What is a mucus plug?
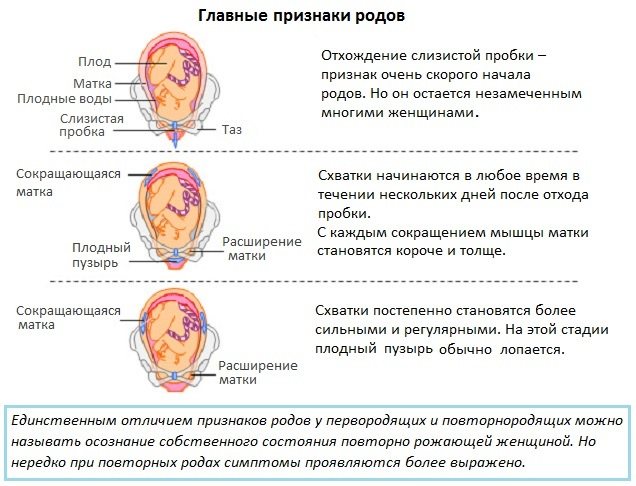
During pregnancy, a mucus plug forms. It is a lump of mucous structure and viscous consistency, which at first glance resembles the white of a raw egg. A mucus plug is formed and located in the cervical canal, which connects the vagina to the sterile uterine cavity.
When the embryo implants and firmly attaches to the uterine cavity, the cervix undergoes softening and swelling of its walls under the effect of hormones. Cervical cells actively begin to produce cervical mucus. Over time, it becomes an increasingly dense clot that is capable of completely closing the entrance to the uterine cavity from the side of the female vagina.
The cork has a protective function : a woman’s body in this position is most susceptible to various infectious diseases, and it does not allow microorganisms to make their way inside the uterus. This can even happen when a pregnant woman bathes in a home bath.
Also, the mucus contains ready-made antibodies, which actively enter the fight in the event of penetration of a pathogenic pathogen . The composition of the mucus plug is renewed throughout pregnancy, because the cells continue to actively produce their cervical secretions. Thanks to this, the cork performs all its necessary functions.
Closer to the natural end of pregnancy, the concentration of the hormone estrogen increases, which helps soften this mucus, so the plug becomes more watery and comes out on its own. This occurs on average several days before labor occurs.
A plug may be released as a result of:
- frequent examinations by a gynecologist;
- excessive contraction of the vaginal muscles during sexual intercourse in a pregnant woman;
- physical activity and other factors.
Rejection of the mucus plug does not mean a complete loss of protective properties; the amniotic sac and the amniotic fluid that fills it also have this function.
But experts still recommend refraining from being in bodies of water or taking a bath: infections during this period are easier to penetrate into the uterus.
Functions of cervical mucus
The secretion produced by the cells of the cervical canal has different colors, volumes and consistency depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. At the beginning, very little fluid is produced, and the woman may even have none at all.
The environment in the vagina during this period is acidic, it is destructive for sperm. During and before ovulation, the production of cervical secretion is maximally active, the fluid becomes more transparent, and its volume increases. This creates a favorable environment for sperm to penetrate into the egg.
At this time, pregnancy is most likely to occur. As you approach the end of the cycle, the mucus changes its consistency to a more viscous, thick one. This occurs due to a decrease in the amount of estrogen. The pH again drops to the acidic side, creating an obstacle to the passage of sperm.
The main function is considered to be protective - a certain barrier is created that prevents the uterus from getting pathogenic agents from the vagina into it.
Also, on certain days of the cycle, it promotes the penetration of sperm to fertilize the egg.
The alkaline nature of mucus protects sperm from the vaginal environment, which under physiological conditions is acidic. There is a kind of screening out of sperm that are not mobile enough, and therefore do not have sufficient viability for fertilization.
Mucus plug color
There are no universal parameters. The literature states that the physiological mucus plug is characterized by a transparent color, but practicing gynecologists claim that color changes can range from beige to slightly brown. No pregnancy pathologies are observed in such cases.
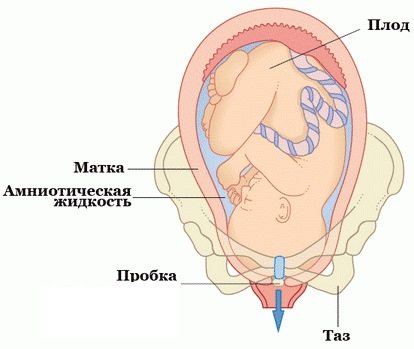
Women often note blood streaks in the removed plug. There is no need to worry and immediately contact a gynecologist in this situation: their appearance is associated with injury to small vessels in the cervical area when the plug is separated. This may also indicate the upcoming shortening and maturation of the cervix for childbirth.
Volume
In most cases, the volume of the released plug is small, approximately 50 ml. The mucus is secreted in a dense lump; it does not spread and is not absorbed into the fabric, so women usually see it immediately on their underwear. The size of the released plug is about 2 cm.
Consistency
The structure of the mucous lump is viscous and thick. Its separation is quite difficult to miss: a jelly-like lump will be visible on the underwear, which differs from the woman’s usual discharge. This will differ from the amniotic fluid that flows immediately before birth.
Mucus plug: what is it?
Expectant mothers are right in their assumptions. Indeed, there are a number of signs that the long-awaited moment of childbirth has already arrived. One of these first signals of the onset of labor is not pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, but the release of a lump of mucus from the vagina. This is nothing more than a mucus plug that closes the entrance to the uterus throughout pregnancy. The mucus plug has a complex composition:
- mucus (secretion product of the vaginal glands);
- collagen fibers (form the framework of the cork);
- leukocytes (a protective factor that protects against infection).
The mucus plug is a mechanical and biological barrier that separates the uterus with the baby and the external environment. The components of the plug are renewed, but it itself remains in place, tightly closing the cervical canal, and comes off only before childbirth.
Signs of removal of the birth plug
Removing a plug from the cervical canal of a pregnant woman is a harbinger of an imminent birth. Often the mucous lump comes off when a woman wakes up, during morning water procedures, or when visiting the toilet. The body is in a relaxed state in the morning.
The mucus plug can come away in one moment, and the woman understands that something seems to have fallen out of the vagina. After this, a lump of mucus is found on the underwear, which differs in size and consistency from daily discharge. When the plug is removed, a woman may experience discomfort, a sensation of stretching in the lumbar area or uterus.


In some situations, it turns out that cervical mucus is released gradually over the course of several days. When collecting anamnesis, it turns out that discharge from the genitals has become more abundant and more frequent. The pregnant woman herself may not attach any importance to this, thinking that the plug has not yet come out.
To convince yourself that the plug has fallen out, you can conduct a simple test: if a woman coughs and no new discharge appears, then there is no need to rush to the maternity hospital.
How does it turn out for first-time mothers?
In a certain percentage of women who are about to give birth for the first time, the plug comes off at a later date ; this can happen directly at one of the stages of labor. Their cervical opening is narrow, and its walls are denser in comparison with women who are expecting the birth of a child not for the first time.
In primigravidas, the plug more often comes off with blood streaks , but women often do not notice the presence of negative symptoms in the form of pain and heaviness. It can separate either gradually in parts or as a single clot.
How does it work out for multiparous women?
In women with a history of one or more pregnancies, the walls of the cervical canal have a looser structure. Their mucus plug is most often released at once, while admixtures or streaks of blood are rarely observed.
How long after the plug comes out do contractions begin?
The time interval between the release of mucus from the cervical canal and the onset of contractions is usually very short and is 1-2 hours or less. Most women experience almost no cramping or abdominal pain at the beginning of contractions. The first contractions do not interfere with walking and preparing to go to the hospital. However, you must be prepared for the fact that the pain can quickly intensify.
It is advisable to ensure that the woman is delivered to the maternity hospital as quickly as possible. Since the amniotic fluid may break at any time, it is necessary to protect clothing during transportation with a sanitary pad or a clean cotton napkin or gauze folded several times.
Differences between plug and amniotic fluid
Some women, especially nulliparous women, confuse processes such as the rupture of amniotic fluid and the release of a mucous clot.
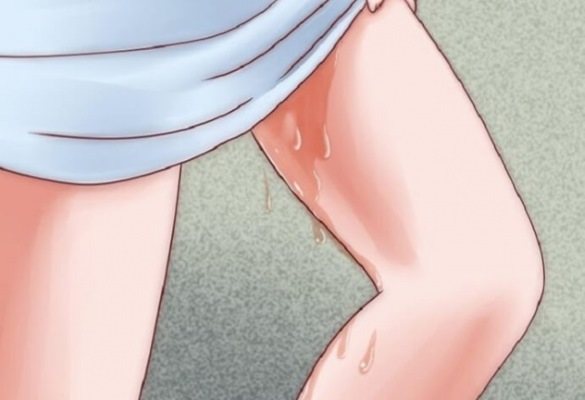
The release of the mucus plug and the discharge of amniotic fluid should not be confused. If the plug comes off, this does not mean that labor is imminent, while the outpouring of water indicates the beginning of labor.
You need to be able to differentiate these conditions, because their further tactics are completely different:
| Evaluation parameter | Cork | Amniotic fluid |
| When does it leave | A few days before labor begins | At the beginning of labor |
| Consistency | Viscous | Watery |
| Color | Slimy beige, possibly streaked with blood or a brownish tint | Normally the waters are clear |
| Periodicity | At once or portionwise over several days in small clots | There is a symptom of a cough impulse, constant leakage |
| Further actions | Observation | Head to the maternity hospital |
What is a “mucus plug”?
There are glandular cells on the cervix that produce secretions. An increased amount of this secretion is released during ovulation, which is noticed by almost every woman. If pregnancy does not occur, the accumulated mucus comes out along with menstrual flow. When the egg has been fertilized, mucus accumulates in the cervix and thickens, causing the lumen to become tightly blocked. Nature has provided this so that no infection can enter the uterus, where the unborn child is formed. Thus, the mucus plug in the cervix performs an important protective function. The composition of the formed plug is constantly updated, since the secretion of cervical cells does not stop. Thus, the cork always remains fresh and fully performs its functions.
The mucus plug fills about 5 cm of the cervix. It clogs the lumen very tightly, leaving no void between the walls. The mucus contains ready-made antibodies that will immediately begin to fight the infection if this happens.
The amount of mucus is quite small, approximately two tablespoons. The consistency is similar to jelly or jellyfish. The color of the cork may vary slightly. In some cases, small amounts of blood may be present.
Not all women notice the removal of the plug. For each pregnant woman, the harbingers of labor may be individual - someone’s stomach begins to pull, someone’s water breaks, someone notices the passage of a mucus plug. Apart from seeing the jelly-like mass itself, the passage of the mucus plug cannot be noticed. That is, if she passed away in the toilet and the woman did not feel her, then the pregnant woman may not know that labor will soon begin. In some cases, mucus from the cervix comes out in parts, rather than in one piece.
How long will it take for labor to begin after the plug comes out?
The beginning of the process of removing the plug from the cervical canal is a signal of major hormonal changes in the body of a pregnant woman. The number of estrogens is steadily increasing, and the amount of the pregnancy hormone progesterone is decreasing. These changes are necessary to prepare the birth canal and uterus for the upcoming birth.
The plug has come out, but it is unknown when labor will begin, since everything happens very individually for each woman.
Therefore, for some, labor develops a couple of hours after the recorded passage of the plug, and some pregnant women can arrive at the maternity hospital three weeks after the separation of a dense clot.
What to do after a lump of mucus has passed
Quite often, having discovered a traffic jam, a woman panics and does not know how to proceed. Should I run to the maternity hospital or stay at home, should I tell the doctor if I can move? These and many other questions worry the expectant mother.
The removal of a protective plug from a woman’s vagina is a harbinger of the imminent beginning of the birth process.
The incident must be reported to the doctor immediately. Based on the accompanying symptoms, he will be able to guess when to expect labor and how to proceed.
What you can do:
- control the further state of the body;
- take a shower;
- analyze the regularity and time interval between uterine contractions, if they begin;
- to pack;
- check the required documents.
What not to do:
- to take a bath;
- insert medications or foreign bodies into the vagina;
- lift heavy objects;
- engage in excessive physical activity.
What to do after the plug comes out
The mucus plug can be removed from the cervix both before the immediate birth and in advance of it. For this reason, you need to pay attention to additional symptoms. If, after the mucous lump has passed, there are no unpleasant symptoms in the form of increasing pain in the lower back, as well as in the lower abdomen, then you should relax.
It is impossible to miss the onset of labor, even if it begins at night. If the above symptoms begin to bother you, then most likely this indicates the onset of labor. You need to start preparing for the maternity hospital, having first called a doctor to your home.
The plug has come out (a woman needs to know when labor will begin in order to react in time), and, therefore, a number of rules must be followed:
- Completely limit water procedures in any bodies of water, do not take a bath even at home. You should limit yourself to just washing yourself in the shower, and the stream flow should not be directed directly at the entrance to the perineal area.
- Refrain from sexual contact. Male secretions may contain microorganisms and other substances that can adversely affect the unborn baby.
- Be more careful about the cleanliness of underwear and change it more often to prevent the penetration of the provocateur of the infectious process into the uterus.
- Wash yourself at least twice a day, observing the first rule.

This is necessary so that no infection gets through the softened cervix, which is most vulnerable in the last stages of bearing a child. Contractions begin regardless of the desire of the pregnant woman, so the woman must be ready to go to the maternity hospital at any time.
The plug has come off (not a single obstetrician will tell you when labor will begin) - which means the woman needs to collect all the documents and other things for the maternity hospital, since this is often a harbinger of an imminent birth.
Is leaking amniotic fluid dangerous?
In the “classic” (which is more common) version of the birth of a child, amniotic fluid drains with the first attempt. Sometimes they start to leak earlier, go away, but there are no contractions. One midwife, whose speech I listened to at the obstetric conference “Midwifery today” in Russia, shared her experience, saying that if after the water breaks, contractions do not begin in the first 12 hours, then they will begin in three days.
The strangest myth, but actively spreading in society, is that the child will then suffocate. But a child is not a fish; he does not breathe through gills in the water. It “breathes” (receives oxygen) through the umbilical cord, which is attached to the placenta, and the placenta is attached to the uterus. Without water, the umbilical cord dries out, and this is dangerous, but the whole point is that the baby cannot stay there without water (provided it is a full-term pregnancy in the cephalic presentation), since he closes the exit with his head and the water continues to be renewed every few hours.
This is dangerous only because the amniotic sac is not intact and there is a risk of infection getting to the child, so it is necessary to avoid vaginal examinations and going to public places as much as possible.
There is another danger in early rupture of water, such as prolapse of the umbilical cord (so that it does not dry out without water), but there are also observations that the probability of prolapse of the umbilical cord in a full-term singleton pregnancy in the cephalic presentation of the child without polyhydramnios and artificial opening of the bladder is zero.
And this is logical. Before birth, the baby already sinks lower into the pelvic floor, the umbilical cord remains behind him, and if the “front” waters leak or break (those that flow out before the baby plugs the outlet with his head), then it is safe.
Advertising
Are there cases when the plug does not come out?
The plug exists in the body of every pregnant woman, so its removal from the cervical canal also necessarily occurs in everyone. In its absence, pregnancy would be almost impossible due to the fact that the infection would constantly penetrate upward into the uterine cavity.
Some women simply do not notice the moment of its departure. Most often, the mucus plug is released in the morning: when going to the toilet, and also happens when taking a shower. There are situations when a mucous lump comes out immediately before the baby is born. This is not a pathological condition.
Appearance and purpose of the mucus plug

The release of the mucus plug indicates the body's readiness for childbirth.
The mucus plug is a kind of barrier between the outside world and the fetus developing in the womb. It is formed at the beginning of pregnancy from mucus, intensively secreted by the body under the influence of hormones. Gradually its thickening is observed. By the end of pregnancy, the plug is a dense jelly-like substance.
After 38 weeks, the expectant mother’s body stops producing progesterone. As a result, the cervix shortens and softens, and the mucous plug gradually moves away. This process takes from several hours to two weeks. Sometimes the release of the mucus plug occurs immediately before childbirth.
Each case is a variant of the norm. The separation of the plug does not mean that the woman will give birth at that moment. This is a signal indicating the body's readiness for delivery.
When to see a doctor
There are several situations in which the help of a specialist will be necessary to preserve the health of both the woman and the child:
- If there is a suspicion that a mucous clot has separated from the cervical canal, and there is still more than a month before the expected due date. This situation is dangerous because the uterus will remain in an unprotected state for a long time, and there is a high risk of inflammatory processes occurring during pregnancy. This may also indicate the onset of premature labor.
- Suspicious coloration of the mucus plug. For example, a scarlet color may indicate that bleeding has begun due to placental abruption. Here you may need urgent help from specialists, so the best solution would be to go to the maternity hospital. Also, a mucous lump can get this color due to an examination in a chair by a gynecologist. The cervix is quite tender, so any careless movement can cause microtrauma to the mucous membrane with damage to small capillaries, as a result of which the mucus plug acquires a scarlet tint due to the soaking of this lump with blood.

It is important for the expectant mother to maintain a positive attitude throughout her pregnancy and listen to her body.
If symptoms appear after the plug comes out that are embarrassing or cause discomfort, it is better to consult a gynecologist.
Only he is able to assess the condition of the pregnant woman, more accurately say when labor will begin, and also assume all possible risks to the health of the unborn child.
Article design: Svetlana Ovsyanikova
Recommendations for pregnant women after the plug has come out
As soon as the protective lump leaves, you must follow the basic recommendations and rules in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy:
- Ensure the correct psycho-emotional mood. We must try to get rid of the fear that every pregnant woman has. Childbirth is a normal physiological process as intended by nature. It is worth replacing all negative attitudes with positive ones, studying positive examples of easy childbirth.
- Provide adequate nutrition. This is important not only at the finish line before the birth of a child, but also throughout the entire period of intrauterine development. The health status of mother and child largely depends on the completeness of the diet.
- Engage in acceptable physical exercises and gymnastics for pregnant women. After the plug comes out, you should pay attention to breathing forms of training.
The separation and release of the lump is not a reason for bed rest. Therefore, there is no need to completely limit yourself from your usual way of life.
If the general condition of the body allows, you should not make drastic restrictions on your activities.
It is necessary to always have documents and a telephone number with you for communication, so that the long-awaited process of childbirth does not take you by surprise.