June 20, 2018
Averyanova Sveta
Red spots on the body, itching, fever are clear signs of a herpes infection. The name of the disease is translated from English as “chicken skin.” The pockmarks actually resemble the pimples on the body of birds after plucking.
How chickenpox begins, what complications it causes and how to deal with them - these are the main questions that caring parents ask themselves. Let's talk about this in detail and in order.
How do they get infected?
There are several options for transmitting the disease:
- Airborne path . The source of infection is sneezing, mucus released during coughing, and normal breathing into the external environment. The child becomes dangerous to others on the last day of the incubation period and remains so for another five days after the rash disappears.
- Contact method . A rare type of infection. The virus can be transmitted through fluid from chickenpox blisters. It gets on the mucous membrane of a healthy person when the papule bursts and remains on clothes and bedding.
- Vertical path. The question of whether a baby can get chickenpox interests many mothers.
The answer is yes. The Varicella virus is transmitted to the fetus during the antenatal period.Infection of a child before 12 weeks of pregnancy threatens miscarriage and pathologies of the baby’s intrauterine development.
Infection in a later period threatens congenital chickenpox. If the mother becomes infected five days before giving birth, the infant is in danger. He will receive from the woman in labor the virus and antibodies that the mother’s body has managed to produce. For this reason, it is so important for pregnant women not to become infected with chickenpox.
What could be the causes of infection?
Chickenpox in newborns and infants can occur for several reasons:
Airborne infection
A child can become infected with chickenpox from a carrier of the virus. If the newborn is on artificial nutrition, or the mother is breastfeeding, but has not had chickenpox, the likelihood of infection through contact with a sick person is high.
Chickenpox is transmitted by airborne droplets. The virus can travel several meters from its host.
The incubation period for chickenpox lasts from 10 to 21 days (1). At this time, the person has no visible manifestations of the disease. Meanwhile, it is contagious a day before the first symptoms appear.
If the mother has previously had chickenpox and is breastfeeding, the newborn’s immunity is strong. But there are cases when infection cannot be avoided. This happens because the baby’s immunity is not able to cope with the infection.
Intrauterine infection
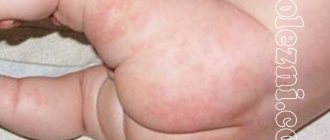
Occurs if the mother did not have chickenpox and became infected during pregnancy. The baby is at risk of becoming infected with intrauterine chickenpox (chickenpox) from the mother. Infection of the fetus does not always occur. Each case is considered individually.
The most dangerous period is up to 12 weeks. The placenta is not formed and does not protect the baby well. Infection with the virus can lead to fetal death or serious damage to internal organs.
Congenital chickenpox
What does it look like
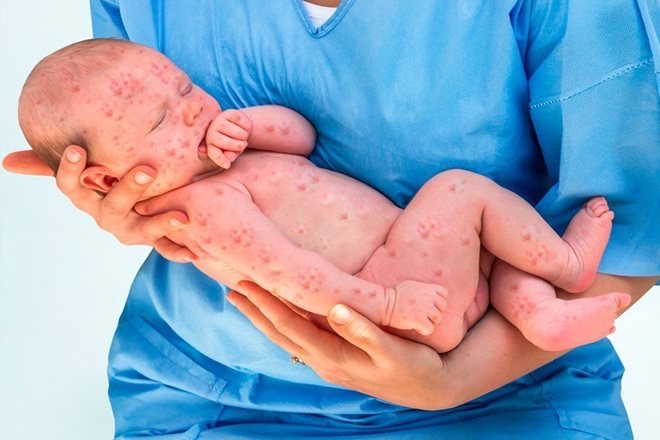
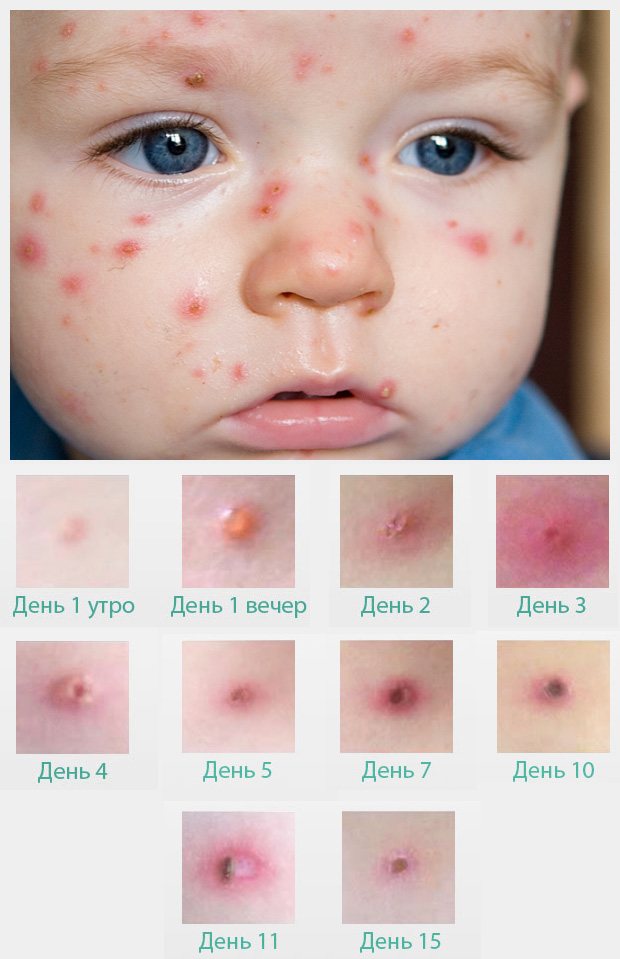
Chickenpox in young children appears externally as red spots all over the body. In the first days of the active development of the disease there are several of them. Then the rash spreads rapidly. In children, the face, back, arms, legs, stomach, even the head and back of the head are more often affected. It can look very scary.
Gradually, the red spots fill with liquid, its drops are visible on the surface of the blister. The affected areas become inflamed, swollen, and have a dark scarlet rim around them. The rash renews itself several times. Old wounds dry out and a gray crust forms on them.
You can find out in detail what chickenpox looks like by studying the photo below.
Differences between measles and chickenpox
- There is a difference in the length of the incubation period, which lasts 10-21 days for chickenpox and no more than 14 days for measles.
- In both cases, there is a high body temperature and a red (pink) rash. But with measles, an increase always precedes the rash (by 3 days or more), and with chickenpox, the temperature does not always appear 1-2 days before the first spots and accompanies the appearance of each new wave of rashes throughout the entire illness. Sometimes atypical chickenpox occurs in children without fever or with subfebrile levels (37.0-37.5°C).
- Measles spots appear primarily on the mucous membranes - throat, palate, tonsils, which causes inflammation and pain in the throat. Then, within 3 days, the spots spread literally throughout the body. In patients with chickenpox, the rash appears in waves, first in the form of red spots, which quickly develop into blisters with transparent contents, and then dry out and fall off.
In any case, whether a child has atypical chickenpox or the standard form, the first rule is to call a doctor at home, and if the condition is severe, call an ambulance. The doctor will expertly recognize the disease and prescribe treatment. The main thing is not to miss the deadline for contacting a specialist and not to provoke complications.
In general, chickenpox has a typical course, but in adults it is much more severe than in children. The same applies to people with immunodeficiencies at any age. Atypical chickenpox in children, which manifests itself in a mild form of the disease, occurs quite often, but with severe symptoms it occurs extremely rarely and requires immediate hospital treatment.
How long does it last
The chickenpox virus, entering a child’s body, begins to actively develop, settling in a new home. The course of the disease can be divided into several stages with their characteristic symptoms:
- Incubation period . Takes from 7 to 21 days. There are no external signs of infection. The virus is busy reproducing.
- Prodromal period . Lasts 24 hours. For children, it is often asymptomatic. In older children, the symptoms are similar to acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, and colds. This is an increase in temperature (up to 37.5°C), migraine, sleep disturbance, appetite disturbance, and occasionally soreness in the nasopharynx.
- Rash period . A small rash appears on the skin. The child's general somatic condition deteriorates sharply. Body temperature reaches 39°C and above.
- Recovery period . The rash disappears, the blisters heal, and the crust falls off. Antibodies to Varicella Zoster have formed and are able to cope with the disease.
It is important to be able to distinguish chickenpox from other skin diseases in a child.
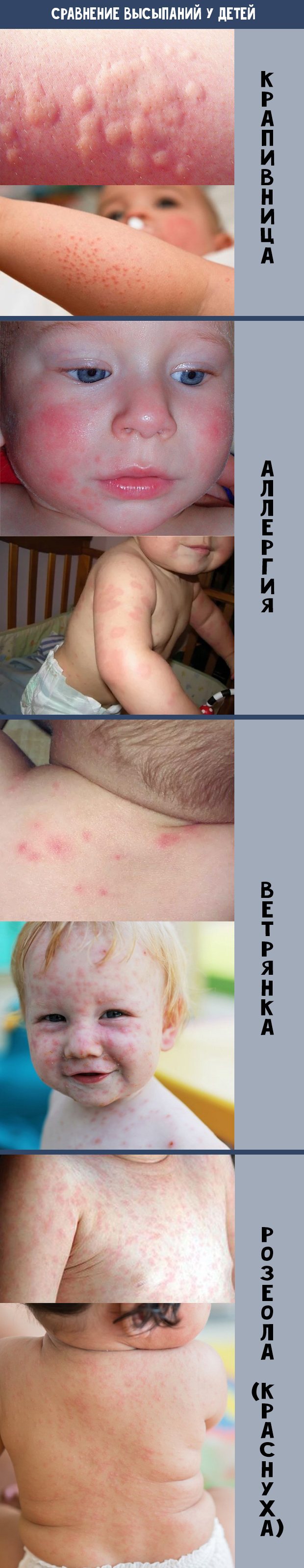
And you can more simply see the difference in diseases in this picture:

How does chickenpox manifest in children: how long after exposure?
The incubation period for chickenpox is 21 days; in children it can last from 11 to 12 days. During this period, the child has already become infected with chickenpox, but there is no rash yet, and there may be no symptoms.
In total, there are 4 periods of chickenpox:
- incubation period - the child has already become infected, but there are no symptoms;
- prodromal period - lasts 1 - 2 days before the onset of rashes;
- period of rashes;
- period of healing and formation of crusts.
Chickenpox is most often associated with a child covered in green paint.
Incubation period
Not dangerous to others. The virus is only gaining strength, actively multiplying, adapting inside the small organism, attaching itself to the nasopharyngeal mucosa. At the early stage, the child feels great, there are no clinical symptoms of infection.
The duration of the passive period is 7, 14, rarely 21 days. After this time, Varicella overcomes the baby’s immunity and enters the blood and mucous membranes.
After this, the active period of development of chickenpox begins: the first redness on the skin, weakness, and temperature rise.
How long does chickenpox last in children?
The temperature with chickenpox, on average, lasts from 2 to 5 days, in severe cases – up to 10 days. New rashes appear within 2 to 9 days. A child is considered contagious for another 5 days from the moment the last rash appears.
If chickenpox is detected in children in kindergarten, how many days will pass before infection, and how long the child will be sick - it is impossible to say for sure. To stop the spread of the disease, pediatricians recommend a 21-day quarantine for children who have been in contact with chickenpox patients.
Parents have many questions if their child has chickenpox: is it possible to bathe the child, is it possible to use shower gel or skin cream?
It all depends on the form of chickenpox in children. If the disease is severe, the child has a high fever or suppuration and ulcers on the skin, it is better to hold off on water procedures. If the child feels well and the rash dries up, hygiene procedures will only be beneficial. Bathing in warm water with a slightly diluted solution of potassium permanganate will help relieve itching and dry out the rash.
First signs and symptoms
The end of the latent period of chickenpox is easily recognized by the first clinical indicators of infection. This:
- Intoxication
The baby complains of a headache, weakness, and does not want to eat. Parents most often mistake this condition for a cold or ARVI.
- Temperature increase
Hyperthermia lasts a long time, from 3 to 7 days. The temperature ranges from 37-38°C, in severe cases - 39-40°C.
- Rash
Sometimes it is the only sign of the disease. Noticeable on the first or second day after the temperature rises. The wave of rashes repeats several times. Red spots and blisters are found on any part of the body, even the palms.
- Itching
The body itches constantly, the child cannot sleep or play peacefully. Scratching the blisters spreads the viral fluid to areas of the body that are not affected by the blisters. The wave of rashes repeats.
- General malaise, weakness, muscle aches, joint pain may occur
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Pay attention to the baby's head; if there is a lump behind the ear, then the lymph nodes are inflamed.
- Moodiness, tearfulness
- Nausea, rarely vomiting, if parents force the baby to eat
Important ! Babies feel constant itching.
They find it difficult to cope with the urge to scratch the affected areas. But tearing off the scab is fraught with the spread of the virus to healthy areas of the body and scars after the wound heals, which remain for life. It is very important to eliminate this particular symptom of the disease, to ensure that the child does not scratch himself while sleeping and awake.
Forms of the disease
The severity of the infectious disease depends on the child’s immunity and age. Chickenpox is rarely diagnosed in infants, but its course is often mild. There are several forms of infection in children:
- Lightweight
It occurs without hyperthermia or deterioration in the general somatic health of the baby. The rash is localized in small areas; there may be less than 10-15 blisters. The duration of the active period of the disease is reduced to two to three days.
A mild form of chickenpox occurs in newborns, in families with strong immunity and hereditary resistance to Varicella.
- Average
The temperature rises to 38°C. This is followed by the appearance of papules, tolerable itching, and general intoxication.
- Heavy
It is extremely difficult to tolerate in childhood. The picture of the condition looks like this: in the first days of the active period of development of the disease, the child’s body temperature rises sharply - up to 39-40 ° C, and an extensive rash appears. Headache, weakness, muscle spasms, fever, severe itching do not go away for more than five days. This leads to nervous breakdowns and insomnia.
Chickenpox is further divided into two subtypes: typical and atypical . The first is the most common form of the disease. It occurs with the symptoms familiar to us. The second is rare and is transmitted to children with weakened immune systems or congenital developmental pathologies.
Atypical chickenpox has its own varieties:
- Visceral
A fatal form of chickenpox. Blisters appear on the skin and internal organs. Most often diagnosed in infants. Photos of the symptoms of this type of infection can be found on the Internet.
- Gangrenous, hemorrhagic
Occurs in children with bleeding disorders.
- Bullous
A severe form of infection, accompanied by severe intoxication. Liquid vesicles are huge and difficult to treat.
More common in children with HIV.
- Vestigial
This is a hidden form of the disease. Rash, sores, and other symptoms practically do not appear. The child and parents may not notice the infection.
Six-month-old babies most often remain completely safe because they received antibodies from their mother in the womb, who had already had chickenpox before.
Features of the course of chickenpox in young children
Regardless of the patient’s age, chickenpox goes through several stages during its development. The main difference between adults and children in the nature of the manifestation of the disease is that the baby is less likely to experience complications. In addition, the intensity of general symptoms is influenced by the current state of immunity.
The duration of development of the disease varies within different limits. After infection, the pathogen does not provoke pronounced changes in the patient’s condition. During this period, the virus replicates inside the body. Sometimes in patients whose body is weakened by a concomitant disease, activity decreases during incubation of the pathogen.
10-21 days after infection, the first signs of chickenpox appear:
- general malaise;
- slight increase in body temperature (rare);
- lethargic state;
- red spots on the body.
Within 1-2 days, bubble formations with liquid contents form on the body. This stage is characterized by intense itching in the area where the rash is located. During this period, the following symptoms may bother you:
- high body temperature (up to 39-40 degrees);
- intense headaches;
- feverish condition;
- intestinal disorder.
During the period of bubble formation, lymph nodes in various parts of the body may enlarge, which indicates an active fight of the immune system against the virus.
Within 5-7 days, the rash opens up on its own, and small wounds appear in the affected area, which over time become covered with a dense crust. Bubbles on the body form in waves. Therefore, the child often simultaneously reveals new elements of the rash, open wounds and crusts on the skin.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis at the initial stage of the disease, an external examination is necessary. The doctor will distinguish chickenpox blisters from allergic rashes, insect bites, and parasitic diseases.
If in doubt, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests:
- serological blood test to determine the causative agent of infection;
- light microscopy of papules using silver nitrate.
When the first clinical symptoms of a herpes infection are detected, parents should urgently go to the hospital. You cannot make an appointment or visit the clinic in person with your child. Call your pediatrician at home by phone.
Do this urgently if:
- The baby has pathologies of the immune system, asthma, eczema.
- Hyperthermia, a temperature of 39°C, has been observed for more than a week.
- Ulcers appear, papules swell, and white liquid is released from them.
- The child has difficulty walking, breathing, constantly sleeps, is delirious, is afraid of light, and has difficulty swallowing. There is vomiting, diarrhea, cough.
Possible complications
Chickenpox in newborns is considered a mild childhood disease. Only a small percentage of babies have complications from chickenpox. These include:
- Pneumonia. Inflammatory foci are found throughout the lung tissue.
- Encephalitis. The central nervous system is affected, convulsions occur. This is due to the ability of the virus to infect nerve tissue. Diagnosed in the first or second week of infection.
- Purulent lesions of the epidermis. These are boils, abscesses. Occurs due to contact of chickenpox fluid inside the papules with other dangerous microorganisms.
- Myocarditis. Pain in the heart and dullness of tones are caused by inflammation of the heart muscle.
- Hepatitis
- Keratitis
- Otitis, gingivitis, laryngitis. Associated with suppression of the baby's immune system.
- Nephritis. The kidneys cannot cope with intoxication. There is a malfunction in the urinary system. Most often, it does not require treatment; everything improves on its own after toxins are removed.
- Scars, cicatrices. Remains after scratching, tearing off crusts on vesicles, and from wounds suppurating.
- Dangerous atypical forms of chickenpox that lead to death. This is hemorrhagic, visceral.
Treatment
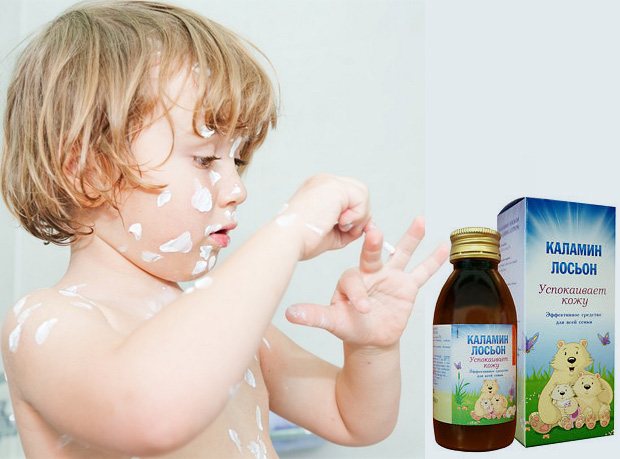

Before starting treatment for chickenpox in children, you need to decide what to treat and why.
1. The child is bothered by itching.
Dr. Komarovsky primarily speaks about the need to eliminate this particular symptom in his programs and books.
Open wounds become a source of infection and are susceptible to secondary infection.
Thus, it is imperative to protect the baby from complications with the help of ointments, brilliant green, antihistamines, and baths.
What antipruritic drugs are used:
- Zinc cream. Dry the skin, relieve itching. This is a suspension, or mash, “Tsindol”; "Kalamin" ("Kolomin"). They are colorless.
- Antiallergic drops. Taken orally. These are Zirtec, Zodak, Claritin, Loratadine, Suprastin.
- Local antihistamines. Transparent gel "Fenistil".
- "Chlorophyllipt". The composition of the herbal remedy includes eucalyptus.
Skin rashes spread, heal poorly due to scratching, ulcers can fester, and a scar forms.
2. The chickenpox vesicle needs to be dried to help wound healing..
- Zelenka, solution of potassium permanganate. Used as an antiseptic and drying agent. Only new pimples need to be cauterized.
- "PoxClean." Good foam made from natural plant ingredients, including aloe vera. Soothes the skin, relieves redness and inflammation around papules.
- "Fukortsin". Works the same as brilliant green.
- Salicylic alcohol. Safe wound healing agent.
- “Kontraktubeks”, “Dermatix”, “Medgel”, “Panthenol”, analogues of “Kalamine” (“Kolomina”). They eliminate scars remaining after peeling off the dried crust from papules and regenerate the tissue.
- "Baneotsin". Contains antibiotics, treats ulcers. It is important not to exceed the dosage - one gram of the substance per day.
- "Levomekol". Medicine for relieving suppuration on the skin.
- Spray, ointment "Neotanin". Treatment with the product relieves itching and heals ulcers.
Important ! In rare cases, children may develop papules in the mouth. To treat them, use Miramistin, gargling with chamomile, furatsilin.
If the blisters are painful, then anoint the baby’s gums and cheeks with Kalgel or Kamistad.
3. The virus continues to multiply on the mucous membrane and skin.
A severe form of chickenpox requires help in eliminating the causative agent of the disease, the Varicella virus. The doctor prescribes Acyclovir tablets.
4. High temperature.
You can reduce the temperature with medication that is appropriate for the child’s age. These are paracetamol, Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Ibuklin and others. These are syrups. If you are weak, stay in bed. For children from 1-12 months, use suppositories. The dosage is determined by the doctor based on the patient’s age.
Important ! Never give your baby aspirin. The popular drug has a lot of side effects. Prohibited for children under 12 years of age.
5. Decreased immunity.
Fighting the virus and producing antibodies takes a lot of energy from a small organism. He becomes weakened. After recovering from chickenpox, children quickly pick up new infections. This is due to immune deficiency. Help your child cope with this problem, use antiviral medications:
- "Viferon";
- "Arbidol";
- "Cycloferon";
- "Kipferon";
- "Kagocel";
- "Ergoferon";
- "Tsitovir;
- "Anaferon";
- oxolinic ointment.
They help fight the virus during the active reproduction of harmful microorganisms and increase the child’s immunity. Particularly weakened children require a two-month rehabilitation course with vitamins and immunomodulators. It is important to follow the instructions for use.
6. Moodiness, insomnia.
Excitability reaches extreme limits in children due to itching, the inability to sleep peacefully, play, or rest.
Use natural sedatives - chamomile teas, herbal preparations “Notta”, “Nervohel”.
You should not rush to the pharmacy for all the listed medications after the first signs of chickenpox appear. Perhaps your even three-month-old baby was lucky to have a mild illness. Only a doctor can determine the course of therapy.
Important ! Don't ask your doctor to prescribe antibiotics. They are not able to fight viruses. Serious antibacterial medications are used only for complications after chickenpox.

Features of the course of chickenpox in older children
People who have previously had chickenpox develop strong immunity to this disease. In this regard, if a person was not infected in childhood, the risk of infection remains as they grow older.
The course of chickenpox in older children is accompanied by more severe symptoms. This is due to the fact that during this period hormonal changes occur, due to which the body is not able to resist the activity of pathogenic agents. Therefore, adolescents who are not carriers of the virus are recommended to get vaccinated against chickenpox.
The disease in people over 10 years of age has the following features:
- Intense symptoms during the incubation period. A day before the formation of the first elements of the rash, the teenager’s body temperature rises, muscle pain and headaches occur, and signs of general intoxication of the body are observed. Convulsive twitching of the limbs and increased sensitivity of the eyes to light are also possible.
- Extensive (generalized) spread of the rash that appears on the mucous membranes. The formation of blisters is accompanied by unbearable itching.
- Each “wave,” characterized by the appearance of a new rash, causes a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.
- High risk of tissue suppuration in the affected area. After the crusts fall off, the possibility of the formation of pigment spots and scars remains.
- In rare cases, chickenpox is mild. The older the patient's age, the more acutely chickenpox is tolerated.
In older people, there is a high probability of the virus spreading throughout the body, which leads to the development of meningitis, arthritis, nephritis, bursitis and a number of other serious diseases.
Why and how much to smear with brilliant green
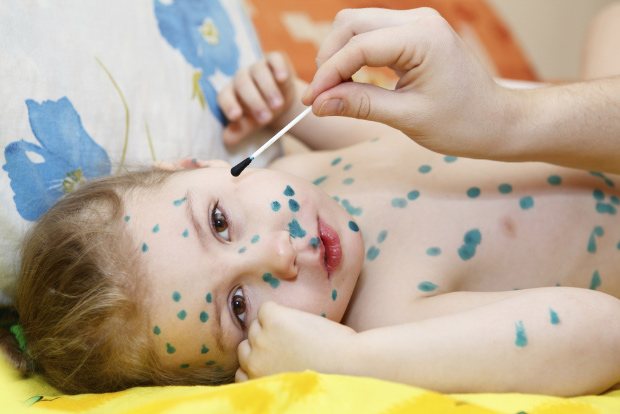
According to most doctors, brilliant green does not have the wonderful property of curing chickenpox that our grandparents talk about. It is a myth. The drug does not remove the rash or relieve itching. But using it is very useful for others, and not for the infected person himself. Let's explain why.
A child with chickenpox is contagious. And it remains so for another five days after the last wave of skin rashes. Then he can calmly communicate with peers, relatives, goes for a walk, and will no longer be in quarantine.
How can you understand which blisters appeared yesterday and which today, whether there are still a few new pimples in the morning or whether the contagious period has already ended? The answer is simple, with brilliant green.
Medically stained papules are considered old. If there is nothing else to treat on the body, then we wait five days and understand that the child has recovered. You can use any colored marker in the same way, although this is not necessary. It is much safer to use brilliant green.
What else can you smear besides brilliant green?
You can replace the green dye with analogues.
- Aqueous methylene blue solution. This is an alcohol liquid. It has antiseptic properties and turns chickenpox blisters dark.
- "Fukortsin". Raspberry antiseptic. The solution is thick, so it looks like an ointment.
- "Betadine." Yellow antifungal ointment. Use no more than twice a day.
- Boric acid. Use a 1% solution.
- "Chlorhexidine." It has no side effects.
Important ! When thinking about how to replace brilliant green, remember that iodine cannot be used to lubricate wounds.
How to alleviate a child's condition
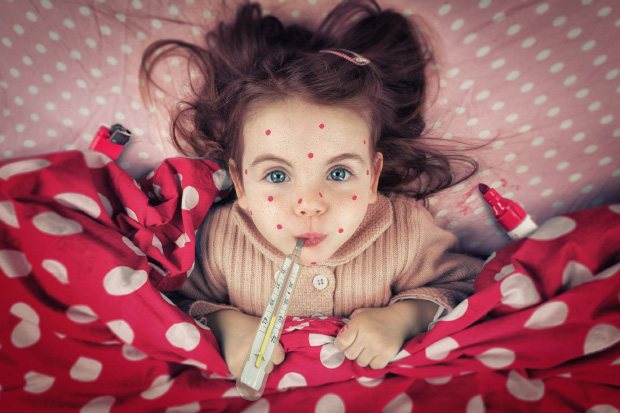

A child infected with chickenpox has a hard time. There is no opportunity to walk on the street or fully communicate with others. Constant itching and high temperature are annoying and cause a lot of whims and complaints to parents.
Proper organization of temporary isolation and creation of conditions for recovery help the little ones cope with the infection. Parents need to worry about the following:
- Provide your baby with fresh air . Ventilate the bedroom and playroom several times a day. Go for a walk in the entrance, on the balcony.
- Create favorable conditions for sleep . The baby needs cool, moist air. Close the batteries completely and turn on the humidifier. Do not wrap your child up - sweat causes itching on the skin.
- Change bedding and underwear every day. Traces of viral infection remain on the bed and sheets. Change pajamas and panties three to four times a day, especially if the baby sweats a lot and has a fever.
- Bathing is possible if there is no hyperthermia , the itching does not intensify after a shower. The baby should not wash with soap, just rinse him before and after sleep in the shower with warm water. Do not rub your wet body with a towel, just blot your skin. Maintain basic hygiene every day. The child will itch less.
- Don't force people to eat . Include salads, fruits, broths, and fish in your diet menu. Don't force feed. Nutrition will improve gradually on its own.
- Monitor the amount of liquid you drink . Water helps remove toxins and fight infection. Let the baby nurse more often during this period. When bottle-feeding children under one year old, let them drink from a bottle or spoon. Do not cancel night feedings of one-year-old babies; sucking calms the child. The consequence of a lack of fluid can be dehydration and severe weakening.
Causes and routes of infection of chickenpox in infants
A child can become infected with the Varicella Zoster virus in the following ways:
- in utero, if the mother was not sick before she became pregnant and became infected with the virus during pregnancy. It is most dangerous if a woman is diagnosed with chickenpox in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is during this period that the virus can provoke serious pathologies in the fetus;
- by airborne droplets (sneezing, coughing);
- if the child is touched by a person who has chickenpox or shingles. This infection often occurs when the baby is more than 6 months old. During this period, the protection of maternal antibodies weakens, and the child becomes susceptible to viruses;
- contact with personal items such as dishes or toys of an infected child.
Congenital chickenpox is dangerous for an infant who is not adapted to external pathogenic factors. This type of disease develops when the mother becomes infected 7 days before birth or 5 days after.
Folk remedies
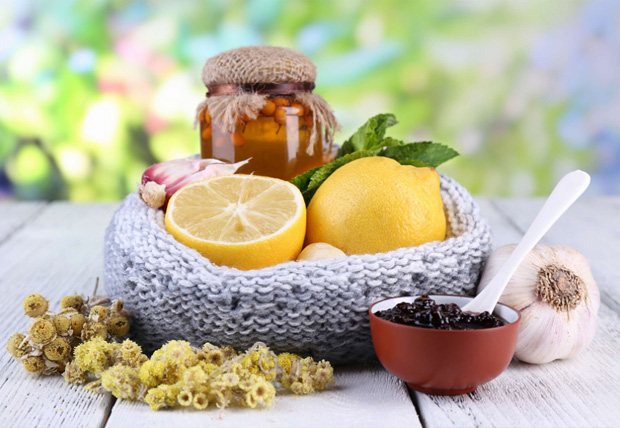

Pharmacy medications are an effective remedy for treating chickenpox. But traditional medicine offers its own means of combating the disease based on herbal components. Their use is no less effective.
- Soda solution for rinsing foci of infection on the skin and mucous membranes
Soda, 1 teaspoon, diluted in 1 glass of water. The tampon is wetted in the liquid. The product is applied to the skin pointwise.
- Essential oils
Helps cope with itching. Use menthol, eucalyptus, olive oil. Apply them to the sores daily.
- Lemon juice and honey
Mix and drink two to three times a day. Helps alleviate the condition and reduce the number of skin manifestations of the disease.
- Drinking from herbs
Prepare a collection of plants: chamomile, lemon balm, basil, calendula. Herbs need to be brewed, infused and drunk every day. The infusion reduces nervous excitability and itching.
- Garden parsley infusion
Collect green leaves (1 teaspoon) and pour boiling water (1 cup). Give the patient 150 milliliters before feeding. The product is even used to treat one-month-old babies.
- Camomile tea
Soothes the skin if used as a lotion, stabilizes the nervous system if drunk instead of tea, water. Add to the bath for infants and older children.
- Sage
Used to prepare a tincture for rinsing the mouth affected by chickenpox blisters. 20 grams of the substance are poured into 2 glasses of hot water, infused, and filtered. For children under one year old and eight-month-old infants, blot the oral mucosa with a swab; for older children, let it remain in the mouth for several minutes.
- Oak bark
Used as a remedy for diarrhea during intoxication. The tincture is taken once or twice a day, a teaspoon.
Important ! Some plants are not safe for children prone to allergies. Use these recipes only after consulting with your doctor and with full confidence that they are harmless.
Treatment of chickenpox with folk remedies
In case of chickenpox, it is recommended to use the following traditional medicine methods:
- Chamomile decoction - you need two tablespoons of dry herbs, pour half a liter of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Add to the bath when bathing a child. Use twice a day, allowed from birth. The course of treatment until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear;
- Calendula decoction - pour two tablespoons of calendula flowers with a glass of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. Wipe the area with the rash twice a day, the course of treatment is up to 10 days. Used when the child reaches 1 year of age;
- Celandine decoction - pour three tablespoons of celandine into a liter of boiling water and leave for 40 minutes. Strain the infusion and pour into bathing water. Bath the child for 15 minutes, then pat dry the body with a soft towel. It is recommended to use every other day until the unpleasant symptoms completely disappear. Allowed for use from the age of 6 months;
- Lotions with baking soda - mix a tablespoon of baking soda with a glass of warm water and stir thoroughly. Using a cotton pad, apply lotions to the areas of greatest accumulation of rashes. Used for children over 3 years of age. The course of treatment is up to 7 days.
When using traditional medicine methods, it is necessary to conduct a test for the child’s individual sensitivity to the drug.
When acute signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to use an integrated approach to treatment and use folk remedies with medications.