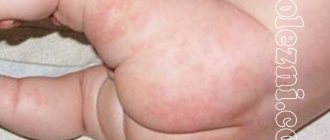
Burns in children from boiling water are quite common. It’s not easy to keep an eye on a small child: he tries to touch a hot mug or a pot of boiling water. Such contact poses a great danger to the baby’s health, even with a mild degree and small area of damage. Therefore, in case of a burn, he should be taken to a doctor as soon as possible, who will provide qualified first aid, prescribe therapy, and, if necessary, hospitalize him in a hospital.
Degree of damage
There are 4 degrees of burn in total:
- A first-degree burn is characterized by the appearance of redness where boiling water comes into contact. In addition to hyperemia, swelling is observed in these areas of the skin, and they begin to hurt greatly.
- A second-degree burn is accompanied by the appearance of blisters on the skin, resulting from peeling of the surface layers of the dermis. The bullae contain serous fluid and can increase in size and burst.
- There are two types of third degree burns. With degree 3A, not only the epidermis is affected, but also the superficial layers of the skin, including the papillary layer. With 3B, the entire thickness of the dermis is damaged, including hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Black scabs or blisters with hemorrhagic contents may form on the skin.
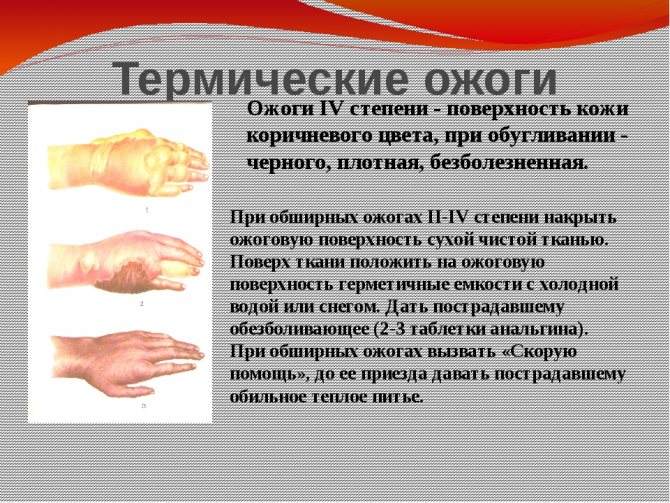
- A fourth degree burn is accompanied by damage to deeper tissues, muscles, tendons, and bones. The wounds are deep, their healing is very difficult and long, with the formation of a rough scar. This cannot be done without plastic surgery.
Types of burn classification
Burns are diagnosed through a visual examination by a combustiologist. It also checks for infection. Burn injuries are classified according to the following criteria:
According to the circumstances of receipt: industrial, household and military.- According to the depth of the lesion, they are divided into 4 degrees:
- 1 - redness of the skin;
- 2 - the appearance of blisters;
- 3 - necrosis of all layers of skin;
- 4 - charring of tissues.
- By severity: light, moderate, severe and extremely severe.
- By localization:
- skin burns;
- eye;
- respiratory tract and inhalation damage.
- According to etiology:
- thermal (flame, steam, water, heated objects and others);
- chemical (acids, alkalis, household chemicals, phosphorus);
- electrical (electric energy and lightning);
- radiation (solar radiation, light radiation from a nuclear explosion, electric welding).
There is a percentage ratio of lesions of the whole body in relation to healthy ones, it helps to assess the patient’s condition . For the head and for each hand, 9%. Chest, back and each leg - 18% each zone.
Severity of damage
The severity of the burn is determined based on the size and depth of the damage: the greater the volume of damaged tissue and its depth, the more difficult and longer it will be to heal. Regardless of the factor that provoked the burn, according to the depth of tissue damage, they are divided into 4 degrees:
- First degree burns. In case of contact with the influencing factor, redness and swelling appear on the skin, and severe pain is felt. No special rehabilitation is required, there will be no burn marks left, and self-healing will take from 5 to 7 days.
- Second degree burns. Redness and swelling appear in the burn area, blisters form with a cloudy-transparent or yellowish liquid inside. If the bladder is punctured, the reddish color of the epidermis will be visible, and accidentally touching it will cause great pain to the victim . Often the surface of the wound is affected by infectious inflammation, for this reason the complete healing process takes approximately 2 weeks. Scars appear very rarely after healing.
- Third degree burn. It is characterized by cessation of vital tissue activity and possible blood loss. The damaged area becomes covered with a gray or brown crust.
- Charred skin, deep damage to muscle tissue, and sometimes damage to bones and tendons are signs of a grade 4 burn, which is considered the most severe. Rejection of dead tissue, charring of the injured area, and sometimes bones are involved in the process. The rehabilitation and recovery period is slow and lengthy; deep scars and scars remain at the site of damage.
The most difficult to treat are burns of the last two degrees, namely 3 and 4. Read more about them.
Why is a burn dangerous?
The danger of being burned by hot water is the possibility of developing a burn disease. This is a serious condition that can cause death in a child. It occurs at high degrees and a large area of damage.
Through the damaged surface, plasma and extracellular fluid are lost, the blood thickens, and toxic substances are absorbed from the destroyed tissues.
The baby’s organs begin to suffer due to lack of nutrition, a state of shock develops, and the functioning of many body systems is disrupted. The child’s resistance decreases, and a purulent infection appears in the area of the burn wounds. It is quite aggressive, difficult to treat and can lead to blood poisoning (sepsis).
What should you not do after a burn with hot water?

Do not apply oils to burns
As a rule, a hot water burn does not pose a serious threat to human health or life. The consequences of injury can be treated with great success using effective folk remedies. If the victim’s condition is unstable or unsatisfactory, then it is better to send the victim to a medical facility.
There are several erroneous actions that subsequently complicate treatment. What should not be done when providing first aid during a burn with hot water?
- Do not apply tight bandages or dense compresses to the injury site.
- It is forbidden to treat the injured area with iodine or brilliant green.
- It is not recommended to apply a bactericidal or antiseptic patch to the painful area.
- You should not get carried away with painkillers. These can be used only immediately after injury, but not during the course of direct treatment.
First aid at home
If a child is burned by boiling water or pours hot water on himself, first of all you need to remove wet clothes from the burned surface. This must be done carefully, since the baby’s skin is already irritated, very painful, and blisters begin to appear on it. If the clothes are very stuck or tight, then it is better to cut them off with scissors .
The affected areas should be immediately cooled with water by pouring it into a basin or pan. It is worth calculating so that the entire burned surface is immersed in water. You can use a low pressure shower. After this, cover the wound with a clean bandage and consult a doctor. You can give your child a pain reliever.
First aid
Most burns from hot water are grade 1 or 2 and can be easily treated at home.
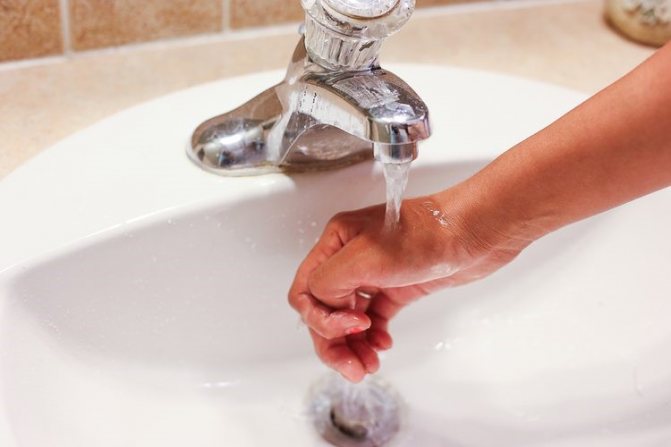

If you are burned by hot water, first of all you need to quickly calm down and assess its severity, and then proceed to the following actions:
- As soon as possible, place the affected area under running cold water for 10-15 minutes - cold water for a burn helps reduce the temperature at the burn site, thereby preventing the spread of damage and reducing pain.
- Apply a sterile napkin or piece of gauze soaked in cool water to the damaged skin.
- To reduce pain, you can take painkillers (Ketorol, Ibuprofen).
- Next, treat the burn site with a special anti-burn spray (Olazol, Panthenol) or liquid antiseptic (Furacilin, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine - aqueous).
- To prevent the appearance of an allergic reaction and swelling on burned skin, you can take an antihistamine (Suprastin, Cetrin, Tavegil, etc.).
Important! If clothing is stuck to the damaged area, under no circumstances should you tear it off yourself - it is better to go to a hospital emergency room or emergency room.
After emergency assistance, the victim needs rest and plenty of fluids.
If, after providing first aid, the victim’s condition worsens, or the measures taken did not produce results, you must go to the hospital or call an ambulance.
Important! Immediate attention is required in cases of hot water burns in children and the burn area in an adult exceeding more than two palms.
What not to do
In severe cases of damage, clothing should not be torn off using force. This will increase the pain and worsen the shock. It is forbidden to pop blisters on the skin yourself: you can cause an infection and significantly slow down the wound healing process.
Do not lubricate the burn with butter or any other oil, badger fat, or moisturizer: this can only aggravate the condition of the burned skin. It is forbidden to apply iodine, alcohol and other aggressive chemicals to the wound.
In what cases should you urgently seek medical help?
You should immediately consult a doctor if a very young child is burned. His condition can worsen in a very short period of time, even with small areas of burn wounds. In older children, you should see a doctor if a large area of skin is affected and the burn is severe.
If a state of shock develops, a drop in blood pressure, or severe pain, you should immediately call an ambulance. Doctors will take the necessary measures to restore the child’s condition, alleviate his suffering and deliver him to a medical facility..
Changes in the body that occur during a burn
The mechanism of a thermal burn is as follows: high temperature has a direct effect on tissue proteins and causes them to coagulate.
• In case of first degree burns, only the protein substances of the surface layer of the epidermis coagulate.
• In second degree burns, the coagulation process reaches the papillary layer.
• With a third degree burn, in addition to coagulation of skin proteins and underlying tissues, other more significant lesions occur in the traumatic focus.
Protein coagulation is not the only local change. In the tissues located under the layer subjected to protein coagulation, major pathological changes also develop. The vascular and nervous systems are most significantly affected. Aseptic inflammation develops (in the first moments), which is accompanied by expansion of the capillaries and an increase in the permeability of their walls. Vascular thrombosis develops in the blood vessels located in the protein coagulation sector and partly in the underlying layers.
The latter has an important pathogenetic significance for the development of one of the most serious complications of burns in children - thrombotic embolism.
As a consequence of irritation of a huge number of skin receptors and a constant massive flow of pain afferent impulses, the nervous system is involved in the painful process, and it comes to the disruption of the cerebral cortex. All this is accompanied by rapid and dangerous disorganization of important systems and functions of the body, an increase in the permeability of arterial and venous capillaries occurs and conditions are created for the transition of liquid components of the blood into the surrounding tissues at the site of the lesion and the formation of edema. First degree burns are accompanied by slight swelling. In case of second degree burns, the blood plasma that accumulates in large quantities quickly permeates the surrounding tissues and lifts the stratum corneum of the skin. This creates bubbles of various sizes. In third degree burns, fluid penetrates into the interstitial spaces and forms significant swelling. The loss of plasma released from the blood vessels can assume alarming proportions, and so-called “white bleeding” occurs. With a burn that covers 16-17% of the skin surface, in the first day the body of an adult loses more than 3 liters of blood plasma. As a result, a significant thickening of the blood occurs with a relative increase in the formed elements of the blood. In the first hours after a massive burn, the number of red blood cells can exceed 10 million, and hemoglobin can be more than 150. This is the result of significant thickening of the blood. If the burn is not complicated by infection, normal capillary permeability is restored in 5-6 days, anhydremia improves and then the presence of significant anemia is detected. The latter can be detected in the first days if large amounts of fluids are introduced into the blood circulation. Consequently, anemia has a primary origin, it is caused by:
• primary hemolysis;
• violation of the regenerative ability of the bone marrow;
• bleeding from a burned area of skin;
• hypovitaminosis C;
• suppurative processes on the burned surface.
One of the most important points in the pathogenesis of a burn is the large loss of proteins that occurs in the body of a burned child. It is based mainly on the loss of plasma from the blood vessels and partly on the breakdown of protein in the affected tissues. In severe cases, the amount of protein in the blood may decrease below 5%. Taking into account the huge role of globulin fractions of plasma proteins in immune reactivity, and in general plasma proteins in maintaining oncotic pressure and water-electrolyte balance, assessment of the oncoming severe hypoproteinemia requires rapid and systematic treatment to increase it.
Burns cause important changes in the body's electrolyte balance. The content of blood chlorides decreases, and the amount of residual nitrogen increases in the first hours. Initially, hyperglycemia is observed, which in the second week is replaced by hypoglycemia.
Even in the first hours, the activity of oxidative processes in the body decreases and the respiratory coefficient decreases. The alkaline-acid balance shifts towards acidosis.
All changes in metabolism that occur in a burned child in the first hours and days after injury are consequences of a violation of neurohumoral regulation.
Features of treatment
Treatment for a burn depends on its severity. The main goal is to cleanse the wounds and completely epithelize them. The first degree of burn goes away on its own. Painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain.
The second degree is treated under the supervision of a doctor. Formed blisters are eliminated, and the bottom of the wound is healed with ointments until young skin appears. Only a doctor can remove bullae: he will do this in compliance with all the rules of asepsis and antisepsis, thereby preventing infection and the development of complications.
Third degree A requires more serious treatment. The black crust is removed and a special ointment is applied to the wound until it heals. The scab is excised under short-term anesthesia so that the process is painless for the baby.
The third B and fourth degrees are severe lesions.
The wounds will not heal on their own, so doctors achieve the granulation stage and perform skin grafts . It is taken from other parts of the child’s body - its own material takes root better and is not foreign to the baby.
Pharmacy drugs
There are many anti-burn remedies in the pharmacy. There are mainly 2 forms used: ointment and spray. The most popular ones are listed below.
Panthenol
It comes in the form of an aerosol in a can; after spraying, a white foam forms on the skin. The product is universal, used not only to treat burns, but also to heal wounds, abrasions, and scratches. The main active substance is dexpanthenol, which penetrates well into tissues and has a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect.
Bepanten plus
The cream contains dexpanthenol and chlorhexidine hydrochloride. The drug allows you not only to get rid of burns, but also to prevent the development of bacterial infection in the wound area. The burned surface must be cleaned before application. The product is used once a day.
Olazol
Olazol contains:
- antibacterial component chloramphenicol;
- painkiller benzocaine;
- sea buckthorn oil.
It cleanses infected burn wounds well, and after application it temporarily relieves pain.
Radevit
The ointment contains vitamins:
- tocopherol;
- retinol;
- calciferol.
They activate reparative processes and accelerate wound healing. The new skin is moisturized and does not crack, so the likelihood of infection is reduced.
Dermazin
The cream contains silver, which has an antiseptic effect. Dermazin is recommended to be applied in a thin layer to the burned surface once a day after preliminary cleansing of the burn wound. Its use does not cause pain, it does not leave marks on clothes.
Argosulfan
The drug contains sulfathiazole silver salt. The product is antibacterial, promotes faster healing of wounds, prepares the affected surface for skin grafting, and has an analgesic effect.
Dermazin and Argosulfan are allowed to start using from two months of a child’s life.
Folk remedies
There are many traditional methods of treatment. The most common ones include:
- Beeswax. It is mixed with vegetable oil in a ratio of 1: 2. The ingredients are boiled together until a homogeneous consistency is formed, a bandage is soaked in the resulting mixture and, after cooling, applied to the affected surface.
- Aloe juice. When squeezed onto the skin, it will soothe it and speed up healing.
- Freshly grated potatoes. It is distributed over the surface of the wound, after 30 minutes it is carefully washed off under running water.
- Sour cream. Used for first degree burns to soothe the skin.
Hot water burn severity
Doctors distinguish between 3 degrees of hot water burns. Depending on the extent of the injury, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.

Scars and other possible consequences
A first-degree boiling water burn in children, as a rule, heals without a trace, or a small area of skin remains, which differs in color from the surrounding undamaged areas.
Severe burns from boiling water lead to the formation of serious consequences in the form of rough keloid scars. With age, they begin to tighten the surrounding tissue. If joints are located nearby, their contracture develops, and the range of movement in them is sharply limited. Burns on the face can lead to tightening of the eyes and lips, and the face becomes disfigured. Correction may require more than one plastic surgery.