A priori, a person wants to know for sure whether he is sick or not, what is the likelihood of developing a particular disease? This is a particularly exciting topic for parents. Is there a high temperature as a response to the Mantoux test in a child? If it exists, then what explains it? How do the periods after administration of the drug differ in a one-year-old infant, a child of the 2nd year of life, and adolescents?
From the first days of life, the need to protect a child arises instinctively and continues to be relevant even when children become adults. Maximum efforts are made by both parents and medical professionals to strengthen the immune system.
In the first few days of life, an injection of a vaccine called BCG is given, which is an artificially modified drug against tuberculosis. A year later, the child’s immunity status and the development of a possible disease are checked. In this case, it is a method for diagnosing the presence of tuberculosis in the body. This testing is called the Mantoux test. What to do if the performed manipulation caused complications?
If the temperature rises after the Mantoux reaction in a child, then you need to consult a doctor. It is important to remember that in a health-threatening situation, hyperthermia alone does not exist. Along with it, various processes occur, which you need to know everything about in order to avoid undesirable consequences.
Normal reaction to a tuberculin test
In the first days after birth, the child is given BCG according to the approved schedule.
This is a vaccine that protects the body from infection with tuberculosis. The effect of the drug lasts for up to seven years. Therefore, revaccination is carried out periodically. Some children are not vaccinated due to the decisions of doctors or parents. Tuberculosis can occur hidden. Therefore, if the mother later wants to vaccinate her baby with BCG, she will have to do Mantoux.
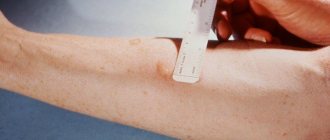
The reaction to a tuberculin test is the appearance of a red spot at the injection site. The diameter of the formation is used to judge the presence of immunity or pathology. For one-year-old infants, a questionable or positive reaction is considered normal.
The diameter of the papule in the injection area is within 1-1.5 cm. For children aged 2-6 years, its size should be up to 1.6 cm, 3-5 years - 0.6-1 cm. These standards are given for those vaccinated with BCG kids. Pediatricians correlate the diameter of the papule with the size of the post-vaccination scar.

Children 6-7 years of age have a questionable or negative reaction to the test. This is explained by the fact that the immunity formed during vaccination weakens.
At 7 years of age, routine revaccination is carried out. The papule after Mantoux at this age should not exceed 1-1.6 cm. If the test is repeated at 10-12 years, the diameter of the spot will be smaller - 0.5-0.6 cm.
As a rule, no changes in the child’s well-being are observed after a tuberculin test. Sensitive individuals may experience weakness and headache. Unpleasant symptoms usually go away after a few days. Doctors classify more serious changes in health status as adverse reactions.
The test has been successfully used for more than 70 years in all countries of the world. So far, this is the most accessible method of identifying the disease and the formation of protective forces against infection with the tuberculosis bacillus.
Could there be a fever?
Some parents complain that their child has a fever after Mantoux. There are many reasons for this reaction. A competent pediatrician will be able to determine what led to the fever.
The main reasons for the increase in temperature after Mantoux in a child:
- high sensitivity to tuberculin . In this case, the injection site becomes very swollen, red, and painful. Fluid may leak from the puncture. The temperature rises to critical levels. Mantoux is contraindicated for children with such an organism reaction;
- allergy _ Some people perceive tuberculin as a type of allergen. The immune system reacts strongly to try to get rid of the substance. The baby has the following local manifestations: severe swelling, rashes, itching, redness. General health also worsens. The temperature can rise from the level of low-grade fever to critical levels. In severe cases, respiratory function and heartbeat may be impaired;
- infection . It can occur as a result of infection of the body with microbes through the injection site due to physicians’ failure to comply with asepsis rules or when a child introduces an infection into a puncture with dirty hands. In this case, severe swelling and discharge of pus from the puncture will be observed. If a child has latent tuberculosis, the Mantoux test can become a provoking factor in the transition of the disease to an open form;
- the presence of inflammatory foci in the body . For example, sinusitis and chronic tonsillitis can worsen after a tuberculin test due to a decrease in the body's defenses;
- incubation period of pathology . Hyperthermia can occur with an infectious or viral disease or a cold. In this case, elevated temperature is not a complication of Mantoux, but a consequence of the development of pathology;
- use of low-quality material to perform the Mantoux test . If a drug was used to perform diagnostics, which was produced in violation of technology or stored incorrectly, then the baby may develop a fever, vomiting, dizziness, and loss of consciousness.
In addition to high fever, a child may experience the following accompanying symptoms:

- diarrhea;
- weakness;
- vomit;
- cough;
- headache;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- poor appetite;
- moodiness;
- insomnia;
- rhinitis.
To exclude the development of adverse reactions to Mantoux, it is necessary to thoroughly examine the child before performing the test.
What is the Mantoux test?
This manipulation is performed to solve the following problems:
- assessing the body’s response to the use of the tuberculosis pathogen antigen and determining the ability of the immune system to resist infection;
- detection of Koch bacilli infection;
- assessment of the effectiveness of tuberculosis treatment.
During the procedure, tuberculin is injected under the child's skin. This substance is an extract of Koch's bacillus. As a result of using the product, a small inflamed area forms on the skin. This is due to the reaction of specific blood cells - lymphocytes. Mycobacterial particles attract cells containing Koch's bacilli.
The more infected cells in the body, the more severe the inflammation. The Mantoux reaction in this case confirms the presence of infection with Koch bacilli. By measuring the inflamed area, it will be possible to determine the ability of the baby’s immune system to resist tuberculosis infection.
What to do if your child has a high fever?
If the thermometer shows up to 37.2 degrees, the baby does not have any symptoms of illness, then there is no need to worry. This is a normal reaction to the test, associated with the characteristics of the body.
If the temperature does not go away and rises rapidly, this means that it is caused by pathological reasons. In this case, you need to contact your pediatrician. Doctors do not recommend lowering the temperature to 38 degrees.
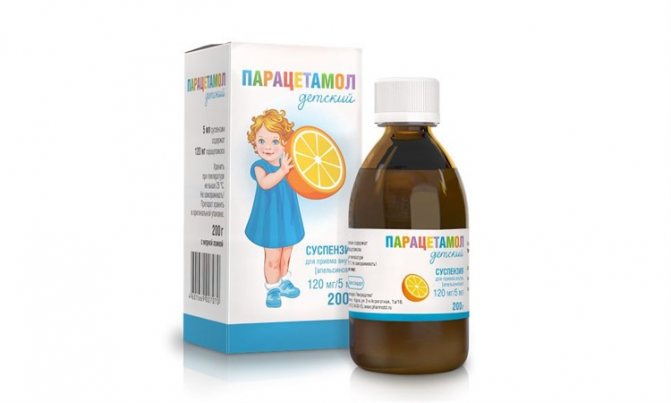

Paracetamol syrup for children
If your child has a fever, you can give him Ibuprofen or Paracetamol. If there are signs of allergy, it would be useful to introduce an antihistamine into therapy. If medications do not help, then you need to call an ambulance.
Parents should be especially alert to the following symptoms accompanying fever:
- muscle pain;
- convulsions;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- severe swelling of the limb in which the injection was given;
- frustration, loss of consciousness;
- incessant vomiting.
If such manifestations are present, it is necessary to call an emergency medical team.
How many days does it usually last?

The temperature after the Mantoux test can last for different times. It depends on what caused its increase.
If hyperthermia is a normal reaction of the body, then it can be observed for several days after the injection. The fever goes away on its own without taking medications. But it is easy to get rid of it in a day if you give your child antipyretic medications.
With the development of an infectious-inflammatory process, the temperature can remain at a high level until competent medical care is provided.
Children prone to hyperthermia should be given antipyretics on the eve of the tuberculin test and for 2-3 days after it. This will help prevent the thermometer from rising.
How long does hyperthermia last after Mantoux?
There is no immediate reaction to the injection of tuberculin; usually the first unpleasant symptoms appear six hours after the injection. As in many other cases, after pathogenic agents enter the body, the temperature can last up to three days, after which it gradually stabilizes. Condition - it should not exceed 37.5 °C. Then it is not necessary to take antipyretic drugs.
If the mark on the thermometer is more than 37.5 °C, medication support is needed. The high temperature should be brought down and you should consult a doctor as soon as possible for consultation.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
You can read a lot of stories in the media about how the Mantoux test led to severe side effects. Experts have different opinions on this matter.
Some argue that an increase in temperature in a child after a tuberculin test is a normal reaction of the body. Others note that this is a sign of sensitivity to the drug.
Most doctors advocate Mantoux, since it is an accessible and effective diagnostic method, and hyperthermia is a rare reaction to tuberculin.
To prevent an increase in temperature after the Mantoux test in a baby, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of specialists. Usually, before administering tuberculin, doctors inform parents about all possible reactions to the drug and give advice on preventing their development.
The famous doctor Komarovsky recommends:
- examine the child before performing a tuberculin test. Before the procedure, you need to measure your body temperature. The sample is allowed to be taken if the thermometer shows no more than 36.8 degrees;
- if the baby is unwell, the procedure is rescheduled;
- If an infectious or viral pathology is suspected, the test should be performed at another time. The test is allowed to be done a week after complete recovery;
- if the child is teething, it is better to postpone the test;
- in case of exacerbation of a chronic disease, Mantoux should be postponed until the pathology enters the remission stage;
- The injection site should not be wetted, touched or scratched for three days. Therefore, you need to closely monitor the baby all this time. Infants can bandage their hand with a bandage, but in such a way that the material does not squeeze the limb;
- if the baby has an individual intolerance to tuberculin, then Mantoux should be abandoned.
Many parents know that children who are prone to allergies should be given an antihistamine (for example, Fenistil, Zyrtec, Claritin, Zodak, Suprastin, Cetrin) the day before and for several days after vaccination. But Dr. Komarovsky notes that the Mantoux test is not a vaccination and it is not worth giving medicine to prevent an intolerance reaction before assessing the result.
After all, the essence of the test is to analyze the immune response to tuberculin. And an antihistamine may interfere with obtaining a reliable result. Such medications are used only when the child has a severe allergic reaction to tuberculin, which is accompanied by swelling, shortness of breath, and fever.
How to avoid fever
To prevent negative consequences, it is advisable to follow the advice of specialists. Most importantly, a full medical examination must be carried out to determine any contraindications. Secondly, on the day of vaccination the baby must be absolutely healthy. In addition, you need to measure the temperature in a timely manner and, at the slightest increase, wait until it is completely restored and the child recovers.
In order to obtain reliable results after Mantoux vaccination, all measures for caring for the injection site must be observed.
To ensure accurate results, you should adhere to the following tips:
- Do not neglect the rules of hygiene - hands, like the clothes you wear, should always be clean, the injection site should not be scratched, and contact with pets should be limited for several days.
- Make sure that the baby does not become hypothermic or overheated.
- Avoid the use of brilliant green, iodine, ointments and plaster - any antiseptics.
- Avoid eating allergenic foods: berries, exotic fruits, citrus fruits and all kinds of sweets.
- If the above requirements are violated, the subsequent vaccination of mantu must be postponed for at least a year.