A bend or bend of the gallbladder is the loss of the natural shape of the organ due to certain reasons. The gallbladder serves as a storage facility for bile; it is supplied to the esophagus in situations where the body needs it. Deformation of an organ by bending reduces its performance, and in special cases can completely stop its functioning. A bend in the gallbladder in a child is most often hereditary. Due to certain circumstances, during the development of the fetus, disruptions occur that do not allow the organ to fully form.
What is a bent gallbladder in a child?
In a newborn child, changes in the shape of an organ are not always diagnosed. This is due to the fact that the pathology may well not manifest itself until a certain moment. Situations often occur when a congenital inflection of the gallbladder in children is not detected either during diagnosis in the maternity hospital or during adulthood. Many people diagnose the disease only by chance, conducting an ultrasound examination to identify other possible diseases. But often, due to the irregular shape of the organ, people experience certain symptoms, which, during examination, are confirmed as cholelithiasis and other dangerous diseases.
The gallbladder, when deformed, reduces its ability to fully accumulate bile. As a result, stagnation of bile in the ducts can form stones. Stones obstruct the flow of fluid through the channels and can lead to very serious consequences. One of them, with an extreme degree of development of the pathology, may be complete removal of the organ through surgery. This means that the body will be subjected to great overloads, and throughout life it will be necessary to reduce them, adhering to certain recommendations.
Many people know first-hand what a bend in an organ is, what consequences pathology can bring, and how one has to adapt to life in conditions of complete or partial dysfunction of one of the body’s parts. The disease is quite common, and therefore there are also quite a lot of treatment and prevention methods.
A bend in the gallbladder in a child is most often congenital. During pregnancy, for certain reasons, the organ does not develop fully. This may be due to an unhealthy lifestyle during gestation or heredity, as a result of which the baby has deviations from the moment of birth.
Why kinks occur, specific factors influencing the formation of an organ, in addition to heredity, have now been studied quite well by medicine. Tobacco smoking or, for example, taking medications not authorized by a doctor can easily affect the development of this pathology. Pathology can seriously undermine health; bending in the area of the organ body is especially dangerous. In cases where deformation appears precisely in this part of the bladder, surgical intervention is often performed.
Causes related to nutrition, stress and strain
Errors in nutrition, neuroses, and poor physical activity can lead to the development of stagnation in the gallbladder in children.
Prolonged stress and other psycho-emotional disorders lead to malfunctions of the gallbladder. In particular, its contractility is impaired. This contributes to poor flow of secretions into the intestinal lumen.
Neurosis can also lead to metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances. They affect the composition of bile. Its thickness depends on the ratio of the components of the secretion. It is more difficult for concentrated bile to flow out of the bladder.
It also negatively affects the processes of bile excretion:
- abuse of fatty foods;
- spicy products;
- fried foods;
- long intervals between meals;
- following strict diets
Sudden changes in diet can lead to disruption of metabolic processes. As a result, the nuances of the synthesis of liver secretions also change.
It is also a mistake to force a child to eat if he does not want to. The diet should be age appropriate.
Lack of physical activity and low activity can often lead to stagnation. With computers, boarding schools and various gadgets, children spend a lot of time in a sitting position. This provokes disturbances in the evacuation of bile.
Thus, when bile stagnation occurs in a child, its causes can be varied. The gastroenterologist should determine the leader.
Types of gallbladder kinks in children
The bends of the gallbladder in children are divided into several types - those obtained from the moment of birth and those that arise during life. Regardless of the nature of the pathology, deformation occurs in the following parts of the organ:
- in the cervical area,
- in the body area,
- in the bottom area.
The curved organ in the cervical part is most common . Such deformation can seriously harm the entire digestive system. A child's gallbladder may take on a hook-like shape. There is an opinion that bending in the area of the body of the organ is most dangerous. Volvulus may well cause a tissue breakthrough, which will inevitably lead to acute peritonitis of the abdominal cavity. Without urgent medical attention, such a scenario can lead to death. It is important to identify the functional inflection of the gallbladder in a child as early as possible. The main symptoms are:
- pain under the ribs on the right side of the chest,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- changes in skin color,
- a sharp decrease in body weight,
- loss of appetite,
- allergy.
A bent organ will definitely make itself felt . Many factors accumulate and lead to complications, most often serious. One of the consequences may be biliary cirrhosis of the liver. If a child’s gallbladder is curved from birth, there is a high probability that there are pathologies in other areas of the body’s functioning. The most common are:
- heart disease,
- pathologies in the structure of the skull,
- disorders in the structure of the spine,
- malfunctions of the musculoskeletal system.
The acquired nature of the disease also provokes a large number of complications. Twisting of the organ leads to stagnation of bile and the formation of stones, thereby disrupting the digestion process and developing many diseases of the intestines, stomach, and liver.
In addition to the already described variants of organ deformation, there are also some less common ones. One of them is the labile bend. The gallbladder is twisted in such a way that it can rotate. Wrapping an organ most often occurs as a result of some kind of physical activity and can only temporarily change its shape.
There is also a double bend of the gallbladder, or S-shaped. It occurs in the neck or body area. Deformed in this way, it becomes hook-shaped.
Causes of pathology
The bending of the gallbladder in a child, according to the causes of its occurrence, can be congenital or acquired. In the congenital form of the pathology, the anomaly is observed even in the intrauterine development of the baby. This pathological process is characterized by an asymptomatic course.
The occurrence of acquired inflection of the gallbladder in a child is observed under the influence of various provoking factors. Often the pathological process develops when the baby is malnourished:
- overeating;
- irregular food intake;
- fasting.
If the liver, gall bladder or right kidney enlarges, this becomes the cause of the pathological process. It appears in patients with obesity. If a child leads a predominantly sedentary lifestyle, then he is at risk of developing pathology. The disease most often appears in children who engage in weightlifting.
When internal organs prolapse, prolapse may occur. If the gallbladder becomes excessively mobile, this leads to a labile bend. In case of inflammatory processes in the organs of the biliary system of a chronic nature, the occurrence of the disease is diagnosed.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of inflection in children, so parents should be attentive to their health.
Causes of inflection
Congenital bending of the gallbladder in a child develops in the womb at 2-3 months of pregnancy. The reasons may be the following factors:
- smoking,
- alcohol consumption,
- unsuitable ecology,
- taking medications,
- limited physical activity,
- infectious diseases.
There is also a possibility that the pathology will be transmitted hereditarily from the mother . During pregnancy, an infection may occur that can harm the process of formation of the internal organ system. During pregnancy, the mother also runs the risk of gallbladder deformation. As body weight increases, the uterus enlarges, which puts pressure on the internal organs, resulting in a change in their shape. Another cause of congenital pathology can be the incorrect process of feeding a child. When switching from breast milk to other types of food, a bend in the gallbladder can sometimes occur. This happens because the organ begins to stretch and by the age of 3-4 years it becomes curved.
The acquired nature of the disease in children most often appears due to poor nutrition . For example, when you are with your child for a long time on a walk or on other errands outside the home, there is no way to eat on time. Then, upon coming home, children often overeat heavily. Sometimes to such an extent that they cannot even breathe fully. During this time, the following processes can occur in the body:
- with prolonged fasting, there is no outflow of bile due to the lack of need for it,
- after eating a large meal, the stomach becomes irregularly shaped and puts pressure on the gastrointestinal tract,
- With further food intake, the outflow of bile is disrupted.
Prognosis and prevention
Timely treatment of bile stagnation is in most cases effective and allows you to avoid unpleasant consequences. In the future, it is important to follow a diet and follow all doctor’s recommendations to eliminate the risk of recurrence of the disease.
To prevent the development of gallbladder pathologies in children, it is necessary to pay attention to nutrition, level of physical activity, and daily routine. If your child goes to kindergarten or school, it is worth finding out how meals are organized there. At home, the regime also needs to be followed. You should not perceive a child’s poor appetite as whims - it often indicates digestive problems, including impaired flow of bile. To maintain the overall tone of the body, moderate (not excessive) physical activity is necessary.
Symptoms
The bending of the gallbladder in children can be asymptomatic up to a certain point, but it can also make itself felt by the manifestation of symptoms. To a greater extent, signs of gallbladder bending appear between the ages of one and five years. Main symptoms:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting during and after meals,
- sharp pain in the abdomen and side,
- sleep disturbance,
- change in normal skin tone,
- fluctuations in body temperature.
A fixed bend will definitely make itself felt, most often expressed in the form of the indicated signs. If a child has a bend in the gallbladder in the fundus, the main symptom will be pain in the left side of the abdomen or in the center. It is necessary to pay attention to how the baby behaves; if his stomach hurts, he will be constantly irritated, and it is quite possible that he will not sleep enough. Problems with the gallbladder at this age definitely cannot be acquired. Only a doctor can diagnose a congenital pathology based on the symptoms and prescribe treatment, and a visit to whom should not be postponed under any circumstances.
Symptoms of pathology
When the bend occurs, patients are diagnosed with a variety of symptoms, which manifest themselves in accordance with the location of the disease. Common symptoms include broken stools. In young patients, diarrhea may alternate with constipation. Young patients complain of pain in the right side. It can radiate to the area of the shoulder blade or thoracic back.

The pathological process is accompanied by bloating, which is accompanied by bursting pain. The disease is accompanied by sudden changes in body temperature. If an inflammatory process is diagnosed during pathology, the child’s skin takes on an earthy hue. All other symptoms appear in accordance with the location of the inflection:
- Neck. A small patient experiences pain in the left hypochondrium. The pathological process is accompanied by constant nausea. Patients experience weakness and general malaise. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by fever. When sick, gas formation may increase and flatulence may appear, which is caused by increased body temperature. The penetration of bile from the bladder into the abdominal cavity causes the development of peritonitis.
- The junction of the body and the bottom of the organ. This is the most common type of deformity, which causes pain in the abdominal area. It can radiate to the collarbone and scapula. After eating, the child experiences vomiting. Most patients complain of frequent attacks of nausea. In the corners of the mouth during the course of the disease, the appearance of jams is noted. The pathological process is accompanied by an appearance on the tongue. During the course of the disease, hyperhidrosis appears, which is accompanied by excessive sweating. The whites of the eyes in children acquire a yellow tint.
- Combined bend. With this form of pathology, there is a bend in several zones of the gallbladder. Children experience acute localized abdominal pain. This form of pathology leads to a pronounced gag reflex. The disease causes nausea and increased body temperature.
In pathology, pronounced symptoms are noted, which manifest themselves in accordance with the location of the inflection. If a child shows the first signs of the disease, he should be shown to a doctor. Only an experienced specialist, in accordance with the data of the studies conducted, will be able to prescribe effective therapy.
What is the danger of a bent gallbladder in a child?
A bend of the gallbladder in a child is most dangerous due to the development of new pathologies, and can also stop the full development of the baby. In children under 3 years of age, the body is not yet able to fully resist the progressive disease, so therapy and observation by a doctor will be extremely necessary. Complications that are caused by a bend in the gallbladder in a child:
- liver diseases,
- digestive disorders, which can result in diseases of this part of the body,
- pathology of skeletal bones.
Gallbladder diseases that occur in childhood
All diseases of this organ in a child can be grouped according to the reasons that provoke them. These are the reasons:
- functional diseases. This group of pathologies is characterized by a disruption of the normal motility of the organ itself and its ducts. In medicine, such ailments are called dyskinesias, which are divided into hyperkinetic (too strong contractility of the walls of the bladder and/or its ducts) and hypokinetic (on the contrary, too sluggish contractility of the muscles of the organ);
- inflammatory pathologies. This group of diseases develops as a result of inflammation of an acute or chronic nature as a result of the presence of concomitant diseases or infectious lesions. Such ailments are divided into cholecystitis (inflammation of the walls of the organ itself), cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts) and cholecystocholangitis (general inflammation of the bladder and ducts). Such diseases are quite possible in a child;
- metabolic pathologies that arise as a result of disturbances in the normal course of the metabolism of cholesterol, bile pigment (bilirubin) and bile acids. As a result of such disorders, the chemical composition of bile changes, which leads to the formation of gallstones. In addition, cholelithiasis can also provoke cholestasis (stagnation of bile in a child in the bladder cavity), which can be caused by dyskinesia, inflammation and other pathological processes that impede bile outflow;
- congenital abnormalities of the development of this organ, which cause disturbances in its normal functioning (found in newborns). Such diseases include kinking of the gallbladder, its complete absence, hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the organ, its location inside the liver, wandering gallbladder, double (accessory) organ, the presence of internal partitions in the organ cavity, diverticula (protrusions) of the bladder walls, atresia (lack of holes for the outflow of bile) and various cystic formations in the organ itself and its ducts;
- parasitic lesions of the organ (helminths or lamblia). This group of diseases includes: opisthorchiasis (infection with the Siberian fluke), giardiasis (infection with Giardia), fascioliasis (infection with the liver fluke), dicroceliosis (the parasite is the lanceolate fluke) and clonorchiasis (infection with the Chinese fluke);
- various pathologies associated with benign and malignant tumors. As a rule, such diseases are diagnosed very rarely in children.
Read also: How to take antibiotics for gallbladder inflammation?

Diseases of an organ such as the gallbladder, as well as the biliary tract, can occur in children for many reasons, but most often such pathologies are either congenital in nature or associated with improper diet and a sedentary lifestyle of the child.
Treatment
The doctor prescribes treatment for a bent gallbladder after an examination and it depends on the degree of development of the pathology and most often individually for each patient. A bend detected in a child at an early stage is most often treated prophylactically, observing how the body adapts to existing conditions. What you need to do first is to change your diet to what your doctor recommends. This approach will facilitate the work of the liver and gallbladder, which means that the less load on the deformed organ, the better. The treatment method will be mainly aimed at increasing the tone of the body and its ability to function fully. A specialist will treat with medications or surgical intervention only in the most serious cases.
Diagnostic methods
Making a diagnosis begins with an initial examination and collection of anamnesis, on the basis of which the doctor decides to prescribe certain diagnostic tests. Since many gallbladder diseases have similar symptoms, such studies cannot be avoided.
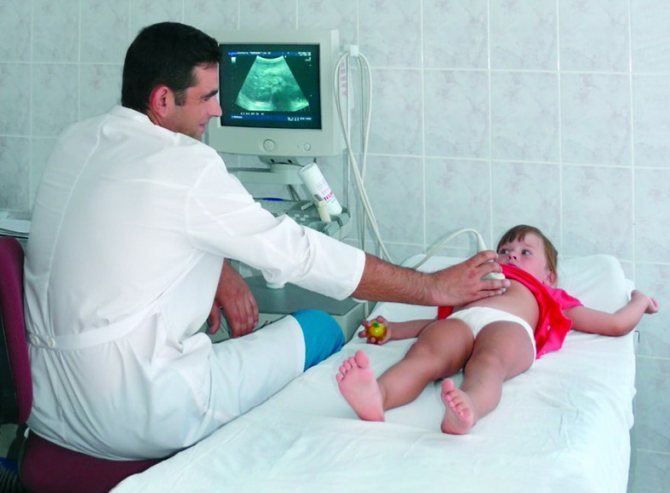
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Based on primary data, the doctor can prescribe the following instrumental and laboratory examinations (in combination and separately):
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | biochemical and general blood tests |
| 2 | Ultrasound of the abdominal organs |
| 3 | urine and stool tests |
| 4 | duodenal intubation |
| 5 | computed tomography (CT) |
| 6 | magnetic resonance cholecystography (MRI) |
Read also: Symptoms of various gallbladder diseases
An ultrasound will have to be done several times, since this study should show the development of the pathology, the results of its treatment and the condition of the organ after the end of the course of therapy.
Drug therapy
The method, which involves treatment with tablets, is designed to eliminate symptoms, strengthen the immune system and help the child avoid surgery to remove an organ. Medicines will help relieve attacks of nausea and vomiting, reduce the intensity of abdominal pain and eliminate acute manifestations of pathology. The use of a drug such as “Hofitol” will be very effective when bending the gallbladder, which will become a catalyst for the complete outflow of bile.
In some cases, when the course of the disease resolves against the background of inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed. Traditional medicine can be beneficial in certain situations, but treatment by this method must be agreed with a doctor.
Clinical picture and signs of gallbladder diseases in children
The symptoms of various diseases of this organ in childhood may vary, but common complaints with pathologies of the gallbladder are as follows:
- children complain of pain in the right side of the abdomen (immediately under the ribs), the intensity of which may increase after eating, with increased physical activity and in stressful situations;
- children one year old and younger may burp during feeding and cry during the feeding process, since the baby is not able to complain about being unwell in any other way;
- nausea occurs, which may be accompanied by periodic and unrelief vomiting, the masses of which may contain bile;
- the child feels a bitter taste in the mouth;
- he suffers from heartburn;
- dyspeptic disorders occur (diarrhea alternates with constipation);
- bloating and flatulence occurs;
- the color of the stool changes (stool becomes light and urine becomes dark);
- the skin and sclera of the eyes acquire a yellowish tint.
If a child complains of several of the above symptoms at once, this is a signal to immediately contact a therapist and gastroenterologist. The sooner an accurate diagnosis is made, the shorter and more effective the treatment will be.
Diet is the key to quick recovery
Excluding foods harmful to the body from the diet and proper nutrition can support the functioning of the gallbladder and improve the general condition of the body. What should you avoid first:
- fried and fatty foods,
- dishes containing a large amount of spices,
- spicy food,
- coffee.
You can saturate your body with useful substances by using foods such as pumpkin. It is possible to prepare a lot of dishes from it, and also use the seeds of the fruit, which are also very healthy. Diet implies not only the consumption of certain foods or the exclusion of harmful ones, but also the correct diet. You need to eat 5-6 times a day, preferably in small portions.
Treatment of gallbladder diseases in childhood
Treatment of any pathologies of this organ (both in adults and children) must be carried out in conjunction with a diet called “Treatment Table No. 5”. Without this, any therapy will be a waste of time and money.
Food restrictions in such cases concern not only the diet, but also the child’s diet. He will have to eat little by little, but often (five to six times a day). Food should be warm, since hot and cold negatively affect the digestive process. Food can only be cooked by steaming, boiling or baking. Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended. Fried, spicy, fatty and smoked foods, fast food, any kind of pickles, canned food, mushrooms, legumes, sweets, flour, chocolate, baked goods, carbonated drinks and a whole range of other foods harmful to the body should be excluded from the diet.
It is allowed to eat lean dietary meat (white meat chicken, veal, rabbit) and fish (pike perch, pike). The basis of the diet should be fresh and boiled vegetables, soups with vegetable broth, porridge based on buckwheat, semolina, rice and oatmeal, as well as cottage cheese and low-fat fermented milk products. Bread should be consumed either yesterday or dried. For sweets you can have dried fruits, marshmallows and honey.
For some pathologies of this organ in children (for example, for the treatment of cholestasis), doctors recommend physical therapy exercises under the supervision of qualified specialists, as well as some types of physiotherapeutic procedures.
If we talk about medications, then for each case the doctor selects them individually. The pain is relieved with the help of antispasmodic drugs (“No-spa”, “Drotaverine”, etc.). Stagnation of bile can be cured by choleretic drugs (for example, Allohol). In the presence of inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are used. If the parasitic nature of the pathology is discovered, drugs from the group of nitrofurans, nitramidazoles and benzimidazoles are prescribed. Sometimes there is a need to take hepatoprotectors (Essentiale Forte) and enterosorbents (activated carbon).
Read also: What are the symptoms of an irregularly shaped gallbladder with a bend?
Inna Lavrenko
auto RU
It should be remembered that many medications have age restrictions, so depending on how old the child is, different medications are prescribed. Medicines intended for children under one year old, from 2, 10 or 12 years of age have a corresponding warning in the instructions. Therapy can be carried out simultaneously with two or more types of drugs.
In cases where conservative methods do not bring the desired result, surgery is used.
The most common operation is removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy), which is usually performed using the least traumatic laparoscopy, from which recovery is fairly quick.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky recommends treating the bending of the gallbladder in a child by influencing the causes of the disease. The causes of cholecystitis lie in disruption of the biliary tract. The disease can also be a consequence of increased physical activity, sleep or eating disorders. Thus, treatment will be prescribed not only to relieve symptoms, but also to eliminate the reasons why the channels cannot fully fulfill their purpose.
Increased physical activity should be recommended by a doctor; in other cases, you should limit yourself to simple gymnastics. A video where a doctor talks about ways to resist the disease can be easily found on the Internet today.
Bend gallbladder in a child - symptoms
When a child develops a bend in the gallbladder, symptoms of the pathology do not appear immediately. Their character directly depends on where in the bladder the pathology occurs. By assessing the observed signs and symptoms, doctors are able to make the first assumptions about the nature of the disorder and the location of the inflection. This information is crucial when choosing methods of treating a pathological process.
Bend of the body of the gallbladder in a child
Based on the characteristic signs, the mother can independently determine the inflection of the child’s gallbladder - the symptoms of the pathology are pronounced. An inflection in the area of the gallbladder body may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdominal area;
- pain in the collarbone, sternum, under the shoulder blade;
- nausea that worsens after eating;
- vomit;
- plaque on the surface of the tongue;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth.
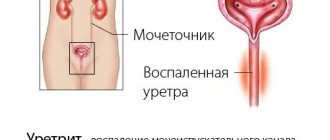
Bend of the gallbladder neck
When a bend of the gallbladder occurs in a baby in this form, specialists on ultrasound observe an elongation of the neck of the bladder or sagging of its body. As a result of such changes, the risk of cervical necrosis increases. This situation is fraught with the entry of bile directly into the abdominal cavity and the development of peritonitis. Because of these features, early diagnosis plays an important role in preventing these complications.
It is possible to suspect a bending of the gallbladder and the symptoms of this disorder only with a correct assessment of the child’s condition. A bend in the neck of the gallbladder in a child is accompanied by the following clinical picture:
- pain in the abdomen, localized in the area of the left hypochondrium;
- bloating;
- attacks of nausea;
- increase in body temperature.
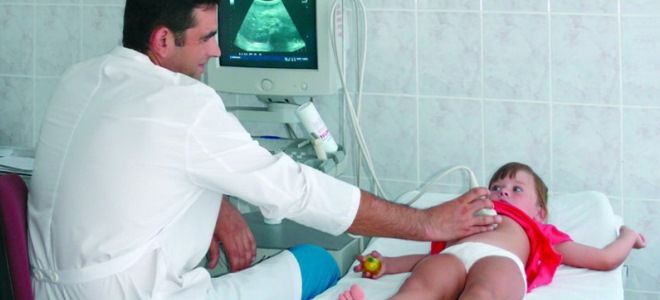
Bend of the bottom of the gallbladder in a child
With this type of disorder, signs of a bent gallbladder are characterized by painful sensations in the abdominal area. The pain radiates to the right hypochondrium. In parallel with the painful sensations, other symptoms are observed:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- stool instability (diarrhea).
If an infection occurs against the background of impaired bile outflow, additional symptoms of inflection appear:
- increased sweating;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- earthy complexion.
Double bending of the gallbladder in a child
Twisting of the gallbladder in several places is a rare form of pathology. Experts call an increase in the size of the bladder as a factor provoking the development of torsion. Pain when the gallbladder is bent in two places is more intense. Otherwise, the symptoms of this form of pathology do not differ from the types mentioned above.