What are lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes help a person fight diseases. These are the main cells of the immune system and are a type of white blood cell. The main functions of these blood cells are the destruction of foreign agents (viruses, bacteria, fungi) and affected cells of the body, so their number increases when the body is threatened.
To determine the concentration of white blood cells, it is recommended to take a blood test. As the disease develops, lymphocytosis is often detected, which is characterized by an increase in their level. Deviations in the tests allow the specialist to suspect the presence of a bacterial infection or damage to the body by viruses.
What to do to reduce
If lymphocytes are elevated to 64-65% in a one-year-old child, a more thorough examination should be performed. The following studies may be needed:
- Ultrasound;
- CT and MRI;
- bone marrow examination;
- tests for tumor markers;
- bacteriological, virological serological studies;
- biopsy;
- cytological analysis;
- radiography.
If there is an excess of lymphocytes in an infant, treatment will depend on the underlying disease. For viral pathology, antiviral drugs are used (Tamiflu, Nomides, Ingavirin, Ergoferon, Zovirax, Acyclovir-Akrikhin, Valtrex).
If lymphocytes are slightly higher than normal due to bacterial diseases, antibiotics are indicated. For tuberculosis, effective drugs are: Ethambutol, Ekoks, Etumbusin, EMB-Fatol 400, Pyrazinamide-Nikka, Pisina, Streptomycin-KMP, Rifampicin, Makoks, Farbutin.
Important information: What do low monocytes in an adult indicate (monocytopenia in women)
If lymphocytosis up to 62-63% is observed due to poisoning, the following is required:
- gastric lavage;
- enemas;
- taking sorbents approved for children (activated carbon, Polysorb MP, Lactofiltrum);
- use of antidotes;
- detoxification therapy.
With lymphocytosis up to 48-66% against the background of acute lymphocytic leukemia, the following can be performed:
- Chemotherapy. Antitumor agents (cytostatics) are prescribed. These include Cytarabine-Lance, Cytosar, Cyclophosphamide, Endoxan).
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
- Irradiation.
If a high level of lymphocytes (up to 68-74%) is due to toxoplasmosis, the following medications can be used:
- Biseptol;
- Lincomycin;
- Rovamycin (tablets 1.5 million IU);
- Spiramycin-Vero;
- Metronidazole;
- Tinidazole;
- Delagil.
An important aspect of treatment is ensuring proper care for the child by the parents. For this purpose, it is necessary to normalize nutrition, eliminate exposure to toxic substances on the body, not expose the child to stress and eliminate contact with allergens. It is recommended to feed the baby only with breast milk or highly adapted formulas.
When lymphopenia (decreased white blood cells) is detected in a child under one year old, it is necessary to increase the lymphocyte count. For older children, immunomodulators can be prescribed (Likopid, Immunal, Estifan, Echinacea, Immunorm).
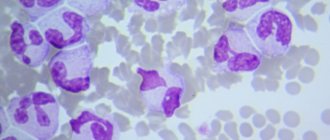
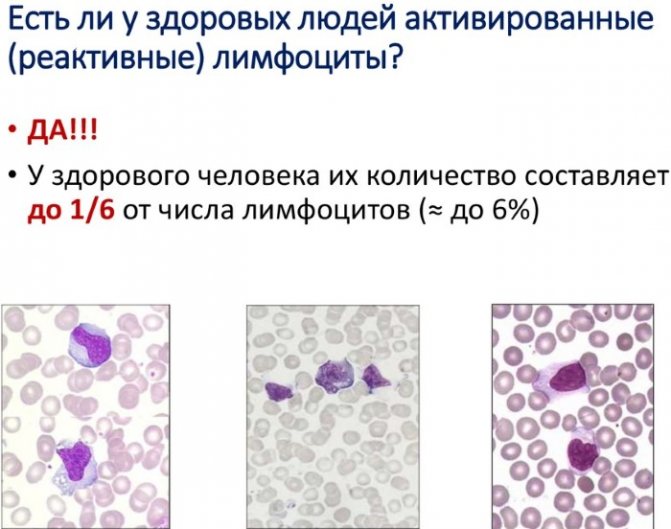
What type of lymphocyte is called reactive?
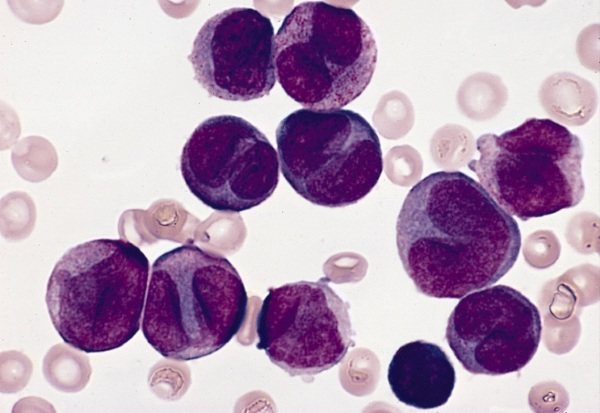
White blood cells are normally round in shape and have clear outlines. With the development of the pathological process, lymphocytes of irregular shape and size appear, which perform the same functions. They are called reactive, or atypical, and they are formed in response to the penetration of an infectious agent or allergy.
As a result of the proliferation of microorganisms, the functions of the body are disrupted, which causes changes in the appearance of cells and structure. Normally, atypical blood cells should be absent; their presence indicates a disease.
These blood elements differ in some features:
- external characteristics. Atypical cells have jagged contours and have a curved polygonal shape;
- size. Reactive cells are larger in size than normal cells. This indicates an intensive pathological process;
- core shape. When examined under a microscope, you can notice that the size of the nucleus of the blood cells is increased, the presence of spots and cracks is noted, which indicates the spread of the pathological process;
- color. Reactive cells have a pronounced red tint, which is clearly visible under magnification.
Valid values
The content of blood cells depends on the age of the patient. It must be taken into account that deviations in the analysis in children are not always a sign of pathology, since the immune system has not yet been fully formed.
Lymphocyte norms for patients of different ages:
| Age | Index, % |
| 3-4 days after birth | 22-25 |
| 4-7 days | 40-42 |
| second week of life - 8 years | 45-65 |
| 9-17 years old | 30-45 |
| Adults | 20-40 |
The level of blood elements in women is influenced by the period of the menstrual cycle. Also, indicators change during pregnancy and any hormonal fluctuations. In a woman carrying a baby, the concentration of white blood cells is most often reduced (16-18%), which is a variant of the norm.
Prevention
To prevent various conditions that provoke an increase in the number of protective bodies in the body, the efforts of parents should be aimed at strengthening the child’s defense system. To do this, you should listen to the following recommendations:
- Maintaining a proper and balanced diet. Your son or daughter should have all the necessary vitamins and minerals on their table for healthy growth and development.
- Sufficient physical activity, encouragement to play sports. You should walk outdoors more often in any weather.
- The child should not be allowed to become hypothermic or overheated. You should dress your son or daughter according to the weather. It is better to choose clothes from natural materials. This will help avoid excessive sweating.
- Parents of teenagers should ensure that their children do not develop bad habits. Try to establish trusting relationships, talk with your child more often.
- You should try to eliminate stress and anxiety, as this negatively affects the child’s body.
You may be interested in: Low hemoglobin with normal ferritin in children
In addition, experts recommend taking a blood test twice a year.

This will help to timely identify certain pathologies and begin their treatment.
What does an increase in white blood cells in the blood indicate?
Reactive lymphocytes, both in adults and children, are most often found in cases of infection or allergies. The level of atypical cells can sometimes increase even if there is no pathological process. Therefore, a specialist must interpret the results of the analysis.
In an adult
If deviations in the analysis are insignificant, this may be caused by:
- increased physical activity;
- overheating in the sun;
- stressful situations;

- errors in nutrition;
- climate change;
- period of the menstrual cycle in women.
If the norms are exceeded 2-3 times, most likely the body is forced to fight a certain pathology, which requires significant effort.
In a pregnant woman
Normally, when pregnant, the concentration of white blood cells may be slightly reduced. This is necessary so that the mother’s body does not reject the fetus. If the number of lymphocytes increases, the likelihood of spontaneous abortion increases. Therefore, pregnant women should regularly have their blood tested.
The child has
In young children, rates are elevated in the first years of life. The reason is that to protect the baby’s body from infections in conditions of insufficiently developed immunity, an increased number of blood cells is necessary. This condition is completely normal and does not require intervention.
Reactive lymphocytes are also elevated in a child if the baby is afraid and cries a lot during the collection of biomaterial. In this case, it is possible to obtain inaccurate data. Excessive physical activity also affects the test result.
If the indicators deviate significantly from the norm, it is necessary to look for the cause of such a violation.
Normal indicators in children of different ages
Let us recall that in a newborn infant, lymphocytes are somewhat elevated, and after 5-6 years their level is the same as in an adult. Exact percentages can be found in the table.
You might be interested in: What blood type will the child have if the parents have 1 and 1?
| Age | Quantity in percentage |
| In infants from the first days after birth | 32 |
| 4-5 days of life | 50 |
| 10 days of life | 60 |
| From 1 to 5 years | 65 |
| After 5-7 years | 55 |
| In children after 10 years | 45 |
If a blood test shows elevated results, doctors call it lymphocytosis. There are relative and absolute types of pathology, that is, the absolute and relative content of these cells in the blood.
In the first case, the number of protective cells only appears to be increased due to a decrease in the level of other blood cells, such as segmented neutrophils, platelets, basophils, monocytes, eosinophils, erythrocytes, granulocytes and others. Absolute is caused by a really large number of lymphocytes.
Causes of leukocytosis
An increased concentration of atypical lymphocytes is a disorder that requires attention.
White blood cells are:
- reactive;
- post-infectious;
- malignant.
A large number of reactive and post-infectious cells is most often a sign of infectious processes. With further progression of the pathology or development of oncology, malignant lymphocytes are formed.

An increase in the concentration of atypical blood elements in patients of any age can be observed when:
- progression of infectious pathologies, which is accompanied by disruption of the normal state of the body. Deviations in tests are found in chickenpox, pneumonia, mumps, hepatitis;
- taking antibacterial (for example, Tetracycline) or other drugs that provoke an allergic reaction;
- brucellosis, when many organs and systems are affected;
- toxoplasmosis, which disrupts the immune system;
- whooping cough, which affects children of any age and contributes to the appearance of atypical cells;
- syphilis, with the progression of which atypical blood elements also appear;
- hyperthyroidism, in which there is increased production of hormones. This in turn affects white blood cell levels;
- systemic diseases affecting connective tissues. With rheumatoid arthritis, myasthenia gravis, and lupus erythematosus, it is difficult for the immune system to differentiate foreign blood elements. Pathogenic microorganisms are recognized as their own, and the immune system attacks its own cells. In this case, a violent reaction occurs, which is accompanied by an increase in the level of lymphocytes;
- purulent processes. The concentration of lymphocytes increases in pathologies such as bronchitis, pleurisy, tuberculosis, furunculosis, adnexitis, and tonsillitis.
The life-threatening cause of deviation in the analysis is oncology of the hematopoietic system. During the oncological process, the concentration of blood cells is exceeded 6 times.
Suspicions regarding the occurrence of malignant changes in the body arise when their number exceeds 3 times. The most common diseases that are accompanied by lymphocytosis are lymphoblastic leukemia in acute and chronic form.
An acute pathological process is characterized by the formation in the bone marrow of immature immune cells that are unable to cope with their tasks. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in children. When performing a blood test, an increase in lymphocytes is noted. At the same time, the levels of red blood cells and platelets decrease.
The chronic form of the pathology is typical for older patients. The progression of the disease is slow, but it cannot be treated.
Reactive lymphocytes are elevated in a child in most cases when he is sick:
- ARVI, rubella, chickenpox;
- whooping cough, tuberculosis;
Reactive lymphocytes are elevated in a child with whooping cough! - toxoplasmosis.
Increased blood cell levels may also be affected by:
- vaccination;
- vitamin deficiency;
- injuries that are accompanied by bleeding and infection;
- stress;
- physical exercise;
- chemical poisoning.
An increase in the concentration of lymphocytes in children caused by malignant processes is fortunately rare.
Reasons for the high rate
An increase in lymphocytes in a child’s blood is provoked by physical activity, stress, and emotional experiences. A significant increase in the indicator indicates serious illness. These include tuberculosis, Filatov's disease, and cytomegalovirus. With oncological pathologies, there are many lymphocytes in the child’s blood.
Causes of lymphocytosis in children:
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- HIV infection;
- splenectomy;
- bronchial asthma;
- chemical poisoning (arsenic, lead);
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, anti-epileptic drugs.
An increased level of lymphocytes in a child’s blood signals a disease, because the body needs more immune cells to fight infection. After recovery, the indicators may be higher than normal for some time. But gradually the level of white blood cells will fall.
Symptoms
There are no specific signs for deviations in the analyzes. Only enlarged lymph nodes may be observed. Other manifestations depend on the cause that provoked the disorder.
The following symptoms may occur:
- feeling of weakness, apathy;
- poor appetite. This symptom is most pronounced in children, who may refuse to eat at all;
- sleep problems, anxiety;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- elevated temperature;
- headaches, dizziness;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- rashes on the body of various types;
- manifestations of anemia;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent colds, inflammatory processes of the respiratory system;
- fever, chills.
Changes in the clinical picture and a combination of different manifestations are possible. With stress, poor nutrition, or taking medications, symptoms may worsen.
Diagnosis of high concentrations of reactive lymphocytes
The main task of diagnosis is to determine the type of lymphocytosis, that is, the reason that provoked deviations in the analysis. The specialist must find out whether this happened under the influence of external factors, or whether there is severe pathology. However, at the initial stage, it is difficult to determine the cause of the increase in blood cells.
To get a more accurate picture, evaluate the level of other indicators:
- if an increase in the total level of white blood cells is detected, most likely the disorder is caused by the penetration of viruses or malignant pathologies of the hematopoietic system;
- if, simultaneously with lymphocytosis, a high concentration of platelets is detected, which is very rare, it means that several unfavorable processes are occurring in the body;
- with a reduced concentration of platelets and an increased level of white blood cells, autoimmune pathology is suspected;
- with a low number of neutrophils and a high concentration of lymphocytes, the cause may be drug poisoning or the influence of a virus;
- At the same time, white and red blood cells increase in those who smoke too much;
- An increase in lymphocytes and a decrease in monocytes may be a manifestation of malignant pathology.
To make a correct diagnosis, a blood test alone is not enough. In order to determine the causes of the violation, it is recommended to conduct additional tests, ultrasound diagnostics, and radiography.
Taking a blood test
In order for the result to be as reliable as possible, proper preparation is necessary before taking the test, since the level of blood cells is influenced by many external factors. The biomaterial for the study is venous blood, which is taken from the ulnar vein.
24 hours before the test, the patient must stop taking alcoholic beverages and medications. If medications cannot be stopped, you should notify a specialist about their use.
It is also necessary to avoid physical and emotional stress, which also affects the final result. Dinner on the eve of the study should be light; it is better not to eat fatty foods. In 30 min. You should not smoke before the test.
Reactive lymphocytes are elevated in a child who behaves restlessly during the test. Therefore, parents should ensure that the baby is not nervous or too physically active before the test. Also, the day before the test, you should not give your child medications unless it is vitally necessary.
If deviations are found in the analyses, repeated testing will be required to eliminate the error. If the data is confirmed, additional diagnostics will be required to determine the cause of the violation.
Carrying out analyzes
Lymphocytes are determined during a general (clinical) blood test in a child. This is a mandatory medical examination if any disease is suspected in children. In a teenager and a younger child, not only the content of white cells per unit volume is determined, but also the percentage of the total number of leukocytes.
Indications for blood sampling in children 6 years of age and older are:
- routine examination (upon the child’s admission to kindergarten);
- suspicion of infectious pathology (whooping cough, influenza, ARVI, mononucleosis, sore throat, pneumonia, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, chicken pox, etc.);
- suspicion of non-microbial diseases (neoplasms, leukemia, endocrine diseases);
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy;
- examination before admission to the hospital.
No specific preparation is required before clinical analysis. Children should refrain from eating food in the morning the day before sampling. You should also refrain from taking medications and avoid stress, because... this may affect lymphocyte levels.
Important information: How to quickly and effectively lower blood platelets at home using folk remedies (which products reduce them)
In children 4-5 years of age and older, blood is taken from a vein (venous) or from the ring finger (capillary). For right-handers, the fence is carried out from the left hand, and for left-handers - from the right. When collecting venous blood, a puncture is made in the elbow area. The ulnar vein is located there. First, a tourniquet is applied, then the skin is disinfected with alcohol and a needle is inserted, moving it through the vessel. The child's hand should not be suspended. It is placed on the table on a cushion.
For a child aged 3 years and older, blood can be taken from a finger of the non-working hand using a special thin glass tube with marks (capillary). To obtain the material, the finger tissue is pierced with a scarifier. The required amount of blood is placed in a test tube, signed (indicates the number, dates, last name and first name of the patient) and sent to the laboratory.
There are the following methods for counting lymphocytes: using a Goryaev camera and a microscope. The resulting blood is diluted (this makes cell counting easier). The liquid is placed in Goryaev’s chamber and leukocytes in 100 squares are counted using a microscope. For this purpose, automatic analyzers are widely used. Without special dyes, lymphocytes will not be visible. The obtained values are adjusted depending on the blood dilution. The LYMPH content is recorded per 1 liter of blood. A multiplier of 10 to the 9th power is used.
What treatment is prescribed?
Lymphocytosis is not a pathology, but evidence that a pathological process is occurring in the body. After a comprehensive examination and diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy, which depends on the cause of the disorder.
Adult patients
Different treatments are recommended for different diseases:
- for a viral infection, vitamin therapy, an increase in the amount of protein in the diet, and a sufficient amount of warm liquid are recommended to reduce signs of intoxication. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs; in severe cases, human immunoglobulins are recommended for the body to obtain ready-made antibodies. In case of bacterial infection, antibacterial agents can be used;
- for typhoid fever and tuberculosis, it is recommended to consult a specialist. The final diagnosis is established on the basis of data from a microbiological study, which confirms the presence of the pathogen;

- in case of allergic reactions, their cause is determined, the allergen is eliminated if possible, and antihistamines are prescribed;
- if an autoimmune process is suspected, consult a rheumatologist, who will provide treatment;
- In case of hyperthyroidism, a visit to an endocrinologist is necessary. The doctor will recommend taking a hormone test, after which he will prescribe therapy, taking into account the patient’s condition;
- If a lymphoid tumor is detected, first of all, it is necessary to determine the type of cells, after which a treatment strategy is chosen. Chemotherapy and blood transfusions are most often used, and sometimes a bone marrow transplant is recommended. The effectiveness of therapy depends on how advanced the process is and on the degree of malignancy of the tumor.
Pediatric patients
If deviations in the baby’s tests are not caused by a disease, then it is enough to follow the general requirements to normalize the indicators.
Parents should ensure that the child:
- ate a full and balanced diet;
- was not exposed to stress;
- walked in the fresh air every day;
- I didn’t overexert myself physically.
These tips can also be used for preventive purposes. Parents should be attentive to the baby’s well-being, regularly show him to the pediatrician, take all necessary tests and undergo research. It is important not to prescribe medications to your child yourself; for children this is much more dangerous due to their imperfect immune system.
Reactive lymphocytes are elevated in a child, most often due to an infectious process or allergy.
In such cases, the following groups of drugs may be recommended:
- antiviral (for influenza, ARVI, hepatitis);
- antibacterial (for whooping cough, tuberculosis, brucellosis);
- antihistamines (for allergies);
- anti-inflammatory (if there is severe tissue swelling);
- antipyretic (when the temperature rises).
Most often, an increased concentration of white blood cells does not pose a danger to children, and over time the levels will return to normal on their own. The disorder may be caused by a malignant process.
Therefore, to exclude severe pathology, it is better to consult a hematologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, chemotherapy and cytostatic agents will be required. Severe cases require bone marrow transplantation.
Every person should regularly monitor the concentration of not only lymphocytes, but also other blood parameters, so as not to miss the development of various diseases at an early stage. Parents should be especially attentive if this concerns a child.
However, if an increased level of reactive lymphocytes is detected, you should not panic. Violation can have various causes, many of which are not dangerous. But for your own peace of mind, it is better to undergo a full diagnosis and exclude serious pathologies that can cause changes in the tests.
What to do?
If, during a routine examination, an increase in lymphocytes in the child’s blood is detected, then it is necessary to contact a pediatrician. The doctor conducts a comprehensive examination of the body. It is important to determine the reason why a child’s lymphocytes are elevated. Based on the test results, treatment is prescribed.
Features of drug therapy:
- If lymphocytes are elevated due to infection, then antibacterial medications are prescribed. The most commonly prescribed are Suprax and Amoxicillin.
- Inflammation is eliminated by Ketoprofen, Naproxen, Phenacetin. For children, only non-steroidal drugs are prescribed.
- If a child has allergic reactions, he will be helped by antihistamines such as Tavegil and Suprastin.
- During treatment, it is necessary to follow a balanced diet, exclude junk food, and saturate the diet with vitamins and microelements.
If an increased level of lymphocytes in a child’s blood is caused by cancer, then treatment is prescribed individually. The doctor is guided by the type of pathology and the degree of its development. Self-medication is prohibited.
If lymphocytosis therapy is neglected, complications develop.