April 22, 2019
Averyanova Sveta
Measles (lat. Morbilli) is an acute viral infection with a characteristic cyclical course, manifested by intoxication, catarrhal inflammation and rashes on the body (ICD-10 code - B05). It has the highest degree of infectiousness. Before the invention of antibiotics and the introduction of preventive vaccination, the population was considered a dangerous disease. And today the mortality rate remains high. According to WHO statistics, in 2020 the measles virus claimed the lives of 110 thousand people, mostly children.
Causes of the disease
The etiology of measles is well studied. The disease is caused by an RNA virus belonging to the group of large myxoviruses. It first received its description in 1954. Four years later, Russian researchers under the leadership of Anatoly Aleksandrovich Smorodintsev isolated the virus from the nasopharynx and blood of sick people.
This marked the beginning of scientific work to create a vaccine in our country. Thanks to vaccination, the incidence rate has dropped sharply. Vaccinations and antibiotic therapy have made measles curable.
The measles virus has the appearance of an irregular sphere with a diameter of 120 to 250 nm. It has a complex antigenic structure. The stability of the virion in the external environment is low. The pathogen is sensitive to ultraviolet and visible light. In droplets of saliva on which the sun shines, it dies within half an hour. When it dries out, it dies instantly.
The virus can be isolated from the blood or swabs from the nasopharynx of sick people during the catarrhal period and in the first hours of the rash phase. Weakened strains are used to create measles vaccine.
After the first vaccination, 85% of children develop immunity. To ensure 100% immunization, revaccination is carried out.
You cannot get measles twice. If a person has been ill, antibodies are produced to the pathogen. They last a lifetime.
Routes of infection
Measles is an anthroponotic pathology (the source of infection is exclusively a sick person). Susceptibility is almost 100%. The only ones who have protection against the measles virus are newborn babies who have received antibodies from their mother. Provided that the mother had measles before pregnancy or was vaccinated. Until the age of three months, the baby will not get sick, having innate immunity.
By 6–10 months of age, children can become infected and develop measles. Those babies to whom antibodies were not transmitted (the mother was not sick or was not vaccinated) are susceptible to infection from birth. Infection of the fetus during the antenatal period (pregnancy) is possible.
The main route of transmission of the disease is airborne droplets. The infectiousness of the patient begins from the last days of the incubation period, persisting in the catarrhal period and with the appearance of a rash. From the fifth day from the onset of the rash, the child is considered non-infectious.
The virus spreads when someone who is sick sneezes, talks, or coughs. The method of transmission through things or third parties is practically excluded, since virions quickly die outside the human body. However, there have been cases where the measles pathogen could be transferred over significant distances within the same building through the ventilation system.
Therefore, if a carrier of infection is in a kindergarten, he can infect children not only from his group.
The pathogenesis of measles consists of stages:
- fixation of the virus at the entrance gate (mucous membranes of the upper respiratory system);
- spread of virions into the submucosal layer and further into the lymphatic system;
- reproduction in lymph nodes;
- entry into the bloodstream;
- damage to various organs (spleen, liver, tonsils, gastrointestinal tract, bone marrow, etc.
); - an increase in viral intoxication, skin damage in the form of characteristic rashes, a weakening of the body’s defenses;
- the occurrence of complications.
The main pathogenetic mechanism is damage to all lymphoid tissue. Bacterial infections often occur against the background of reduced immunity.
Historical fact! Before medicine had antibiotics, measles was known as the “baby plague.” It claimed millions of lives.
In his video, Dr. Komarovsky talks in detail about this disease:
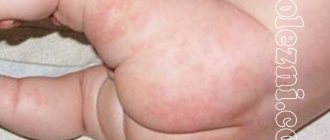
Determining the symptoms of measles in infants at home
The first manifestations of measles in infants occur after the incubation period has expired. You can easily identify them at home using our photos. First of all, the baby experiences an increase in body temperature to peak levels, and a characteristic rash appears, which is initially localized on the head, and after a few days spreads lower down the body.
Note to moms! The measles virus in infants, entering the body, spreads through the bloodstream, so this disease may not manifest itself for a long time. Therefore, it is impossible to start quickly relieving symptoms.
Depending on the period, measles in infants is usually divided into several stages:
- incubation, which occurs without any symptoms. The child feels well, there is no increase in temperature;
- Catarrhal is characterized by the appearance of the first rash on the child’s skin. At this time, the baby begins to have an increase in body temperature, difficulty breathing, hoarseness, and a barking cough. All this is reminiscent of a cold or flu;
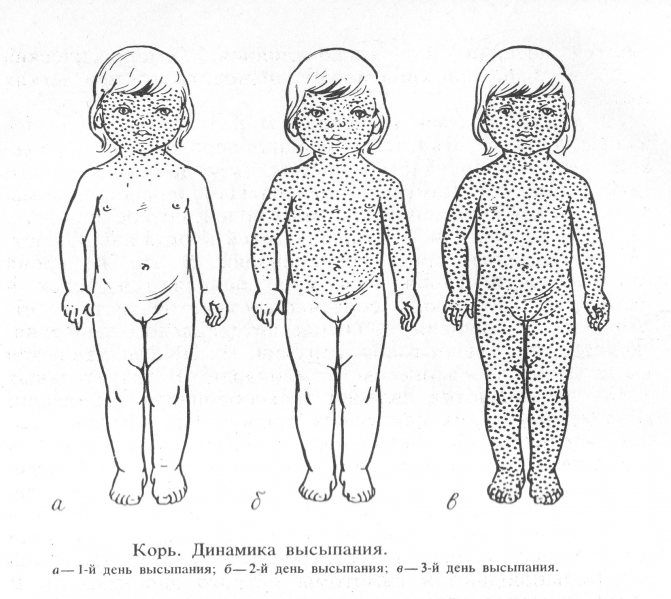
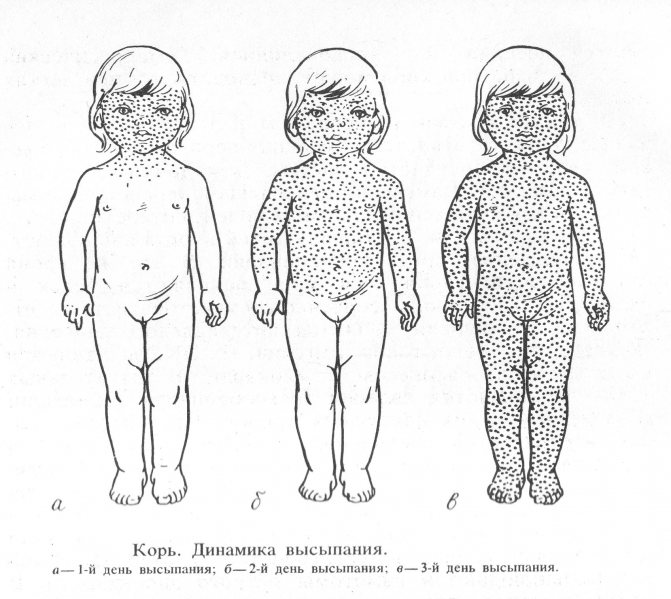
Depending on the degree of rash, measles in infants is divided into three types
- The period of rash is characterized by the appearance of a rash in the form of semolina on the tonsils, palate and the inside of the baby’s cheeks. There is a general inflammation of the throat and redness of the mouth. Next, a rash appears on the head and after a few days begins to spread throughout the body, last of all affecting the legs.
Be sure to watch the video from Komarovsky, what he thinks about measles in infants.
You can study the signs of measles in a baby in more detail using the photo below. The nature of such rashes is quite difficult to confuse with other infections.
Important! If a baby develops measles, try not to look for the source of the disease (you will only waste time). They can be anyone, not necessarily a close or relative. The baby could have caught the virus in a store or other public place, since the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets.
Stages of the disease
There are 4 stages of measles:
- incubation period;
- catarrhal stage;
- rashes;
- pigmentation.
The onset of the disease is acute. A number of authors consider the catarrhal period to be prodromal. Its duration is on average 3–4 days, with possible deviations from one day to a week.
The early stage of the disease is manifested by two syndromes - intoxication and catarrhal.
Then follows the stage of rashes. Its duration does not exceed 3–4 days. The extent of clinical manifestations will depend on the severity of the disease. With a smooth course of the disease, the pigmentation stage will be a recovery.
The state of immunosuppression (measles anergy) can persist for 3–4 weeks or longer. How long the decline in immunity lasts depends on the individual characteristics of the child. At this time, the risk of developing a bacterial or fungal infection is very high.
The classification of measles is as follows:
- by severity: mild, moderate and severe;
- by typicality: typical and atypical;
- downstream: smooth and non-smooth.
Most often, the disease typically occurs in mild or moderate form. If there are no complications, it will last no more than ten days. By the end of the disease, persistent post-infectious immunity will begin to form.
The percentage of atypical forms is low (no more than 5–7%). These include: abortive, erased, asymptomatic, mitigated, hypertoxic and hemorrhagic. The last two variants are observed in adolescents with weak immune systems and adults. They are severe and can be fatal.
Symptoms of the disease

Typical measles in children has characteristic symptoms. It starts off sharp.
Stage 1
Signs of intoxication and catarrhal inflammation appear. Initial symptoms include a dry, annoying cough, nasal congestion, sometimes with moderate mucus discharge.
The temperature rises within the subfebrile range. On the first day of illness, local manifestations will be scanty: slight redness and looseness of the oropharyngeal mucosa.
Stage 2
On the second or third day of the catarrhal period, the signs of measles become more pronounced. The cough intensifies and can be sharp and rough. Conjunctivitis begins to appear. Swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia, and photophobia are observed. Quite large spots of dark red color are visible on the soft palate. The cheek mucosa is swollen, hyperemic, loose.
Stage 3
1–2 days before the onset of the rash, Belsky–Filatov–Koplik spots can be seen. This symptom is specific to measles. If the child opens his mouth, characteristic small whitish dots bordered by a red rim will appear in the area of the small molars, on the cheeks, gums and inner surface of the lips.
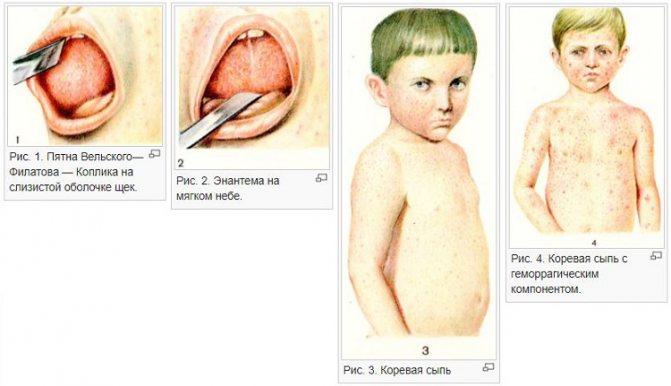
These spots do not merge. They look like pimples and are areas of dead epithelium. Often their appearance is accompanied by a grayish coating on the gums and tongue. Gastrointestinal dysfunction may develop due to the introduction of the virus into the intestinal mucosa.
Stage 4
Symptoms of intoxication in the catarrhal phase will be moderate or mild. Body temperature does not rise above 38°C, less often - 39°C. A sick child experiences malaise, weakness, loss of appetite, and headaches. If early complications develop, the baby’s well-being will be significantly worse. By the end of the catarrhal period, the child has a characteristic appearance: a puffy face, swollen eyelids, tears in the eyes, snot flowing from the nose.
Stage 5
On the fourth or fifth day of illness, a rash begins. Changes in the oral cavity persist. The patient is bothered by a runny nose. The cough becomes more frequent, sometimes painful. The throat becomes sore. Hoarseness may occur due to damage to the larynx. In children of the younger age group, especially infants, dyspeptic disorders are possible.
Intoxication increases. The thermometer shows high values (from 38.5 to 40°C). There may be severe headache, delirium, vomiting, increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure and other symptoms. Lymphadenopathy is observed.
The exanthema will appear within 3–4 days, strictly in stages. The transformation into pigmentation will be just as consistent. The first elements of the rash appear behind the ears and on the nose. Then they spread to the chin, neck, and upper shoulder girdle. On the second day, the exanthema covers the skin of the torso, and on the third - the upper and lower extremities. The rashes are initially spotty, then they grow, merge and become maculopapular.
Stage 6
After 2–3 days from the appearance of the first elements of the rash, the period of pigmentation begins. Pigmented areas appear in the same sequence: head, body, limbs. You can observe the following picture: pigmentation is visible on the face and upper body, and a bright rash is visible on the arms and legs. This distinctive feature of the rash helps in making a differential diagnosis.
Stage 7
With a smooth course of the disease, the pigmented elements will gradually disappear.
By the seventh to ninth day, the symptoms of catarrhal symptoms will disappear. In severe forms and the addition of a secondary infection, the duration of the disease will increase. This will not be a smooth course of measles. The nature of the symptoms will depend on the location and etiology of the complications.
Important! If your child shows any symptoms of the disease, you should contact your pediatrician. The doctor will make a diagnosis and explain to the parents what to do and how to treat the baby.
Symptoms and stages of the disease
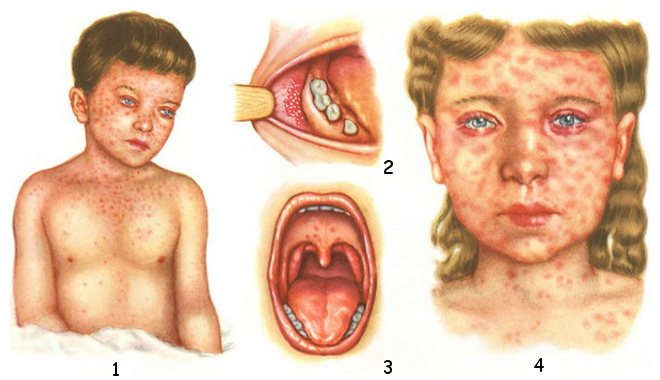
2 - Belsky-Filatov-Koplik symptom; 3 - enanthema in the prodromal period Measles is an insidious disease that develops in stages. In the first days, the disease may not manifest itself at all, the children remain cheerful and playful. The virus spreading throughout the child’s body is still completely invisible to the sensitive eyes of parents. This is the insidiousness of the very first period of the disease, and there are four of them in total.
1. Incubation period
This is the time period that begins at the moment of infection and continues until the first signs of the disease appear. It is generally accepted that this period in children is 7-14 days. At this stage, the virus multiplies “quietly” in the body, there are no symptoms of measles, and the child is not bothered by anything at all. In this case, the baby becomes infectious to others only in the last 5 days of the incubation period.
2. Catarrhal period
During this period, the child develops symptoms that strongly resemble a cold:
- general malaise, weakness, lack of appetite;
- increase in body temperature up to 40°C;
- headache;
- dry cough;
- runny nose and hoarse voice;
- increased lacrimation, swelling and redness of the eyelids, conjunctivitis (drops and ointments for conjunctivitis);
- abdominal pain and loose stools;
- runny nose with purulent mucous discharge from the nose;
- lacrimation, photophobia;
- Infants may experience a decrease in body weight.
Documentary
The catarrhal period of the disease lasts no more than four days, during which all the symptoms of measles gradually turn into more severe forms. At the moment when all manifestations reach their highest levels, a rash begins to appear.
3. Period of rash
As already noted, the rash appears at the peak of all signs of the disease. Spots of a dark red hue appear primarily on the head. Gradually growing and merging with each other, they form large foci of rashes. It is for this reason that the child’s face swells, and the lips become dry and often crack.
On the second day of this period, the rash begins to appear on the arms and upper torso. The third day is characterized by the appearance of rashes all over the child’s body. The duration of the entire period is 4 days.
The period of rash is characterized by a decrease in body temperature, weakening of the cough and the appearance of appetite. The child becomes mobile and active. About a week after the onset of the rash, catarrhal symptoms disappear completely.
4. Pigmentation stage
The rash leaves behind pigment spots, the appearance of which occurs in the same sequence: first on the face, then throughout the body. These spots gradually begin to peel off and eventually disappear completely.
At the pigmentation stage, the child’s condition gradually returns to normal, sleep and appetite are completely restored, and body temperature does not exceed normal values.
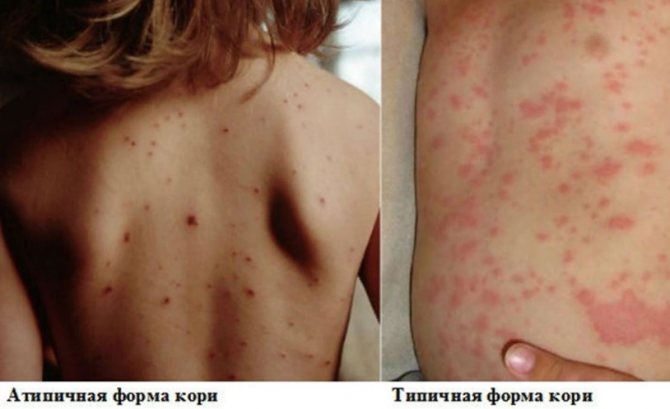
Non-standard forms of measles
If a child gets measles, you will not always be able to notice the development of this disease. Measles may not occur as usual, but in a different form. Such forms of the disease are usually called atypical.
Mitigated form
Children who have been in contact with an infected child receive immunoglobulin for prevention. In such children, the overall picture of the disease becomes blurred:
- the incubation period lasts 21 days;
- in the catarrhal period there is a slight cough and runny nose;
- all periods of the disease, except incubation, are reduced;
- the rashes are not abundant and appear without observing stages;
- there are no characteristic spots on the cheeks;
- pigmentation is less dark.
Abortion measles
With such an atypical form, all signs of the disease appear according to the standard pattern. But after about 2-3 days, all symptoms of the disease suddenly disappear. The rash concentrates on the face and upper torso.
Erased form
This form of measles is very similar to mitigated measles. Here, catarrhal signs of the disease are also insignificant. However, unlike the mitigated form, the erased form is characterized by the absence of a rash. This factor greatly impedes making a correct diagnosis.

Reminder - Beware of Measles!
Atypical forms
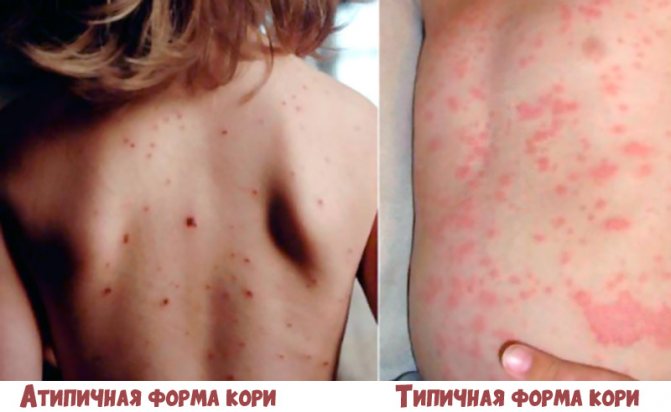
Atypical forms that occur easily include:
- Abortive (cut off) begins typically. On the first or second day the rashes stop. The rash is small, single, and does not affect the limbs. Body temperature rises slightly on the first day of the rash or remains normal.
- Mitigated disease is even milder and does not have the characteristics of measles.
- Erased.
- Asymptomatic.
Such variants of the disease develop in children who received gammaglobulin or blood products during the incubation period. In isolated cases, atypical measles will be detected in those who have undergone active immunization or without objective reasons.
Hypertoxic and hemorrhagic forms are extremely rare. The first option is characterized by severe intoxication. The temperature rises to high levels and can last for several days. Symptoms of acute cardiovascular failure (shortness of breath, tachycardia, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, etc.) and meningoencephalitis (impaired sensitivity, severe headaches, etc.) appear.
In the hemorrhagic variant of the disease, against the background of general intoxication, numerous hemorrhages are observed in the epidermis, mucous membranes and internal organs.
Blood is present in stool and urine. The prognosis is unfavorable, the patient's death is possible.
Symptoms of measles in children
The presence and severity of measles symptoms in children depends on the period of illness. Typical measles has four sequential stages:
- Incubation period.
- Catarrhal (prodromal period).
- Exanthematous (period of rash).
- Resolution stage (period of appearance of pigmentation).
The incubation period for measles in children lasts on average 9–17 days. Initially, the virus multiplies in the cells of the ciliated epithelium and alveolocytes of the upper respiratory tract, in the submucosa of the nasopharynx. The virus infects the lymphoid system and blood vessels, then penetrates the general bloodstream and spreads to almost all organs and tissues.
At the end of the prodromal period, the maximum concentration of the measles virus occurs in the patient’s body.
The duration of the catarrhal period in children is 3–5 days. The following symptoms appear:
- headache;
- lethargy, loss of appetite;
- acute increase in temperature up to 39 ° C;
- the appearance of a runny nose with copious serous and then mucopurulent discharge from the nose;
- sneezing, dry, obsessive cough;
- vomiting, heartburn, belching;
- hyperemia of the pharynx, granularity of the posterior pharyngeal wall;
- hoarseness of voice;
- conjunctivitis (accompanied by intense swelling of the eyelids) with purulent exudate;
- photophobia, blepharospasm;
- puffiness of the face, eyelids;
- the appearance of a characteristic rash on the skin and mucous membrane of the mouth near the molars (Velsky-Filatov-Koplik spots and measles enanthema).
Source: likar.info
Velsky-Filatov-Koplik spots are separately located grayish-white small papules surrounded by a rim of hyperemia. They appear 1–3 days before the onset of the rash and disappear with the appearance of a typical measles rash.
Measles enanthema is pinkish-red spots of irregular shape that appear 1-2 days before the rash on the mucous membrane of the soft and hard palate. Sometimes, during the catarrhal period, a small dotted or spotty rash appears on the skin, giving way to a typical measles rash.
At the end of the prodromal period, the maximum concentration of the measles virus occurs in the patient’s body.
The period of rash begins on the 4th–5th day of the disease, characterized by an increase in symptoms of the inflammatory process and intoxication:
- the appearance of a small maculopapular rash against the background of unchanged skin;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- severe headaches;
- new high temperature rise;
- nausea, vomiting;
- decrease in the amount of urine excreted;
- deterioration of the cardiovascular system;
- delirious stupefaction, delirium.
In mild cases, treatment of measles in children is carried out at home. The room must be ventilated and humidified. The sick child is provided with bed rest, plenty of fluids, and light conditions.
On the first day, elements of the rash appear behind the ears, on the back of the nose, and on the scalp. The rash quickly spreads to the face and neck. On the second day, the rash covers the upper chest and back, and upper arms. On the third day - legs and lower arms. A measles rash can cover the entire surface of the body; in severe cases, continuous fields of erythema and small hemorrhages form on the skin. The appearance of a rash is caused by the formation of large immune complexes, which are formed as a result of the interaction of antigen viruses with antibodies. In an uncomplicated course of the disease, on the 3rd–4th day after the appearance of the rash, a period of pigmentation begins, the duration of which is 7–10 days. Its signs:
- the general condition of the child is normalized;
- body temperature decreases slightly;
- catarrhal symptoms gradually disappear;
- the rash turns pale and turns brown.
The elements of the rash begin to fade in the same order as they appeared, leaving behind pityriasis-like peeling and pigmentation.
On the fifth day after the rash appears, the child is no longer contagious and can attend childcare facilities. After measles, stable immunity develops; recurrent diseases are extremely rare and occur only in people with severe immunodeficiency.
Possible complications
What's scary about measles is its complications. Russian scientists have proven that the measles virus leads to the suppression of local and general immunity. Against this background, pathogenic and opportunistic flora begin to attack the weakened body.
More often, complications arise and are severe in young children, as they are very susceptible to bacterial infections. The baby is at risk:
- with malnutrition;
- with a lack of vitamins and microelements, in particular patients with rickets;
- having chronic foci of infection and various somatic diseases;
- bottle-fed infant.
Complications of measles are classified depending on:
- origin: own and secondary;
- terms of development: early and late;
- the organ that is affected (heart, lungs, eyes, brain, etc.).
Internal measles complications (otitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, diarrhea) will appear in parallel with the main clinical signs and weaken along with them. The exception is measles encephalitis. It develops on the third to fifth day after the first rash.
Encephalitis and meningoencephalitis are extremely rare. Inflammation of the brain can occur with any form of the disease. More often it is diagnosed in severe cases and in adult patients. Deaths with encephalitis reach 25%. During recovery, residual effects may persist (paresis, memory loss, dementia, etc.).
Secondary complications can occur during any period of the disease. Their consequences can be deadly. When they develop in the early stages, they are difficult, aggravating the course of measles. The occurrence of late complications is indicated by the persistence of temperature after the onset of the period of pigmentation or its new rise.
Secondary complications from the respiratory system often manifest themselves as laryngitis and pneumonia. Bacteria that cause inflammatory processes in the lungs: pneumococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus, mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Disturbances in the digestive system are often manifested by various stomatitis. A number of pathogens can cause intestinal inflammation (salmonella, shigella, staphylococcus, etc.). The clinical picture will depend on the characteristics of the microorganism.
The eyes, inner ear, skin, urinary system and other organs may be affected. If the etiological factor is identified in time and antibacterial therapy is started, the risk of negative consequences is reduced.
Important! If complications occur, the patient should be examined by a doctor. For emergency indications, hospitalization and treatment in a hospital are performed.
Treatment of measles in children
In mild cases, treatment of measles in children is carried out at home. The room must be ventilated and humidified. The sick child is provided with bed rest, plenty of fluids, lighting (dimmed lighting), hygienic care for the mucous membranes and skin, and nutritional therapy. Several times a day you need to wash your eyes and rinse your mouth with a soda solution. As necessary, you need to free the nasal cavities from mucus and crusts using cotton swabs soaked in Vaseline oil, and lubricate chapped lips with moisturizer.

Source: gstatic.com
Drug therapy is symptomatic. In the acute period of the disease, antipyretics, vasoconstrictor drops, expectorants, glucocorticoid hormones, and antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs are prescribed. For complications associated with the addition of a secondary infection - antibiotics, for psychomotor agitation - sedatives and nootropics. In case of hyperkinesis, anticonvulsants are prescribed.
If there is a high risk of complications, the patient is hospitalized.
After recovery, it is necessary to provide the child with a gentle regime, a balanced diet, and regular exposure to fresh air. School-age children should reduce physical and intellectual stress until full recovery.
Diagnostics
A doctor must diagnose the disease. Sometimes parents, after looking at a photo on the Internet of what a child with measles looks like, draw the wrong conclusions. They may confuse this pathology with other diseases. Incorrect diagnosis and erroneous treatment can lead to death.
Clinical and epidemiological data and laboratory tests are important for diagnosing measles.
The latter include:
- blood analysis;
- virus isolation by immunofluorescence;
- determination of antibody titer in the blood (immunoglobulins M and G);
- cytological examination (morphology) of a nasal smear or sputum.
An antibody test allows you to distinguish measles from other pathologies and determine the stage of the disease. Antibodies of class M are responsible for acute measles infection, IgG indicate a previous illness or that the person has been vaccinated. A general blood test will show a low level of white blood cells.
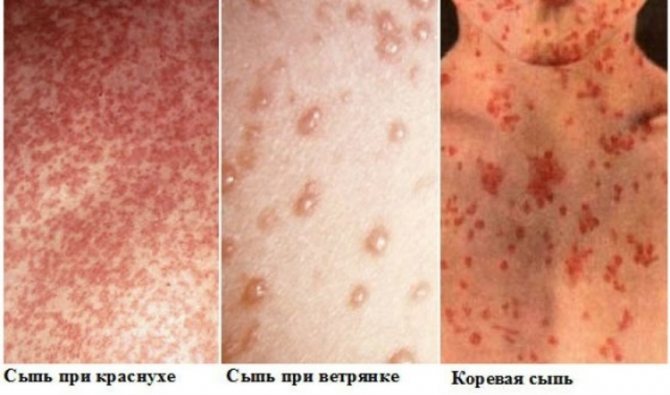
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases: colds, ARVI, allergies, urticaria, infectious mononucleosis, scarlet fever, rubella, chickenpox and other pathological conditions.
During the catarrhal period, measles should be recognized among other infections that are caused by a virus (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus or rhinovirus infection). During the period of rashes, a false diagnosis can be made, without distinguishing measles rash from enteroviral exanthema, drug-induced disease or scarlet fever.
The following features of the rash will help determine whether it is measles or allergies: elements of an allergic rash will appear first on one part of the body, then on another, changing their shape. They will be varied (spots, pimples, blisters, papules). They may hurt and itch. Itchy skin almost always accompanies allergies.
Treatment methods
In the treatment of patients with measles, an important place is occupied by the creation of conditions that exclude secondary infection and the development of complications. If the patient cannot be isolated or there is a severe form of the disease, the child will be in the hospital.
If the baby is at home, you need to minimize his contact with other people. It is important to provide proper care. Strictly monitor the hygiene of the patient and the room in which he will live during his illness.
At home, you should constantly wash your baby’s hands and face with baby soap, rinse your eyes with clean boiled water, and clean your mouth after eating (give babies more fluids to drink). During a fever, you should not break bed rest and swim. Nutrition should be complete and gentle.

There is no specific treatment for measles. Measles immunoglobulin can be given during the incubation period only to unvaccinated people with confirmed contact with a sick person.
Drug therapy is used depending on symptoms and complications. The doctor makes the appointments. He decides which product, how much and how often to use.
Important! Each medicine has its own contraindications, so any drug cannot be given (administered) without a doctor’s recommendation. This may harm the baby. For example, aspirin should not be used to treat measles.
- At high body temperatures, antipyretics are used (paracetamol, Nurofen, etc.). For purulent conjunctivitis, a 20% solution of sodium sulfacyl and similar drugs are dripped into the eyes. Do rinsing with strong tea or baking soda. It is recommended to treat the skin with synthetic tannin (Delaskin).
- Nasal congestion is eliminated using a 2% solution of protargol or vasoconstrictor drops. For purulent discharge, anti-inflammatory antibacterial ointments can be applied and physiotherapy can be performed. An obsessive cough can be cured using herbal decoctions and special mixtures.
- Bacterial complications should be treated with antibiotics. The doctor writes out a diagram indicating the drugs and their doses. Infants are prescribed medicine in the form of drops or suspension. Adult children are prescribed tablets.
- If there are sores on the skin, they need to be smeared with antiseptics and antimicrobials. Treatment of mucous membranes is carried out very carefully, especially in young children. The sooner antibacterial therapy begins, the greater the chance that the complication will be completely cured.
- Together with antibiotics, immunostimulants, vitamins (especially C and A), and antiviral drugs are used. It is possible to prescribe physiotherapeutic methods.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment at home includes the following traditional medicine recipes:
- Raspberry tea: 1 tbsp. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over dried raspberries and leave for about 30 minutes. Take 2-3 times a day, 150 ml with the addition of honey. The decoction improves immunity and fights high body temperature.
- Viburnum tea. Pour 1 tbsp into a glass of boiling water. dry berries. Let it brew for 5 hours. For a drink made from fresh berries, you need to mash 2 tbsp. viburnum and pour 1 tbsp. hot water. Drink 4 tbsp three times a day. Tea relieves inflammation and improves the patient’s well-being.
- Lime tea. In a water bath for 10 minutes. heat 1 tbsp. boiling water and 1 tbsp. dried linden flowers. Take half a glass before meals 2 times a day. The decoction reduces fever, eliminates cough, and fights intoxication.
- Decoction of tricolor violet. 2 tbsp. dried violets pour 2 tbsp. boiling water, place in a warm place or wrap in a blanket. Leave for about 1.5 hours. Pass the tea through cheesecloth. Take small sips throughout the day on an empty stomach. Violet inhibits the formation of new rashes, removes the virus from the blood, relieves abdominal discomfort, and fights high fever.
- Infusion of garden parsley roots. 1 tbsp. Finely chop the parsley root and add to 200 ml of boiling water. Place the broth in a warm place and let it brew for about 4 hours. Take 100 ml 4 times a day before meals. The infusion prevents stains from spreading throughout the body and removes toxins from the body.
Prevention
Nowadays, vaccination is considered the main preventive measure. A live measles vaccine (LMV) has been developed, which, along with Pentaxim (an analogue of DPT), is included in the vaccination table in accordance with the relevant order. The measles vaccination is given at one year of age.
There is no side effect in the form of a local reaction to the administration of the drug. A general vaccination reaction occurs in 10–13% of children as a short-term infectious process (mitigated measles). There is no risk of infection for contacts. It is extremely rare for an allergic reaction to occur.
Most people develop a strong immune response after the first vaccination. The second vaccination is given at 6 years of age. LCV can be used in preschool educational institutions as an anti-epidemic agent if a measles outbreak has been recorded. In this case, children two years old and older who have not had measles before, are unvaccinated and have no contraindications to vaccination are subject to vaccination. Those who were in contact with an infectious child no later than 5 days ago should be vaccinated.
Passive immunization (prevention with gammaglobulin) helps protect children who cannot be vaccinated from the disease. It is used to prevent the spread of the virus when it is introduced into children's healthcare facilities. Only children who do not have antibodies to measles can be protected in this way.
Important! Dr. Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky and authoritative representatives of world pediatrics advise getting vaccinated against dangerous diseases. Parents who refuse to protect their child through vaccination must understand that such a position threatens the health and life of their child.
Listen to his detailed opinion on this matter:
The rules of nonspecific prophylaxis are as follows:
- recognize the endemic situation;
- promptly identify sources of infection;
- isolation of sick people (from the onset of the disease to the fifth day of rash, if there is pneumonia, the period is increased to 10 days);
- act according to the protocol (the room where the patient was is ventilated for 30–45 minutes, no disinfection is required);
- Children who have been in contact with the source of infection and have not received gammaglobulin are subject to quarantine for 17 days; those who received it are subject to quarantine for 21 days;
- All preschoolers, upon admission to kindergarten, must provide a vaccination certificate and be examined by a doctor;
- place information stands “What is measles and why is it dangerous” with photographs and medical articles in preschool educational institutions and children's healthcare facilities.
You need to protect yourself from measles by getting vaccinated. This is an effective and safe way. If a one-year-old baby has contraindications for vaccination, contact with sick people should be avoided, since infection occurs through airborne droplets.
Have you vaccinated your child against measles?
- Yes 67%, 4 votes
4 votes 67%4 votes - 67% of all votes
- No, but I plan 17%, 1 vote
1 vote 17%
1 vote - 17% of all votes
- No and won’t 17%, 1 vote
1 vote 17%
1 vote - 17% of all votes
Total votes: 6
22.04.2019
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
If a girl or boy in the next building has measles, they will not pose a danger as long as they are not in close proximity. In close contact, infection will occur.
In recent years, cases of measles among adolescents and adults have increased. This indicates the need for serological testing to determine antibodies in older people.
Symptoms
Once a person gets measles, the virus multiplies in the back of the throat and gradually begins to spread throughout the body.
to show symptoms. The most common early symptoms are:
- Cold symptoms such as runny nose, sneezing and cough
- High temperature or fever
- Inflamed, conjunctivitis
- Sensitivity to light
- Gray-white spots inside the cheeks, mouth and throat
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Pain and illness
About three to four days after the first symptoms appear, a skin rash usually begins to appear. The rash is perhaps the most noticeable symptom of measles and is recognized by:
- Red-brown spots, flat or slightly raised, that may join together to form spots
- The spots usually start on the head and neck and then gradually spread down the entire body
- The rash may turn pale when pressed at first, but will gradually disappear and remain red when pressed.
- Mild itching
Typically, the rash covers the body for two to three days, taking a few more days to disappear, starting on the head and disappearing in the same order in which it appeared. Because other symptoms begin earlier, affected people usually feel most ill on the first or second day that the rash appears.
Symptoms of measles usually begin to appear on average 7-14 days after exposure.
In general, most people with measles feel better within seven to ten days after symptoms first appear. Sometimes a dry cough can persist even after all other symptoms have disappeared.
During measles infection, the immune system develops resistance to the virus. Therefore, it is extremely unlikely that anyone will get measles more than once in their lifetime.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Is it possible to walk with measles?
A sick child should not walk outside.
Is it possible to bathe a child with measles?
You cannot wash yourself or go to the pool while you are sick. It is dangerous to bathe a small child for several weeks after measles. A wet baby with a weakened immune system may again catch an infection or catch a cold.
Is it possible to get measles again?
You cannot get measles a second time. If a person has been ill once, the virus will be destroyed again by the antibodies of the immune system.
Can a parent get infected from a child?
The short answer is yes, it can.
Is it possible to protect yourself from measles with a disposable mask?
On this issue, doctors explain that a disposable mask does not provide absolute protection against the measles virus.