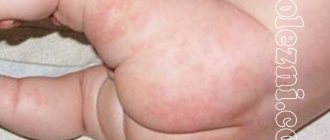
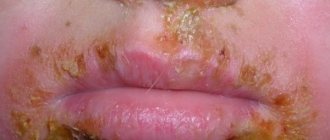
Allergy to the sun (solar urticaria) occurs in children at any age. Photodermatitis is increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. For characteristic rashes to appear, just walking in direct ultraviolet rays is enough. Solar urticaria affects children with fair skin, red hair and freckles. Diseases of the endocrine system, kidneys, and liver contribute to the development of photodermatitis. The illness may go away in one day, or it may drag on for a long time.
What is a “sun allergy”
“There is no medical diagnosis of “sun allergy”. There is a group of diseases “photodermatitis or photodermatoses” that appear with the participation of sunlight. When ultraviolet light hits the skin in the dermis, the radiation comes into contact with certain cell proteins and an antigen or allergen is formed. In response, rashes appear, as well as other symptoms,” says Elena. Essentially, this is an allergy, but not “to the sun,” but to the products of the interaction of UV rays with various substances in the skin.
On average, photodermatitis occurs in 20% of people. The rash may mark an autoimmune disease, be hereditary, or appear as a response to food or cosmetics. Of course, to find out the nature of the rash or other “sun troubles,” it is best to consult a dermatologist or allergist. But you can try to figure out whether you are dealing with an allergy yourself. If you are the victim of a complex of symptoms associated with sunny weather: rashes (such as solar urticaria), rhinitis and swelling, then it looks like an allergy. If you have a reaction to the sun, but two days later with the same insolation it is not there - perhaps it is just a skin marker of lupus erythematosus. But such fortune telling is not good for health. It's better to get tested.
Photodermatitis is often confused with phototraumatic reactions. Sunburn, large red spots due to insolation or radiation, elastosis, when the skin becomes rough, wrinkled, thickened and saggy, are also consequences of excessive contact with UV, but they are of the nature of injury, not allergies.
Treatment
It is recommended to treat allergies in children using traditional methods. When using traditional recipes, a child may have an unexpected reaction to herbs. However, if the skin rashes are isolated and you already have experience with the successful use of the plants used, compresses made from them will be very useful.
Drugs
Drug treatment for allergies involves taking antihistamines. For children they are produced in the form of drops. Taking such medications has a time limit of no more than 5 days.
The most common:
- Zyrtec;
- Zodak;
- Loratadine;
- Fenistil;
- Suprastinex.
Local ointments, gels, creams will help get rid of skin rashes and pain:
- Fenistil;
- La Cree;
- Advantan;
- Desitin;
- Wundehill;
- Gestan.
Enterosorbents will not be superfluous; they remove allergens from the body:
- Activated carbon;
- Smecta;
- Polysorb.
They are taken for 3-5 days.
During allergies, it is recommended to take vitamins A, B, E, C. Their deficiency can be compensated for with food or purchased in the form of tablets at the pharmacy.
Folk remedies
The first assistants to traditional methods of treating allergies are considered to be herbs and vegetables. Effective home recipes:
- Chamomile is used as a tincture, which improves the general condition of the body, and also as a compress to relieve inflammation;
- Nettle infusion relieves redness, itching and burning of the skin;
- Aloe compress restores the epidermis, cut it and apply it to the affected areas twice a day;
- Apply a mixture of potato and cucumber to the areas of inflammation;
- Use juice from squeezed cabbage and potatoes to wipe the rash;
- While bathing, add infusions of chamomile, string or valerian to the water.
All traditional methods are good in combination with drug treatment. Do not use unfamiliar traditional medicine. Children are not objects for experimentation.
Solar pigment and photodermatitis
Whether exposure to the sun will result in tanning, burns and rashes, or whether it will not affect you at all, depends largely on the production of melanin. This pigment comes in three types: eumelanins, pheomelanins - these are “coloring” pigments, and neuromelanins. The sphere of influence of this pigment is quite wide - “black” melanin is needed by the retina for clear vision, and neuromelanin is needed by the cytoplasm of the brain to protect against radiation. In matters of photodermatitis, coloring pigments play a major role.
When we are exposed to UV radiation, melanin prevents free radicals from destroying cells, creating a natural barrier - tanning. In the skin of mammals there are cells - melanocytes; melanin accumulates in them, and then spreads along branching processes throughout the epidermis, as well as the outer layer of hair and into the iris of the eye.
According to research, skin cancer is statistically less common in dark-skinned and dark-skinned people. Therefore, a boom in melanoma is occurring in the “white colonies” - Australia, New Zealand, and also in Europe. While Africa boasts low rates of this disease.
Previously, scientists believed that the darker the skin, the more melanin there is in a person's skin. But recent studies have proven that skin tone depends on the location of this pigment. And the number of melanocytes is approximately the same in everyone. In people with dark and black skin (indigenous Africans, for example), melanin is based in the upper layer of the epidermis. In addition, it has been proven that the darker the skin, the more painless it is to interact with the sun. In dermatology there is the concept of “phototype”. So people with skin phototype 6: with black eyes, hair and skin never get sunburned and can use moisturizer instead of sun cream.
Children "in the sun"
Infants suffer from photodermatitis extremely rarely. Most often these are birth defects, for example, albinism, when the body does not produce melanin at all. However, doctors still recommend 50SPF sun protection for children and not to be in direct sunlight from 10:00 to 17:00.
In children older than one year, the symptoms of an allergic reaction to the sun are:
- swollen lips,
- nasal congestion,
- itchy rashes on exposed skin.
In adults, you can see more manifestations of sun allergies. Symptoms, for example, may include conjunctivitis, dysfunction of internal organs, hypertrichosis (active hair growth unusual for this area of the body) and hyperkeratosis (thickening of the stratum corneum), photophobia and even neurology. As a rule, an allergy to the sun appears on the face, as well as on the entire upper half of the body.
Related topics
- “Allergies in newborns” can be a serious challenge for new parents. But if you follow all the recommendations of the pediatrician and allergist, then your baby will have a fulfilling childhood.
- We are all accustomed to the fact that various dairy products are necessary for the full development of a baby, but what to do if he has an allergy to milk? You will learn about this and much more from this article.
- When diagnosing any intolerance in a child, you need to know the symptoms of allergies in children, otherwise a false diagnosis can be made. But do not forget that only an allergist can do this.
- In modern pharmacology, there are many types of allergy medications for children, and depending on the individual diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment.
Dear mothers, leave your comments on the topic of this article. Tell us how your child’s allergic reaction proceeded? How did you fight this disease and what medications did you use?
Photodermatitis and female hormones
At risk are teenagers during puberty. Due to the hormonal boom, when there is active production of estrogen, progesterone and cortisol, the risk of photodermatitis increases in girls. They need to use creams with a high protection index. Also at this age, it is necessary to begin covering the mammary glands on the beach.
As for naked children at sea and in other situations, this is a psychological issue, says Elena. The genitals, like the whole body, can be irradiated with UV in boys and girls, of course, in moderation and with the use of sunscreen.
Mothers also need to take special care of themselves: women need a high level of sun protection a few days before and during menstruation.
Pregnancy and sun allergies
Pregnant women are extremely at risk of sun allergies. Measures as for infants: 50SPF cream, long sleeves and sun protection. The danger of a reaction arises due to hormonal changes in the expectant mother.
In pregnant women, the levels of progesterone, estrogen and melanocytes increase (which in turn stimulates the hormone melanotropin, which is responsible for the growth of the uterus, melanin production and metabolic processes). As a result, hyperpigmentation appears on the face and body, which intensifies in the sun. If you do not apply protection, the stains will persist for a long time. Excessive UV exposure can affect a child's health.
Why does photodermatitis occur?
Allergies to the sun on the skin appear for various reasons. Increased or unprotected insolation is not always to blame. In addition to hereditary and hidden diseases, rashes can be caused by substances in cosmetics and products. Among the common reasons:
- Medicines - not only ointments, but also systemic drugs, and most importantly - photosensitizers (this is a large group of drugs, for example, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, retinoids, barbiturates, antipsychotics, oral contraceptives and others). If you or your child have already had cases of photodermatitis, then when taking medications in the summer, it is better to consult a doctor. In addition, always study the instructions, advises Elena.
- Oil got on your skin, you came into contact with some plants (umbelliferous plants are dangerous, most of all hogweed). Other provocateurs are bergamot, rose and sandalwood oils, parsley and dill juice.
- Strengthen the skin's reaction to the sun and foods: carrots, celery and parsley.
- Chronic damage to the liver and kidneys adds to the chances of photodermatitis.
First aid
If alarming symptoms appear, you need to:
- immediately protect from ultraviolet rays, place in the shade;
- then you need to wash the skin with clean water to cool it a little and reduce the negative impact;
- you can apply a fabric compress to the affected area or spray it with panthenol spray;
- the child should drink as much fluid as possible and immediately take an antihistamine;
- You also need to measure your temperature and, if necessary, give an antipyretic.
If the redness does not subside, swelling or blisters appear on the skin, then you need to call a doctor.
Histamine and allergies
One of the common causes of delayed photodermatitis, for example, rashes a few hours or a day after sun exposure, is histamine intolerance. Under the influence of UV rays, solar urticaria occurs, then the effect of the allergen goes away. Histamine levels and concentrations in the blood decrease. But the body’s susceptibility to this substance remains high. As a result, hives symptoms may continue even without exposure to sunlight. This situation requires the intervention of a specialist.
A hypoallergenic diet recommended for photodermatitis and during treatment is also associated with histamine. There are products that are histamine liberators. For example, citrus fruits, chocolate, coffee, spices, alcohol - they increase the release of histamine from cells and, as a result, aggravate the course of any dermatitis. Therefore, your doctor will recommend that you avoid them during treatment and active sun exposure.
Preventing sun allergies
If you or your child are faced with photodermatitis, the doctor may prescribe, in addition to sun protection measures and regimen, drug treatment. An interesting way to combat this is “solar hardening” (you shouldn’t do it yourself). This is dosed UV radiation to create resistance to solar insolation.
Among the preventive measures, first of all, the prevention of excessive insolation. For example, you should not rush to sunbathe in the first spring sun. Despite the coolness, the sun's rays are already quite active, and during the cold season the skin has become “unaccustomed” to UV. And even treatment for solar urticaria, which is banal at first glance, may involve medication, so it’s not worth the risk.
The doctor may also advise:
- Give cosmetics and perfumes that trigger your rash, and select new products together with a dermatologist.
- Use SPF 50 cream, hats, umbrellas, sunglasses and light-colored, natural clothing with long sleeves. At the same time, make sure that there is no lack of vitamin D; it is best to continue preventive intake even in the summer.
- Avoid aggressive cosmetic procedures before sun exposure.
- Do not visit the solarium.
- Tattoos before summer and a seaside vacation are a bad idea.
- It is better to completely cover the body and mucous membranes when working in the garden, on the property and mowing the grass. Some plants, including meadow grasses, secrete furocoumarins; they settle on the skin and enter the mucous membranes, causing “meadow photodermatitis.”
Localization of the rash
As the disease develops, the localization of the rash is most often observed on areas of the body such as the face, forehead, and ears. But folds where sunlight does not reach, for example, the neck or the area behind the ears, do not suffer.
You might be interested in: Children's drinking yogurt Agusha
More often, allergies of this type appear with the onset of warm weather, that is, in spring and summer. Most cases of visiting a doctor with photodermatosis occur in May, June, and July. If a child is prone to illness, it is important for parents to especially closely monitor the condition of his skin in the spring and summer. In particular, this applies to countries with hot and dry climatic conditions.
I need to see a doctor
Despite the apparent simplicity of treating photodermatitis, it is worth going to the doctor. Because photodermatitis is not just a disease that significantly reduces the quality of life, like any allergy. This is a disease that, if left untreated, can cause a lot of complications. These are skin defects, disruption of internal organs, thrombosis and skin neoplasms.
- share with your friends!
Experts: Elena Vladimirovna Timoshina
Follow us on Facebook:
Diagnostics
The symptoms of photodermatitis are similar to the symptoms of almost any allergy, so you should not make a diagnosis yourself. If you notice signs of allergies in your baby, you should immediately consult an allergist. To detect an allergy before its symptoms appear, a specific area of the skin is irradiated with ultraviolet rays. This procedure will help identify photodermatitis. If the symptoms of this disease have already appeared, then there are no special tests to diagnose it. An allergist determines the type of allergy visually and using general urine and blood tests.