Main reasons
Thrush in the mouth is otherwise called candidal stomatitis. The disease develops due to the rapid proliferation of fungal microorganisms, which are always present in certain quantities on human skin and mucous membranes. The growth of fungi, in turn, occurs due to disruption of the natural microflora of the oral cavity, which is possible in several cases:
- When the child's immune defense decreases. Premature and frequently ill infants are more susceptible to thrush;
- Failure to comply with basic hygiene standards;
- After antibiotic therapy. Candidiasis often occurs in babies if a nursing mother receives antibacterial treatment;
- If the baby is given sweetened water.
The appearance of a cheesy coating on the tongue during the neonatal period may be associated with infection of the child by fungal microorganisms as it passes through the birth canal. This happens if a woman with genital candidiasis in the last stages of pregnancy has not been treated.
There are several periods during which thrush is most likely to appear on the tongue, cheeks and gums of a baby:
- First 6 months of life. At this time, the baby’s immune system is just “learning” to perform the functions assigned to it, so it cannot always cope with the body’s defense against pathogens;
- Teething period;
- The time when a child begins to actively explore the world around him. Closer to 8-10 months, the baby begins to crawl, and naturally at this time only clean objects do not always get into his mouth.
The likelihood of a cheesy coating forming on the tongue is greatly increased in premature babies in the first months of their life and in bottle-fed infants. In the latter case, infant formula, unlike mother's milk, cannot fully supply the baby's body with the nutrients necessary for good immune function, which can cause thrush.
Candidiasis of the tongue in infants is often confused with the usual plaque that remains after feeding with milk or formula. You can distinguish the normal variant from cheesy deposits in thrush in the following ways:
- Milk deposits are clearly visible after feeding. After one or two hours, the tongue can be completely cleared; this process is accelerated if the baby is given regular water to drink.
- Removing plaque during candidiasis leads to the appearance of reddish spots on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
- Thrush on the tongue in infants can occur with general symptoms. That is, the child becomes capricious, cries, and refuses to eat.
A baby may be affected by several causes predisposing to candidiasis. All of them need to be installed and further effects on the body minimized, only this will help in the future to avoid relapse of stomatitis.
Symptoms of thrush in newborns in the mouth

The typical pseudomembranous form of candidal stomatitis, or thrush, usually has an acute onset and most often affects the inner lining of the cheeks, the mucous surface of the tongue and, less often, the palate.
Depending on the location of the infectious process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Fungal cheilitis, when Candida affects the outer corners of the mouth like jams.
- Candidal glossitis, or isolated lesion of the tongue.
- Fungal stomatitis.
Clinical manifestations of neonatal thrush usually begin to appear between 6 and 14 days of life. At first, plaque appears in the form of dots, which increase over time and do not cause pain. Outwardly they resemble the appearance of curdled milk or curdled sediment; when scraped with a spatula, they are easily removed.
Often, only isolated areas of plaque are observed, in which the child’s general well-being is not disturbed, but in some cases, total damage to the oral mucosa is possible, accompanied by anxiety, mild regurgitation, refusal to feed and sleep disturbances.
Isolated thrush in newborns on the tongue is characterized by the appearance of a thick whitish-gray coating on it, which, when rejected, reveals bright red areas of the mucous membrane (erosion) that do not bleed profusely. The child may be capricious, irritable, refuse to eat, and have a specific sour smell from the mouth.
Symptoms of thrush in infants also depend on the extent of the process; classic signs:
- Swelling and hyperemia of the epithelial lining of the oral cavity.
- Pinpoint or confluent rashes on the inside of the lips and cheeks, tongue, and tonsils.
- Curd-like coating.
- Decreased appetite or anxiety during feeding.
- Severe itching.
- Bleeding gums are possible.
- Weakness and capriciousness.
- In rare cases, a slight increase in body temperature.
- Unpleasant breath of a sour nature.
What does candidiasis look like in a baby's mouth on the tongue?
It is visually quite simple to determine that it is thrush in an infant’s mouth: against the background of a swollen and red mucous membrane, dense whitish-gray areas of plaque are visible.
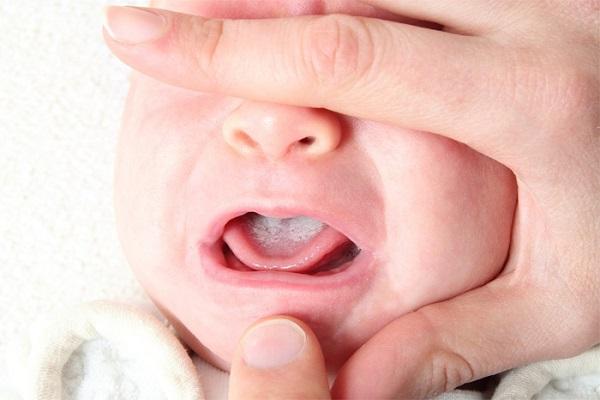
On the tongue they can be either single or cover its entire surface. If you perform a gentle, gentle scraping with a spatula or a small spoon, the plaque will easily come off and reveal small, shallow erosions.
Signs of the disease
The earliest signs of thrush are reddish spots on the tongue, but at this stage few parents pay attention to the problem that has already appeared. Very often, the immune system of a healthy baby copes with the problem itself, and the disease stops progressing. But if this does not happen, then individual lesions begin to appear on the tongue, covered with a whitish coating; over time, it becomes loose and cheesy.

As the disease progresses, fungi begin to move from the tongue to the cheeks and gums, causing the formation of pathological foci in these places. Common symptoms include irritability, restless sleep. The affected areas cause pain and burning, which forces the baby to be capricious and refuse the breast and pacifier.
Thrush in a child’s mouth is divided into stages:
- The mild one appears only as reddish spots, on which plaque appears on top over time. General health does not suffer, and correctly selected treatment at this stage allows you to defeat the disease in 2-3 days.
- The middle stage of candidiasis is indicated if the cheesy plaque is already dense and its separation leads to erosions and pain. The baby sucks poorly and is worried.
- At the third stage, bleeding wounds begin to form; they are localized not only on the tongue, but also on the cheeks, inner surface of the lips, and gums. Fungal microorganisms can infect the upper palate and the walls of the larynx. The general signs of the disease are also clearly expressed - weakness, lethargy, body temperature rises, and the baby practically stops eating. Disruption of microflora also leads to dyspeptic disorders. With severe thrush, the child in the first months of life needs hospital treatment.
Possible complications
Thrush on the tongue of a baby is not dangerous only at the first stage of its development. As the disease progresses, not only the general well-being of children suffers, but there is also a risk of developing unwanted and difficult-to-treat complications.
Bleeding wounds on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity are an ideal gateway for the penetration of any pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, thrush can be complicated by secondary infections. In advanced cases, fungal microorganisms spread far beyond the tongue, cheeks and gums, causing:
- Fungal cheilitis - damage to the lips;
- Glossitis is a mycotic inflammation of the walls of the throat;
- Formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
- Mycotic stomatitis is an inflammation of the entire oral cavity.
In the later stages of thrush, the cheesy film becomes dense and spreads to the larynx, while swallowing food and even saliva causes sharp painful sensations. The child has a high temperature, loose stools, and enlarged lymph nodes. Diaper dermatitis may occur; irritation around the anus leads to irritation and the appearance of erosions. Thrush in the mouth in female infants often causes genital candidiasis.
Due to the refusal of food and water, the baby loses weight and dehydration occurs; thrush can also cause candidal sepsis.
Complications of thrush in children
If thrush is not treated in time, it can have much more serious consequences than curdled discharge. Candidiasis is considered a rather dangerous and complex disease, despite its prevalence and the numerous methods to combat it. Lack of proper treatment for thrush in children can develop into:
- Fungal infection of internal organs
- Dehydration and severe weight loss
- Candidal sepsis
Among other things, thrush can be fatal in premature babies.
Treatment
How to cure thrush on the tongue of a baby can be decided independently only if the disease is still at the initial stage of development. At this time, increased care of the baby and the use of some home remedies with medicinal properties will help defeat candidiasis.
With the progression of candidal stomatitis, the pediatrician prescribes systemic agents with antifungal components - Diflazon, Diflucan. Their dosage is selected based on the baby’s age, and is administered through a syringe or from a spoon. Local therapy consists of the use of antifungal ointments and solutions. Treatment usually lasts no more than 10 days.
When treating oral thrush in a child, the following is often used:
- Nystatin. This may be nystatin ointment or an aqueous tablet solution. Treatment is carried out up to two times a day;
- Levorin suspension. It is prepared from a tablet of 100 thousand units, which must be crushed and mixed with 5 ml of water. Tongue treatment can be repeated every 4-5 hours;
- Vinylin. A cotton swab is soaked in the balm and used to wipe away areas of white plaque. You can use Vinilin 3-4 times a day, 1-1.5 after meals;
- Candida solution. Used for treatment 2-3 times a day.
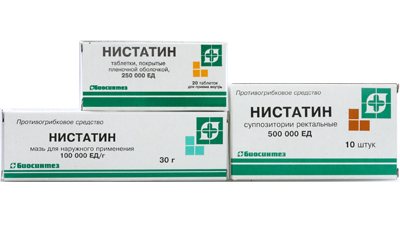
Nystatin
Levorin
Cholisal gel will help numb the mucous membrane during thrush and reduce inflammation. It can be applied to the tongue before feeding for 3-5 minutes. The gel reduces pain, making it easier to suck on a bottle or breast.
In severe cases, the child must be treated in a hospital. In addition to fungal agents, he may be prescribed antibiotics, saline solutions to treat dehydration, and immunomodulatory agents.
Baby care
Immediately when a cheesy coating is detected in the mouth, the mother should do the following:
- Rinse and boil in soda solution all nipples, bottles and toys that the child puts into his mouth;
- Review your diet if your baby is receiving breast milk. For a while, you should exclude from your diet all foods that promote the growth of fungi. These are sweets, fatty foods, spices;
- Before each feeding, rinse your breasts with warm water and soap;
- After feeding, remove any remaining food from the baby's tongue with a swab soaked in plain water. There is no need to lubricate the oral cavity with antifungal agents every time; most often, the frequency of their use is no more than 4 times a day.

Enhanced care and the use of simple folk methods to combat thrush will help get rid of the disease and restore calm to the baby in just 2-3 days. And most importantly, these measures will prevent further progression of thrush.
Diagnosing thrush in a young child
Compared to an adult, the manifestation of thrush in an infant has a specific manifestation, which is very difficult to confuse with other diseases. In order to diagnose thrush in a child, you will need to pay attention to:
- Oral plaque. They have their own characteristic smell (something sour). It can be easily removed with your finger.
- In the initial stages of the disease, the baby does not have a temperature, or it does not rise more than 37.5 C
Parents can recognize thrush on their own, but it is better to consult a doctor for treatment. That is why, after you notice signs of candidiasis, visit a pediatric dentist or pediatrician to prescribe further treatment.
During a doctor's examination, a scraping may be taken for laboratory examination. This is necessary in order to determine the strength and sensitivity of the fungus. This examination can greatly help in the treatment of thrush.
Traditional methods
Treatment of thrush on the tongue of a baby involves the use of products that are easy to find in any home.
Soda
Soda solution perfectly stops the proliferation of fungal microorganisms and helps restore the mucous membrane. Prepare a solution from a teaspoon of dry soda and a glass of warm boiled water. After thorough mixing, the solution is ready for use:
- Before treating the oral cavity, you must wash your hands well with soap and trim long nails;
- Wrap your index finger with a bandage or gauze so that there are no protruding threads;
- The wrapped finger is well wetted in the soda solution;
- It is necessary to wipe not only the tongue, but also the inner surfaces of the lips, cheeks, and gums.
The procedure should be carried out approximately half an hour before feeding. You can also treat the nipples of a nursing woman with a soda solution. During cleansing, you should not be too zealous; it is not necessary to achieve complete removal of plaque, as this can lead to bleeding erosions.
Sage
Sage herb has antiseptic properties. Treatment of the oral cavity with sage decoction can be alternated with the use of a soda solution. The decoction is prepared from two spoons of dry herbal raw materials and a glass of boiling water. The drink is heated in a water bath for about 15 minutes, infused and filtered. It is advisable to prepare the broth fresh each time.
If you don’t have sage in your home medicine cabinet, you can replace it with calendula flowers and St. John’s wort.
Honey
In two tablespoons of warm water you need to dilute 10 grams of liquid honey. The resulting sweet water is used to treat the membranes of the oral cavity up to 5 times a day.
Magnesium permanganate
Potassium permanganate has antiseptic properties; its use not only stops the proliferation of fungi, but also prevents secondary infection. A slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate is suitable for treatment; a finger wrapped in a bandage is moistened in it and the inflamed areas are sanitized. The magnesium permanganate solution must be prepared very carefully. First, a few grains of potassium permanganate are dissolved in a container with warm water, then the initial solution is poured into a mug, jar and diluted with the required amount of water. Failure to comply with this rule can lead to damage to the mucous membrane - undissolved grains of magnesium permanganate cause a burn.
When treating thrush, one should not forget that the microclimate in the room also affects the condition of the mucous membranes of the mouth. The air in the child's room should be clean and humidified. In a dry room, saliva becomes viscous and viscous, and this reduces its protective properties and therefore contributes to the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. You can humidify the air in the room using special devices, or by placing containers of water near heating radiators. The baby's nose also needs regular cleansing - breathing through the nose increases the body's resistance to infections.
If traditional methods of treating thrush are ineffective for 2-3 days, the child must be shown to a doctor. Prescribing antifungal agents will help cope with the disease in the shortest possible time.
How to treat thrush in infants?
For a speedy recovery of the baby, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately and prevent the disease from developing to a severe form. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to adjust the child’s diet, as well as create the ideal temperature and humidity in the room where the baby is.
In some cases, these simple actions may be quite enough to stop the Candida fungus from multiplying, and its amount in the baby’s body returns to normal. You can avoid drinking sugary drinks and take frequent walks in the fresh air.
Depending on the age of the child, he should be prescribed medications and the process of treating thrush. In order to get rid of thrush in a baby, medications are rarely prescribed, as they can do more harm than good. During your appointment with a specialist, you need to discuss the treatment process. First of all, you should worry about what medications a newborn baby may have an allergic reaction to.
The method of treating a child under one year old may not differ from the process of treating newborns. As soon as the child turns 6 months old, he can take general medications that have antifungal properties.
If thrush begins to appear in newborns, then it is necessary to find the cause of the inflammation. If candidiasis begins to develop due to regurgitation of the child, then adjustments to the technique of feeding the child will be required. For treatment, you can use oral treatments using a 1% peroxide solution or a weak solution of potassium permanganate (bare pink). It is often advised to try to treat candidiasis in infants with soda. To do this, you need to mix one teaspoon of soda in 200 milliliters of water. Make a gauze swab, soak it in liquid and treat the baby's oral cavity.
It is important to know that treatment of thrush in young children is always carried out in 3 successive stages:
- It is necessary to clean the oral cavity from food debris using boiled water.
- Afterwards, you need to treat the affected areas with a special solution that has antiseptic properties. It is necessary to wrap gauze around your finger and use sweeping movements of your finger to clean the mouth. Start with the cheeks, then clean the tongue and finally the baby’s lips. This treatment should be carried out 3 to 6 times a day.
- After all the procedures, the baby can apply special medications that have an antifungal effect to the affected areas of the oral cavity, using a targeted method. This procedure should be carried out 3 times a day after meals.
Prevention
In most cases, it is possible to avoid the development of thrush in a child’s mouth by following just a few rules:
- In the first year of a child’s life, all his pacifiers and bottles should be regularly doused with boiling water and periodically boiled in a soda solution.
- Hygienic procedures must be strictly observed. Mothers should wash their hands after changing diapers, when feeding the baby, and before dispensing baby food.
- After meals, give two or three spoons of water. It helps remove milk residues and thereby reduces the likelihood of fungal growth.
- A nursing mother should take antibacterial treatment only as indicated. When prescribing antibiotics, it is better for a woman to temporarily stop breastfeeding.
- Adhere to the timing of introducing complementary foods. An early transition to another food can provoke the growth of pathogenic microflora, which will lead to the appearance of candidal stomatitis.

Thrush on the tongue in children of the first year of life is a fairly common problem, which, in most cases, parents can cope with on their own. But if the condition of the oral cavity and the general well-being of the baby worsens, it is necessary to consult a local pediatrician.
Causes of thrush
Oral candidiasis found in children is the result of the proliferation of a yeast-like fungus of the Candida species, which lives under normal conditions in the body of any person from birth. Candida is a parasitic microorganism that prefers a moist and warm environment, therefore it lives on the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth, intestines and genitals. It reproduces with the help of spores and long threads of mycelium, releasing waste products into the bloodstream.
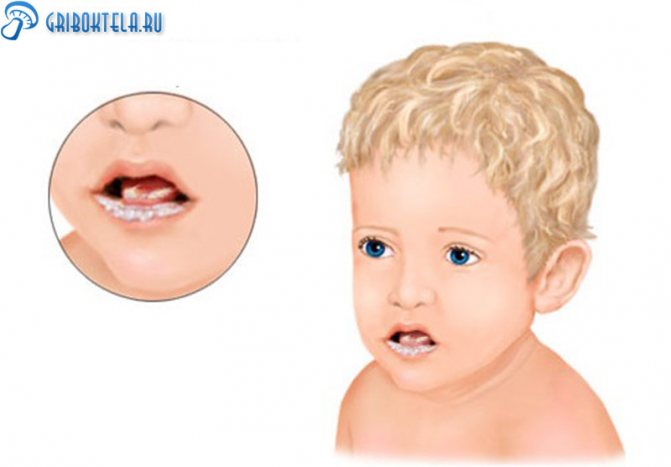
Thrush in children, which develops in the mouth, has many causes:
Internal reasons:
- imperfection of protective forces, especially in premature babies;
- severe chronic diseases and infections (oncology, HIV, tuberculosis);
- endocrine system disorders;
- allergic reactions;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
External (when thrush appears in the baby’s mouth):
- through a mother’s birth canal infected with thrush during childbirth;
- with an insufficiently treated pacifier, pacifier or bottle;
- if a nursing mother violates the rules of personal hygiene (incorrectly treats the nipple before or after feeding, holds a pacifier in her mouth);
- in case of poor quality cleaning and low air humidity in the room where the child is located;
- when your child’s drinking regime is not well organized (leads to thickening of saliva and disruption of its acid balance);
- when regurgitating, when the baby has not removed the remaining milk from the mouth, thereby causing their fermentation;
- due to non-compliance with hygiene rules when interacting with pets.
For older children, external circumstances leading to thrush may include:
- dirty hands after walking and visiting the toilet;
- unwashed toys and dishes;
- drinking raw water or milk, dirty vegetables, fruits and berries;
- joint storage of prepared and raw foods in the refrigerator;
- using someone else's toothbrush;
- sick children visiting childcare centers due to parental neglect;
- when taking hormonal or antimicrobial drugs.
Pushed by the above conditions, candidal infection in the oral cavity spreads very quickly.