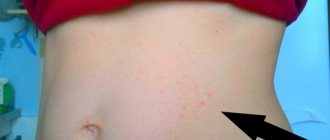
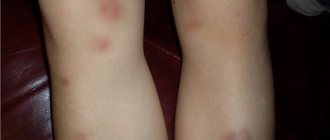
Facial swelling in children is a cause for concern
The danger of swelling in the area between the eyebrows is the risk of breathing problems. Also, inflammation can spread from the frontal sinuses to the brain due to its close location. In addition, the inflammatory process can spread to the eyes with the appearance of severe symptoms and dangerous complications.
Pain and burning, breathing problems cause stress in the baby, which negatively affects the nervous system. A hysterical state aggravates the course of the disease. Breastfed babies have difficulty sucking and breathing at the same time when they are swollen, so they may become malnourished and not gain weight. A weakened child gets sick longer and has a harder time recovering.
Inspection and first aid after an impact
If a child hits his head and a lump quickly begins to form at the site of the injury, you need to remain calm and provide first aid. The most dangerous areas of the skull are the temporal and occipital lobes. In these places, the bones are thinner, and a large number of nerves and blood vessels pass through here. Impacts to the frontal bone are less dangerous and in most cases pass without consequences.
A large bump on the forehead can frighten any parent, so it’s worth knowing in advance how to give your child first aid:
- the best method to relieve pain and prevent the appearance of an extensive hematoma is a cold compress (you can put ice, but not on the skin, but on a piece of tissue);
- You should not pour cold water on your child’s head - the effect of this procedure is low, and it can cause inflammation of the ears;
- if an abrasion occurs during an injury, it is treated with hydrogen peroxide or other available antiseptic;
- you need to monitor the child’s well-being - decreased coordination of movements, nausea and drowsiness are the first signs of a concussion.
Falls are especially dangerous for infants, since the bones of the skull are not yet strong enough and cannot fully protect the brain from a concussion.
The first aid scheme does not differ from that needed for older children. A head injury in a newborn must be shown to a specialist. To make sure there are no serious injuries, your doctor may order an encephalogram.
Why is the bridge of my nose swollen?
Swelling of the bridge of the nose is usually a manifestation of an inflammatory process, which can have many causes:
- Inflammation of the nasal mucosa (infectious, vasomotor, allergic rhinitis). In the acute phase, swelling is noted, in the chronic phase, tissue growth occurs due to pathological cell division (proliferation).
- Sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses). Its types are sinusitis (inflamed maxillary sinuses), frontal sinusitis (frontal sinuses are affected), their combination with inflammation of the ethmoid bone (frontoethmoiditis, maxillary ethmoiditis).
- Foreign body inside the nose. The area around it becomes inflamed, the body reacts with an accumulation of white blood cells (pus).
- Injury to the bridge of the nose. When struck, a hematoma (consequence of internal bleeding) and swelling with blue (sometimes black) under the eyes occur.
- Congenital or traumatic curvature of the nasal septum or anatomical narrowness of the canals. The breathing process is difficult, the mucous membrane easily becomes inflamed and swollen.
Swelling can occur due to hormonal dysfunction, incorrectly selected drops or ointments, problems with the kidneys, blood vessels, and heart. The symptom is often accompanied by discomfort in the nose (dryness, burning). In some cases, the ability to perceive odors is lost.
Swelling is a consequence of injury
Damage to soft tissue and blood vessels can occur due to impact or fracture of the bones of the nose and upper jaw. Bone fragments further destroy them, preventing rapid healing and reducing swelling. A comminuted fracture may require surgery. After this, the bones are fixed for several days by packing the nose. Sometimes, when the jaw bones are fractured, the lips are fixed with staples and the patient is given only liquid food.
For any injury to the nose, it is advisable to take an x-ray to check the condition of the bones. A fracture that does not heal properly will cause breathing problems and recurring swelling in the future. If the nose is injured, cold should be applied to the damaged area to prevent swelling.
Foreign body in the nose
When a small child explores the world around him, he “tastes” things - he tries to put them in his mouth or nose. These can be small parts of toys, peas and even tablets. In nature, insects, poplar fluff or dandelion seeds can get into the nasal passages. When swimming, microorganisms living in the water can crawl in. The task of parents is to organize the space for children in such a way that small objects and medicines are out of their reach. It happens that during medical procedures a fragment of a tampon or a piece of an instrument remains in the nose.
The presence of an object in the nose impairs the ventilation of the sinuses, leading to an inflammatory process (even suppuration) and swelling. If the object is not removed for a long time, polypous tissue growths, dysfunction of the lacrimal process, suppuration and swelling of the conjunctival sacs are possible. The presence of a foreign object can be indirectly determined by the release of exudate from the affected nostril.
Complication of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis of viral or bacterial origin often occurs in children during seasonal epidemics. Children attending nurseries and kindergartens are especially susceptible to them. They occur in combination with rhinitis and sinusitis, cough, and fever. Inflammation of the conjunctiva and nasal mucosa can cause swelling of the eyelids and nasal area. The baby's condition is aggravated by a painful and uncomfortable eye condition.
If a child is prone to allergies, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimal sac and nasal sinuses often occur simultaneously. The child's eyes become swollen and the bridge of his nose swells.
Inspection of the injured area and first aid to the child after an impact
If a child falls and hits his head, an initial examination should be performed immediately. A hard landing on the asphalt may be accompanied by external damage - scratches, abrasions on the forehead. In this case, they should be treated with hydrogen peroxide. If the skin is not broken, the injury is assessed in stages:
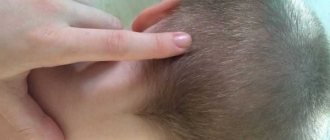
- A lump indicates a bruise of the soft tissues of the head (we recommend reading: why does a lump appear on a baby’s head?). As a rule, in children it disappears within 1-2 hours.
- A hematoma may form at the site of injury - its appearance indicates damage to the blood vessels. However, a bruise can also occur due to a crack in the skull, which is much more dangerous.
- Severe bleeding and a deep wound are a reason to call an ambulance.
After examining the bruise, ice should be applied to the child's forehead. Its pieces should be wrapped in a clean cloth (handkerchief) and pressed onto the affected area for 10-15 seconds. Then take a short break (5-10 seconds) and press again. Instead of ice, you can use a chilled spoon, frozen meat or other cold object. The procedure should be carried out within a quarter of an hour. Usually these actions are enough for the lump to disappear, and the hematoma to become smaller and resolve faster.
Other causes (tumors, skin diseases)
Sunburn, frostbite, and exposure to hot air can also cause swelling on the forehead. It will pass when damaged cells are regenerated.
In adolescents, at the onset of puberty, the sebaceous glands produce excessive amounts of sebum. This often occurs on the face, especially the forehead. When the sebaceous gland cannot cope with the removal of fat, a cyst or atheroma (a bag of sebum) appears under the skin, which looks like swelling. Sometimes cysts transform into abscesses, and in their place boils filled with pus appear.
Swelling on the forehead and bridge of the nose can be caused by a bone growth (osteoma), a fatty deposit (lipoma), or a basal cell tumor on the skin of the forehead and nose (carcinoma). Tumors of various etiologies, cysts in the nasal area cause narrowing of the respiratory passages from the inside and swelling from the outside.
Main and accompanying symptoms
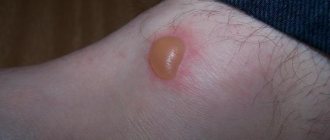
A lump on the forehead can be detected immediately after injury or within the first few hours. At first, the skin will acquire a red tint, then fluid will begin to accumulate in the subcutaneous tissue, which will form dense swelling. This fluid enters the intercellular space from blood vessels - their walls are damaged when bruised. The contents of the lump can be dense or liquid, and when palpating the impact area, the patient complains of pain.
A lump can appear on the forehead even after a minor bruise; it goes away with the use of special ointments in a few weeks. If a child is hit hard and feels severe pain, it is necessary to monitor his well-being. A number of symptoms may indicate a concussion, and they may appear several days after the injury:
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- blurred vision, appearance of black dots in the visual zone;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fainting.
If the lump does not go away for a long time and becomes dense, this should be a reason for a full examination.
A mobile or inactive formation that does not change in size and causes pain on palpation often turns out to be an encapsulated hematoma - a clot of coagulated blood in a capsule. Some patients are diagnosed with post-traumatic osteomas - benign bone growths that form after a severe injury. Such pathologies can only be cured surgically.
Who should I turn to for help?
If swelling of the bridge of the nose and forehead rapidly progresses, you should immediately call an ambulance, because there is a risk of blocking the airways and stopping breathing. The formation of a swelling after an impact requires a visit to a traumatologist and an x-ray. In other cases, you should contact your pediatrician - he will prescribe the necessary tests and, if necessary, refer you to specialists.
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, graduated from Samara State Medical University with a degree in Pediatrics. Read more »
Associated symptoms after hitting your head
If the head impact was not too strong, there may be no associated symptoms at all. In case of an unsuccessful fall, the following manifestations are possible:
- Redness of the skin.
- Abrasion or wound.
- A lump is a swelling at the site of impact measuring 3-5 cm. A larger size requires the intervention of a specialist.
- Hematoma is a bluish discoloration of the skin caused by damage to blood vessels. A bruise, unlike a bump, does not appear immediately, but within 1-2 hours after the incident.
- Pain at the site of the injury, aggravated by pressure.
- Sometimes, 2-3 days after hitting the forehead, the child develops blue discoloration under the eye above which he received the bump.
How long does it take for a hematoma to disappear after an impact?
If a child hits his forehead, a lump may appear at the site of the injury, which will resolve within 1-2 hours. However, there are cases when the compaction does not go away for a long time - up to several days or even weeks. Very rarely, complications arise after an injury, and the lump does not go away without the intervention of a surgeon. The doctor may recommend performing a puncture - using a syringe to remove the contents of the tumor. However, first you should try to get rid of the hematoma on your own.
In general, when a bruise occurs, blood vessels are damaged and burst. Blood flows out of them. On all parts of the body except the head, it is absorbed into the subcutaneous layer of tissue, which leads to a characteristic change in the color of the skin in the bruised area and the appearance of a bruise. This layer of fiber is almost absent on the head. There is nowhere for blood to be absorbed from the burst vessels. It flows directly into the space between the scalp and the bones of the skull. A lump appears on the head. The more blood has accumulated at the site of the bruise, the larger the size of the lump.