Physiology of snoring
The main physiological cause of snoring in both children and adults is a mechanical obstruction that occurs in the respiratory tract. This phenomenon contributes to the disruption of natural air circulation. The role of such an obstacle is often played by:
- Uvula, the natural size of which is increased.
- The palate itself, if its muscles lose their former elasticity.
- Enlarged tonsils.
- Adenoids.
Important! In rare cases, even an incorrect bite in a child can interfere with normal air circulation in his nasopharynx. However, it is strictly not recommended to consider such a deviation as the norm.
A dangerous phenomenon in which the nose breathes, but the child snores, is considered to be the child’s tendency to have epileptic seizures, which can manifest itself both from birth and after suffering psychological trauma. This condition must be treated immediately, since epilepsy in an advanced stage can provoke apnea.
Diseases of the nasopharynx
Sometimes snoring may not be so dangerous if the nature of its occurrence is related to the consequences of a previously suffered pathology of the ENT organs. Indeed, as practice shows, after a sore throat, pharyngitis or tonsillitis, the child’s tonsils remain enlarged for some time, preventing normal air circulation in his nasopharynx.
Enlarged tonsils and tonsils can be identified not only by touch, but also by the accompanying symptoms characteristic of such a deviation. For example, if a child sleeps with his mouth slightly open, and his nose is stuffy (but there is no snot in it), then this is a clear sign of enlarged adenoids, which make it difficult for the baby to breathe in his sleep.
The relationship between snoring and adenoids
Inflammation of the adenoids in children is not a rare phenomenon. This inflammatory process occurs exclusively in the baby’s nasopharynx, causing swelling of the tissues in this area. And the resulting swelling, in turn, becomes the cause of enlarged tonsils, which impede normal air circulation.
Therefore, many parents see a solution in surgical removal of adenoids from their baby’s nasopharynx. But even such treatment is not always able to guarantee a 100% result, due to possible relapses:
- The appearance of an allergic reaction after the operation. Such a relapse can occur not only as a result of medical negligence, but also under the influence of hereditary factors.
- Untimely removal of adenoids. If such an operation is performed too early, the baby may experience serious breathing complications, which will cause further snoring.
- Careless removal of tonsil tissue.
However, you should not ignore enlarged adenoids, since this is a very serious problem for babies that can cause hypoxia in them.
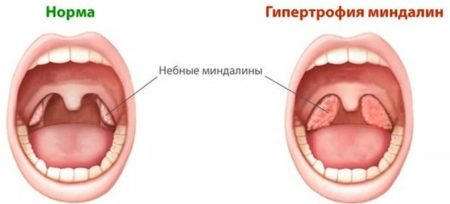
The danger of rochnopathy in children and adolescents
Depending on the volume and intensity of snoring, you can determine the harm it causes to the baby’s body. For example, if a child snores very loudly, and the frequency of manifestations of this deviation is frequent, then parents have reason to worry. Since all of the above signs are the initial mechanism for the development of apnea. If snoring occurs rarely, in the initial stages of sleep, then this phenomenon can be considered safe for the child’s health.
Why does a child snore in his sleep?
Approximately 10-14% of children aged 2-6 years snore during sleep. Is this normal or pathological? Why might a child snore?
The mechanism of children's snoring. Uncomplicated and complicated snoring
At the moment of inhalation, air enters the mouth or nose, goes through the pharynx into the larynx, then into the trachea and then through the bronchi into the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
If there are no obstacles in the path of the air stream, breathing is silent. Snoring occurs when the lumen of the pharynx narrows, and its walls begin to touch, and even hit each other when breathing. It is the vibration and beating of soft tissues that give the effect of snoring. If you notice that your child snores while sleeping, know that this is not normal. With uncomplicated snoring, air enters the airways with every breath, so the oxygen supply to the lungs is not impaired. But 1-2% of children develop complicated forms of snoring . Such children snore in their sleep, and they periodically experience pauses in breathing lasting 10 seconds or more. This condition is a disease and is called obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, or OSA for short.
It would be very indicative to recall one clinical example. Several years ago, a woman contacted us, whose child for a long time could not be diagnosed with apnea syndrome and prescribed treatment... You can read more about this in the letter of gratitude that she wrote after successfully solving the problem.
Child snoring: is it dangerous?
Only a doctor can determine sleep apnea syndrome during a special polysomnographic examination. If a child snores in his sleep, and at the same time he has obvious sleep apnea, the situation is definitely serious. The brain and all internal organs of the sleeper experience oxygen starvation. If the problem is ignored, the patient’s sleep at night and general well-being during the day worsen. Very often, such children develop attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, they do poorly at school, and lag behind their peers in physical development .
Causes of snoring in children
The most common cause of snoring in a child is enlargement of the pharyngeal (adenoids) or palatine tonsils (usually this occurs with chronic tonsillitis). Overgrown lymphoid tissue creates a mechanical obstacle to the air flow. At night, when the muscles of the pharynx relax for natural reasons, its lumen narrows so much that snoring and even stopping breathing occurs. If the reason lies in the enlargement of the tonsils, then, as a rule, the child snores after a cold, when he still has inflammatory swelling of the pharynx.
The second most common reason why children snore in their sleep is childhood obesity. If you are overweight, adipose tissue is deposited not only in the subcutaneous fat, but also in the soft tissues of the pharynx. As a result, its lumen narrows, and snoring occurs.
The third reason for snoring in children is the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the skull bones. A child with a small, posteriorly sloping lower jaw snores much more often than children with a normal facial structure. This feature may be genetically determined, or may be a consequence of long-term nasal breathing impairment.
If a child aged 2-10 years has difficulty breathing through his nose and breathes through his mouth, then he gradually develops a “bird face”: narrow, with not pronounced cheekbones, a strongly protruding nose with a hump, crowded teeth and a small lower jaw. Such changes in the structure of the skeleton develop secondarily, but pose a threat of not only snoring, but also OSA. This is explained by the fact that in people with a “bird face” there is a persistent narrowing of the airways at the level of the pharynx.
Snoring associated with a cold
The appearance of snoring during acute respiratory infections is a common situation.
When you have a runny nose, the nasal mucosa swells and swells - nasal breathing worsens, which in itself can provoke snoring. In addition, the body’s natural reaction to respiratory infections occurs - activation of the lymphatic system, which can manifest itself in enlargement (hypertrophy) of the palatine or pharyngeal tonsils. Hypertrophy of the tonsils, especially against the background of existing adenoids, additionally provokes snoring during illness. If a child snores after a runny nose, this may indicate the formation of adenoids or chronic tonsillitis. Parents should take their child to an ENT doctor.
Snoring in newborns
Children in the first days of life can also snore, but this is most often the norm. The cause of snoring is the narrowness of the nasal passages. In this situation, we can recommend that parents carefully clean the crusts from the child’s nose using cotton wool. This will make his breathing easier. If the child is already 1-2 months old and continues to snore, you should definitely visit a doctor to determine the cause of this condition.
Unfortunately, an ENT doctor does not always have the necessary equipment to diagnose snoring and OSA. If following his recommendations does not solve the question of why the child snores in his sleep, the surest step would be to contact a specialized sleep center in your city for consultation.
If you live in Moscow or the Moscow region, you can get the necessary help with snoring, OSA and any sleep disorders in a child at the sleep medicine center of the Barvikha sanatorium. The center employs qualified somnologists who will conduct the necessary examination and determine why the child snores. Depending on the causes of the condition, treatment will be carried out that will relieve the little patient from snoring and all the problems associated with it.
You can read more about why a child snores in his sleep and what to do about it in the practical recommendations: “Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in adults and children.” On the site you will also find information about snoring and apnea in adults and their treatment.
Specialists will be interested in watching the following video about the causes and mechanism of apnea development in patients of different ages.
SleepNet.ru>
Symptoms accompanying snoring
Snoring in a child never appears without accompanying symptoms, since this phenomenon is considered a consequence of some disease or abnormality. Common symptoms of snoring include:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose. The nasal passage may be clogged with mucus resulting from inflammation of the tonsils. When breathing through the mouth, the baby may develop a cough due to an acute lack of air.
- Frequent awakenings in the middle of the night. Older children may also talk about nightmares that bother them.
- The appearance of nasality in the child’s voice. This happens because the baby’s nasal cavity is clogged and cannot pronounce many sounds normally, which affects the intelligibility of speech.
- Hearing impairment. With a strong enlargement of the tonsils, the child’s auditory tubes will partially overlap, which will worsen the perception of sounds.
- Open mouth in a dream. With a clogged nasal passage, children will experience an acute lack of oxygen, which they will compensate by breathing through the mouth.
Important! Prolonged ignoring of the above symptoms of snoring can cause serious deformation of the child’s skull. And this deviation can manifest itself: in a broken bite, a narrowed nasal passage, or even in the visual features of the face.
In severe cases, the baby may also experience symptoms of oxygen starvation (chronic fatigue, deterioration of memory and perception of information, prolonged apathy, periodic headaches and dizziness). But with such concomitant symptoms of snoring, it is better for parents to seek medical help from specialists.
The main causes of children's snoring
Adenoids
In some cases, one of the most common causes of snoring is a pathological process associated with the pharyngeal tonsil. With weakened immunity, it grows and reaches sizes that interfere with unhindered inhalation and exhalation. In the second stage of adenoids, children snore at night and breathe with their mouths open during the day. This disease must be diagnosed by an otolaryngologist. And treatment can proceed both conservatively and surgically.
Diseases of the nasopharynx
Sinusitis, sinusitis, laryngitis, and other similar diseases inevitably lead to snoring during sleep. Mucus and inflammation reduce the opening through which air is inhaled. Snoring that occurs for this reason disappears with recovery.
Presence of a foreign body in the upper respiratory tract
If a child accidentally inhales a small object, then in addition to snoring, pain in the nasal passage and headache may occur. At the slightest suspicion of such a situation, you need to go to the emergency room, where the doctor will make a diagnosis using X-rays.
Allergy
In most cases, allergies cause swelling of the larynx, thereby making breathing very difficult. If you suspect an allergic reaction, you need to identify the allergen. In a living space, this could be food, animal dander, indoor flowers, carpets, dust, cleaning products or mold. Congenital pathology of the structure of the skull and nasopharynx.
Obesity
Excess weight leads to the formation of a layer of fat on the internal organs, which can make breathing difficult.
Deviated nasal septum
Deviation of the nasal septum, resulting from injury or congenital. It entails breathing problems and can be treated surgically.
Uncomfortable body position during sleep
The air is too dry
Dry air in the room where a child sleeps can also lead to nighttime snoring. The thing is that such air acts on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, drying them out. As a result, crusts may form that can block part of the respiratory lumen.
Nasal polyps
These benign neoplasms appear in children for many reasons - the specific structure of the nasal cavity, asthma, sinusitis, heredity, rhinitis. The danger of this disease is characterized by the difficulty of diagnosing it. At the initial stage of development of the disease, it can be mistaken for a runny nose or ARVI. Gradually, the polyps grow, blocking the nasal sinuses, while the sense of smell disappears, the auditory canals are blocked, and the blood supply is disrupted. To diagnose this disease, rhinoscopy is performed.
Asthma
Asthma may be one of the causes of children's snoring.
Epilepsy
The disease is diagnosed in childhood in 75% of cases. The attacks occur during sleep, while the patient makes sounds similar to snoring. Apnea syndrome can occur in an epileptic person during snoring, which is dangerous due to respiratory arrest and death.
How to cure snoring in a child?
Treatment for snoring can be divided into only two types: medical therapy and folk remedies. The first type of treatment is used in cases where the symptoms of snoring in a child include: sleep apnea, prolonged insomnia, mental disorders, or other signs of serious disorders associated with the ongoing pathology.

If the child snores, but there is no snot, and you are sure that he is completely healthy, then the second type of treatment comes into force - traditional medicine. It usually consists of choosing the right pillow for the baby, as well as choosing a suitable sleeping position (on the side or on the stomach).
How is epilepsy related to severe snoring?
Very often, epilepsy causes a feeling of fear and panic in patients, which, in turn, increases adrenaline in the blood. Due to this change, the intensity of a person’s breathing also increases significantly, and when inhaling through the nose, he may sniffle loudly or even snore. If you do not consult a doctor in time, the epileptic seizures will intensify and may well lead to death.
Therapeutic methods for dental pathology
If, after a medical examination, it turns out that the cause of snoring in a child is dental pathology, then the situation can be corrected through therapeutic dentistry. This medical branch includes a lot of modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment using fluoride or calcium. Moreover, all operations performed are practically painless and safe.
Other types of snoring treatments
In addition to the above therapy, special nasal drops help to cope very well with snoring in children. Sprays are able to completely clear the nasal passage, allowing the baby to calmly inhale oxygen deeply. This will not only relieve your child from snoring, but will also reduce the chance of sleep apnea or hypoxia.

Important! Nasal drops should be used no more than twice a day: in the morning and in the evening (before bed). Otherwise, the medicine may burn the baby’s mucous membrane, causing him significant discomfort.
Also, another painless method of combating snoring, which can be used for children over 1 year old, is oral gymnastics. Exercises aimed at toning the muscles of the palate and nasopharynx will allow your child to get rid of snoring in just 1-2 weeks, and due to the significant expansion of the nasal passages, it will become a little easier for him to breathe at night while sleeping.
Treatment of snoring in children
In children, snoring must be eliminated by treating the cause of its occurrence. There are medical and surgical methods of treatment, as well as with the help of folk remedies and special physical education.
We recommend: Cough in a child in the morning
The medicinal method consists of prescribing:
- rinsing the nasal sinuses with saline solutions or products based on sea water;
- vasoconstrictor drugs to eliminate swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- antihistamines to relieve allergic reactions;
- antiviral drugs if swelling is caused by viral nasal congestion;
- anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics (at the discretion of the doctor);
- irrigating the throat with ready-made antiseptics, suitable for age, to relieve swelling of the tonsils caused by the proliferation of bacteria.
Surgery may be required to remove adenoids or polyps. It may also be necessary to correct the nasal septum, but only starting in adolescence. Surgeries are performed only if drug treatment does not produce visible results.
As a treatment with folk remedies, you can try:
- drip carrot juice diluted with water or aloe juice into your nose;
- steam your feet with the addition of mustard powder;
- rinse your nose with a solution of table salt and water;
- make an infusion of a tablespoon of rose hips and 2 cups of boiling water, give to the child throughout the day;
- make tea with raspberries or linden.
Before using folk remedies, you need to make sure there are no allergies. The effect of them usually occurs no earlier than 10-14 days from the start of treatment.
The following exercises aimed at improving respiratory function are suitable as physical therapy:
- breathe deeply, while turning your head to the sides (repeat 2-3 times on each side);
- inhale deeply, inflating your stomach to the limit, then slowly exhale (5 times);
- close 1 nostril with your finger, inhale and exhale 6 times, then repeat the same with the second;
- place your palms on your shoulder, take a deep breath, stretch your arms as high as possible and lower yourself (6-7 times);
- inhale, arms forward, then bend low and exhale loudly (5 times).
It would not be a bad idea to change your pillow to an orthopedic one, because perhaps the reason lies in the incorrect position of the head during sleep.
Psychosomatics of the disease
Many people believe that snoring is more characteristic of men than women. But such a judgment is fundamentally wrong. After all, the pathology of snoring can occur equally in both sexes, with the difference only in the age category (snoring occurs earlier in males).
At the same time, rhochnopathy also has individual psychomatics, which is explained by the lack of treatment with medical drugs. After all, snoring is most often treated with traditional therapy, and in rare cases, through surgical intervention. Most people are generally inclined to believe that snoring does not interfere with their lives, simply ignoring its manifestation.
Genetic predisposition
In some cases, rhonopathy occurs in children as a result of a genetic predisposition, which includes the following factors in the development of pathology:
- Congenital narrow neck.
- Malocclusion.
- Abnormally enlarged adenoids.
- Predisposition to diseases that cause rhonopathy (allergies, asthma, sore throat, etc.).
Unlike pathologies that cause snoring in children, genetic predisposition cannot be controlled. And most often it has to be treated surgically.
Doctors' opinion about children's snoring after ARVI
As the famous pediatrician E.O. said. Komarovsky (author of a video blog about medicine):
“Children’s snoring can occur as a result of just two main reasons - enlarged adenoids and the presence of mucous secretions in the child’s nose, which can clog his airways. In order to determine whether it poses a threat to the baby’s health, you should understand its course in advance.”
However, as for snoring that occurs after suffering from an acute respiratory viral infection, as a rule, it does not pose any danger to the child. Moreover, this condition goes away on its own. It should also be noted that snoring after ARVI does not occur in all children, and its occurrence can be prevented through banal prevention.
Prevention of childhood rhonopathy
Preventive measures for children’s snoring differ significantly from those for adults, and include the following measures:
- Clearing mucus from the nasal passages using wet wipes.
- Carrying out special gymnastics to tone the muscles of the throat and palate.
- Changing your sleeping position. If you snore, it is recommended to sleep exclusively on your stomach or side.
- Adjusting your diet.
Having considered the reasons why a child snores at night but there is no snot, we can draw conclusions about whether to take the child to the doctor or try to solve the problem through traditional medicine. After all, snoring in childhood does not always indicate serious abnormalities, which means raising a panic ahead of time does not make sense.