Types of leukocytes
White blood cells - leukocytes
Leukocytes are white bodies of different sizes that are part of the blood. This is a general name for groups of cells, each of which performs its own function, and all together are active defenders of the body.
Types of leukocytes:
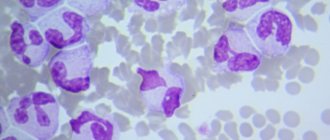
- Neutrophils (NEU). They absorb and digest bacteria, fungi and some viruses. When dying, neutrophils release a large amount of biologically active substances that destroy the remaining harmful substances.
- Eosinophils (EOS). Their function is to combat the allergen, as well as helminths and their larvae. They absorb foreign proteins and dissolve them with their enzymes. In the fight against larvae, eosinophils destroy their granules, which leads to the destruction of worm embryos.
- Basophils (BAS). Helps expel and destroy ticks and helminths. But the main task is to maintain natural blood flow, protect blood vessels from the formation of blood clots, and help other leukocytes reach the source of inflammation.
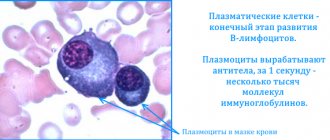
- Lymphocytes (LYM). They destroy viruses, bacteria, dead and cancer cells, regulate the activity of other leukocytes, and produce antibodies. The production of antibodies, that is, protein molecules, allows the body to create protection against each individual virus and bacteria, neutralizing their effect and preventing reproduction.
- Monocytes (MON). The largest leukocytes not only absorb large particles of viruses, microbes, bacteria, but also clean the site of the pathogenic factor. They free the body from dead cells and promote the restoration of damaged tissues.
What is leukocytosis and leukocyte norms in children

Eating leads to a transient increase in leukocytes
Leukocytosis is an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood. The number of white cells in the bloodstream varies throughout the day. There are a little more of them after physical activity, emotional experiences, and eating food. But significant growth indicates the presence of a pathological process in the body.
The normal level of leukocytes directly depends on the age of the child. When a baby is born, it only encounters millions of bacteria, so its immune system works especially actively. The number of protective cells during this period is high, the immune system is just being formed. Gradually, having learned to fight harmful pathogens, leukocytes decrease in number.
In the analysis form, leukocytes are abbreviated WBC. For a more reliable study, it is recommended to know not only the total number of leukocytes, but also the percentage of their varieties in the child’s blood (leukocyte formula).

White blood cell levels in children depend on age
| Age | Leukocytes (10^9/l) | Band neutrophils (%) | Segmented neutrophils (%) | Eosinophils (%) | Basophils (%) | Lymphocytes (%) | Monocytes (%) |
| 1 day - 1 month | 8,5 — 24,5 | 1 — 17 | 45 — 80 | 0,5 — 6 | 0 — 1 | 12 — 36 | 2 — 12 |
| 1 – 6 months | 6,5 — 13,5 | 0,5 — 4 | 15 — 45 | 0,5 — 7 | 0 — 1 | 40 — 76 | 2 — 12 |
| 6 – 12 months | 5,5 — 12,5 | 0,5 — 4 | 15 — 45 | 0,5 — 7 | 0 — 1 | 42 — 74 | 2 — 12 |
| 14 years | 6 — 12 | 0,5 — 4 | 15 — 45 | 0,5 — 7 | 0 — 1 | 38 — 72 | 2 — 12 |
| 4 – 7 years | 5 — 12 | 0,5 — 5 | 25 — 60 | 0,5 — 7 | 0 — 1 | 25 — 60 | 2 — 10 |
| 7 – 12 years | 4,5 — 10 | 0,5 — 5 | 35 — 65 | 0,5 — 7 | 0 — 1 | 24 — 54 | 2 — 10 |
| 12 – 15 years | 4,3 — 9,5 | 0,5 — 6 | 40 — 65 | 0,5 — 6 | 0 — 1 | 22 — 50 | 2 — 10 |
Causes of elevated white blood cells
The main causes of elevated white blood cells in a child’s blood include:
- Radiation sickness;
- Acute infection (measles, rubella, smallpox);
- Cancerous tumors;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Viral and bacterial infections;
- Poisoning;
- Injuries, burns;
- Bleeding;
- Pathological processes occurring in the bone marrow;
- Splenectomy (removal of the spleen);
- Diabetic coma;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Anaphylactic shock;
- Renal colic;
- Allergic reaction.
A physiological increase in leukocytes can occur against the background of the following situations:
- Poor nutrition;
- Time of day: in the evening the number of elements increases;
- Crying, fear of taking the test;
- Change of temperature;
- Taking a hot bath;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Emotional stress;
- Staying in the sun, tanning;
- Hypothermia;
- Taking certain medications (antibiotics, antispasmodics).
Symptoms of elevated white blood cell levels in children
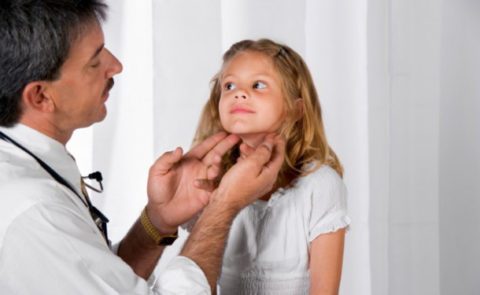
Enlarged lymph nodes may occur with leukocytosis
Symptoms of leukocytosis in children may not be pronounced at the initial stage. Therefore, doctors recommend periodically taking a leukocyte level test as a preventive measure in order to identify the disorder as early as possible. There are some characteristic signs of a child’s condition with leukocytosis that are worth paying attention to:
- lethargy, drowsiness,
- loss of appetite,
- temperature increase,
- bowel disorder,
- restlessness, moodiness,
- increased sweating,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- rash,
- blurred vision.
Causes of leukocytosis in children

Leukocytosis during the transition to artificial feeding
Children's leukocytosis differs from adult leukocytosis. Defense mechanisms learn to respond to external stimuli, and white blood cell levels may increase many times during the day. Changes in air temperature, active games, a hot bath, a hearty lunch - affect the growth of white cells in the blood. Meat products contain antibodies, to which the child’s body reacts by increasing the number of leukocytes.
The level of immune cells in children depends on changes in their usual lifestyle. For example, when a child is weaned, there is a surge in the number of white blood cells as the child's body stops receiving antibodies through mother's milk. The period of exposure to new foods, new friends and surroundings can all affect the growth of immune cells that experience unknown particles and molecules for the first time.
Thus, children often experience such a phenomenon as physiological leukocytosis. This is a natural increase in the level of white cells in the blood. But the cause of growth may also be pathological leukocytosis, provoked by various diseases.
Diseases in which the level of leukocytes increases

Asthma can cause leukocytosis
Pathological leukocytosis is caused by:
- ARVI,
- chicken pox,
- rubella,
- flu,
- parasite infection,
- pneumonia, bronchitis,
- asthma,
- injuries of various natures,
- renal failure,
- inflammatory processes in the tissues of internal organs,
- oncological diseases of the blood.
The cause of the growth of leukocytes may be allergic reactions to a new type of complementary food, dust, pollen, or the introduction of a vaccine.
Diagnosis of leukocytosis
First of all, of course, it is worth doing a detailed blood test, which can show the level of leukocytes in the blood; different types of leukocytes are indicated as a percentage, which is derived using a special formula, it is called a “leukogram”. The leukogram is compiled taking into account the age of the child, because each age has its own norm. If the number of eosinophils in the body increases, this indicates that the child is experiencing an allergic reaction; neutrophils increase during inflammatory processes in the lungs. It is best to donate blood for analysis in the morning, and it is advisable that the child does not eat anything. Increased leukocytosis in a child’s blood may not always indicate pathological processes in the little person’s body, so after a while it is recommended to undergo repeated tests.
Diagnosis of leukocytosis
Detection of leukocytosis is possible in the laboratory
A blood test is used to determine the level of white blood cells in the blood. Before donating a blood sample, you need to prepare:
- The child should not eat for 8 hours before the blood sample is collected. In newborns, blood sampling occurs between feedings.
- Physical activity should be limited.
- It is not recommended to take medications on the day of the test. If it is impossible to cancel the appointment, tell the doctor about the medications your child was taking. Some of them may affect the result.
- Try to calm the child immediately before the blood removal process. Emotional outbursts increase the level of leukocytes in the blood.
If necessary, additional examinations are prescribed. A bone marrow and lymph node biopsy may be necessary.
Classification of causes
Elevated leukocytes in a child’s blood have the following forms:
- Physiological (natural) leukocytosis;
- Pathological – against the background of various changes;
- Pathological-symptomatic – occurs in infectious diseases;
- Neutrophilic surge - manifests itself against the background of acute infections, chronic inflammation;
- Short-term – suddenly appears and disappears;
- Monocytic – for bacterial infection and cancer;
- Eosinophilic – for allergic reactions;
- Basophilic – with nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
Treatment of leukocytosis in children
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor
If physiological reasons for the increase in leukocytes are excluded, then leukocytosis is caused by a certain disease. To lower your white blood cell count, you need to get rid of the underlying cause. After finding out the reasons, the doctor prescribes a treatment method.
- Antiviral drugs are used to fight viral infections.
- Infections caused by bacteria can be treated with antibacterial agents and antibiotics.
- Antihistamines will be prescribed in case of a severe allergic reaction in a child.
- Infection with parasitic worms requires treatment with anthelmintic or anthelmintic drugs.
- The doctor may recommend, in addition to drug treatment, to adhere to a special diet, regimen, and also prescribe a course of vitamins and microelements.
How to downgrade
Physiological leukemia does not require treatment. But if its cause was a violation of the process of preparing for the analysis (eating), then repeated blood donation is recommended.
A pathologically increased number of leukocytes in the blood disappears after the cause is eliminated. During the examination of a small patient, the doctor carefully collects anamnesis. Based on symptoms and test results, he creates the most effective treatment regimen.
In case of inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed. For the treatment of children, the most effective dosage of the drug is selected. The course of antibiotics should be completed in full to prevent recurrence of the infectious disease.

For a viral disease, antiviral drugs are prescribed. Prescribing antibiotics in these cases is inappropriate and harmful. For soft tissue injuries, local antimicrobial agents are used. Anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed to relieve soft tissue swelling and eliminate inflammation.
Children prone to allergies are prescribed antihistamines. They prevent the development of an allergic reaction, incl. for medicines. Enterosorbents are used to remove toxic substances caused by disease from the body. They also normalize the functioning of the digestive tract.
With a strong and prolonged increase in the number of leukocytes, leukapheresis is prescribed. During this procedure, the blood is cleared of excessive white blood cells.
The use of non-traditional remedies is always agreed with the doctor as an addition to the previously prescribed course of treatment. Most often used:
- a decoction of berries and lingonberry leaves;
- decoction of birch buds;
- decoction of strawberry leaves and berries.
Important information: What is ESR in a blood test and the norm in adults
To obtain decoctions, 1 tbsp. raw materials are poured with 1 glass of boiling water, boiled for 10 minutes, infused for half an hour. The resulting medicine is consumed ¼ cup 2 - 3 times a day. Duration of treatment is at least 2 weeks. Giving these decoctions to a newborn is strictly prohibited. The minimum age for treating children with this aid is 4 months.
Diet plays an important role in treatment. The menu is based on:
- stewed vegetables, fruits;
- compotes;
- porridge;
- jelly;
- fermented milk dishes;
- soups prepared with low-fat broth;
- lean meat or fish;
- legumes;
- nuts.
Prohibited:
- fatty or spicy foods;
- pasta;
- sweets.
Parents should:
- carry out wet cleaning of the room where the child is located every day;
- maintain hygiene;
- change bed linen;
- When the temperature rises, give plenty of warm fluids.
Prevention

Fresh air has a beneficial effect on the child's condition
Helping the child’s body cope with the attack of dangerous bacteria and viruses is the task of every parent. Preventive measures will help build a strong immune system.
- Complete nutrition. A lack of microelements in a child’s diet negatively affects the protective functions of his body.
- Fresh air. Every day you should ventilate the rooms where the child is located and take walks away from highways.
- Hygiene as a habit. The habit of washing your hands, eating only clean vegetables and fruits, brushing your teeth in the morning and evening will save your child from many unpleasant consequences.
- Sufficient time for rest. A child's body needs a lot of strength to maintain health.
- Positive emotions. A state of stress reduces the body's protective functions, while joyful emotions provoke the release of hormones that stop inflammatory processes.
The immune system begins to emerge in the womb and is formed before the completion of puberty. Daily care of the child and timely visit to the doctor will help maintain the natural strength of the body.