Prerequisites for the appearance
The main factor contributing to the appearance of pain is the structure of the child’s ear canal. The Eustachian tube, which connects the ear to the nasopharynx in children, is shorter and wider than in adults. Through it, bacteria easily penetrate from the inflamed nasopharynx or from the outside into the inner ear cavity.
The absence of fever during ear pain should not reassure parents. Otitis externa in young children often occurs without visible complications. Pain can also become a symptom of serious diseases: lymphadenitis, rupture of the eardrum. Therefore, ear pain cannot be ignored.
How to get rid of water in the ear
Doctors do not recommend jumping to get water out of the ear, just as they do not recommend tormenting the ear canal with your finger. Doctors consider it most correct and effective to clean the ears with cotton swabs. You can also remove water by swallowing movements, lying down on the desired side, or making a compress.
Water can appear in the middle ear due to mistakes in diving or water getting into the nose. Nasal decongestants will help cope with the problem. If you cannot cope with the disease on your own, you must immediately consult an otolaryngologist, since the fluid inside thickens and rotting begins.
How to recognize
It is not always possible for a child to report pain independently. Actively speaking children themselves talk about their illness. Kids can show where it hurts. Diagnosing ear pain in infants and newborns is particularly difficult.
There are a number of signs by which you can determine whether a baby has ear pain: • Pressure on the ear protrusion (tragus). When lightly pressed, the baby begins to cry out sharply; • With prolonged pain, the child tries to scratch his ear on the pillow, showing the place where it hurts; • If you warm the inflamed area with your palm, the baby will calm down. Symptoms characteristic of any age: • Hearing impairment; • Decreased appetite; • General poor health; • Restless sleep.
How to relieve ear pain in a child
The first question that will worry mom and dad is what to do if the baby is in pain?
Therapy at home
- Careful examination of the auricle. If there is something in your ear, you can try to remove it, but you need to be as careful as possible so as not to push the object even deeper. In general, such manipulations are usually carried out by a doctor.
- If a child’s ear hurts, what should you do when it’s impossible to see a doctor right away for some reason? Measure t, measure pressure. If the indicators are off-scale, give pharmaceuticals so that his condition returns to normal.
- If a child’s ear hurts at night and hyperthermia is noted, then the situation needs to be corrected. Usually, parents give medicine that will help eliminate pain and inflammation. Such pharmacological agents include Ibuprofen, Efferalgan, Nimesil, etc.
- The solution may be nasal drops, the property of which is to constrict blood vessels. Even if your child does not have a runny nose, it is necessary to put drops into the nose, since thanks to such actions you can reduce the pressure and the pain should subside. Popular drugs are Xymelin, Otrivin, Nazol.
- If your child has severe ear pain, it will be important to instill drops that will eliminate the unpleasant symptoms. Medications Otipax, Otirelax - they contain a substance called Lidocaine in their ingredient composition, which has an analgesic effect. Novocaine solution is also quite effective.
If there is no fever, make a lotion with the addition of various oils and medicinal herbs, but it is important for parents to remember that such procedures require regularity - the little person’s condition will not get better just once.
Warming up and compresses
To relieve acute pain, you can apply warm compresses without fever. And in order not to cause harm, parents need to understand the reason why their child has severe ear pain. It is important to know for sure that there is no pus in the ear, as well as pathogenic microorganisms - if there are none, then warming up will be very useful.
You can do the following procedures for otitis media, since they have a complex effect:
- improve blood circulation in tissues;
- promote drug absorption;
- remove toxins;
- contribute to the activation of regeneration processes;
- reduce pain;
- Help the baby relax and calm down.
Important! It is advisable to do compresses only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Types of compresses:
- Wet. In this case, it is very important to choose the right impregnation - a warming liquid. It is worth remembering that if a child is not yet 4 years old, then he cannot be given lotions with ethanol. A good option is warming oil compositions.
- Dry lotions and compresses for ear pain in a child are effective because they reduce pain. It is not necessary to do this if there is pronounced inflammation: the tissues are swollen, there is redness. The most popular option is hot salt, which needs to be transferred to a clean cloth and applied to the auricle, avoiding the area where the lymph nodes are located. It is noteworthy that the procedure allows you to get rid of purulent masses that accumulate in the ear canal during otitis media.
- Alcohol compress. Before doing such warming, you should definitely consult with your family doctor. If the pediatrician has approved this method, the parent must remember that ethanol must be diluted - 1 part alcohol and two parts boiled, clean water.
Causes
Inflammation can be triggered by hypothermia, inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx, water getting into the ear while swimming, insect penetration, or stuck small objects. Teething and the appearance of wax plugs also contribute to pain.
Infants are susceptible to ear inflammation due to incorrect posture during feeding. If a mother feeds her baby while lying down, mucus from the baby's nose flows into the ear, causing inflammation.
Depending on the cause, the symptoms of the inflammatory process may vary. 1. Pain due to teething. In this case, the ear and nose hurt. 2. Water getting inside the ear cavity. Stagnation of water provokes inflammation, which causes discomfort and contributes to the onset of otitis media. 3. Sulfur plug. In this case, the pain is bursting, there is a significant decrease in hearing, and tinnitus. Pain in and around the ear. 4. Allergies. A runny nose provokes swelling of the nasopharynx and ear canal. Pain may occur as a consequence of allergic rhinitis. 5. Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes). The baby has an increase in nodes behind the ears and on the neck. With lymphadenitis, the area around the sink, the throat when swallowing, and the neck when turning the head hurt. 6. Traumatic injury. The cause may be an ear bruise or loud, sharp sounds. The child complains of congestion, possible bleeding, and pain inside the ear. 7. Foreign bodies: small objects, toys, insects. Once inside, they provoke swelling of the skin, cause pain, itching, and hearing loss. 8. Increased intracranial or blood pressure. There are unpleasant sensations in the back of the head and temples. The baby has a headache and hearing loss.
If you suspect ear pain, your child should be seen by a doctor. He will give specific recommendations applicable to different cases.
Pain behind the ear
Pain behind the ear is a symptom that may indicate the development of an infectious or inflammatory process. Often the manifestation of this symptom is accompanied by an enlarged lymph node behind the ear and the formation of a painful lump. Treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor, after conducting the necessary laboratory and instrumental examination. Self-medication is unacceptable, as this can lead to the development of serious complications, including irreversible pathological processes.
Etiology
Pain behind the ears can be caused by the following etiological factors:
In infectious and inflammatory diseases, pain is accompanied by inflamed lymph nodes behind the ears.
Symptoms
In this case, there is no general clinical picture, since the nature of the symptoms will depend on the underlying factor.
An extremely rare cause of pain behind the ears is mumps, characterized by the following clinical picture:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- formation of swelling behind the earlobe;
- when pressed, the lump behind the ear hurts;
- pain may intensify when swallowing, talking and other movements that involve the jaw;
- unpleasant sensations radiate to the neck.
Signs of mumps
The inflammatory process is observed both on one side and on the other, but begins only from one ear.
The cause of pain behind the ear may be an inflammatory or infectious disease of the hearing organ itself. In this case, the symptoms may be as follows:
The cause of pain behind the ear on the right or left is sometimes lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), which is characterized by the following clinical picture:
If such a clinical picture occurs, you should immediately seek medical help, since inflammation of the lymph nodes can be a sign of a serious pathological process.
The manifestation of such a symptom in dental inflammatory diseases is no exception. In such cases, there is a throbbing pain in the ear, which will radiate to the occipital region.
If discomfort behind the ear is accompanied by pain in the head, then the symptoms may be signs of osteochondrosis. The patient may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- crunch in the neck;
- stiffness of movements;
- headache;
- Pain behind the ear appears periodically and is stabbing and sharp in nature.
In addition, the manifestation of such a symptom can also be observed during acute respiratory infections, which will be characterized by the following symptoms:
Symptoms of respiratory infections
Regardless of what exact symptoms occur, if you have pain behind the ears, you should consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Diagnostics
If a child or adult has such a symptom, you should consult an otolaryngologist. You may also need to consult an infectious disease specialist and a surgeon.
The diagnostic program will include the following laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
- blood sampling for general and biochemical studies;
- general urine analysis;
- radiography;
- MRI;
- immunogram;
- biopsy;
- ELISA.
The exact diagnostic program is determined individually, depending on the current clinical picture and the collected medical history during the initial examination of the patient.
Treatment
The treatment program will depend on the identified underlying disease. Drug treatment may include taking the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- interferon and its synthetic analogues;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- glucocorticoids;
- painkillers;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
Taking any medications on your own or heating the affected area is strictly prohibited.
In most cases, treatment is conservative; radical methods of eliminating symptoms are used extremely rarely. The basis of treatment is eliminating the underlying cause.
As for prevention, there are no targeted recommendations. If such a symptom occurs, you should seek medical help and not self-medicate.
Share this article:
Mastoiditis is an inflammatory lesion that covers the area of the temporal bone and is of infectious origin. Most often, this disease occurs as a complication of otitis media. The most common symptoms are pain in the mastoid process of the ear, swelling and decreased hearing function.
…
Neuralgia is a pathological condition that progresses due to damage to certain parts of the peripheral nerves. This disease is characterized by the occurrence of acute and intense pain along the entire length of the nerve fiber, as well as in the zone of its innervation. Neuralgia can begin to develop in people from different age categories, but representatives of the fair sex are more susceptible to it after 40 years.
…
Facial nerve paresis is a disease of the nervous system characterized by impaired functioning of the facial muscles. As a rule, a unilateral lesion is observed, but total paresis is not excluded. The pathogenesis of the disease is based on a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses due to trauma to the trigeminal nerve. The main symptom indicating the progression of facial nerve paresis is facial asymmetry or the complete absence of motor activity of muscle structures on the side of the lesion.
…
simptomer.ru
What to do
The main misconception of most parents when it comes to ear pain is trying to make a diagnosis on their own, to determine where it hurts. An examination of the ear is necessary, but it must be done as carefully as possible.
Pay attention to the surface of the auricle. There should be no swelling or redness. Gently press on the protrusion near your ear. If this movement does not cause discomfort, most likely the pain is associated with other organs: teeth, inflammation of the nasopharynx. Examine the external auditory canal. Dark or green discharge indicates internal inflammation. When a foreign object or accumulation of sulfur is discovered, many people try to remove it themselves. You can't do this. The slightest wrong movement will damage the eardrum and cause serious health problems.
Give your child a pain reliever. Before visiting the clinic, doctors recommend drips of vasoconstrictors into the nose. This should be done by tilting the baby's head to the side. This way the drops will penetrate into the ear cavity and relieve swelling of the ear canal, significantly alleviating the condition.
Calm yourself and calm your baby. Try to distract him, don't get irritated or show your fear. Instill confidence that everything will pass soon.
What causes the pain
Inflammation in the ear has various factors of occurrence. If inflammation is accompanied by pain, you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the root cause and make an accurate diagnosis. Do not ignore this problem, as any diseases in the ear can lead to serious consequences.
Remember that self-medication does not always benefit the patient.
Thus, you can cause significant harm to your health, resulting in dire consequences.
Ear pain can be caused by various reasons:
- Diseases of the ear canal.
- Inflammation of the middle ear.
- Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Inflammation in the inner ear.
- Dysfunction of the auditory ossicles.
- Traumatization of the external ear.
- Lack of hygiene.
- Dental health problems.
However, the two most common causes of ear pain are wax buildup and water ingress.
In the first case, you need to consult a doctor to eliminate the problem. At home, if there is a small accumulation of sulfur, the problem can be eliminated with the help of specialized drops "Remo-Vax" or "Uhonorm". These products effectively, but gently and delicately remove sulfur in a short amount of time.
If water gets in, it is necessary to take immediate action, as stagnant liquid can cause serious damage to the structure of the ear. In addition, water can cause hearing loss, and in some cases lead to complete deafness .
Symptoms of ear pain
If water gets into your ear after taking water treatments or swimming in the pool, you should eliminate the liquid as soon as possible. Otherwise, the water can cause serious pain.
Once water enters the outer ear, it quickly spreads to the middle ear, causing dysfunction of the malleus, ridge, and incus.
Removing water from the outer ear
is not difficult .
Simply swipe a cotton swab over all areas. Vata will quickly absorb excess liquid. However, if liquid gets into the middle area of the ear, urgent measures must be taken, since water is a dangerous provocateur. ignore this situation , as the situation is very serious.
In order to protect yourself when swimming, you need to wear specialized earplugs and a bathing cap on top. They will exclude contact with water.
When water enters the ear canal, it flows out on its own. To do this, just tilt your head to the right and left. However, there are cases when water passes through the ear canal further into the middle and inner ear. In this position, the liquid cannot flow out on its own and begins to stagnate.
In this case, the water provokes swelling of the sulfur and the formation of plugs. This leads to serious inflammatory processes, including otitis media.
It is known that earwax can fill seventy percent of the ear canal.
Pay attention to the following symptoms . Typically, the following signs are the first signal to contact a specialist:
- feeling of water transfusion in the hearing organ;
- a feeling of fullness in one or two ears at once;
- loss of sharpness of sounds;
- incorrect perception of sounds;
- slight dizziness.
In some cases, nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite and sleep disturbances are noted.
If you experience these symptoms after each use of water procedures, consult a doctor.
Pay attention to pain when fluid gets into your ear. If pain is associated with a violation of the integrity of the tympanic area, you will experience the following symptoms:
- significant hearing loss;
- severe dizziness;
- ear congestion;
- acute pain in the middle ear;
- discharge from the ears.
In this case, the patient should not delay going to the doctor, as it is necessary to urgently determine the degree of perforation and begin urgent treatment.
Causes of inflammation
In general, pain in the ear after swimming is a common occurrence. This can be caused by several reasons:
- Excessive water ingress.
- Along with the fluid, an infection in the water can get into the ears.
- Violation of the integrity of the eardrum. Perforation of the membrane can be caused by diving.
- Inflammatory processes can be caused by hypothermia after swimming.
Usually, after swimming in the pool, the child’s ear hurts. This is due to the anatomical structure of the body .
Since the Eustachian tube and the entire hearing organ in babies are more susceptible to bacteria and infections, pain causes extremely serious complications. It is important to know that pain may not occur immediately. Therefore, carefully examine your child's ears after each bath. Remember that long-term presence of fluid in a child’s ears causes inflammation, and ear pain increases.
Often with such symptoms there is noise and crackling in the ears. In this case, immediately contact an ENT doctor.
After the examination, the specialist makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes a course of treatment. It includes various physiotherapy and heat treatments.
In addition, the patient is prescribed ointments, creams and anti-inflammatory medications.
Bad advice
According to doctors, most advice on how to get rid of ear pain in a baby is wrong.
1. Warm compress. This cannot always be done. If prescribed independently, it will do more harm than good. Heating during purulent otitis media will cause the infection to spread, increasing pain and inflammation. You cannot warm a child’s ear without a doctor’s recommendation.
2. Instillation of anesthetic drops. The advice is not always effective. If a child has cerumen, the drops will cause it to swell, which will only worsen the condition.
3. Tapping the ear canal with your palm to dislodge the plug or trapped water. The method is partially effective. Tapping should be done carefully. Water may leak out, but this method will not affect the position of the plug in any way.
4. Laying geranium leaves. The plant is often recommended as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent. Children should not plant geranium. A common cause of ear pain in children is allergic rhinitis. Geranium essential oils will increase swelling, worsening the condition.
Folk remedies or drug treatment will only help with a correct diagnosis. Various procedures can only be performed after consultation with a doctor. Therefore, it is better not to experiment, but to contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Symptoms
The baby may clap his ears with his palms and act out mischievously - this is a clear sign that he has severe pain in the ear. These symptoms cannot be ignored - ear pain is very poorly tolerated, so it is possible that your little mischief maker will become lethargic, very capricious and will be mischievous with or without cause.
You need to take your temperature - it often rises if the cause is viral infection. With otitis media, hyperthermia will also be present, up to 39 degrees.
Parents can press on a small cartilage - visible to the naked eye, located opposite the auricle, round in shape. If the baby cries and removes your hands, this means that he is uncomfortable and in pain.
Symptoms:
- frequent whims;
- tries to lie on the side where the ear hurts;
- in the area of the lymph nodes (under the ear) swelling, the skin is irritated and red;
- there are discharges.
The last symptom is alarming, especially if the child has an earache and the temperature has risen, and there is also vomiting.
Ear pain in infants
Any doctor will say that the sooner a problem is detected and therapy is started, the easier it will be to get rid of it in the future without causing complications.
The following symptoms are alarming:
- the child is restless, constantly capricious, hysterical;
- hyperthermia;
- refuses breastfeeding;
- presence of discharge - if the child has otitis media.
Doctors warn mothers that if a child’s ears begin to hurt and the temperature is more than 38 degrees, they should not hesitate, it is advisable to quickly seek special help.
In children under 5 years of age
It is easier for parents of children under 5 years of age to recognize the symptoms. You need to find out why the child is experiencing pain, and there are many of them:
- injury;
- mosquito bites, flies, etc.;
- water ingress is a very common problem;
- wax plugs form, which also causes pain in the ear area.
It is quite difficult to discover the cause on your own. The best option is to go to the doctor. Based on the specifics of the disease, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Every mother must remember that if a child suddenly develops an earache, you can help yourself, but you also need to go to the doctor.

Prevention measures
Feed your baby by lifting his head, or after feeding, hold his head up a little. This will help protect the baby from mucus flowing into the short ear canal and subsequent inflammation. Don't give babies small objects to play with that they might stick in their ears. Children over 3 years old can only be given small objects under parental supervision.
Maintain good hygiene standards. You need to clean your child's ears carefully, without using sudden movements. You should not try to insert the cotton swab deep into it. This may cause injury. It is recommended to bathe babies carefully, avoiding water getting into the ear. When bathing older children, it is necessary to protect their ears using a special cap.
Treat a runny nose promptly. Prolonged or chronic inflammation of the nasopharynx allows microbes to enter the child’s ear, causing inflammation. Avoid drafts and hypothermia. Don't bundle up your baby, dress him according to the weather. Strengthening the immune system, proper varied nutrition, and frequent walks will help prevent ear pain in children.
The absence of fever during ear pain should not be a reassuring factor for parents. At the first suspicion that your child has ear pain, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Do not attempt to do the procedure yourself or prescribe treatment. Following competent medical recommendations will help your baby quickly get rid of pain and discomfort.
Dr. Komarovsky about what to do when a child has an earache?
Dr. Komarovsky also gives useful recommendations on what to do if a child has an earache:
“The best remedy for otitis media is special vasoconstrictor drops for children, which quickly reduce swelling. You need to drip them into your nose. If a child has a damaged eardrum, then drops in the ears can only cause harm. Therefore, it is common practice throughout the world not to use drops in the ear until the child has been examined by a doctor and confirmed that the eardrum is not damaged. If a child has a high temperature, you need to give him antipyretics. But Dr. Komarovsky categorically does not recommend warming your ears. If pus has accumulated in the ear, heating it will only make it worse. If fluid leaks from your child's ear, the eardrum is perforated (damaged). In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor.”
We also want to note that when treating ear pain, antibiotics are used as a last resort. And then under the strict supervision of doctors, after a detailed examination and tests.
Why does my ear hurt after swimming?
During water procedures, especially diving, scuba diving or diving, the pressure in the ear canal changes - this helps fill it with liquid under pressure. If water is not completely removed from the ears and stagnates, irritation of the mucous membranes occurs, and they become vulnerable to pathogens, which give rise to an inflammatory process in the outer ear - otitis. Also, water can get through the nasal cavities and mouth into the middle ear, in these cases otitis media develops. The onset of inflammatory processes is very violent and is always accompanied by pain.
Water getting into the ear
The cause of pain can also be injury to the eardrum, which can be caused by sharply changing pressure in the ear canal during diving or scuba diving.
At risk are people with a large amount of wax in the ears, which, under the influence of water, swells and clogs the ear canal, provoking the appearance of inflammatory processes.
Signs of water getting into your ears
The first symptoms indicating water getting into the ear:
- congestion in the ear;
- distortion of sound perception;
- itching;
- noise in ears;
- tingling;
- swelling and redness of the ear canal.
If unpleasant signs are detected, a number of actions must be taken to prevent the occurrence of inflammatory processes. They consist in eliminating the irritating factor and the possible consequences caused by it, these are:
- instillation of alcohol diluted with water 1:3 into the ear, no more than 2-3 drops 3 times a day;
- douching of the ear canal with a soft solution of furatsilin. To do this, you need to crush 2 tablets of the drug and dilute it in 200 ml of water, the temperature of which is at least 40 ° C, and rinse the ear with a syringe. After this, a dry cotton wool is inserted into the ear;
- lubricating the ear canal with salicylic-zinc paste at night.
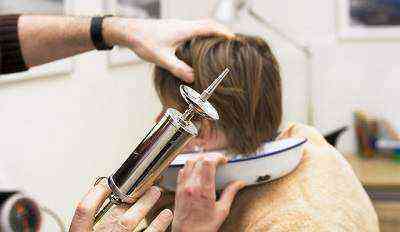
Ear douching
If pain does appear, you need to contact an otolaryngologist who will make an accurate diagnosis. If there is no quick access to a doctor or the pain is excruciating at night, you can relieve it yourself with the help of medications or folk remedies.