0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.22
407
Leukocytes
Blood composition indicators in a child are of great importance, since the doctor can use them to judge the health or presence of diseases that need treatment. One of the main indicators is the level of leukocyte cells. It can increase or decrease under the influence of various factors.
What are leukocytes?
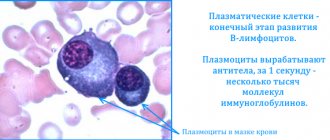
Leukocyte blood cells are white cells whose function is to destroy foreign bacteria, microbes or viruses. Active synthesis of these particles occurs when pathogenic microorganisms enter the body, causing a great risk to health. The number of leukocytes that are formed in the blood indicates the functioning of the immune defense. If there is a low level of leukocytes, then the child’s body’s vulnerability to disease increases. Reduced leukocytes in the blood of a child indicate the development of pathological processes that cause a decrease in the synthesis of protective cells.
Leukocytes
Danger of low white blood cell count
The state of immunity directly depends on the number of these particles. When the number of white blood cells decreases, it can be said that there is a danger of infection. It turns out that the child is defenseless against any attack by foreign bacteria. Low is an average value less than 4 units. It should be considered more correct if the number of leukocytes is lower by 2, relative to the norm for the child’s age.
With leukopenia, the child receives reduced immunity, frequent incidence of various pathologies and a very slow unstable recovery. In addition, diseases of the skin, mucous membranes, and severe infections are possible.
Normal indicators in children
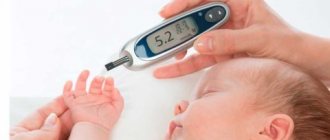
The content of leukocyte cells is determined using a laboratory test of a blood sample from a finger. This process is planned, especially in children. For each childhood age period, its own norm of leukocytes is established. The difference in values is determined by changes associated with the child's development.
For example: immediately after birth in a newborn up to 2 years of age, the immune system is especially strong, since it needs to protect the helpless body from the penetration of infections and viruses. Therefore, the limits of leukocyte counts at this age in children are higher than in adults.
During a detailed blood test, the doctor takes into account the indicator of total leukocyte cells in the blood and their type as a percentage:
- The number of neutrophils is 60%.
- The number of lymphocytes is 45%.
- The number of monocytes is up to 8%.
- The number of eosinophils is up to 5%.
- The number of basophils is up to 0.99%.
If a child’s white blood cell count is low, this condition is called leukopenia.
Analysis in a child
Causes of leukopenia
A low number of leukocyte cells in children's blood (less than 4 grams per liter) is a cause for greater concern than exceeding normal levels. Let's consider the reasons for the reduction of leukocytes.
The lack of white blood cells leads to the fact that the child’s body is left without protection from pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms.
Why do leukocytes need to be increased? The condition of leukopenia is dangerous, because it can lead to:
- The occurrence of sepsis.
- Too rapid spread of infection in the body.
- Inability to effectively cure the disease.
- Life-threatening.
Leukopenia can be moderate, uniform, and sometimes characterized by a decrease in specific forms of leukocytes (for example: only lymphocytes, only neutrophils or group 3 leukocytes decrease).
The main reason why leukocytes in the blood begins to decrease is a malfunction of the bone marrow, during which the required number of protective cells ceases to form. This condition occurs after:
- Radiation or chemical therapy.
- Intoxication of the body, especially derivatives of heavy metals.
- Excessive intake of antibiotic drugs and sulfonamides (if you stop using the drugs, the white blood cell count will normalize on its own after a while).
- Hereditary blood pathologies.
- Severe stress and shock.
- Experienced serious operations.
- The appearance of cancer cells.
There are other reasons for a decrease in white blood cell counts in children:
- Exhaustion of the child's body.
- Lack of building substances for cell growth and production.
- Wrong diet.
- Frequent fasting reduces the production of protective cells.
- Condition after a severe infectious disease (measles, influenza, herpes, etc.).
In such cases, it is necessary to take the necessary measures to restore the composition of the blood and protect the child’s body. To do this, provide a fortified diet rich in beneficial microelements.
Low level of leukocytes in the blood of a child Komarovsky
White blood cell levels may change throughout life. And even in healthy people, under the influence of external factors, a slight increase in their blood levels can be observed. But if leukocytes in the blood are low, this is always a cause for concern.
Diagnosis of diseases in this case should be based on a comprehensive examination and analysis of all blood parameters. A low number of white blood cells always indicates the presence of a disease.
Leukopenia what is it
Leukopenia or low level of leukocytes in the blood is a condition when the leukocyte balance in the body is disturbed towards a decrease. This deviation cannot be caused by food intake or physical activity. Low white blood cells are always a sign of a certain disease.
Today, doctors identify three main reasons for the low level of leukocytes in the blood:
- Low levels of vitamins needed to form white blood cells. This reason is most common among patients. This deviation can develop due to poor nutrition or problems with the absorption of vitamin substances. In this case, other blood parameters are also reduced. Patients have severe anemia, vitamin B deficiency, and low levels of copper and folic acid.
- The body's fight against infection. When an infection is chronically present in the body, white blood cells actively fight it. At the same time, they leave the bloodstream and are localized in the affected tissues. In this state of affairs, it is important to determine the level of neutrophils in the blood. Also, a decrease in leukocytes can occur during intoxication. In this case, the patient will have a deficiency of both mature and young neutrophils.
- A low white blood cell count may also indicate problems with the bone marrow.
Symptoms of leukopenia
A condition where leukocytes in the blood are low does not in itself have any specific symptoms. You can suspect that white blood cells are below normal based on your general health. With prolonged deviation, a person becomes more susceptible to various infectious diseases. This comes from the fact that leukocytes primarily perform protective functions.
A leukocyte is a cell of the immune system that fights various infections, bacteria and fungi.
If you notice that you are getting sick more often or that common colds are dragging on for several weeks, you need to get tested for leukocytes. Leukocyte analysis will accurately determine the level of each type of protective cells and their ratio in relation to the total number of leukocytes. Based on these indicators, the doctor will be able to make an initial diagnosis and send you for additional diagnostics.
Possible diseases
A low leukocyte count is observed in any chronic inflammatory diseases. Also, a decrease in the total number of these cells can be caused by diseases such as:
- Viral diseases (flu, rubella, chickenpox).
- Oncological diseases (especially blood cancer).
- Thyroid diseases.
- Infectious diseases (sepsis, tuberculosis, brucellosis).
- Presence of parasites.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Intestinal diseases.
- HIV.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Pathologies of the spleen.
- Bone marrow diseases.
In addition, white blood cells can decrease with aggressive chemical and radiation treatment, which is used for cancer. Also, a decrease in immunity is observed in people living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Standards and dangerous deviations
In healthy people, both children and adults, the number of leukocytes may vary depending on age. Doctors consider a dangerous decrease when the total level of leukocytes in a blood test is below the limit of 4 g/liter of blood.
With such a decrease, the patient urgently needs to undergo additional examinations and identify the cause of the deviation. The condition when there are few leukocytes is especially dangerous for children.
The child's body is most susceptible to attacks from viruses and infections, and decreased immunity can lead to severe and long-term illnesses.
Monitoring white blood cell levels in pregnant women is also of particular importance. During pregnancy, leukocytes may rise slightly, but a decrease always indicates danger for the baby and his mother. For this reason, gynecologists managing pregnancy always closely monitor this indicator in tests.
Set of indicators
A decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood is always accompanied by deviations in other indicators of a clinical blood test. It is by the combination of these deviations that doctors can assume the presence of a particular disease. What do the tests say?
- Reduced leukocytes in the blood along with a decrease in platelets and red blood cells. This condition usually indicates a malfunction of the bone marrow. Pathologies can be caused by serious poisoning, radiation, and disorders of hematopoietic tissue.
- Leukocytes are reduced along with lymphocytes. Most often, this deviation indicates congenital pathologies, mutations or autoimmune diseases. In some of them, there may be a complete absence of one type of leukocyte.
- The level of leukocytes in the blood is decreased, but monocytes are increased. Most often, such tests are obtained by people who have recently suffered from an infectious or viral disease. The indicators indicate the onset of the recovery phase. In rare cases, these results may indicate the development of cancer or tuberculosis.
- Neutrophils and leukocytes are reduced against the background of increased lymphocytes. Such results are observed in patients with lupus erythematosus, lymphocytic leukemia, tuberculosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment
If you have few leukocytes in your blood, you need to identify the cause of this deviation. Only therapy for the underlying disease can bring positive results. If the reducing factor is not known, additional examinations of the whole body must be performed.
It is worth noting that diagnostic blood testing is an extremely important activity in pediatrics. If the child had a normal indicator, and at the next examination it is reduced, the cause must be urgently identified. To do this, the baby is given a repeat test after a certain time.
If the indicator is still low, this may indicate the early stages of a serious blood or bone marrow disease.
In the case where the repeated analysis did not show any deviations, it can be assumed that an infectious or viral disease could have reduced the indicators. If the child is on the mend, the number of leukocytes will be restored. Children need a blood test at least once a year. Also, the study must be carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
Reasons for the downgrade
Let's look at the most popular reasons for a decrease in white blood cells.
Autoimmune diseases
This group includes diseases that “force” the immune system to perceive healthy cells in the body as hostile. Prominent representatives of the group:
- lupus;
- scleroderma;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Lupus
Impaired functionality of the endocrine system
A reduced concentration of white cells is provoked by diabetes mellitus (congenital and acquired) and hypothyroidism. Also, leukopenia can be a consequence of improper functioning of the thymus gland (thymus).
Taking medications or toxic poisoning
Leukopenia may be a consequence of taking:
- antispasmodics (Analgina, Papaverine);
- sulfonamide drugs (Etazol and Sulfazin);
- antibiotics (Levomycetin);
- barbiturates;
- antiparkinsonian drugs;
- anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- NSAIDs.
Papaverine
Vitamin B deficiency
The development of vitamin deficiency in children is often accompanied by a decrease in immunity and a violation of the norm of leukocytes, erythrocytes and platelets. Ideally, children should get all their vitamins from food, but this is not always possible. To replenish vitamin B reserves, your baby should eat:
- nuts;
- green vegetables;
- greenery;
- beef;
- poultry meat.

Vitamin B
Other reasons
White blood cells may decrease due to:
- typhoid fever, malaria and influenza;
- oncological diseases;
- congenital diseases;
- HIV.
How does leukopenia manifest itself?
Leukopenia can be chronic, acute or recurrent. If the decrease in leukocyte particles occurs steadily, then the child’s lymph nodes become inflamed and increase in size. Children in this state become weak, lethargic, often restless, irritated, and feel pain in the head. However, there are no specific clinical symptoms by which leukopenia can be determined.

Symptoms
A reduced level of leukocytes manifests itself clinically when immunity declines against the background of an infectious disease. In this case, the symptoms of a low white blood cell count will be:
- Heat.
- Increased heart rate.
- Pain in the head.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- General weakness.
- The appearance of blood from the gums while brushing your teeth.
- Chills.
- Exhaustion.
If there are fewer leukocytes after a chemical therapy procedure, then the child:
- Hemorrhagic syndrome appears.
- He falls into a feverish state.
- The skin turns pale.
- The baby becomes weak and broken.
Low leukocytes in a child’s blood: what is this connected with and what should parents do?
The information obtained after a blood test raises many questions among parents. A common problem is an increased or decreased level of white blood cells in a child’s blood.
Young leukocytes continuously move from the place of formation throughout the body. The journey from bone marrow to tissue takes about 10 hours.
The bulk of leukocytes is located in the bone marrow, some in the tissues of the body, another part in the vessels, attaching to the wall.
Each group of cells plays its own role in the defense system. Deviation of leukocyte counts from normal numbers may occur due to one of those indicated in the series.
At different ages, the content of leukocytes in the blood varies. For example, in the first hours of a child’s life, the number of these cells is 18-20x10 liters due to a number of granulocytes.
Next, there is not only a decrease in the total number of these cells, but a change in the qualitative composition of the leukocyte formula.
The number of lymphocytes increases and by the age of one month predominates over neutrophils by two times. Only from the second year of life the number of lymphocytes begins to slowly decline.
A low level of leukocytes in a child’s blood (a decrease in the total number below 4 g/l) is more alarming than an increase in the level. Poch
Leukopenia is a decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood, characterized by fever, pneumonia, blood infection, exhaustion, and headaches.
How to increase white blood cells?
Getting rid of leukopenia requires complex therapy, which consists of both drug treatments and folk remedies.
Treatment with medications
If there are few leukocytes in the blood, then drug therapy is aimed at increasing the production of these substances in the body. The doctor may prescribe medications such as: Leukogen, Pentoxyl or Methyluracil. These drugs help activate regenerative processes and restore immune function.
In addition, in the treatment of leukopenia, medications are used that are aimed at activating the bone marrow, due to which the process of production of leukocytes is enhanced. Among such drugs are Sargramostim, Filgrastim, Leograstim.
To enhance the body's immune function and improve health, biological supplements and other related medications are prescribed.
Attention! Special medications intended for enhanced production of leukocytes have no contraindications. They are used regardless of the form of leukopenia. But this does not mean that you can take any dose.
During drug treatment, patients need to undergo regular follow-up tests to understand whether the chosen methods are effective.
If a child's white blood cell count is below normal and symptoms of bacterial infectious diseases are observed, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial medications. Usually antibiotics are taken for no more than seven days. The doctor chooses a specific drug taking into account the child’s age and condition.
Leograstim
Lifestyle
In addition to the therapy prescribed by the doctor, parents should help the child overcome leukopenia. For this, a proper diet with a high content of fresh fruits and vegetables, natural protein, vitamins and healthy elements is recommended. It is advisable to exclude too fatty foods, and give sweets in doses. Milk-based products, nuts, and cereals are good for a child. It is not recommended to use a lot of salt, spices and herbs.

Proper nutrition
Traditional methods
Folk remedies will be an auxiliary way to raise the level of leukocytes, but not the main one. Therefore, any unconventional methods should be discussed with a doctor so as not to harm the child.
Effective recipes that increase white blood cells:
- Wormwood tea. To prepare, take dry wormwood - 30 grams, pour 0.5 cups of boiling water. Infuse the drink for three hours. Give children one small spoon before breakfast and after dinner. Yesterday's decoction should not be consumed; it is better to prepare fresh tea.
- Oat decoction. To prepare, take 40 grams of oats (unpeeled) and pour half a glass of boiling water. Boil the broth over low heat for three minutes. Then the drink should brew for a couple of hours. Children are given the healing liquid 1 teaspoon before meals three times a day.
- Rose hip tea. You will need one handful of berries and 200 ml of boiling water. Everything is mixed and sealed tightly. The drink must be infused for at least 12 hours. You can drink it instead of tea, adding honey.

Self-medication is strictly prohibited; remember that a child can seriously suffer from an incorrect diagnosis and improper treatment. Only a competent specialist has the right to prescribe drugs or other methods of therapy to increase white blood cells.