Important
Children most often suffer from atopic bronchial asthma. Its cause is an allergic reaction, leading to a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi. It usually occurs upon contact with inhaled allergens: house dust, animal hair and dander, plant pollen, mold spores. However, in young children, exposure to food allergens can also trigger the development of asthma.
Article on the topic Bronchial asthma: first symptoms and prevention of attacks Cases of infectious-allergic asthma, which occurs against the background of chronic respiratory tract infections (for example, chronic bronchitis), are recorded much less frequently in children than in adults.
The first signs of asthma in children
Asthma can be quite common in children, and it is very important for parents to know how to recognize the onset of the disease and what to do next. With bronchial asthma, the mucous membranes of the bronchi become inflamed.
As a rule, the cause is an allergy. Inflammation narrows the airway, making it difficult for the child to breathe. Usually asthma is paroxysmal.
When the attack ends, normal breathing is restored. The most important thing is to normalize the child’s breathing during an asthma attack.
At the slightest symptoms similar to signs of asthma, it is necessary to immediately take the child to see a specialist who will prescribe adequate treatment to prevent new attacks of the disease.
Note to mom
Diagnosing bronchial asthma in children is a more difficult task than identifying the disease in adults. This is due to the fact that with moderate manifestations of respiratory discomfort, a child, especially a small one, cannot always adequately describe what he feels.
In addition, in children under five years of age, the bronchi, compared to the bronchi of adults, have a narrower lumen and less developed muscular apparatus. Because of this, the leading manifestations of asthma in many children are not bronchospasm and suffocation (which is typical for adults and children over 5 years old), but swelling of the bronchial mucosa and abundant production of thick sputum. Not only parents, but sometimes doctors mistakenly consider this to be signs of ARVI or bronchitis. So, although the disease can develop from an early age, it is not diagnosed immediately.
However, an attentive parent may notice that the child has more than just a cold. This is indicated by a number of signs.
With asthma, a dry paroxysmal cough in a child occurs (or sharply intensifies) mainly at night or upon awakening.
The baby has wheezing.
Article on the topic
If you have allergies, see a psychologist! Asthma can occur due to stress and nerves. Your child regularly complains of difficulty breathing or you notice that it is difficult from time to time.
Cough or breathing problems occur when in contact with animals, house dust, during trips to nature during the flowering period of plants, during physical or strong emotional stress.
In these cases, you need to take your child to a pulmonologist and undergo an examination.
What happens in the child's body?
So, various substances in the air, one way or another, provoke an asthmatic attack. Each person may have their own active pathogens for an attack of the disease. Even cold air can often cause it.
When a healthy person inhales air, it enters the trachea or windpipe. Next, from the trachea, the air enters the bronchi, which in turn consist of bronchioles.
Accordingly, air from the bronchioles enters the alveoli of the lung, where gas exchange occurs. Healthy bronchi have no obstructions, and air passes through them freely.
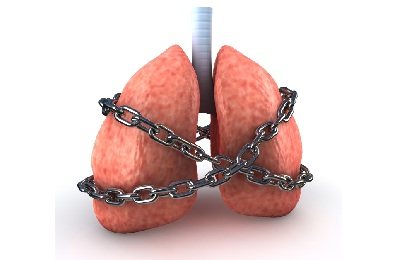
But in bronchial asthma, it is the bronchioles that are most affected. When bronchioles come into contact with allergenic substances, an active inflammatory process occurs in them with the release of a large amount of sputum.
At the same time, all the muscle tissue surrounding the bronchi and bronchioles begins to gradually shrink. Thus, the lumen of the airways decreases. This happens until breathing becomes impossible. The patient develops signs of asphyxia.
Features of asthma in newborns
Asthma in newborns, unfortunately, can appear quite often. Often, parents may not pay attention to the characteristic symptoms of the disease and attribute everything to a cold. So, the manifestations of the disease in newborns are:
- A very severe cough with virtually no phlegm produced. It is typical that the cough develops paroxysmally after sleep (and sometimes in the evening).

If the child is placed upright, the intensity of the coughing attack decreases slightly. If after this you put the child down again, the attack will intensify.- Shortly before the onset of an attack, the baby may be capricious.
- Characteristic development of shortness of breath.
- Intermittent breathing. Moreover, both inhaled and exhaled air leaves the body with noise, sometimes with a whistle.
Such signs may also appear in children under 2 years of age.
Asthma in preschool children
In children after reaching 2 years of age, the main signs of the disease are the same as in newborns, but they are easier to identify.
Children aged 4 to 7 years may have the following symptoms:
- There is a very strong pressure in the chest. It does not allow the child to take a normal breath.
- If a 4-7 year old child tries to breathe through his mouth, a very strong cough appears, which complicates the breathing process.

There may be atypical symptoms of the asthmatic process, such as skin rash and itching. Sometimes the child may be bothered by strong sputum production.- At 4-7 years of age, a severe cough may often appear. It literally torments the child, as it manifests itself over a long period of time. The asthmatic process may resemble bronchitis. It is very important that sputum is not produced during such a cough.
- It is characteristic that signs of obsessive cough can occur under the same conditions. Parents need to monitor exactly in what situations the cough appears and consult a doctor if there are suspicious signs.
Features of asthma in adolescent children
Unfortunately, teenagers do not always take this disease seriously and even consider it harmless. This behavior can provoke an exacerbation of bronchial asthma in children.

Teenagers also forget that they need to administer special medications (some doctors specifically select medications that can be administered into the body once, or maximum 2 times a day).
The signs of this disease are generally no different from those seen in adults. And first aid in such cases is no different from “adult” aid. Teenage maximalism, ignoring treatment, as well as bad habits can provoke the development of complications.
SOS
As a rule, an attack of bronchial asthma begins with a cough; a runny nose and hives may also appear. The child's breathing becomes uneven: inhalation is short, exhalation is difficult. It is accompanied by wheezing and whistling, he “catches air” with his mouth. The lips may become bluish and the skin may become pale.
For such symptoms, the child should be seated in a chair, tilted forward so that the elbows rest on the knees, and the window should be opened to provide air flow (but the room should not become cold). It is necessary to use, according to the instructions, an inhaler with a medicine that relieves bronchospasm (a drug from the group of beta-2-adrenergic agonists). You can also take hot baths for your hands and feet.
It is very important to remain calm and distract the child’s attention, for example, read him a book or give him a favorite toy. The main thing is not to let him get too scared, because fear and panic greatly aggravate the condition during an attack.
Article on the topic
Bronchial asthma: everyone is at risk of getting sick If the attack persists, call an ambulance.
How does bronchial asthma manifest?
You can ask the pediatrician who is observing the child about how bronchial asthma manifests itself in children, and adults can consult a therapist or pulmonologist.
Asthma rarely begins immediately with a severe attack of suffocation - mainly at the first stage of the development of the disease, symptoms may appear that are often observed with relatively harmless colds:
- breathing becomes wheezing
- difficulty breathing when exhaling
- a dry persistent cough appears
- there is a feeling of congestion in the chest, which is not accompanied by pain
Sometimes these symptoms may be accompanied by additional signs of asthma:
- increased sweating
- panic attacks (feelings of intense, unreasonable fear)
Such unpleasant sensations most often appear at night and early in the morning, which has an additional negative impact on the psyche.
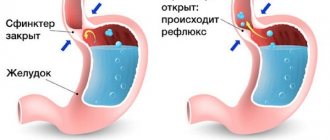
If you do not consult a doctor at this stage and do not begin appropriate treatment, attacks of suffocation may occur, which are caused by the fact that due to chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract (the bronchial mucosa), a lot of mucus accumulates in them. During an attack, with spasmodic muscle contraction, the lumen of the bronchi narrows, and mucus becomes an additional obstacle to the air entering the lungs.
The following factors contribute to the development of specific chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract:
- hereditary predisposition
- professional activities (regular contact with dust and gases)
- poor ecology (primarily air pollution)
- exposure to synthetic detergents contributes to the development of asthma in adults
- smoking
- the presence of food and pollen allergies, as well as urticaria, eczema, neurodermatitis.
With cough asthma, there may be no attacks of suffocation, but in this case there is a strong cough, usually at night. This form of asthma is more common in children.
In another type of this disease, physical exertion asthma, an attack can be triggered by physical exertion, and the deterioration of the condition often occurs not directly during it, but after the cessation of physical effort.
Worsening well-being and breathing after taking certain medications should also cause concern. In so-called drug-induced or “aspirin-induced” asthma, the attack is caused by drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications (paracetamol, diclofenac, indomethacin and others) are usually sold in pharmacies without a prescription, which increases the risk of their use by people with a predisposition to drug-induced asthma.
Risk factors
The nature of bronchial asthma is not fully understood. However, doctors identify several factors that increase the risk of getting sick.
Hereditary predisposition. It has been established that the risk of bronchial asthma is 2.6 times higher in children whose mothers suffer from this pathology, 2.5 times higher - if the father is ill, and 6.6 times higher - if both parents are sick.
Atopic dermatitis (diathesis) in early childhood, as well as other allergic diseases. Over time, they can “transform” into asthma.
Maternal smoking during pregnancy increases the child's risk of developing asthma by 25%. The prognosis also worsens significantly when adults smoke near the baby after birth. The severity of asthma directly depends on the number of cigarettes consumed daily. In such children, the first attacks of difficulty breathing often develop already at one month of age.
Unfavorable environmental conditions, for example, living near large enterprises or where the air is very dusty.
Frequent colds, if they cause complications in the bronchi. According to the results of one Russian study, 25% of children who were diagnosed with obstruction (narrowing of the lumen) of the bronchi caused by viruses subsequently developed bronchial asthma.
Is asthma in a child treatable?
The first question parents ask an allergist and pulmonologist is whether bronchial asthma can be treated, and whether it will manifest itself as the child grows older. Until recently, the answer was unequivocal - this diagnosis cannot be removed, and the patient’s quality of life depends on the frequency of recurring attacks.
Note! Today, patients with asthma are also registered with doctors, but doctors make the diagnosis “bronchial asthma” quite calmly. The disease is so well controlled if treated that the patient practically forgets about his illness.
As with any other allergy, a child may be predisposed to asthma, and whether it manifests itself or not depends on the efforts of adults. With the right approach to treatment and favorable factors, asthma may not manifest itself for many years, proceed non-aggressively, and not interfere with the child’s quality of life.
E. O. Komarovsky about bronchial asthma in children:
Memo to parents
To reduce the number of asthma attacks, it is necessary to minimize contact with allergens that trigger them. Ideally, you first need to find out what exactly these substances are. To do this, allergy skin tests are performed or blood is tested for antibodies to allergens. If these examinations are unavailable for some reason, follow general safety rules.
Article on the topic
Rules of life for asthmatics: how to learn to control the disease As often as possible, carry out wet cleaning in the house and in the room where the child sleeps, does homework, and plays.
Use home air purifiers and humidifiers.
Avoid feather and down pillows, feather beds, replace them with bedding with synthetic filling. You can also use special impermeable covers for mattresses, pillows and blankets.
Remove rugs and rugs from the floor.
It is not advisable to buy soft toys for your child.
Make sure there is no mold in the house and the air is not too humid. Cockroaches should not be allowed to live in the apartment - their waste products are an allergen, very often leading to the development of asthma or an increase in attacks.
Avoid going outdoors during the flowering period of allergenic plants. In severe cases, at this time it is recommended, if possible, to go to a region with a different climate, where the flowering period has not yet begun or has already passed.
Causes of bronchial asthma
- atopic bronchial asthma, associated with the entry of an allergen into the bronchi and the development of an allergic reaction;
- infection-dependent, non-allergic, developing against the background of an infectious lesion of the respiratory tract.
In atopic bronchial asthma, an attack of suffocation develops only in the presence of allergens - various substances that have the common property of causing allergic inflammation.
In children under one year old, food and drug allergens are most often the culprits of the disease: cow's milk protein, complementary foods containing preservatives, citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, strawberries, honey. After two years, food allergens are replaced by household and fungal allergens. The most common are microscopic house mites. They live in baseboards, carpets, blankets, and pillows and are the cause of year-round asthma. The tick is quite tender and dies at low and high temperatures. It’s not for nothing that mattresses used to be taken out into the cold. Household allergens also include: house dust; hair and dander of cats and dogs; fish food, mold spores growing indoors; cockroaches and rodents, in the latter the allergen is the smell of urine and the smell of themselves.
In children over 3-4 years of age, the most common cause of atopic bronchial asthma is an allergy to pollen and cross-reactions with food allergens.
In infection-dependent non-allergic bronchial asthma , severe respiratory infections, pneumonia, bronchitis suffered at an early age lead to damage to the bronchial mucosa, reduce its protective function, promote increased production of immunoactive substances, which leads to bronchial hyperreactivity, manifested by clinical signs of bronchial asthma.
Treatment
In addition to inhaled drugs that relieve asthma attacks, it is important to use drugs that improve the condition of the bronchi during periods of remission. They must be taken regularly, according to the schedule prescribed by the doctor.
A good solution is to conduct a course of allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT), especially if asthma attacks occur upon contact with an allergen that is difficult to eliminate. (For example, not everyone can leave during the flowering period of plants, just as not everyone can allow a child to go to school at this time.) The principle of such treatment is to “accustom” the body to allergens.
Article on the topic
Asthma is not caused by dust, fur or medications, but... by mold! The child is administered small amounts of substances to which he reacts with bronchospasm, gradually increasing the dose. Today this can be done either by injection or without injections. As a result, the immune system “gets used” to the allergen and stops reacting to it so sharply.
According to research, 75% of asthmatics who underwent ASIT did not develop clinical signs of the disease for 20 years; further observations of patients are ongoing.
Stages of treatment
The first step in treating asthma is removing the allergen that triggers the disease. This can be plant pollen, household dust, animal hair and much more.
Fact! There is a method of treating allergies that allows you not only to get rid of the symptoms, but also to cure it. This is allergen-specific immunotherapy - a method based on the introduction of a provoking allergen into the body in microdoses with subsequent increase. That is, the body is taught to respond correctly to a provoking factor.
Bronchodilators are used to treat asthma in children. This is a whole list of drugs that are prescribed by a doctor, and can be long- or short-acting:
- Theophylline (can be used for children from 3 years old);
- Salbutamol (from 2 years);
- Fenoterol (from 6 years old).
The main treatment is basic therapy aimed at reducing the inflammatory response in the form of spasm, inflammation and swelling. In this case, it is removed using special inhalation drugs:
- Flixotide (from 1 year);
- Bekotid (from 4 years old);
- Levalbuterol (from 4 years old).
Inhalations are not done over steam, but using a device - a nebulizer, which sprays the medicine at an ultrasonic frequency so that the smallest particles get into the deepest parts of the bronchi.
Safety regulations
An asthmatic child should always have a metered-dose aerosol or powder inhaler with a bronchodilator with him, because an attack can occur suddenly.
Be sure to notify the kindergarten teachers and the class teacher at school about the illness. Asthma attacks can occur due to stress and emotional distress, and educators should be aware of the risk.
If an asthmatic child catches the flu, ARVI, or suffers from sinusitis or bronchitis, under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Only a doctor can treat such a patient, because with asthma you need to be very careful when choosing medications, including antipyretics and antibiotics.
| Drugs | |
| Beta-2-adrenergic agonists | |
| Combined drugs for the treatment of bronchial asthma | |
| Inhaled glucocorticoids | |
| Other drugs for the treatment of bronchial asthma | |
Remember, self-medication is life-threatening; consult a doctor for advice on the use of any medications.
Buy the printed version of the directory at kiosks in your city or order it from the editorial office by phone or email [email protected] with the mark PM (indicate your full name, postal address and telephone number in the letter).