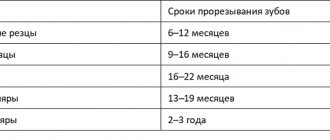
Lactation period - what is it?
Lactation is a natural physiological process of producing a specific nutrient - mother's (breast) milk. The lactation period lasts from the end of labor and the first attachment of the baby to the breast until milk production stops. According to research data and recommendations from obstetrician-gynecologists, a baby should be put to the breast immediately after birth.
Despite this, the mammary gland does not immediately begin to secrete milk immediately after childbirth. However, the mother’s body synthesizes colostrum, which is beneficial for the child’s body, and plays a huge role in the development of children’s immunity.
Lactation, as a physiological process, begins approximately 2-3 days after the end of childbirth. At this time, a woman may begin to experience uncomfortable and even painful sensations: pressure in the chest, enlarged mammary glands, slight nagging pain. This is a physiological norm.
From the moment breast milk appears, the baby should be put to the breast as often as possible. This is the only way that lactation can become quite stable. Neither pumping nor other methods will help establish stable lactation. Otherwise, there is a risk that the milk will go to waste.
14 to 21 days after birth, the next phase of the lactation period begins, the so-called “mature lactation.” In some cases, it may occur later - after 1-1.5 months.
During this phase, there is no longer a need to feed the baby as often as possible. Lactation is stable, which means the baby can be placed at the breast as required. The intervals between each subsequent feeding should be about 2 hours (at least). In the future, as lactation comes to an end, breaks should be increased to 4 hours.
Only in this single case will the entire period of breastfeeding be as comfortable and beneficial as possible, both for the child and for the mother herself.
What is lactation?
In simple words, lactation means the production of milk by a woman’s mammary glands. The goal is to be able to provide food for your child regardless of environmental conditions. This is an important evolutionary advantage of mammals, which includes humans. With milk, the baby receives the entire range of nutrients needed for health and growth - minerals, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, etc.
The lactation period begins during pregnancy. Women's milk flow ends in different ways. This depends on the intensity of the baby's breastfeeding and the general physical and emotional state of the mother.
Physiology of lactation in women
The mammary gland of a sexually mature woman consists of 15–25 segments of glandular tissue - this is where milk comes from. Each area is permeated with miniature vesicles - alveoli. They are covered with collagen membranes and penetrated by thin channels leading to the milk duct. Under the glandular tissue there is a layer of myoepithelial cells. Its function is to contract and thereby squeeze out nutritional fluid from the alveoli into the ducts, and then into the hole at the tip of the nipple.
The ability to secrete milk does not appear after childbirth, but earlier. When a woman becomes pregnant, she begins to increase the production of estrogen and prolactin. These hormones “trigger” the process of transformation of the mammary gland (this stage is called mammogenesis) - the thoracic ducts begin to grow rapidly, the glandular tissue increases. You can see in the photo how the breasts of pregnant women change - every month they seem to fill out, become larger and denser.
From the middle of pregnancy, fluid begins to periodically leak from the female breast. While this is not milk yet, it is colostrum - a secretion secreted by the gland. It is also excreted in the first days after birth - the baby needs this liquid to prepare the digestive system, because in the mother’s stomach the baby was fed through the placenta.
Theoretically, milk can begin to be produced quickly during pregnancy, but this process is inhibited by the increased content of progesterone. After childbirth, this hormone in the body becomes less and another participant enters the scene - oxytocin. It is under its influence that the production of nutrient fluid is established. An increase in hormone levels causes contraction of the myoepithelium, which squeezes milk through the ducts to the nipples, through which the baby absorbs it.
Some women worry why their periods don't return after giving birth. In fact, menstruation may be absent throughout the entire period of breastfeeding. This is how the body maintains the mineral composition of milk (after all, a lot of iron is lost in the blood, which the child may not receive enough). But to be sure that the absence of “red guests” is not associated with any pathology, it is better to consult with your gynecologist and undergo a full examination.
How long does the period last?
It is not possible to accurately calculate the duration of lactation. A woman produces milk as long as there are sharp releases of the hormones oxytocin and prolactin. Their production is stimulated, first of all, by the sucking process - which is why, when you wean a baby from the breast, the fluid comes in weaker and weaker until it disappears completely (this is called involution of lactation). The process stops completely approximately 40–60 days after the child’s last application to the glands.

If lactation is not specifically stopped, it can continue for another 2-3 years, until the child himself begins to lose interest in this method of feeding. There are cases when, with continued breastfeeding, intensive milk production lasted 5–7 years. But such long feeding is impractical.
Lactation without pregnancy?
Induction lactation is the name given to the production of milk by women who have not been pregnant or given birth. Appears after a psychological mood and prolonged mechanical stimulation of a woman’s nipples.
Nowadays, induction lactation is induced using specific hormonal therapy. It is assigned to those who take babies from a shelter or whose children were carried by surrogate mothers. As a rule, after a year of taking hormonal drugs and artificial stimulation of the nipples, milk comes in 95% of cases. If the process does not start, then the reason is most likely a psychological “block” (when a woman does not want to breastfeed) or pathologies of the mammary glands.
A little about lactation as a physiological process
As mentioned, lactation is a natural process during which the synthesis, accumulation and further release of a specific nutrient - mother's milk - occurs. Lactation is an extremely complex process. It is caused by the production of a number of hormones. The main active substance affecting milk production is the pituitary hormone prolactin.
It directly affects the mammary glands, giving them a “command” to produce milk. The intensity of production directly depends on the concentration of the hormone in the blood. Milk accumulates in the glands themselves and in the so-called milk ducts, through which the milk comes out.
Another hormone important for lactation is oxytocin. This active substance is intensively produced during the process of suckling by the baby of the mother's breast. When muscles contract, milk leaves the body faster. The hormone does not directly affect the intensity of milk production, but it helps it to be evacuated faster, which means it prevents stagnation of milk and the development of such dangerous complications as lactostasis and mastitis. In addition, oxytocin helps to contract the muscles of the uterus, and therefore quickly stop postpartum bleeding.
The first two to three days after birth, mothers do not yet produce milk, but colostrum is released. In some cases, colostrum begins to be synthesized during gestation.
It is important to keep in mind: during stimulation of the mammary glands, the hormone oxytocin is released, so women who have colostrum late in pregnancy should not express it. Oxytocin promotes uterine contractions and the onset of premature labor.
Colostrum is replaced by mother's milk approximately 3-5 days after the baby is born.
In the first days of life, colostrum is enough for the baby. You should not supplement your baby with formula milk or anything else.
How does lactation occur?
Stages of lactation
There are several stages in the formation of lactation, but only one of them is involved in the period of breastfeeding - lactogenesis. The process of milk appearance after the birth of a child is directly related to the hormones prolactin and oxytocin, which are responsible for the appearance of lactation. The first is responsible for the emergence of maternal instinct, when a woman begins to put the interests of her baby above all else.
By acting on the brain, prolactin provokes the onset of breast milk production, which is how lactation begins. The direct process of its release from the woman’s gland depends on the work of the second hormone.
The production of colostrum in the breast begins several weeks before the baby is born. During the first 7 days after birth, colostrum is completely replaced by milk, which is divided into early transitional, late transitional and mature.
It is important that its production occurs under the influence of prolactin and does not depend on whether the baby is put to the breast or not. The number of feedings affects the size of prolactin receptors, which adapt the breast to this process.
Formation and process of lactation
During the period of lactation, natural regulation of the amount of milk is necessary. To do this, you must feed the baby every 2-3 hours, including at night; you do not need to express milk after each procedure; it is also undesirable to use bottles and pacifiers. After 1-2 months, lactation is established and mature milk appears. This period is characterized by the following features:
- breast softening;
- filling and production of milk during feeding;
- lack of milk flow.
Thus, there is an understanding that lactation has stabilized.
Once lactation is established, hormones are no longer responsible for the production of nutritional product. Its volume directly depends on the number of applications and the baby’s diligence: the more the child eats, the more fluid will be produced next time.
It is necessary to approach the issue of breastfeeding responsibly. During this period, the mother’s body is weakened and the amount of milk produced directly depends on its condition. Lactation requires the mother to be attentive to herself.
Oxytocin, which is responsible for production, reacts to the physical and psychological state of the mother. Any worry or anxiety unconsciously inhibits the process of milk secretion from the breast, and lactation may be disrupted.
Sometimes there are cases when lactation must be stopped due to medications, illnesses and other reasons. Read the article How to stop breastfeeding painlessly.
Popular questions related to lactation
Is it possible to get pregnant during lactation?
In order to get pregnant, a certain hormonal background is required. During lactation, a woman’s body synthesizes hormones that inhibit reproductive function. These hormones are almost 100% likely to prevent re-pregnancy immediately after childbirth. The concentration of specific hormones in the blood increases the more often a woman breastfeeds her baby. Therefore, frequent breastfeeding reduces the risk of pregnancy during lactation.
However, in some cases there are exceptions. Thus, due to physiological characteristics, in some women (about 10% of the total) reproductive function is fully preserved even during lactation.
Other young mothers need to follow two recommendations to exclude pregnancy:
- You should breastfeed your baby at least 8 times a day. The maximum interval between feedings should be 4-5 hours. It is optimal to adhere to the above scheme and put the baby to the breast as often as possible.
- Do not introduce complementary foods ahead of time or give your baby a pacifier.
If at least one of the two requirements presented is not met, the woman should take contraceptives, since there is a high risk of another pregnancy.
When do periods begin after lactation?
Menstruation is the completion of a natural cyclical process during which eggs mature in the ovary and are released into the fallopian tubes, where they await fertilization, and the uterine endometrium prepares the “soil” for the future embryo. If conception does not occur, the “soil” is rejected and bleeding occurs. Menstruation, like pregnancy and lactation, is stimulated by specific female hormones.
During lactation, the pituitary hormone prolactin is actively produced. It is prolactin that is responsible for stimulating the mammary gland. At the same time, prolactin suppresses ovarian function, and eggs do not mature. This is what causes the inability to get pregnant.
For the same reason, the time frame in which the menstrual cycle returns to its normal “course” depends mainly on how often the woman breastfeeds and what the concentration of prolactin in the blood is.
If breastfeeding continues throughout the entire lactation period, we can talk about several months. As soon as lactation stops, the eggs mature again.
Therefore, keep in mind that when taking specialized medications and herbal infusions aimed at suppressing lactation (for reference, their action is based on suppressing the production of prolactin), as well as when breastfeeding is stopped prematurely, the menstrual cycle is restored much faster.
What to do if your nipple hurts during lactation?
When a baby is applied correctly to the breast, pain is extremely rare.
There may be several causes of pain and discomfort:
- A woman places her baby incorrectly to her breast. Most often, this problem occurs in inexperienced mothers. There can be many variations in this situation: incorrect posture, accustoming the child to the pacifier, as a result of which the child begins to suck incorrectly. The solution to the problem is very simple - seek help from a specialist. The best option would be a consultation directly in the maternity hospital, or with a specialized doctor. Relying on illustrated diagrams and pictures is not entirely reasonable, since it is impossible to track the process over time, and new errors may arise;
- Improper nipple care. Such a delicate anatomical structure as the nipple requires delicate and careful care. However, women often wash their breasts with aggressive substances (soap), treat them with alcohol solutions, etc. This is a big mistake. You need to select special care products and apply special creams to your nipples to prevent cracks and soften the skin;
- Cracked nipples. If the baby is not latched on correctly or there is insufficient hygiene, the nipples may crack. Cracks can also form for natural physiological reasons. (Cracks in the nipples during feeding - what to do, how to treat? Ointments, creams);
- Diseases and pathologies. The cause of pain in the nipples may be hidden in the presence of diseases. Lactostasis, mastitis, nerve damage, etc. In this case, the way to deal with discomfort is to get rid of the underlying disease.
What are the consequences of smoking during lactation?
Many women have such a harmful habit as addiction to nicotine. Even during pregnancy and lactation, a woman cannot give up cigarettes. It has been unequivocally proven that the quality of milk decreases, and, consequently, the effect on the child’s body if the mother smokes is incredibly harmful. To reduce the risk of developing pathologies during gestation, as well as to guarantee the normal development of the child, you can only completely give up smoking in advance. Reducing the number of cigarettes per day will not help here.
A child's consumption of milk from a smoking mother leads to the following consequences:
- Destruction of the nervous system. After the birth of a child, his nervous system still continues to actively form. Nicotine “hits” the nervous system, causing it to become overstimulated. The child becomes anxious, constantly fussing and crying. In the future, the development of severe neurological diseases is possible;
- Respiratory and immune system. Children who eat milk containing nicotine are more susceptible to developing allergic reactions, as well as diseases of the lungs and bronchi: asthma, bronchitis, etc. The reason for this is not only the consumption of poisoned milk, but also inhalation of cigarette smoke. The child becomes a passive smoker from the very first days of life;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. In almost one hundred percent of cases, when drinking milk containing nicotine, problems with the gastrointestinal tract develop, in the first stages they manifest themselves as colic. More severe pathologies are possible in the future;
- Immunity disorders. The immunity of children of smokers is significantly weakened, since the body spends all its strength fighting such an aggressive substance as nicotine;
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system. When consuming milk poisoned by nicotine, a child may develop hypertension, heart defects, arrhythmias, and a host of other dangerous pathologies.
Pumping during mature lactation
New mothers ask many questions at this stage: what is lactation in women in general, how to understand that it has become established, and many others. But the most popular of them are: is it possible, and if so, how to express milk during mature lactation.
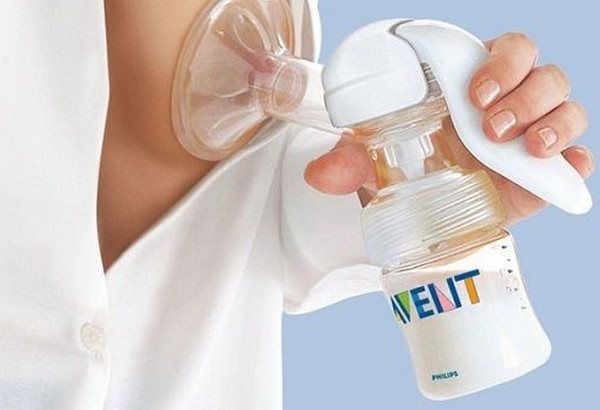
Young mothers need to know that during mature lactation, as much milk appears in the breast as the baby needs to be satisfied. And there is no need to express at this stage, because the process will not only lead to an excess of milk (hyperlactation), but can also provoke stagnation (lactostasis).
Important Sometimes a mother-in-law or other “experienced mothers” can give the wrong advice, which can actually lead to the loss of milk. It is best to consult a specialist and follow only his recommendations.
True, in certain cases, it is indeed possible, and even necessary, to resort to the process. Here is a list of the main reasons:
- excess or lack of milk;
- treatment of lactostasis and mastitis;
- when feeding a weakened or premature baby;
- if the mother cannot feed the baby (work)
How long should you breastfeed your baby?
There is no consensus, both among specialists and among experienced mothers, on this issue. Some believe that you need to breastfeed a child until 1 year, and after a year it is not advisable to do this, some continue feeding longer, and others generally believe that you need to feed a child as much as he wishes.
According to the recommendations of WHO and UNICEF experts, a child should be fed breast milk until two years of age and even longer.
The optimal solution is to feed the baby breast milk for at least the first six months of life. During this time, milk should become the baby's main source of nutrition. After six months, breast milk is no longer able to provide the baby with all the nutrients, and complementary feeding is required.
From the second year, the child begins to eat almost like an adult. In the first and second years of life, milk plays the role of a factor supporting growth and development, but is not absolutely necessary. Moreover, nowadays it is not difficult to choose a high-quality milk formula. Despite this, there is no absolute replacement for breast milk.
Benefits of long-term breastfeeding
There are several advantages of long-term breastfeeding:
- High level of nutritional value. Breast milk is rich in all necessary substances and replacing it, especially in the first months of life, is extremely difficult;
- Stimulation of immune development. Mother's milk promotes the production of specific immunoglobulins;
- Reducing the risk of developing diseases caused by allergies. According to scientific research, the risk of developing allergies is lower in those children who have been fed breast milk for a long time. In addition, mother’s milk itself is not rejected by the child’s body and does not cause an immune reaction;
- Formation of correct bite and development of facial muscles. The sucking reflex contributes to the development of facial muscles and proper bite;
- Optimal physical development.
When should you stop breastfeeding?
You should not stop breastfeeding in two cases:
- If the child is sick or unwell. Children recover faster if they are fed breast milk. With it, children in ready-made form receive the substances necessary to fight the disease, and the body’s immune system itself is strengthened;
- During the hot season (late spring, summer). During such periods, food spoils faster, and the risk of developing poisoning is much higher. Therefore, breast milk is an optimal and complete food product in summer.
Stages of lactation
The formation of the lactation process takes place in several stages, at each of which the woman’s body produces a special type of milk.

At each stage of lactation, milk differs in color and composition.
Colostrum
Colostrum appears in the first 2–3 days after birth, and begins to be produced in the mammary glands already during pregnancy. Some women notice the appearance of colostrum very early - at 13-15 weeks. But even if you didn’t notice anything during pregnancy, this does not mean that you won’t have milk.
As soon as the mother's body is freed from the placenta, the brain gives the mammary glands a signal to produce the first milk - colostrum. It differs from mature milk in its yellow color, high calorie content, and abundance of proteins and minerals. Colostrum contains all the necessary enzymes, antibodies, hormones and other substances that contribute to the development of immunity in the newborn. Colostrum, unlike milk, is not so much, but due to its high calorie content and protein content, the child feels full even after a few drops.
It is very important to put your baby to the breast as soon as possible after delivery. The success of the lactation process, the formation of immunity in the baby and the development of its digestive organs depend on this.
Transition milk
On days 3–4 after birth (sometimes a little later, on days 5–7), transitional milk appears. A woman has a hot flash. The breasts become significantly larger, firmer and hot to the touch. During this period, it is necessary to prevent the formation of lactostasis (milk stagnation).
To avoid stagnation, you need to feed your baby more often. These days it is also advisable not to drink a lot of liquid, so as not to cause excess milk production. It will be difficult for a newborn to latch onto an overfilled breast. Before you start feeding, express some milk from your breast and then give it to your baby. If after feeding you feel that there are hard lumps in your breasts, try to knead them and express the liquid to prevent the development of congestion and inflammation. It is convenient to use a breast pump to express milk. Transitional milk is produced within 2–3 weeks. It contains less protein than colostrum, but more sugars and fats.
Mature milk
Mature milk appears 2–3 weeks after birth. It contains all the necessary substances in ideal proportions for the growth and development of the child. Interesting Facts:
- More than 80% of mature milk is water, so infants do not need to drink water in most cases.
- Mature milk contains a large amount of carbohydrates, including lactose, which promotes good absorption of calcium and iron and helps the baby’s digestion.
- Breast milk fats are suitable for the newborn's body, are easily digested and are an important component for the development of his brain.
The composition of milk will differ at different stages of the same feeding. At the very beginning, the baby receives foremilk. It is more liquid and contains more carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. At the end of the feeding, the baby will receive higher fat and high-calorie hind milk. Thus, the baby quenches thirst with foremilk, and hunger with hind milk. At each feeding, it is necessary to ensure that the baby sucks the breast completely, without depriving himself of nourishing hind milk.
Menu for a young mother to increase lactation
To increase the quantity and quality of breast milk, the mother needs to adhere to a proper diet and consume a number of foods in large quantities:
- Tea. Green or black tea promotes more active milk evacuation;
- Bread with cumin and bran. Cumin seeds increase the amount of milk produced. During lactation, preference should be given not to plain bread, but to bread with bran or caraway seeds;
- Compotes and decoctions from fruits. Decoctions and compotes from dried fruits or fresh berries help increase the vitamin value of breast milk. They should be consumed as often as possible;
- Clean boiled water. Pure boiled water helps increase the volume of milk and at the same time reduce its viscosity. This will help not only the child, but also the mother, as it will reduce the risk of lactostasis;
- Nuts. Walnuts, pine and almonds. You need to limit yourself to 1-2 nuts per day. Only in this case the quality of milk will increase. In large quantities, nuts can harm the baby because they cause gas formation and persistent constipation;
- Herbal teas. Dill, chamomile, etc. contribute to calming the child’s nervous system and its further normal development;
- Lactogonic products. Milk, kefir and other fermented milk products, low-fat cheeses (Adyghe cheese, feta cheese), soups with low-fat broths, vegetables and fruits;
- Fresh juices: carrot, berry;
- Barley decoctions. They also increase the amount of milk produced;
- Radish and honey salads. However, large quantities of radish should be avoided. Radish can cause increased production of intestinal gases in an infant;
- Hercules, oat and buckwheat porridges, or dishes containing these cereals;
- Watermelons and melons;
- Vegetable salads with vegetable oil.
Based on the presented list of products, a nursing mother must independently choose a diet based on her gastronomic preferences. It is important to adhere to the principle of moderation.
Find out more: What can a nursing mother eat?