detected during a general blood test, then all necessary additional diagnostic measures should be carried out, which will help to find out the reason for the increase in the indicator. And also do not forget that the presence of a small amount of these cells is considered normal only for children, and their number should not exceed 1 unit per 200–400 leukocytes.
Only in such a case can parents calm down and not worry prematurely if an increase in the coefficient is detected in the results of the analysis of their baby. However, it is also not recommended to refuse the prescribed set of examinations; on the contrary, you should undergo all of them as soon as possible and get advice from a specialized specialist.
Reference! An increase in plasma cells in the blood may be the result of a common cold suffered shortly before the blood test, since after the disease high levels are observed for several days.
In young patients, the reasons for the increase in the content of the described blood elements are not much different from adults. Although in children the main factor is still childhood infectious diseases, such as measles, rubella, chickenpox and others, since they most often develop at this age.
Separately, it is worth mentioning plasmacytoma, which, although most typical for adults after 40 years of age, can sometimes affect children's bodies.
The essence of the pathology is the malignant degeneration of plasma cells into mutated elements (myeloma).
With this disease, plasma cells in the child’s blood increase to high levels, which can immediately lead the doctor to think about the presence of a severe pathological process.
This disease is accompanied by intense pain in the bones, bleeding, fractures and often increased thrombus formation. Therefore, if a child experiences similar symptoms, it is necessary to consult a specialist as soon as possible to establish a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Methods for correcting the indicator
The first thing to do when detecting an increased content of plasma cells in the peripheral blood is to find out the reason behind this change. To search for a specific harmful microorganism or a developing pathology of another nature, methods with the maximum degree of reliability are used, for example, such as PCR, ELISA and others.
For the purpose of a more comprehensive and thorough diagnosis, venous biomaterial is taken, which makes it possible to calculate not only the formed elements of the blood, but also its other components necessary to establish the pathology, and specifically the antigen itself. Based on the results obtained, a therapeutic course is developed based on the patient’s age and the characteristics of his body.
Features of the course of multiple myeloma - oncological pathology of the hematopoietic system
General recommendations
A general blood test, including determination of the concentration of plasma cells, is performed in almost all cases of patients visiting the hospital. It is especially important to carry out this analysis at the first signs of illness.
These include headache, dizziness, fever, aches in the joints of the limbs and other obvious manifestations of a bacterial or viral infection entering the body.
You should not waste time searching for similar symptoms on forums or comparing your feelings with the indicated manifestations, as this only leads to the loss of precious time that could be spent on diagnosis and treatment.
Such a delay is especially dangerous for the child’s health, because the child’s body is most sensitive to various infections and life-threatening complications can quickly develop.
It would be useful to remind once again that timely diagnosis, correctly identified pathology and a correctly selected therapeutic course will help not only reduce high levels of plasma cells, but also bring the state of health back to normal. A general blood test is a quick and simple method that allows you to find out if everything is in order with the body.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/krov/plazmaticheskie-kletki
Normal blood test values
In an adult, plasma cells should not be seen during a blood test. Their detection indicates a pathology, the cause of which must be immediately established. For children the situation is somewhat different:
- It is considered normal for newborns if there are plasma cells, but their number does not exceed 2% of the total volume of other cells;
- In older children, single similar cells may be observed. So, if there is one plasma cell per 200-400 leukocytes, this is not considered a pathology.
Doctors always recommend retaking the blood test and then, if necessary, prescribe additional examinations. The presence of plasma cells can be detected using a general blood test. The material is collected from a finger, preferably on an empty stomach, so as not to affect the reliability of the results.
Collection of material for analysis
The main thing is that the child is not tired or exhausted; care must be taken that he does not scream or cry. Even emotional experiences can change the outcome. The doctor examines the test results and, if abnormalities are detected, finds out the cause. Only a specialist can understand whether the values are normal or whether the baby needs drug therapy.
Plasma cells in a general blood test: causes and treatment
Plasma cells are a unique weapon of the immune system that waits in the wings before foreign particles invade the body. As soon as a signal is received about the appearance of a bacteria or virus, these cells begin to produce many antibodies to neutralize the harmful object.
The mechanism of appearance of plasma cells
The function of plasma cells is protective
Unlike other immune cells, plasma cells are not constantly present in the blood. They are contained mainly in lymphatic tissues, spleen and bone marrow, leaving their shelters only in case of danger to the body. Their main function is the production of antibodies.
The mechanism of appearance occurs as follows:
- immune cells send a signal to the brain that pathogenic organisms of a certain type have invaded;
- the brain sends a signal to B lymphocytes with information about which particular virus or bacterium has penetrated;
- B lymphocytes move to the lymph nodes, where they transform into plasmocytes (plasma cells) to fight a specific pathogen;
- Plasmocytes begin to develop an immune response, forming several thousand molecules of protein compounds—antibodies—in a second.
During the transformation of B lymphocytes, some of the newly formed cells become so-called memory cells. They live for decades in the bone marrow, carrying antibodies against every bacteria or virus. Plasmocytes die within a few days after their birth.
Causes of plasma cells in blood tests
Infection of the body can lead to the appearance of plasma cells
Thus, plasma cells appear in the bloodstream only when it is necessary to produce antibodies. In the absence of a pathogenic factor, there is no need for plasma cells. If transformed B lymphocytes are found in a blood sample, then an infection is present in the body, or has been present in the recent past.
Factors that provoke the formation of plasma cells:
- flu,
- ORZ,
- ARVI,
- bacterial infection
- infectious diseases,
- mononucleosis,
- tuberculosis,
- dysbacteriosis,
- pathologies of an autoimmune nature,
- oncological tissue lesions.
When is the presence of plasma cells normal?
Plasmocytes may circulate for some time after infection
In a healthy adult, plasma cells should not be present in the bloodstream. They can appear in a ratio of 1-2 per 1000 leukocytes, so they are most often not detected when diagnosing a blood sample.
After the disease, transformed cells continue to circulate in the plasma for some time. Therefore, if plasma cells are detected, it is necessary to retake the test after a few days.
For children, the presence of a small percentage of plasma cells is normal. From the 5th day of life until the end of puberty, the blood may contain from 0.25 to 0.5% plasma cells. The percentage is calculated in relation to the total number of leukocytes.
Plasmocyte detection test
The plasma cell test requires minimal preparation
The doctor may refer you for an analysis to detect plasma cells if the patient is concerned about various ailments: aching joints, lethargy, causeless fatigue, low-grade fever, pain in the abdomen, swollen lymph nodes.
Plasmocytes are detected during a general blood test. Most often, a blood sample is taken from a finger, less often from a vein. Before blood collection, it is recommended not to eat for 8 hours.
If the analysis reveals the presence of plasma cells, it is necessary to undergo additional examinations to determine the cause. Only after this the doctor prescribes treatment.
Factors influencing the result
Plasmocytes in a blood sample in children are not uncommon.
The presence of plasma cells in adults is a clear sign of a pathological process in the body. If the acute stage of the disease is not observed, the doctor may suspect a sluggish chronic infection, which may not manifest itself in any way externally. Subsequent research will reveal the factor that influenced the appearance of plasma cells.
In children, the immune system is just developing, encountering many viruses, fungi and bacteria. To create lasting immunity for life, white blood cells actively develop a response to every dangerous object. Plasmocytes can always be detected in a child’s blood sample. Therefore, the patient's age is one of the factors influencing the result.
An increase in the number of transformed cells is detected after vaccination. It is with the help of plasma cells and memory cells that an immune response is formed to virus particles introduced into the body, which allows the cells to fight back this virus in the future.
Threat of presence of plasma cells
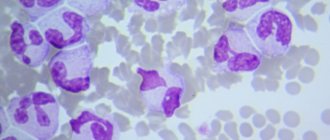
Blood smear from a patient with plasmacytoma
The presence of plasma cells in itself is a consequence of the inflammatory process in the body. If the pathogenic cause is eliminated, the cells will no longer circulate in the blood. However, under the influence of certain factors, plasma cells can form incorrectly and turn from friends of the immune system into its enemies.
This phenomenon is the most common concern of patients who receive a form about the content of plasma cells in the blood.
The idea that all plasma cells pose a threat and are an indicator of oncological changes in the blood is erroneous.
Such a failure at one of the stages of transformation of a B-lymphocyte into a plasma cell occurs in rare cases; a possible cause may be toxic damage to the body, exposure to radiation, or genetic disorders.
As a result of the failure, an atypical plasma cell appears, which, through continuous division, forms a plasmacytoma. The neoplasm is a malignant tumor of plasma cells and poses a danger to human life.
Increase in plasma cells
Detection of plasma cells in a child’s blood above the established norm may indicate the development of one of the following diseases:
- Viral infection, for example, measles, rubella, chickenpox, mononucleosis;
- Autoimmune disorders;
- Tuberculosis;
- Streptococcal infections. They represent a group of pathologies; it is not always possible to immediately determine the cause of the ailment. Scarlet fever is caused only by streptococci, so at the first sign the doctor prescribes the necessary antibiotics. With inflammatory processes in the throat, it is impossible to find out from a blood test what exactly triggered the disease. Most often, children have streptococcal tonsillitis;
- Staphylococcal infections. As a result of the bacteria entering the body, a number of symptoms appear, in particular, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. The child becomes lethargic and refuses to eat. Staphylococcus can affect the mouth, throat, skin, and genitourinary system;
- Flu;
- Fungal infections;
- ARVI.
The higher the indicator value, the more dangerous the pathological process. Only a doctor can determine the reason for the increase. He will evaluate all the indicators in the resulting analysis together, examine the child; his well-being and the presence of additional symptoms are of great importance. If this is not enough to make a diagnosis, the necessary additional studies will be carried out.
Note! Most often, plasma cells grow in children during colds, as well as viral infections that children usually suffer from: measles, rubella and chickenpox.
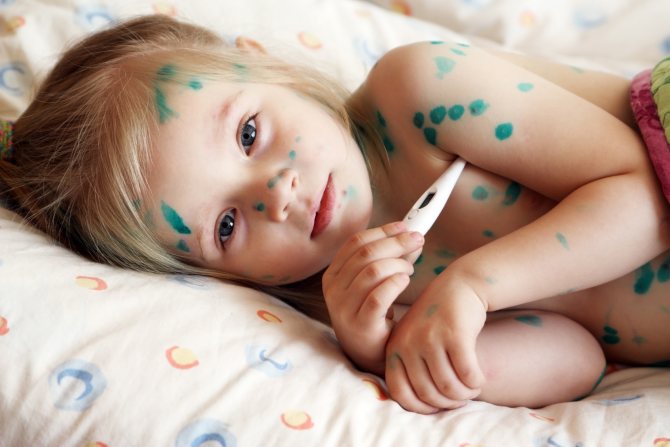

Chickenpox in a child
The reading may remain elevated for several days. Even after complete recovery, cells may be visible in a blood test. They quickly die and everything returns to normal. If, during a retake, a high value of the studied indicator is again observed, this indicates pathology.
In children, immunity is just developing, constantly encountering various infections. That is why a slight presence of plasma cells in the blood is considered normal. They can also appear after vaccination, this indicates that immune protection has appeared and will begin to work when a threat to the body arises. Therefore, when 1 or 2 plasma cells out of 400 others are found in a child’s blood, this does not mean that a pathological process is taking place. You just need to undergo an examination after a few days to make sure that the value of the indicator does not increase.
Plasma cell pathologies
A high concentration of antibodies indicates that there is more than just a virus in the body. There are serious pathologies that often end in death. Disease processes contribute to the development of a number of serious problems that are difficult for the body to cope with.
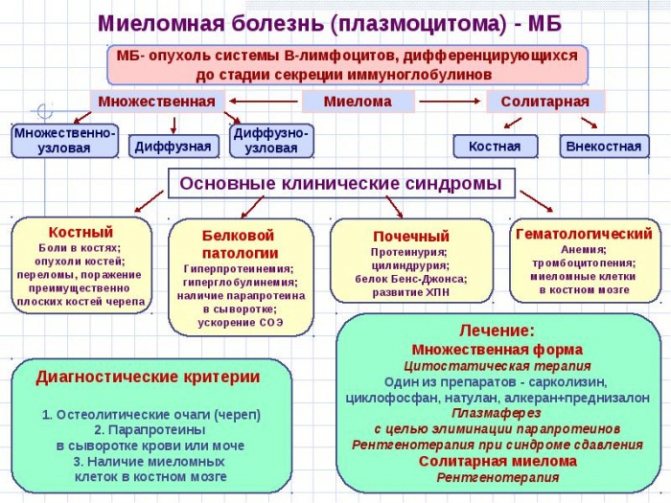
Plasmacytoma (Rustitsky-Kahler disease) is a malignant tumor that is still being studied to this day. The diagnosis is rare, but dangerous: from one affected bone it can quickly spread to the entire body. Genetic predisposition plays a major role.
Waldenström's macroglobulinemia is a bone marrow tumor of a malignant nature. A complex, incurable disease in which life expectancy does not exceed 4-5 years. Destroys the spleen, bone tissue and liver.
Franklin syndrome (heavy chain disease) is a genetically determined pathology, most often affecting men aged 50 years. Accompanied by fever, high temperature, pain in the abdomen and throat. The person experiences general weakness and quickly loses weight. Accompanied by frequent viral and bacterial infections.
Myeloma. Growths that produce pathological proteins, whose nature is not fully understood. Plasma cells form malignant tumors that have a destructive effect on organs and bone tissue. The person dies slowly but surely, feeling constant pain.
Additional diagnostic methods
To determine the number of plasma cells in the blood, blood is taken from a finger prick. This is the simplest and most inexpensive test to assess the child’s condition. Based on the results, you can understand from which side the threat came; they are attacking the body, for example, viruses or bacteria. If all indicators are normal, then additional research is needed to establish the cause of the pathological condition. Blood from a vein is also examined, but in children it is much more difficult to collect blood. In addition, this is a lot of stress for the child. Therefore, they try to make do with capillary blood.
The causative agent of the disease can be identified using the PCR method. Laboratory assistants take a sample from the collected material and use special enzymes to copy DNA and RNA. Even if the disease has just begun, the method allows it to be detected. He will also notice several molecules of a dangerous pathogen in the absence of alarming symptoms.
What does the detection of plasma cells in the blood indicate?
If plasma cells are detected in a general blood test, additional examination may be necessary. To identify the specific causative agent of a particular pathology, there are diagnostic methods with the maximum degree of reliability, such as PCR, ELISA and others.
To perform such an examination, venous blood is taken to calculate, in addition to plasma cells, additional formed elements of the blood flow, which make it possible to establish a specific antigen.
The presence of plasma cells in a blood test indicates the following diseases:
- Influenza, acute respiratory diseases (ARI), acute viral respiratory infections (ARVI).
- Bacterial infections with staphylococcus, streptococcus and other pathogens.
- Septic lesions.
- Various types of infections.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Oncological diseases.
- Consequences of radiation.
- Plasmacytoma, mononucleosis, chicken pox, measles and others.
A clinical blood test for plasma cells is taken at the first symptoms of illness. Such signs include increased body temperature, dizziness or headache, aching joints and other eloquent indicators of the penetration of a bacterial or viral infection into the body. If at least one of the listed symptoms appears, it is necessary to establish the cause of the painful condition as soon as possible, especially when it comes to a child. Moreover, a blood test for plasma cells is a simple and accessible method of laboratory diagnosis.
Source: krov.expert
If a blood test shows plasma cells, it means that you recently encountered a virus, bacteria, or there is an inflammatory process in the body. This information can be tracked even in a general blood test, and a competent therapist can easily determine the reason that could provoke the appearance of plasma cells in the body.
Why do plasma cells appear in the blood?
Do not think that plasma cells are foreign bacteria that have infected the body. Plasma cells are our body’s reaction to an external pathogen, but they are produced from B lymphocytes, which means they are constantly in the lymph nodes, red bone marrow and spleen. The main function of these organs is the production of antibodies, that is, immunoglobulins. The process looks something like this:
- When a pathological process develops in the body, the brain sends signals to places where B lymphocytes accumulate.
- After receiving a signal indicating a specific antigen, the B lymphocyte settles in the lymph nodes and begins to transform into a plasma cell, which is necessary to eliminate this type of problem.
- At the end of the transformation process, the plasma cell begins to synthesize antibodies to the specified antigen.
- Most plasma cells live for about 3-4 days before they die, but some enter a waiting phase. These plasma cells are concentrated in the human bone marrow. These memory cells are activated as soon as antigens of the same type enter the body again. The lifespan of such plasma cells can be 40-50 years. They provide resistance to some infectious diseases.
Dangers and Consequences
With timely treatment of infectious pathologies, it is easy to avoid dangerous consequences. It’s not scary if several plasma cells are observed during illness and illness. They may remain for two to three days after symptoms disappear. This only confirms the presence of a dangerous agent and the fight of the immune system against it. If during the retake all indicators are normal, then there is no need to worry, the inflammation has been eliminated. When deviations are detected again, the cause must be found. Otherwise, infectious processes can develop into chronic ones, which will affect the quality of life of the child and his parents.
Note! There is no need to self-medicate; in deciphering tests and making a diagnosis, you need to trust a specialist. You should not take antibiotics or other medications on your own. Only a doctor determines the advisability of prescribing them and selects the required dosage.

Child at a doctor's appointment
The higher the content of plasma cells, the more dangerous the condition and the higher the threat to the health and life of the child. It’s bad when there are no symptoms, such as sore throat, fever or rash, and the baby has not been sick in recent days. In this case, the presence of cells from a number of leukocytes, especially if they have a large percentage in the total number of others, may indicate the occurrence of serious diseases that require immediate medical attention.
Plasma cells may always be present in a child’s blood. It is not considered pathological if several units are detected. The imperfect immunity of children is formed by adapting to the world and many infections, therefore plasma cells remain active, working to protect the body.