General information
This term, incomprehensible to a person without medical education, causes subconscious anxiety just by its sound. However, you should not always panic, since hypertonicity after birth is completely normal in a baby until it reaches four months, but if it remains with the baby after this age, then you need to sound the alarm and solve the problem.
What is muscle tone from a physiological point of view? It should be understood as involuntary muscle tension, with the help of which a person moves and changes his spatial position. Even if the muscle fibers are relaxed, residual tension still remains in them.
The central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal cord, is responsible for muscle tone. From this we can conclude that tone is a completely normal phenomenon of human physiology. And so that the baby can move normally and acquire motor skills, he simply needs it.
Is hypertonicity always pathological in an infant?
Hypertonicity is usually understood as increased muscle tone, manifested in the form of tightness and stiffness of the muscular system. Because of this, the toddler cannot master motor skills in a timely manner. In addition, it causes discomfort and anxiety in the child. In pediatrics, there is such a term as physiological hypertonicity of newborns.
For all nine months, the baby is in the uterus in the fetal position. His upper and lower limbs are flexed and held tightly to his body, his legs are slightly apart, his feet are crossed, and his chin is tucked into his chest. After birth, the toddler tries to maintain the same position; this is the condition that is called physiological hypertonicity of the newborn.
The tone of the flexor muscle structures is much higher than that of the extensor ones. When the toddler tries to spread or straighten the limb, muscle resistance is felt. For example, if you try to open a baby’s clenched fist, it will not remain open for long.
It should be noted that a newborn, a toddler, is considered to be the first month after birth. Physiological hypertonicity is observed in a child not only in the first month, but also over the next few months. On average, it lasts three months, but up to four months will not be considered a pathology. In newborns, this condition is most pronounced, but every month it becomes weaker, and then disappears altogether.

Why does hypertension appear?
The causes of hypertension can be safe for the baby’s health. However, this symptom may be associated with various neurological disorders. It cannot be ignored.
- Age physiology. There is such a thing as physiological hypertonicity in newborns. The classic position of the fetus in the womb is legs bent and tucked towards the stomach, slightly apart at the knees; arms bent at the elbows, chin pressed tightly to the body. After birth, the baby will remain in this “grouped” position for some time. It will take several months, or even more, for the muscles to gradually return to normal operation. Physiological hypertonicity can persist up to six months of age. There is another opinion on this matter: muscle tension can be observed in infants up to one year old. And this will be a variant of the norm.
- Individual characteristics. Muscle hypertonicity may be present in a child, but this does not affect health in any way. There is such a thing as individual muscle tone. In some children it is naturally higher, in others it is lower. For one baby, hypertonicity is a symptom of a neurological disorder, and for another it is a variant of the norm. Each individual case must be considered. Therefore, it is so important that if pathological hypertonicity is suspected, the baby undergoes a high-quality diagnostic examination. If in doubt, you can show the baby to several specialists.
- Birth injuries. The most common cause of hypertonicity is asphyxia of the child during difficult, prolonged labor, and intracranial hemorrhage.
- Disorders of intrauterine development, congenital diseases of the central nervous system. They may be related to the health and lifestyle of a pregnant woman. Nicotine and alcohol have a negative effect on the development of the fetal nervous system.
At what age can hypertension be detected in an infant?
Hypertonicity can be diagnosed not only in the first month after birth. It is extremely difficult to detect it in a newborn child and before he reaches three months. Only a pediatrician can do this.
If the baby's muscle tone is really high and does not correspond to his age norm, then he begins to have problems with the sucking reflex and latching onto the mother's breast. This happens because tense muscles are very difficult to control, especially for a small child. In addition, hypertonicity also affects the muscle layer of internal organs, for this reason children with such a deviation regurgitate the milk they drink. For this reason, stiffness of the child’s movements and adduction of the limbs cannot be considered the only symptomatology of hypertonicity in the baby.

Symptoms of muscle hypotonia in infants
Nervous tic of the eye in a child under one year old - causes, symptoms
Having noticed weak muscle tone in a newborn, the neurologist continues to examine the baby to determine the extent of the problem. Several manipulations are used to diagnose the disease.
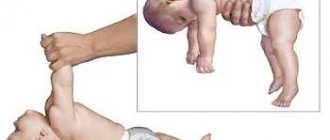
Step reflex
When a baby is placed on a table, with normal development, feeling support under him, he will take a few steps or try to sit down. With hypotonia in the legs of an infant, such reflexivity is absent. The baby cannot straighten his legs, sit down, or even take a step with them.
These actions are practiced on children under 2 months of age. Then the innate reflex fades, and the diagnosis is carried out in a different way.
Lying down
The doctor places the baby on his back on the changing table. She takes the baby by the arms and begins to lift him up, trying to bring the little one into a sitting position. With normal development, the newborn will strain his muscles, pull himself up on his arms, trying to help the adult.

Diagnostic method
For your information. With weak muscle tone, a completely different picture is observed in a child. The little one sticks his stomach out and hangs on his arms. At the same time, the back is rounded, and the head can barely hold on.
How does hypertension manifest in a baby?
With hypertonicity, the following signs appear in the baby, which should cause concern among parents:
- The child sleeps poorly, cries often, has an acute reaction to dim light and quiet sounds in the room;
- The baby is constantly capricious and burps a lot often. His chin trembles, he shudders and cries when exposed to irritants;
- The posture can also confirm the presence of symptoms of hypertonicity. A child with asymmetric muscle tone lies unevenly in the crib, taking a slightly curved position. The baby arches and throws his head back;
- The baby's head is tilted to one side towards the shoulder joint. Thus, he begins to develop torticollis, as the muscles tense unevenly. Even if at the age of one month the baby already holds his head well, this is not yet a reason to rejoice. Perhaps this condition is a consequence of increased tone of the muscular system of the back of the head and neck;
- The toddler rolls over and turns only in one direction. Takes objects of interest with only one hand. This is a sign of pathology, since all newborn babies do not have the concept of right or left and are two-handed until a certain age;
- Hypertonicity can be felt when trying to spread the child's limbs apart. The baby’s arms are constantly bent at the elbows, his fists are clenched and cannot be straightened;
- The thumbs are pressed to the palms. This should no longer happen in children older than four months. When the limbs are separated, the child begins to strongly resist and cry;
- With hypertonicity of the lower extremities, the toddler experiences impaired mobility of the articular joints, especially the hip joints. It is extremely difficult for a child to spread his legs in these places.
- When placing the child on the table, he will not rest on his full foot, but on his toes, while bending his toes;
- When trying to move the lower limbs, the child involuntarily crosses them. In addition, the toddler has a tiptoe gait.
If parents notice the above symptoms in their child, they should be reported to the pediatrician who is monitoring the baby.
Types of hypertension in infants
Such an extensive list of signs of muscle tone is due to the fact that in each toddler the deviation manifests itself differently. It should also be noted that there are three types of hypertonicity:
- Symmetrical - in this condition, the child’s entire muscular system is evenly tense. The position is natural for a baby, and there is symmetry in the position of the upper and lower limbs.
- Dystonic is a complex disorder of muscle tone. It is characterized by strong tension in certain muscle groups and a state of complete relaxation in others. With such pathological changes, the functioning of the child’s limbs is disrupted, which leads to serious deviations and long-term complex rehabilitation;
- Asymmetrical - this pathological condition is characterized by uneven muscle tension on the right and left sides of the child’s body. The baby cannot lie flat, he arches his body, falls to one side and tilts his head to the shoulder where the muscle tension is greater.
If suspicious symptoms are detected in a child, you should not postpone a visit to a specialist until later, in the expectation that they will disappear on their own. The sooner the pediatrician examines the baby, the sooner rehabilitation will begin, which will save the baby from serious health consequences in the future.

Hypertonicity in newborns
Hypertonicity - muscle strain - is a condition with which most children are born. You should worry if it does not go away by 3 months of the baby.

Muscle tone - what is it?
Tone means “tension” in Latin. Muscle tone is normal, this is how they work by contracting and relaxing.
Almost all babies are born with hypertonicity: arms and legs are pressed to the body, fingers clenched into fists. In most cases, there is no pathology in this: try to sit in one position for a long time, your muscles will tighten too. And the child spent several months just like that, grouped together, and is now getting used to living in a world more spacious than his mother’s belly. His brain has not yet learned to give orders to his muscles, and his muscles have not yet learned to obey and execute.
In one-month-old babies, hypertonicity is a common occurrence, and in the extensor muscles it is more pronounced than in the flexor muscles: the fists are clenched, the legs are bent, they move apart with force and only 45%, the head is thrown back.
This condition is called physiological hypertonicity and in healthy babies it goes away within a few weeks. Until what age is physiological tone in newborns - up to three months. If muscle strain remains for longer, there may be serious problems and you should consult a doctor.
Why does hypertension occur?
In addition to the baby’s intrauterine “habit” of curling up into a ball, which causes physiological hypertonicity, many factors can lead to serious problems:
- the course of pregnancy: in what conditions did the expectant mother live, what she ate, what she was sick with and what medications she took; Alcohol and nicotine are especially dangerous for fetal development;
- how the birth took place: the cause of excessive muscle tone may be birth injuries, hypoxia (oxygen starvation), rapid labor, etc.;
- Rhesus conflict between mother and child.
Symptoms of hypertension
How not to miss the moment when you urgently need to show your baby to the doctor?
There are several symptoms, in addition to tightly clenched arms and legs, that should alert parents:
- restless sleep: the baby has difficulty falling asleep, often wakes up crying;
- the child often cries, his chin trembles (doctors call this “tremor”);
- frequent and profuse regurgitation, poor appetite, abdominal cramps;
- painful reaction to light and sound;
- restricted movements;
- The baby holds his head up from birth.
In any case, if you think that your baby has hypertension, do not panic ahead of time. You cannot make a diagnosis yourself; this must be done by a pediatric neurologist.
The doctor will check your concerns using several tests:
- Support reflex: if you take the baby under the arms and place it on a flat surface, he should stand with his entire foot, and not on tiptoes.
- Stepping reflex: the baby, if held upright, tries to take a step.
- Tonic reflex: lying on his back, the child straightens his arms and legs, and if he turns onto his stomach, he bends them.
- Symmetrical and asymmetrical reflex: if you tilt your head to your chest, your arms and legs bend and extend; if you tilt your head to the side, the arm and leg on the side of the tilt will straighten, and those opposite will bend.
Normally, the step reflex should disappear in babies after two months, tonic and symmetrical, and asymmetrical after three months.
Why is hypertension dangerous?
The body of a newborn baby is very flexible and pliable, and if you see a doctor on time, you can prevent many problems:
- If hypertonicity was overlooked and no action was taken, the baby will later begin to crawl and walk, and coordination of movements is impaired.
- Posture is formed incorrectly, and the cervical spine suffers; the result is frequent headaches, fatigue, etc.
- The formation of fine motor skills of the hands slows down, and mental development, speech, etc. are associated with it.
What causes muscle hypertonicity in infants?
The development of hypertension can be provoked by various reasons that affect the child’s central nervous system in the womb and during his birth. Problems in intrauterine development leading to disorders in the nervous system of the fetus are associated with the lifestyle of the expectant mother and her state of health.
Smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages have a negative impact on the baby’s central nervous system. The deviation can also be provoked by pregnancy occurring with pathologies or birth trauma.
Fetal hypoxia or prolonged lack of oxygen during birth can lead to disturbances in the baby’s nervous system. Due to the lack of oxygen, brain cellular structures are severely damaged, and birth injuries resulting from rapid or protracted labor cause microscopic hemorrhages in the brain, which leads to the development of muscle hypertonicity in the baby after birth.
Muscle hypertonicity in infants - what parents need to know
After birth, each baby has functional characteristics - one of them is the tense state of the muscles (hypertonicity).
For certain periods of life, a certain functional state of the tone of various muscle groups.
With its uncharacteristic changes - a decrease (hypotonicity) or an increase (hypertonicity), there is an imbalance of nervous regulation associated with disturbances in the functioning of the brain or spinal cord.
It is important to pay attention to this in a timely manner and normalize the altered processes in the baby’s body as early as possible, contact a specialist and change the increase in tone in the baby using a set of therapeutic measures
What is hypertonicity
Many parents consider the tense state of the child’s muscles after birth to be normal and do not pay due attention to the appearance of certain symptoms of increased muscle tone, and such conclusions often end in failure.
Hypertonicity, or this condition is also called “muscular dystonia,” is a persistent change in the elasticity of certain muscle groups, which is caused by a disruption of the central nervous system and often occurs in a baby during its perinatal development.
At a certain period of a baby’s life (immediately after birth), physiological hypertonicity of newborns is indeed observed, but as the baby grows, signs of muscle tension decrease and disappear completely.
In the first days after birth, a newborn baby maintains the position in which it was in the mother’s womb for a long time:
- legs and arms are bent at the knee and elbow joints;
- fingers clenched into a fist;
- the arms are pressed to the chest;
- the head is slightly thrown back;
- Flexor muscles are much more active than extensors.
This is a physiological norm, with mandatory symmetry of tone on both sides.
Gradually, all the baby’s muscles relax, and the tension in the flexors and extensors is balanced, the baby begins to move more freely, and excessive muscle tension partially disappears by a month or two, and is completely balanced by six.
This is associated with the emergence of many skills and abilities of the baby - the ability to roll over independently, sit first with support and then independently, stand up in a crib, crawl, walk with support.
Any disturbances in muscle tone will disturb the baby, cause discomfort and even pain.
In addition, hypertonicity can be combined with moodiness, anxiety, sleep disturbances - a syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability.
Therefore, it is important to promptly replace the appearance of alarming symptoms and consult a specialist.
Causes of hypertension in infants
The most common cause of excessive muscle tension is:
- chronic intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen starvation of the fetus);
- lack of vitamins, especially group B.
The following is also considered to have a major influence on the formation of dystonia:
- the occurrence of stressful situations during pregnancy;
- serious somatic diseases in the expectant mother;
- intrauterine infections;
- severe toxicosis;
- frequent respiratory infections during pregnancy and taking medications.
But there are situations when, even if all the recommendations of the supervising doctor are followed and the pregnancy seems to be proceeding normally, the baby develops symptoms of hypertonicity after birth.
In this case, problems are possible during childbirth:
- rapid, as many mothers consider, an “easy” birth - this is in some cases much worse than a “difficult” long labor;
- asphyxia during childbirth - tight entanglement of the umbilical cord, prolonged standing in the birth canal;
- birth by caesarean section.
Therefore, when collecting anamnesis, the doctor often asks in sufficient detail about the course of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as about the condition of the baby immediately after birth - in this case, this is important for determining the cause of hypertonicity.
Several reasons to be wary
The following symptoms indicate increased muscle tone in a baby:
- the child is restless, sleeps poorly, often wakes up, there is tremor of the chin and arms;
- the baby is tightly squeezed, during sleep the arms and legs are convulsively tucked in, and the head is thrown back;
- the baby does not eat well, often burps, which is accompanied by arching of the body;
- the baby is excessively constrained, there is no gradual relaxation of physiological hypertonicity; when trying to move an arm or leg to the side, the child becomes worried;
- Sometimes holding the baby's head early is bad - this indicates a muscle spasm in the neck.
The appearance of these signs in a baby is a cause for concern, because only a pediatric neurologist can accurately determine the presence of increased or decreased tone in a baby.
Therefore, if you suspect dystonia in an infant, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. You should also not ignore the necessary routine examinations by a pediatrician and specialists - the first and second examination by a neurologist should be carried out at 1 and 3 months of life.
Types of hypertension in infants
Hypertonicity of the neck muscles - accompanied by throwing the head back or to one side (this is often confused with congenital or installation torticollis)
This condition often appears after a cesarean section.
Hypertonicity of the limbs in newborns - there is a strong clenching of the fists, which prevents the baby from learning to pick up toys in due time, the arms and legs are convulsively tucked, but all the limbs are symmetrical to each other and there is no deformation or shortening, sometimes twitching and cramps of the arms and legs are observed.
Hypertonicity of the back in an infant - there is a constant arching of the baby backwards, pain is often observed when pressing on the back muscles, the baby sits poorly or does not sit for long, and is worried when forcibly disembarked.
What happens if hypertension in a baby is not treated?
Only a doctor can determine and clarify the presence of hypertension in a baby, but you need to know that the line between normal and pathology is very thin, especially in the first months of life, and certain factors must be taken into account:
- during the examination of the baby by a specialist, the baby must be fed so that there is no unnecessary cause for concern;
- the inspection should be carried out in a calm environment;
- The baby should get enough sleep so that the child does not become capricious during the examination.
It is important to remember that even a specified diagnosis of “muscular dystonia” is not a reason for frustration, because hypertonicity is not as dangerous for the baby’s health as it seems at first glance.
But if left untreated or delayed in contacting a specialist, this condition can lead to serious consequences in the future:
- various postural disorders;
- the appearance of regular headaches, migraines;
- clumsiness of the child;
- increases in blood pressure.
All these unpleasant consequences of hypertension in newborns can be completely avoided only through proper comprehensive treatment.
doctor – pediatrician Sazonova Olga Ivanovna
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5d3aa980b96cfd00adb0bf09/5da734b5e4f39f00b1e698fe
How dangerous is hypertension in a baby in the first year of life?
You should always pay attention to signs of increased muscle tone, despite the fact that it is most often physiological. It is very important to contact a pediatrician as early as possible, who can determine whether this is normal, or perhaps the condition is congenital and pathological.
If the diagnosis of hypertonicity is carried out late, this may cause a delay in physical development and the formation of motor skills in the child with a significant delay. In addition, the baby will have problems with fine and gross motor skills and speech development, since they have a relationship.
Hypertonicity of the neck muscle corset leads to restrictions on the rotation of the child's head. A toddler may experience bone asymmetry of the skull if he lies on one side all the time without the ability to roll over to the other due to muscle tension.
A particular danger lies in increased hypertonicity of the muscles of the lower extremities. This deviation leads to frequent cramps, impaired motor activity and improper formation of the arch of the foot. With hypertonicity, there may be a difference in the length of the baby’s limbs, as a result of which he will develop problems with gait and posture in the future.

Causes of the disease
How to understand that a baby has a headache - signs and symptoms
The described developmental pathology can be found not so often. If it appears, it is necessary to clarify the reason that provoked the problem. The predominant factors are usually disturbances in the functions of the central nervous system and improper blood circulation in the body. This situation can be triggered by the following:
- complications during childbirth: fetal hypoxia, asphyxia, trauma;
- rapid delivery;
- bad habits that the woman did not give up during an interesting situation;
- severe pregnancy and related diseases;
- the birth of a baby with low birth weight or prematurely;

Born prematurely
- improperly organized infant nutrition from the first weeks of life;
- infectious and viral diseases that lead to depletion of the baby’s body;
- Excessive intake of vitamin D by the baby;
- developmental pathologies and various defects.
The cause of weakened muscle tone can also be genetics, when the baby inherits a serious illness. Regardless of where hypotension lies, it can have serious consequences. The toddler is lagging behind in physical development; it is difficult for him to learn to sit and walk. In a child who spends most of his time without movement, weak muscles begin to atrophy and bones slow down in growth.
As a result, the growing baby develops skeletal deformation, which leads to scoliosis, changes in gait and other serious consequences. In an effort to keep himself in an upright position, the child strains all the internal organs, this provokes the development of all kinds of pathologies.
Diagnostic examination
To understand what causes hypertonicity and whether it is an age-related feature or whether it was provoked by a neurological pathology, the doctor conducts a full examination of the child, including an initial examination. The most important diagnostic techniques in this case are:
- Neurosonography - this technique is an ultrasound examination of the brain in children under one year of age. The study can be carried out until the child’s fontanelle closes, since it is through the soft tissue in its area that the general condition of the brain structures and the quality of their blood supply can be assessed. The technique is very informative, safe, accessible and does not require immobilization of the child. It is carried out as planned for children under the age of one and a half months.
- Electromyography - it is also used in diagnosing hypertonicity, but much less frequently. The technique allows you to evaluate the speed characteristics of nerve impulses, muscle strength and its symmetrical indicators. In addition, it makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of various muscle groups and their work in a calm state.
In addition to everything described above, an examination by a geneticist can be added to check for the presence of genetic abnormalities that lead to muscle tone.

Therapeutic techniques used for hypertension
Typically, the sooner increased muscle tone is identified, the easier it will be to eliminate it. Children with this disorder are prescribed relaxing massage treatments, therapeutic exercises, swimming and physiotherapy.
Drug treatment is resorted to only in cases of severe illness or if non-drug methods do not produce the desired results.
All of the above procedures should not cause the child to cry or feel discomfort. If the baby shows anxiety and cries, then the tension in the muscular system increases even more, which means they will not bring any positive effect and you need to choose other methods of dealing with the pathological deviation.
Hypertonicity in infants: Massage procedures
Massage, which is performed for muscle hypertonicity, is aimed at relaxing the muscular system and eliminating spasms in it. The procedure should be performed by an experienced children's massage therapist. The massage is done in several courses of fifteen sessions each.
Parents can also give a general massage to a newborn. But first you need to take a few lessons from a specialist. When carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to take into account the situation, the temperature in the room, the place where the massage is performed and the massage technique, and the mood of the baby.
The room where the massage will be performed should be warm, since cold air leads to muscle tissue tension. Before the procedure, the baby needs to be completely undressed and lubricate the skin with massage oil. The room should not be too hot. A child should not be given a massage after eating, or when the little one wants to eat or sleep.
The baby must be completely attuned to the procedure and have a good mood. He should also feel confident, protected and relaxed, which is why parents try to call a massage therapist at home, so as not to scare the baby and make the procedure comfortable for him.
Massage procedures should be carried out on a table covered with a soft, thick cloth and an absorbent diaper. The surface should not slip. The massage therapist's hands should be warm, clean, without long nails and jewelry, which can lead to injury to the baby's skin.
Massage can begin when the baby is two weeks old from birth. For up to one and a half months, it should consist only of stroking. From three months you can add rubbing, vibration and rocking. Kneading muscles, sudden movements, clapping and pressing are not allowed.
Since hypertension can be different, massage procedures will also have their own nuances. Therefore, before you start giving your child a massage yourself, you should take lessons from a massage therapist, or it is better to completely entrust the procedure to a specialist.
Gymnastic exercises for muscle hypertonicity
Performing therapeutic gymnastic exercises allows you to normalize the functioning of the muscular system and stimulate the motor activity of the toddler.
Only a specialist should perform exercises with a baby, after developing an individual complex for the baby, taking into account his age category, stage of hypertonicity and body characteristics.
If you have increased hypertonicity, you cannot do dynamic gymnastics with a child.
Hypertonicity in infants: Physiotherapeutic procedures
For hypertonicity, children are prescribed thermal procedures in the form of paraffin baths. With their help, muscle spasms are relieved and the child completely relaxes under the influence of heat.
Applications are applied like boots to the lower part of the lower leg and foot of the child. The procedure takes from ten to twenty minutes. The full course consists of ten procedures. Heat treatment can be replaced by magnesium electrophoresis.
Hypertonicity in infants: Exercises in water
Exercising with a child in an aquatic environment allows you to normalize muscle tone, reduce spasms and improve coordination of movements.
In addition, water procedures allow you to evenly work all muscles, gradually forming a healthy muscle corset. To relieve hypertension, the water in the bathroom should be warm. Additionally, you can add a decoction of pine, sage or motherwort to it. It is better to take baths before going to bed. The procedure should be enjoyed by the toddler and not cause discomfort, so parents can use various toys and an inflatable ring for the baby’s neck.
The only thing you can’t do while taking water procedures is diving.
Osteopathy for muscle hypertonicity in a child
This technique is very popular nowadays. The procedures should be performed by an experienced pediatric osteopath.
Sessions are prescribed for children who have neurological disorders caused by birth injuries or congenital skeletal pathologies.
Drug treatment of muscle hypertonicity in infants
Drug therapy is prescribed only in exceptional cases in the absence of visible effects of non-drug treatment.
Often, with increased muscle tone, a neurologist prescribes drugs that improve blood flow in the brain and stimulate the functioning of neuron cells. And also lekforms that eliminate congestion, in simple words - diuretics.
Drug treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist.

Important Tips
Children who have been diagnosed with increased muscle tone are prohibited from using jumpers and walkers, as they place additional stress on the spinal column and muscular system.
Also, when teaching a toddler with hypertonicity to walk, it is necessary to use not booties or slippers, but orthopedic boots with a backrest that fixes the heel area and orthopedic insoles. In this way, it is possible to promote the correct formation of the arch of the foot and evenly distribute the load on the muscular system.