How phimosis manifests itself in boys: symptoms and methods of treatment Many parents notice phimosis in young boys, but not all adults know that it is important to constantly monitor the condition of the genitals. The head of the penis is covered by the foreskin; attempts to open it cause pain. Sometimes the skin duplication is so dense that serious urological problems appear and inflammatory processes develop.
Parents of a newborn boy should know what to do if the baby's head of the penis is not exposed. Panic and confusion are bad helpers after identifying a sensitive problem. According to statistics, physiological phimosis in children occurs in more than 90% of boys under 1 year of age. The article describes the causes, types, and methods of treating phimosis in boys of different ages.
Classification
It should be understood that phimosis is not a disease, but a special condition that is associated with the physiological characteristics of the body (age), heredity and damage to the tissue of the foreskin. In this regard, the following forms of phimosis are distinguished:
- Physiological – occurs in most boys before the onset of puberty, and is associated with the functional maturation of the preputial cavity. It is not a pathology and resolves on its own after 7 years.
- Pathological – occurs as a result of inflammation, injury, metabolic disorders and requires treatment;
- Hypertrophic (proboscis);
- Atrophic;
- Scar.
The incidence of one form or another of phimosis directly depends on age. In children, in the overwhelming majority of cases, it is physiological in nature, and in men it is caused by cicatricial changes.
Reasons for the development of pathological phimosis
If infant natural phimosis goes away on its own, then there is phimosis, which has the form of a disease. It is provoked by several reasons:
- genetic disorders in the development of skin tissue of the penis;
- infectious diseases (especially of the genitourinary system);
- inflammation or injury to the penis (most often occurs when the child is carelessly washed or examined);
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
All these reasons are provocateurs for the development of the disease, which is fraught with serious complications (for example, acute urinary retention).
Symptoms
The basic symptom of phimosis in boys or adult men is the partial or complete inability to expose the head of the penis.
In addition, the patient may experience:
- Decreased potency.
- Pain during urination.
- If inflammation is activated, purulent discharge may be observed, the temperature may rise significantly and the lymph nodes on the body will significantly enlarge.
- Disorders of urination - fluid flows slowly, in drops or in a thin stream, the preputial area is swollen due to the accumulation of urine there and the impossibility of its rapid removal.
- With paraphimosis, a sharp pain develops in the head and penis, the pinched foreskin turns blue, the genital organ itself increases in size and becomes inflamed - this requires urgent surgery.
A doctor's help is necessary for the following symptoms of phimosis:
- increased body temperature;
- insufficient stream when urinating;
- swelling of the head of the penis;
- inflammation of the head of the penis;
- blue discoloration of the head of the penis;
- inability to fully open the head of the penis in children over seven years of age;
- enlarged lymph nodes located in the groin;
- the appearance of pus even with light pressure on the head of the penis;
- severe pain when urinating (small children cry for a long time after this process);
- drip urine output (in very severe forms).
The appearance of at least one of these symptoms indicates that phimosis has gone from safe, self-limiting with age, to pathological, requiring urgent treatment. In this case, leaving the child without treatment and waiting for the exacerbation of phimosis to go away on its own is not worth it. This can significantly worsen the child's condition and lead to much more complex treatment. For those mothers who do not want or do not have the opportunity to see a doctor to solve the problem, traditional medicine will come to the rescue, which is easy to use at home.
What is phimosis in a child: symptoms and types of the disease
What does phimosis of the foreskin look like in a child? A physiological deficiency in the development of epithelial tissue of the genital organ is caused by synechiae, that is, embryonic adhesions preserved between the epithelium of the head of the penis and the inner layer of the prepuce.
As the penis grows, the head pushes the synechiae apart, and its release occurs without difficulty.
Physiological phimosis of the foreskin in children, as a rule, goes away by 6-7 years, but in some cases it can persist up to 9-10 years.
It does not require treatment, but requires particularly careful hygiene of the penis and observation by a urologist to exclude the development of secondary, that is, pathological, phimosis.
Classification of phimosis:
- Based on the nature of its occurrence, congenital (primary) and acquired (secondary) phimosis are distinguished.
- Congenital phimosis is diagnosed in children under the age of 10-11 years, if, due to physiological phimosis, the head of the penis still does not open completely.
- Acquired phimosis usually develops as a result of trauma to the penis and is characterized by the presence of scar formations on the epithelium of the prepuce. With this disease, it is imperative to seek medical help. Read more about what cicatricial phimosis is and for what reasons it occurs here.
- According to the type of pathology development, the disease is divided into hypertrophic and atrophic.
- With prepuce hypertrophy, excess epithelial tissue hangs from the head, as a result of which it can be opened only partially, or it is not exposed at all.
- In the atrophic form, the disease develops due to the fact that the thinned epithelium of the foreskin is too tightly adjacent to the surface of the penis.
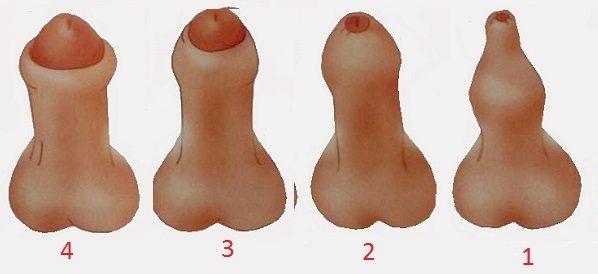
- According to severity, phimosis is divided into 4 stages:
- at rest the head is exposed without difficulty. During erection, the prepuce moves with difficulty, the child may experience pain;
- removing the penis from the skin fold is difficult in a calm state and impossible when an erection occurs;
- the head of the genital organ does not open at all or is only partially exposed in a calm state. Urine may accumulate under the skin before being excreted;
- the child is bothered by pain. It is impossible to remove the head. Urine is excreted drop by drop or in an intermittent stream. Before urination, the preputial sac seems swollen with fluid overflowing it. The foreskin is swollen, hyperemic, covered with cracks.
We invite you to read: Rapid labor – what is it, what are the causes and consequences for mother and child?
ATTENTION: If grade 4 phimosis develops, the child urgently needs the help of a surgeon, since such conditions are dangerous due to acute urinary retention and the development of intoxication of the body.
Symptoms of phimosis in boys are:
- the head of the penis does not emerge due to the insufficiently wide opening at the end of the foreskin;
- problems with urination up to acute retention. This is the child’s reaction to unpleasant or painful sensations. They manifest themselves in attempts, urine comes out weakly, entering the preputial area, causing it to increase in volume;
- inflammation of the head and foreskin;
- pus in the preputial area;
- elevated temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Paraphimosis
A common condition that develops in boys with phimosis. It is important to always remember: under no circumstances should you use great force when trying to expose the head of the penis. The fact is that it gradually expands in the direction from the opening of the urethra, and the shaft of the penis itself is much narrower. As a result of the forced opening of the head, the foreskin stretches somewhat (this can cause a short-term feeling of pain), and then tightly wraps the ring around the penis behind the head.
Manifestations of paraphimosis:
- the head is enlarged and swollen;
- the boy experiences a feeling of severe pain (babies cry and do not allow him to touch the penis).
The compressed blood vessels no longer perform their function, and the tissues of the head begin to lack oxygen and nutrients. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, necrosis or gangrene of the penis may develop, which forces doctors to remove the affected area - the patient becomes disabled.
Disease in children from one to 10 years of age
Untreated pathological phimosis is dangerous for children, adolescents and young men with the following consequences:
- scarring of the skin of the foreskin. Microcracks form on it during erection, when the head of the penis enlarges and stretches the skin. The wounds heal, and in their place microscars form, which make the foreskin less elastic. The disease progresses;
- balanoposthitis is an inflammation of the glans and foreskin of the penis caused by harmful bacteria. Microorganisms multiply in the lubricant of the preputial cavity. Pus is discharged from the openings of the foreskin. Scarring occurs. If left untreated, inflammation spreads to the urethra (urethra) and genitourinary organs, causing urethritis, cystitis (affects the bladder) and pyelonephritis (kidneys);
- paraphimosis. During masturbation or sexual intercourse, the narrow foreskin moves and pinches the head, unable to return to its original place. Blood supply is disrupted. Without treatment, the head tissue begins to die (necrosis occurs). After a certain period, purulent inflammation and blood poisoning (sepsis) develop. Do not delay treatment;
- chronic infections;
- cancer tumor. The development of the disease is facilitated by the accumulation of smegma in the preputial space;
- psychological problems. The guy notices that his penis is different, which is why he feels shy and complex;
- problems during sexual intercourse, associated with both the psychological side and the physiological side.
We suggest you read: How to treat a red throat in a child, how to cure it in an infant
Up to 12-13 years of age, physiological phimosis, like phimosis in a 7-year-old boy, which does not cause pain and does not interfere with the outflow of urine, does not pose a risk to the child’s health.
However, several recommendations should be followed:
- Maintain hygiene. Accumulations of smegma and urine in the preputial sac can provoke stagnation and, in the most severe cases, the formation of smegmoliths - stones formed from accumulations of smegma.
- You should not try to forcefully expose the head of the penis manually. Such methods can lead to tears and cracks in the foreskin and, as a result, scarring.
- It is necessary to monitor the condition of the foreskin: if redness or swelling appears on the skin, you should consult a doctor.
In adolescents over 11-13 years of age, pathological phimosis can cause a number of unpleasant consequences:
- Paraphimosis is pinching of the head of the penis by the narrowed foreskin.
- Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, which developed due to the impossibility of proper hygienic care. The urine accumulated in the preputial sac serves as a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, and increased pressure in the cavity of the foreskin causes reverse flow of urine and the spread of bacteria along the urinary tract.
- With phimosis of 3-4 degrees, fusion of the foreskin with the skin of the head of the penis develops - synechiae are formed. To treat such pathologies, surgical intervention is resorted to.

ATTENTION! Paraphimosis provokes swelling of the head of the genital organ and causes its subsequent necrosis. If the head of the penis is pinched by the prepuce, you should urgently seek medical help.
Physiological phimosis can persist in children up to 10-12 years of age. Normally, this condition does not cause any discomfort to the child.
In the absence of pathology, urine does not accumulate in the area of the preputial sac, the boy does not experience pain, and there is no discharge from the penis.
Phimosis can be not only congenital, but also acquired.
This form of the disease develops as a result of injuries to the penis, inflammation of the foreskin and the formation of fusions of the prepuce with the skin of the head of the penis.
If you have an acquired form of phimosis, you should definitely consult a doctor. This type of disease creates a favorable environment for the development of infections of the genitourinary system.
Stages of development
According to the severity of the process, 4 degrees of phimosis are distinguished:
- In a calm state, the head is completely released; during an erection, its removal is difficult and painful;
- At rest, the head of the penis is difficult to remove; during erection, it is completely covered by the foreskin and cannot be released;
- The head can be partially withdrawn only at rest;
- The head is constantly hidden by the foreskin and is not visible. During urination, urine first fills the preputial sac and only then is released drop by drop.
Classification of phimosis
- Based on the nature of its occurrence, congenital (primary) and acquired (secondary) phimosis are distinguished.
Congenital phimosis is diagnosed in children at 10-11 years of age if, due to physiological phimosis, the head of the penis still does not open completely. This case does not require surgical intervention, but the child must be registered with a surgeon or urologist and, if necessary, receive treatment. Acquired phimosis in a 5-year-old child usually develops as a result of trauma to the penis and is characterized by the presence of scar formations on the epithelium of the prepuce. If a boy has cicatricial phimosis, he should definitely seek medical help. - According to the type of pathology development, the disease is divided into hypertrophic and atrophic.
With preputial hypertrophy, excess epithelial tissue hangs from the head, as a result of which it can be opened only partially, or it is not exposed at all. In the atrophic form, phimosis develops in a 4-year-old boy due to the fact that the thinned epithelium of the foreskin is too tightly adjacent to the surface of the penis. - According to severity, phimosis is divided into 4 stages:
- at rest the head is exposed without difficulty. During erection, the prepuce moves with difficulty, the child may experience pain;
- removing the penis from the skin fold is difficult in a calm state and impossible when an erection occurs;
- the head of the genital organ does not open at all or is only partially exposed in a calm state. Urine may accumulate under the skin before being excreted;
- the child is bothered by pain. It is impossible to remove the head. Urine is excreted drop by drop or in an intermittent stream. Before urination, the preputial sac seems swollen with fluid overflowing it. The foreskin is swollen, hyperemic, covered with cracks.
ATTENTION! When grade 4 phimosis develops, the child urgently needs the help of a surgeon, since such conditions are dangerous due to acute urinary retention and the development of intoxication of the body.
We suggest you read: Pancreatitis in children causes, symptoms, treatment
How to treat phimosis in boys?
Treatment of phimosis in children depends on its degree, as well as the age of the patient. Depending on the extent of the process, the recommended approaches are listed in the table below.
| Phimosis degree | How to treat? |
| IV | Conservative treatment is ineffective; surgical intervention is necessary. |
| III | If possible, conservative methods are used at home; if conservative treatment does not help, phimosis in boys is eliminated with surgery. |
| II | At home, ointments are used and methods of gradually stretching the tissues of the foreskin are used. Any manipulations are carried out only in accordance with the recommendations of the urologist. |
| I | In boys under 13 years of age, no special treatment is required. |
The following methods can be used:
- Drug treatment. It is the use of hormonal ointments, such as Clobetasol, Bepantel, Betameson, Solcoseryl. They are needed to increase tissue elasticity, relieve inflammation, and heal microcracks.
- Non-medicinal. This treatment for phimosis in boys at home consists of mechanical regular retraction of the foreskin. You should move the baby's foreskin by one millimeter twice a week. First you need to take a warm bath for 15 minutes with any antiseptic (decoction of chamomile, calendula or a weak solution of potassium permanganate). It is advisable to lubricate the problem area with baby cream. The maximum movement can be up to 2 mm; sudden jerks are unacceptable. These manipulations should be carried out only after instructions from a urologist.
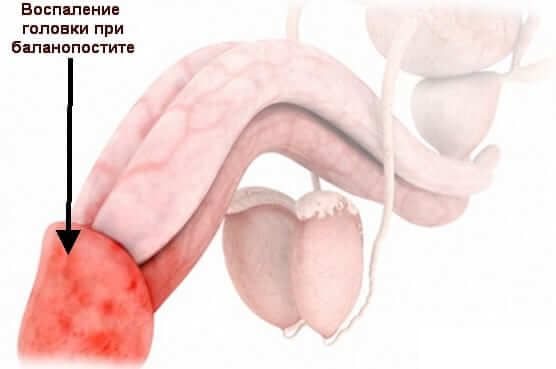
Balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis is the medical name for redness on the glans and foreskin in men.
It should be noted that balanoposthitis occurs in men of different ages. The disease can appear in both adults and preschool and schoolchildren. Irritation on the head of the penis is quite common.
The result of this disease can be phimosis, a narrowing of the foreskin that usually causes pain during exercise and urination. It is worth remembering that any, even the most harmless, redness on the penis can lead to serious consequences.
Doctors distinguish three categories of the disease, and the signs of the disease differ significantly from each other.
The first symptoms at this stage will be: redness of the glans penis, it may increase in size due to slight swelling. In some cases, there is discharge of pus and the appearance of cracks. These symptoms are accompanied by pain and stinging.
Symptoms of this stage were the appearance of a white coating on the penis. Depending on the characteristics of the body, the lymph nodes may become enlarged. The skin of the penis becomes dry and begins to thin.
If you advance the disease to this stage, you can detect the formation of small ulcers on the genitals. They are quite deep and bring great discomfort to a man. In some areas of the penis, you can see dead skin cells as a result of progressive necrosis. The patient becomes lethargic and weak, and a fever may develop.
When is surgery needed?
In many children, physiological phimosis gradually decreases and goes away on its own, without requiring any treatment, much less surgery. Therefore, if nothing bothers the child, it is quite possible to do without surgical intervention. But there are cases when surgery for phimosis in boys is necessary:
- inflammation is regular, and treatment of phimosis does not produce results;
- urination becomes painful;
- adhesions form between the head and foreskin;
- severe swelling with paraphimosis;
- phimosis does not go away until puberty.
If one of the reasons suits you, do not panic too much; in fact, the operation for phimosis is simple, done under local anesthesia and takes only a few minutes. And literally in one or two days you will be able to return home.
In case of developed balanoposthitis, conservative therapy includes the following measures:
- warm baths with a solution of potassium permanganate - 5 times a day for 4 days; treatment with furacillin - according to the same scheme;
- introduction of antiseptic ointments into the preputial sac - 3 times a day for 6 days;
- lubricating the affected area with petroleum jelly - 2 times a day, 7 days.
External antibacterial therapy can be different and is determined in each specific case individually. Antibiotic-based emulsions and powders may be prescribed. When performing the procedure, the foreskin must be moved from the head.
Prevention
Parents need to keep their child's genitals clean. It is recommended to wash the boy with clean warm water every evening. The rest of the time you can use wet wipes. The use of foam for bathing is not recommended. These products contain chemicals that irritate the delicate skin of the penis.
With physiological phimosis, there is no need to expose the head of the penis while swimming. If a child develops inflammation due to dirt accumulated under the foreskin, then it must be removed from there as follows:
- Draw 10 ml into a syringe without a needle. clean warm water or ectericide solution (furatsilin can be used instead).
- Pull the foreskin upward so that the head of the penis is hidden rather than exposed.
- Insert the syringe into the gap that has formed between the foreskin of the penis and its head (this procedure is more convenient to carry out together).
- Release the liquid, thus washing away accumulated dirt.
- Repeat this procedure 1 or 2 more times.
- Drop 2-3 drops of olive or Vaseline oil into the gap between the foreskin of the penis and its head (you can use oil solutions of vitamin A, E).
It is imperative to change diapers for a small child more often. Thanks to this, there will be no prolonged contact of the head of the penis with feces and urine. The inflammatory process will not occur.