Any problem related to the health of a newborn causes concern among parents. Mucus in a baby's stool often causes panic, especially if mom and dad are still completely inexperienced. However, first you need to correctly assess the circumstances that have arisen in order to determine the cause of the unpleasant symptom. To do this, you need to know what is a reason to immediately visit a doctor, and what is a natural physiological process, why such symptoms occur, and what normal feces should look like in a child.
Problems with a baby’s stool often become a cause of concern for parents.
Causes
The following factors can trigger the problem for both guys on breastfeeding and artificially trained ones:
- Introduction of complementary foods. Often, diarrhea and mucus in the stool are explained by the introduction of new foods into the diet, for example, vegetable puree. To reduce the manifestation of a negative reaction, it is worth giving up the problematic product for a while or reducing its share in the diet;
- Diseases of the digestive system. In such cases, it is necessary to analyze the intestinal microflora;
- The natural formation of mucus in newborns is explained by transient dysbiosis. No treatment is required here;
- Diseases of the respiratory system (very rare). For example, when you have a runny nose, part of the mucous secretions that form in the nose is swallowed and then ends up in the feces.
- Taking certain medications (most often these are anti-bloating drugs, such as Espumisan, Bobotik);
- Gluten deficiency.
Interesting. At birth, the gastrointestinal tract of infants is sterile. Soon the baby begins to drink mother's milk, then various microorganisms enter his intestines. In the first month of life, a certain microflora with a predominance of lacto- and bifidobacteria should form. During the period when there is a “fight” between beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms, the child experiences transitional stool. The greenish color of stool and the presence of mucus in it are not signs of the disease.
Mucus in the stool of an artificial child
Stool with mucus in a one-month-old breastfed baby most often indicates inappropriate nutrition. The baby most likely cannot digest the selected product normally for the following reasons:
- allergic reaction;
- any component included in the mixture is difficult to digest;
- a sharp transition to a new type of nutrition (from breastfeeding to IV) or a new mixture.
On a note. Often there is a cumulative effect: in the first weeks there are no visible negative signs, but then it becomes more difficult for the body to absorb the wrong product, and then it is simply impossible not to notice the problem.
Mucus in stool during breastfeeding
Mucus in the stool of a breastfed baby can be caused by the following problems:
- Mother's milk is not sterile. A special analysis helps to establish this fact. In this case, feeding is usually not interrupted, and mother and baby are prescribed a course of therapy.
- Lactase deficiency.
- Mother's diet. Mucus in this case is a sign of intolerance to certain foods by the child’s body. The baby may have an allergic reaction to one or another component (most often it is sweet, fatty, fried, flour). If normalization of the diet does not produce positive results, a blood test for the presence of allergens (MAST test) is recommended. Finding out which product caused a similar reaction in the baby will not be difficult with the help of a food diary.

The appearance of mucus in the stool of babies may be associated with improper nutrition of the nursing mother.
Signs of dysbiosis
This is the most common cause of bowel problems in newborns. This condition occurs when pathogenic bacteria (staphylococci, clostridia, etc.) begin to predominate in the microflora.
A mild form of dysbacteriosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Constipation;
- Flatulence;
- Colic;
- Mucus in stool.
In advanced situations the following are observed:
- Diarrhea;
- Lumps of curdled milk in stool;
- A large amount of mucus;
- The presence of blood streaks in the stool;
- In rare cases, pink or red mucus (indicates damage to the walls of the digestive tract).
Dysbacteriosis requires complex long-term treatment. The first stage is the sanitation of the baby’s intestines, the second is the restoration of microflora.
Important! To prevent relapse, it is necessary to provide the child with proper feeding and careful care.

Colic, abnormal stool and mucus in the stool may indicate dysbiosis
Enzyme deficiency and gastrointestinal immaturity
A newly born baby is not yet able to digest food in the same way as adults. The child's intestines are underdeveloped and do not have all the necessary enzymes to digest food. This is why there may be some mucus in the baby’s stool. This phenomenon is of a natural physiological nature, so parents should not worry. During this period, you need to be more careful with the introduction of complementary foods and carefully monitor the condition and reactions of the child’s body.
Advice. If the situation does not improve or, on the contrary, worsens, it is better not to rush into introducing new foods into the baby’s diet.
Lactase deficiency
The lactase enzyme makes possible the fermentation of lactose contained in milk. In certain cases, babies have a congenital deficiency of this enzyme. Thus, milk cannot be properly absorbed by the body; when the product enters the intestines, fermentation processes begin. As a result, the child experiences symptoms such as:
- Stomach ache;
- Flatulence;
- Loose stools;
- The presence of lumps of milk and a small amount of mucus in the stool.
An accurate diagnosis can be made by testing for carbohydrate content in stool. Therapeutic therapy comes down to a special diet that completely excludes dairy products. A child on breastfeeding is prescribed a course of medications containing lactase. For artificial drinkers, a mixture is selected that does not contain lactose.
Acute intestinal infections
Mucus in the stool of newborns often becomes a sign of a viral or bacterial intestinal infection. The most common diseases of this kind are:
- Stomach flu;
- Dysentery;
- Salmonellosis.
With these and other similar pathologies, elements of mucus in the stool indicate inflammatory processes occurring in the intestines. To exclude dysbacteriosis and establish the presence (or absence) of a bacterial or viral infection, it is necessary to conduct a special analysis by stool culture.
Recommendation. Babies under one year of age who experience noticeable changes in their stool should be seen by an infectious disease specialist. If the doctor insists on hospitalization, it is better to agree to eliminate the risk of serious consequences.
If you suspect dysbacteriosis or infection, you must submit your stool for analysis.
Diarrhea and blood discharge
Sometimes a child may have diarrhea with mucus and streaks of blood. The most common cause of bloody spots in the stool is hemorrhoids, but in early childhood this is a rather rare occurrence. But still, such a reason cannot be excluded, since in rare situations, even in a child 8 months or less, dilation of the veins of the rectum can be observed, which causes diarrhea with mucus and blood.
Bloody discharge during diarrhea with mucus in a 10-month-old child can be caused by the fact that pathogenic strains of microorganisms live in the intestines, which disrupt its normal functioning and also lead to the formation of cracks in the rectum. Typically, blood in the stool indicates damage to the skin or mucous membrane of the anus, as well as dilation of the hemorrhoidal veins.
What should parents do?
What can cause diarrhea in a baby?
If parents notice mucus in the baby's stool, it is recommended to visit a pediatrician. A specialist will help determine the cause and recommend a suitable solution. In most cases, parents are quite capable of coping with this problem:
- Change the mother's diet if she is breastfeeding (avoid flour, fried, smoked, spicy, sweet).
- If the child is bottle-fed, then choose the appropriate formula for him.
- Do not rush to introduce complementary foods.
- After the above measures have been taken, monitor the child’s condition for several days.
- If the mucus was clear and not white, the parents' actions may be effective and the problem will go away. However, in any case, it is recommended to visit a pediatrician for an examination and advice.
Important! You should not resort to self-treatment with medications and other means without consulting your pediatrician.
When is an ambulance needed?
In a situation where yellow diarrhea with mucus is observed in a baby, you should immediately call an ambulance, because the consequences of the symptom may be unpredictable in case of complications. In any case, it is better to entrust the child to specialists, because... treatment at home can not only be ineffective, but also, on the contrary, harm the baby. It is necessary to call an ambulance if the child experiences clammy sweat, chills and severe vomiting, fever, green or yellow stools, severe pain, pale skin and general weakness.
When to go to the doctor
In most such cases, parents do not need to worry. The appearance of mucus in the stool of an infant indicates a disruption of the digestive tract. Deviations may be caused by excessive stress on the children's intestines.
Loose stools in a breastfed baby
The presence of white mucus in the stool should alert parents. In this situation, a visit to the doctor is mandatory. The doctor can determine the following reasons:
- White mucus may indicate inflammatory processes in the infant’s gastrointestinal tract;
- Dysbacteriosis that has developed as a result of taking antibiotics or other drugs;
- Allergy to a particular food product;
- Lactase deficiency;
- Helminths.
Note! There is no way to avoid a medical examination if the presence of white mucus in the stool is accompanied by frequent colic, sleep disturbances, restless behavior of the child, and constant crying.
If a baby has liquid, green, foamy diarrhea with blood clots, urgent medical attention is needed.

Lactase deficiency often causes mucus to appear in children's feces
If a one-year-old baby or older child, in addition to mucus in the stool, experiences diarrhea and elevated body temperature, you must call an ambulance.
Yellow jelly-like mucus in a baby's stool indicates inflammatory processes. This shade is formed due to a large number of leukocytes and pus impurities.
In such cases, parents should pay attention to the following signs:
- The stool has a strong putrid odor;
- The color of the stool is unusual for this child;
- Mucous, heterogeneous stool in infants includes large fragments;
- Bloody impurities are noticeable in children's poop;
- A large amount of mucus.
Important! Dark, black or red-brown mucus in the stool indicates internal damage.
Urgent medical attention is required.
Why does diarrhea with mucus appear?

In order to cure a child’s disorder as quickly as possible, it is necessary to establish what exactly triggered the development of the ailment. The most likely cause of loose stool mixed with mucus in children is poisoning from poor-quality food, medications, and poisons.
Complementary feeding can also become a provoking factor, leading to the appearance of diarrhea with mucus in the child. Unusual food irritates the intestinal mucosa and is not completely digested; foods rich in fiber, consumed in large quantities, increase peristalsis.
Milk, wheat, juices and purees can provoke allergic reactions in infants, which also lead to stool liquefaction. Even from mother's milk, a baby can develop diarrhea if the baby has congenital lactose intolerance.
They can lead to loose stools and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: impaired production of hydrochloric acid, low fermentation.
Pediatricians identify the following diseases that provoke mucous diarrhea:
- Rotavirus infection.
- Salmonellosis.
- Dysentery.
- Helminthiasis.
- The presence of dysbacteriosis.
- Inflammatory processes affecting the stomach and duodenum.
- Cold.
[adsp-pro-2]
Sometimes an imbalance of microflora leads to indigestion, accompanied by the release of mucus in the stool. Diarrhea with mucus occurs if the baby is overfed. The opposite situation may also be true: due to the artificially maintained long interval between feedings, the baby often experiences a feeling of hunger, which leads to digestive disorders. The functioning of the baby’s intestines is also affected by an increase in body temperature that occurs during colds, infections, and teething.
Taking medications
How to collect feces from a baby for analysis - how much is needed for a coprogram
If it is not possible to visit a doctor immediately, the baby can be given Smeka or probiotics. Mucus in the stool is not a pathology, but only indicates a specific problem associated with a malfunction of internal organs. Therefore, it is not the effect that needs to be eliminated, but its cause. Treatment may be as follows:
- If the baby gets sick with bronchitis, ARVI, pneumonia, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs.
- Dysbacteriosis is eliminated with antiseptics and probiotics.
- If intestinal infections occur, a course of antibiotics or antiviral drugs is prescribed.
- Antifungal agents are used to eliminate thrush.
- For intestinal inflammation, glucocorticoids and sulfalazines are prescribed.
- Erosions and ulcers are treated with healing, painkillers.
- For pancreatitis, medications containing digestive enzymes are prescribed.
Important! In each individual case, the course of treatment is prescribed individually.
Features of newborn stool
Normal baby stool may vary in its characteristics due to the fact that the child’s gastrointestinal tract is only adapting to environmental conditions, as well as to the type of feeding (breast or artificial).
The first bowel movement should occur immediately after birth (within 24 hours). This type of stool is called meconium, which is black in color and has a “tarry” consistency.
Green, orange, brown, yellow stool in a baby, as well as combinations of these colors, are normal options. The consistency of stool can vary from liquid to “mushy”, while hard, “fixed” stool, which adults are used to seeing in themselves, is a negative sign for a child and a reason to contact a pediatric gastroenterologist.
The frequency of bowel movements in infants depends on the number of meals; Usually children of this age have a bowel movement immediately after eating.
Let's take a closer look at what impurities parents can find in a newborn's feces:
- Undigested leftover food. They appear when the baby’s diet is incorrect, i.e. if the nursing mother does not maintain an adequate diet, or if the child eats food inappropriate for his age (insufficiently crushed or untimely introduced complementary foods);
- Streaks of blood are a good reason to see a doctor; this may be a sign of hemorrhage in the lower intestines;
- White lumps of the mother's breast milk fraction that have curdled. Their presence indicates that the baby is overeating, and his enzyme system is not yet sufficiently formed to digest significant volumes of incoming food;
- Foam may indicate a functional disorder; in large quantities, it may indicate an intestinal infection;
- Slime. This impurity can be caused by a number of reasons and requires more detailed consideration.
Doctor Komarovsky about intestinal infections
According to the famous pediatrician, Evgeniy Komarovsky, the appearance of mucus in the stool of an infant is a natural reaction of the body to the introduction of complementary foods and the addition of new products to the standard menu. The doctor does not recommend that parents worry too much about changes in the smell, color and consistency of stool, since in the first months of life the baby’s digestive system is just getting started. It is for this reason that symptoms may occur in the form of mucous discharge in a child’s stool.
On a note. In the first year of life, the main indicators of a baby's health are optimal weight gain, good sleep and moderate activity. If the baby’s growth and development correspond to the listed standards, then the mucus in the child’s stool should not bother the parents.
If suspicious situations arise, a reputable doctor recommends:
- Stop panicking.
- Carefully monitor the baby for 3-4 days.
- If the changes affected only the composition of children's feces, then nothing needs to be done. When the baby’s digestive system improves its functioning, the unpleasant symptom will disappear on its own.
- If the baby is not yet ready to accept “adult” food and is breastfed, it is necessary to adjust the mother’s diet.
- Call an ambulance immediately if you notice liquid, foamy, green diarrhea mixed with blood clots.
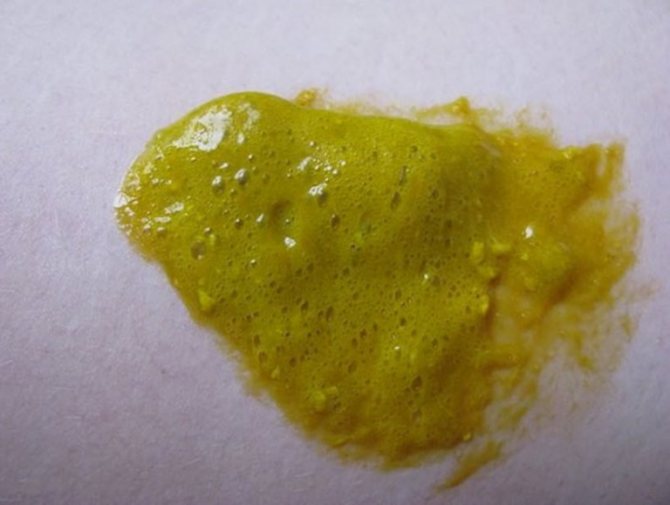

Green, foamy stool that has a liquid consistency is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
So, if a baby poops mucus, but there is very little of it, and it appears rarely, then there is no serious reason for concern. If an unpleasant symptom makes itself felt with every bowel movement, accompanied by a sharp unpleasant odor and other negative manifestations (sleep disturbance, diarrhea, bloody spots in the stool, frequent regurgitation), then we can talk about certain disturbances in the functioning of the child’s internal organs. In this case, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
What does it look like
The consistency of a newborn baby's stool is thick, viscous (tar-like), and black or black-green in color. A few days after the baby is born, the stool changes its color to gray-green, and a month later - to yellow. Evidence of normal microflora is the presence of a sour smell of feces and the presence of a small amount of mucus impurities. A lot of mucus in a baby’s stool signals the body’s protective reaction to the pathological process occurring in it.
If, after a newborn has pooped, jelly-like mucous patches, streaks, or a noticeable lump of mucus, clearly different in consistency from feces, is observed in his feces, you need to pay attention to the color of the discharge. The color depends on the enzymes produced and can indicate the reason for their increase. The presence of pathological processes is indicated by:
- deterioration of the child’s condition, decrease in activity and rate of weight gain;
- bad breath;
- stench of feces;
- sleep disturbance;
- diarrhea, constipation.