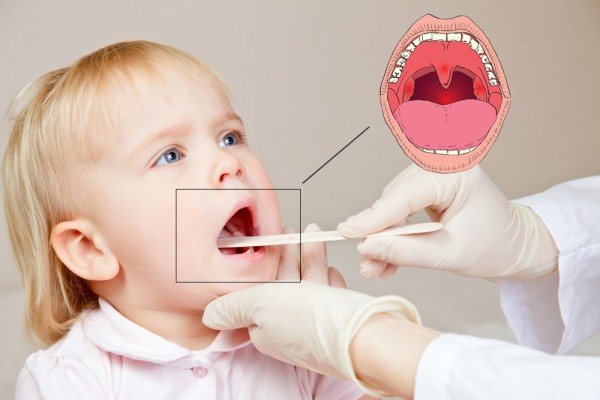
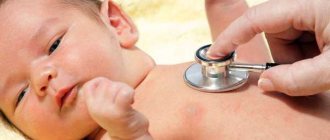
If you suspect a child has a sore throat, it is imperative to consult a doctor, because specialists have more opportunities to diagnose and prescribe adequate therapy. Parents need to remember that follicular tonsillitis in a child occurs in the event of a bacterial or viral infection. However, redness and plaque in the oropharynx are also characteristic of mononucleosis, stomatitis and diphtheria. Diseases of different etiologies require different approaches to treatment.
Follicular tonsillitis is one of the types of acute tonsillitis
In public clinics, the appointment resembles a factory assembly line: the standard time per patient is 12 minutes, as a result, the doctor sees 5 patients per hour. Doctors rarely manage to delve deeply into the problems of each visitor; there is simply not enough time to discuss many issues.
Pediatricians give detailed recommendations to mothers of children under one year old; as the baby grows up, they dwell less and less on the intricacies of child care. It is not surprising that parents are left with a swarm of questions in their heads about modern drugs and analogues, and possible complications of the disease.
The most common types of sore throat:
Catarrhal
A less severe version of the disease with simple treatment. The child feels pain and burning in the throat, it hurts him to swallow. The mucous membrane of the oropharynx is hyperemic, with a whitish coating.
Follicular
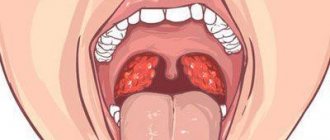
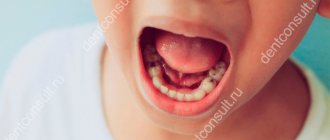
Purulent follicles appear on the palatine tonsils; they stand out against the background of swollen and reddened lymphoid tissue. Symptoms of general intoxication occur.
Most often, follicular tonsillitis develops after infection with streptococci and is accompanied by lymphadenitis.
Lacunarnaya
The appearance of yellow plaque in the lacunae of the palatine tonsils is characteristic. Severe sore throat, nasal voice.
If a child complains of a sore throat and neck, his temperature has risen, or his appetite has worsened, then it is necessary to call a local pediatrician at home. For less severe cases, you should make an appointment with a doctor and take a swab from the oropharynx. You may need to consult an ENT doctor.
Symptomatic therapy

Medicines for angina include the mandatory use of antipyretics, because this disease is characterized by a lightning-fast and persistent rise in body temperature. It is very difficult to knock it down until the plaque on the tonsils is removed.
Most often, antipyretic drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are used for this purpose. They are approved for use by children almost from birth and have a minimum of side effects and complications. In addition, medications from these groups have not only antipyretic properties, but also anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Thanks to this, the patient’s condition can be significantly alleviated, since one of the main symptoms of the disease is severe sore throat. If the temperature rises again some time after taking the drug, these medications should be alternated. You cannot use the same product more than 3-4 times a day.
Antipyretics can be used in any dosage form: rectal suppositories, syrup, tablets or capsules. It depends on the age of the child: it is more convenient for babies under 1 year to put candles, and for older children it is more convenient to drink syrup or tablets.
In parallel with the use of antibiotics, you need to take antihistamines: Fenistil, Cetrin, Suprastin, Loratadine, Diazolin, etc.
Since antimicrobial agents can cause disruption of the normal balance of intestinal microflora, it is advisable to use probiotics - Linex, Bifiform, etc.
Development of follicular sore throat
The infection enters the throat through airborne droplets, as well as through the use of shared utensils, towels, and other household contacts. During the cold season, the load on the lymphatic system increases. The risk of infection by viruses and bacteria increases. If a doctor diagnoses follicular tonsillitis in a 3-year-old child, then most likely the infection occurred due to contact with sick children in kindergarten or in the yard.
Symptoms of follicular tonsillitis:
- redness of the tonsils and palatine arches;
- feeling of dryness of the oral mucosa;
- temperature above 38°C lasts for several days;
- chills, general weakness, joint pain, headache;
- sore throat, gradually increasing pain radiates to the ear;
- enlarged lymph nodes, their pain on palpation;
- loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea.
Lymphoid follicles are responsible for the production of lymphocytes, macrophages and other local immunity factors. The formations are included in the structure of the tonsils and are scattered along the back wall of the pharynx. The average size of a follicle is about the size of a millet grain. They are filled with pus not immediately, but gradually. Pharyngoscopy at an appointment with an ENT doctor can reveal white-yellow or grayish formations in the tonsil area and changes in the pharyngeal ring.
Treatment of sore throat in children
Treatment of the disease depends on the nature of the pathogen. The body produces antibodies against the viral infection approximately 5 days after the first symptoms appear. It is mandatory to comply with bedtime at temperatures above 37.5°C. Is it best to discuss with a pediatrician whether it is possible to bathe a child with a sore throat? Water procedures are not contraindicated for children with normal temperature.
How to treat a sore throat in a 1 year old child:
- Antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, and antihistamine drugs are given to relieve symptoms.
- Immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs are used only as prescribed by a doctor in case of severe sore throat.
- Offer more warm drinks, preferably fortified.
- Irrigate the throat with chamomile infusion.
- They give Rotokan drops based on herbs.
Bacterial sore throat is treated with antibiotics appropriate to the type of pathogen and the age of the patient.
If a sore throat in young children is accompanied by an increase in temperature, then an antipyretic is given (at 38.1–38.5 ° C). A child who has previously had seizures is “brought down” to a temperature above 37.5°C. Parents doubt whether there is a sore throat without fever. The catarrhal form is easier, all symptoms are less pronounced. Temperatures may rise only in the evening.

It is recommended to give antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of syrup and use rectal suppositories at an early age. The medicinal components in such products are paracetamol or ibuprofen. Aspirin is contraindicated for young children. Medicine in the form of syrup may cause allergic reactions due to the presence of flavorings and flavoring additives. Candles are safer in this regard.
In combination with anti-inflammatory drugs, Fenistil, Zyrtec, Parlazin drops should be used. Antihistamines reduce irritation and sore throat and relieve other symptoms. The new generation of drugs does not have the hypnotic effect characteristic of Diphenhydramine and Suprastin.
In addition to systemic medications, local procedures are used, but to a limited extent.
Children aged 1 year do not yet know how to gargle or dissolve tablets. To relieve a sore throat, you can drink tea with linden blossom, chamomile, or rosehip decoction. Instead of rinsing, spray a soda solution onto the mucous membrane of the cheeks. Apply a dry bandage to the neck to warm the sore throat.
Treatment of follicular tonsillitis in children with antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs should be prescribed to the child by a pediatrician. The doctor selects antimicrobial agents based on the clinical picture of the disease, the results of a laboratory test of a throat smear and a general blood test. Symptoms and treatment of follicular tonsillitis in children depend on the infectious agent. New generation antibiotics reduce symptoms and shorten the duration of the acute period only in the case of bacterial tonsillitis. Antibacterial drugs will not help with viral infections.
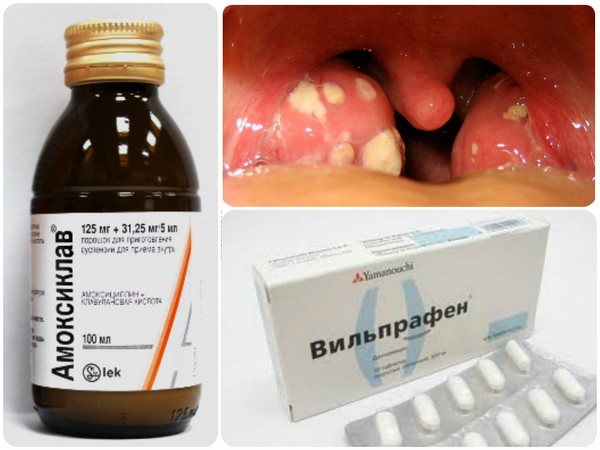
Treatment of acute tonsillitis in children and adults is carried out using substances belonging to three classes of antibiotics: penicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides. At the same time, the pediatrician recommends performing gargles, foot baths and other procedures at home to alleviate the condition of the little patient.
Penicillins have good bioavailability when taken orally. They suppress the development of streptococci, but they themselves need protection from bacterial beta-lactamases. Therefore, it must be taken in combination with clavulanic acid. Trade names of the drugs: “Amoxiclav”, “Augmentin”, “Amoxicillin”, “Flemoxin Solutab”. They are low-toxic and have less effect on the intestinal microflora than other groups of antibiotics.
Cephalosporins are also effective for acute tonsillitis. Trade names of drugs in this group: “Cefuroxime”, “Cefotaxime”. Macrolides are used to treat various types of sore throat in children. Effective and low-toxic drugs are Azithromycin and Sumamed.
It is convenient to use antibiotics in the form of a powder to treat children, which is diluted with water and given to the children to drink.
The drug "Sumamed" is popular due to its wide spectrum of antimicrobial action and short course of administration. Children over 6 months of age are given a suspension prepared from powder and water. The drug is prepared at the rate of 10 mg of the drug per 1 kg of body weight. Take the antibiotic, observing the frequency and order of administration indicated by the doctor. Manufacturers in the instructions for the drug recommend drinking the medicine once a day for 3 days.

It is better to entrust the solution to the problem of treating follicular tonsillitis in children not to one, but to several specialists. You can make an appointment not only with a pediatrician, but also with an ENT doctor, as well as the head of the pediatric department. Parents who heed this advice will notice the influence of the “human factor” on approaches to treating the same child.
Experts have different assessments of the importance of concomitant therapy: inhalations, gargling, compresses.
Antibiotic therapy should be carried out according to the schedule and doses determined by the doctor. Medical specialists constantly remind that improvement of the condition is not a reason to discontinue the antibiotic. The fact is that in order to suppress the infection, the concentration of the drug in the blood must reach certain values and be maintained for some time.
Treatment with antibiotics
Antimicrobial drugs are the basis of treatment for sore throat. After all, the cause of the disease is most often pathogenic microorganisms, which will be very difficult to cope with without antibiotics. Moreover, this disease can lead to the development of serious complications, such as tonsillitis, bronchitis, otitis, regional lymphadenitis, infection in the blood, the development of sepsis, encephalitis, damage to the heart, joints and kidneys.
As a rule, antibacterial agents for angina in children are prescribed in the form of a suspension. This will make it easier to take the necessary drug, especially if the child is small. In addition, this dosage form will ensure an accurate dosage of the drug. In some cases, the doctor may decide that it is necessary to prescribe additional topical antibiotics in the form of a throat spray. In severe cases, it is advisable to use injectable forms of antimicrobial agents.

Before starting treatment, it is impossible to know which microorganism triggered the development of the disease. After all, the results of bacteriological culture to determine the pathogen and its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents will be ready only in a few days, and treatment should begin immediately. Therefore, broad-spectrum drugs are prescribed, but taking into account the fact that most often the cause of the disease is streptococcus:
- First of all, penicillin-based antibacterial agents for sore throat are prescribed. These include Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, etc.
- In case of individual intolerance to antibiotics from the penicillin group, macrolides are prescribed. The most famous representatives are Sumamed, Clarithromycin, Hemomycin, Azicide, Erythromycin, etc.
- Drugs for angina from the group of cephalosporins are very popular due to their high effectiveness: Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, Cefotiam, etc.
Before using an antibiotic, it is necessary to conduct a sensitivity test so as not to provoke an allergic reaction to the drug and not worsen the patient’s condition.
The required dosage, frequency of use and general course of treatment should be prescribed by a specialist, taking into account the baby’s condition, clinical manifestations of the disease, the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant chronic diseases and a history of allergic reactions.
Traditional medicine recipes for a sore throat
Drinking plenty of water improves the child’s condition and maintains the water-alkaline balance in his body. It is recommended to prepare linden tea with raspberry jam or honey, chamomile infusion, and rosehip decoction for sick children. Raspberries and blackberries, which are no less valuable for treating throat problems, can be frozen or dried, and during illness, brewed and drunk as tea. This way, phytochemical compounds that are not resistant to heat are destroyed less.

A healer's recipe for treating a sore throat with lemon (chewing a slice of lemon) has been passed down from generation to generation. Small children may cough and choke on bits, so they are given tea with lemon. Syrup made from chopped green pine cones infused in sugar is good for colds and sore throats. You can replace it with pine decoction, but when heated, vitamin C is destroyed.
Rinsing with a solution of kitchen salt or baking soda “pulls out” pus from the follicles of the tonsils. A decoction of oak bark, eucalyptus leaves, and aloe juice diluted with water helps remove pus. An infusion of thyme and St. John's wort for gargling has a bactericidal effect. During the treatment of follicular tonsillitis in children, you should not give solid food or dishes with an irritating taste and smell.
Why does a child get a sore throat?
According to available statistics, sore throat is the most common disease among children in the autumn-winter season. The most susceptible to the disease are those children who do not eat well and eat not very healthy food. If a child rarely goes out into the fresh air in the village and is deprived of active games and training, you need to understand that any hypothermia is a great stress for his immune system. It is enough to take one sip of a cold drink or cool your feet once in winter, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the lacunae of the tonsils is inevitable.

List of all factors influencing the development of the disease:
- weakened immunity;
- poor, irrational nutrition;
- past viral infections;
- close contact with a sick person.
In view of all of the above, you need to constantly work on improving the child’s immunity: take him out into the fresh air, harden him, perhaps give him some medications for prevention, if the treating pediatrician confirms the advisability of taking them.
If your child does get sick, there is no need to despair. The main thing is to do everything correctly and in a timely manner. Often, parents may confuse a sore throat with the flu or a common cold, which can cause a delay in seeing a doctor. Let's try to learn to understand the difference and be able to distinguish the symptoms of sore throat from other diseases. How to understand that it is a viral sore throat in a child? What are its symptoms?
Catarrhal sore throat. Symptoms in children. Treatment
When a child suffers from catarrhal tonsillitis, the temperature does not rise too much, but the baby becomes lethargic, complains of pain during swallowing and mild nausea. With catarrhal tonsillitis, the inflammatory process is not very intense, so the use of antibiotics is not always appropriate. Antibiotic treatment is often replaced by a topical throat spray. Previous generations treated such sore throats exclusively by gargling with herbs. The main condition for children with catarrhal sore throat is bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and gargling. Treatment lasts about a week until complete recovery.
Treatment
Treatment of follicular tonsillitis takes place in a hospital setting and at home, depending on the child’s well-being. The disease can be quickly cured only with the help of antibiotics.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics must have reduced toxicity and high efficiency in suppressing bacterial flora. Antibiotics are taken as prevention against complications such as rheumatism. In the future, chronic rheumatic disease after a sore throat can provoke the appearance of severe valvular heart defects and give complications to the nervous system.
Antibiotics can be used both for home treatment and for hospital treatment.
The following medications are prescribed by specialists:
- First-line antibiotics are penicillins. It is necessary to take antibiotics for a certain period (10 days), in addition to treating accompanying symptoms. Among the best antibiotics we note Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Augmentin.
- Second-line antibiotics are macrolides. The most common home treatment is Azithromycin (Azitrox, Sumamed). The course of treatment is 5 days.
The doctor can determine how effective antibiotics are during the first 72 hours of the disease. It is determined how long the temperature lasts, how quickly it was lowered and how quickly the main symptoms were relieved. If treatment with certain antibiotics fails, medications from a different group are prescribed.
- Take note: Grammidin for red throat
It is necessary to take antibiotics (Azithromycin, Amoxicillin and others) even after the initial relief of symptoms. If you stop treating a child prematurely, the bacteria may develop resistance and, in the future, it will be even more difficult to treat the disease.
Symptomatic
How long is symptomatic treatment necessary? Until the symptoms completely disappear. Sore throat is very contagious, so the child must remain in bed, not go out and have more time to rest so that negative consequences and complications do not arise. At home, you should take not only antibiotics, but also remedies that will help quickly cure a sore throat.
The following tips should be followed:
- To reduce fever and pain, anti-inflammatory drugs - Nurafen, Ibuprom, etc. If allergic reactions occur, you can use antihistamines - Claritin, Cetrin, Clarisens, etc.
- Drinking regime and nutrition at home should be aimed at the patient’s recovery - it is necessary to limit the intake of solid food, and the temperature of food and liquid should be neither hot nor cold.
- Local procedures. To relieve swelling, you can use inhalation (aerosol) agents - Bioparox, Gevalex, Ingalipt, Hexoral, etc. Antiseptic treatment of the tonsils with Iodinol, Dolphin is recommended One of the best remedies is Lugol.