What is fetometry
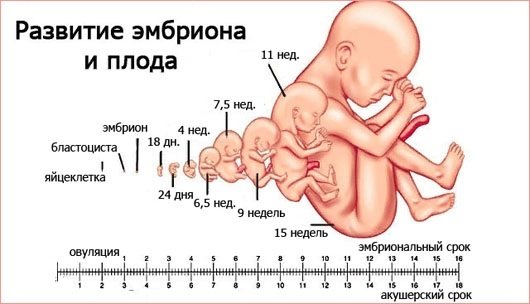
The name of the study consists of two words: Latin “foetus” and Greek “metreo”. They mean "fruit" and "measure" respectively. Fetometry is the measurement of the size of an embryo . Based on screening data, the gynecologist determines the development of the embryo, the presence of abnormalities and the gestation period.
Each measurement is recorded by special devices and recorded, giving values in millimeters. The ultrasound specialist enters these results into a table where the measurements taken and their acceptable values are indicated.
Fetal fetometry by week (a table of indicators, understandable and correctly filled out, the professionalism of an obstetrician-gynecologist - all this makes it easier to control the development of the embryo, helps to notice and stop any possible problems in time) allows you to determine the date of delivery with an error of several days.
How is the fetal abdominal circumference measured and what is its average?
The circumference of the fetal abdomen (hereinafter referred to as the OB) is measured in the plane where the stomach, umbilical vein, and gall bladder are visible.
The table below shows the average life expectancy indicators corresponding to each week of development. However, it should be remembered that these figures are only average data; they may differ for each child.
Table of values of the main fetal measurements by week
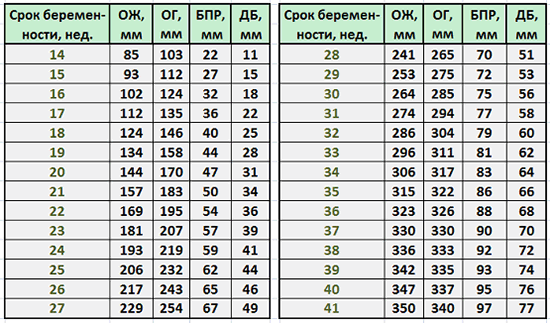
coolant
– fetal abdominal circumference
OG
- Head circumference
BPR
– biparental head size (distance between the temporal bones)
DB
– thigh length
When and how does the research take place?
Pregnancy is divided into 3 stages, in each of which one ultrasound is performed. If necessary, the gynecologist prescribes additional examinations.
Fetal measurements are taken:
- at 12-14 weeks - first trimester;
- at 20-22 weeks - II trimester;
- at 30-32 weeks - III trimester.
The timing of screening may be changed by the attending physician.
They depend on:
- well-being of a pregnant woman;
- previous studies;
- there are suspicions of abnormal development of the embryo or pathological processes during gestation.
When undergoing an ultrasound scan in the first trimester, the ultrasound specialist clarifies the gestation period and sets a preliminary date for delivery. During this period of pregnancy, it is important to timely diagnose congenital pathologies and intrauterine defects in the formation of the embryo.
The most informative will be data on the coccygeal-parietal size (CTR), abdominal circumference, nose size and width of the cervical fold.
After this, the ultrasound specialist will determine:
- heartbeat;
- blood circulation;
- location of the embryo in the uterus.
Fetometry in mid-pregnancy is a key study to confirm the absence of pathologies.
This ultrasound determines:
- biparietal size (BPR);
- KTR;
- Head circumference;
- abdominal girth;
- size of the frontal bone and occipital part;
- thigh length;
- humerus bone size.
At this time, the ultrasound specialist can already accurately indicate the gender of the child.
In the later stages, the gynecologist checks only the well-being of the child, as well as some measurements:
- length;
- weight;
- head circumference;
- belly size.
The doctor also looks at the symmetry of growth of all limbs. The data obtained determines what kind of birth there will be: natural or through a caesarean section. If the results of the study are normal, then no further ultrasound examinations are performed.
The fetometry procedure is the same as a regular ultrasound:
- Transvaginally in the early stages, since it is difficult to accurately determine all fetal parameters through the abdominal wall. A special sensor, on which a condom is placed before the procedure, is inserted into the vagina.
- Transabdominal . This method is suitable if the specialist can clearly see the child through the abdominal muscles. A small amount of gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen and the sensor is passed over the entire abdominal area.
It is customary to carry out both types of examinations at once in order to obtain error-free results of measuring the fetus. It is advisable to carry out the first and second screening with a full bladder , and in the last weeks the uterine cavity is clearly visible due to the accumulation of amniotic fluid.
Abdominal girth measurement functions

By about 12-14 weeks, the uterus is similar in size to a large orange; accordingly, it does not yet exert such pressure on the wall of the abdominal cavity from the inside. But starting from the 16th week, a pregnant woman will definitely notice a jump in its growth. Of course, every mother is individual, just like her baby, so this moment may come a little earlier or a little later. But from about this point on, your tummy will be of even greater interest to your obstetrician-gynecologist. Now, at each appointment, the doctor will measure not only your blood pressure and perform other routine procedures, but also measure the abdominal circumference (AC) and the height of the uterine fundus, and perform palpation. These manipulations are necessary and help to diagnose multiple pregnancies, the state of fetal development, polyhydramnios, the appearance of tumors and other deviations from the norm. Carrying out the procedure at a later date makes it possible to determine the presentation of the fetus and its readiness for the upcoming birth process.
Basic nuances of fetal examination
Fetal fetometry week by week makes it possible to determine its length and size of body parts. The table with the entered measurements clearly shows the dynamics of fetal formation at each stage of gestation. But the child’s growth is uneven, and the indicators may not coincide with the acceptable values.
Due to the hereditary characteristics of each organism, differences in characteristics from the table values may be acceptable and not reflect developmental pathology. The mother or father may be tall and thin or, conversely, short and rather heavy-set - these hereditary factors affect the examination results.
The numbers obtained from it will differ greatly from the table values.
For this reason, conclusions about a child’s developmental abnormality based on one measurement of ultrasound screening are not made , but additional studies are prescribed. When pathologies are confirmed by an obstetrician-gynecologist and geneticists, a preliminary diagnosis is made - “intrauterine developmental delay.”
This diagnosis has 2 forms:
- asymmetrical , when only some indicators differ from normal at a given stage of pregnancy;
- symmetrical , in which all indicators decrease.
Developmental delay has several degrees, differing in the severity of pathologies:
- I degree: data differ from normal values by 2 weeks;
- II degree: data differ by 3 weeks;
- III degree: the difference in indicators is 4-5 weeks.
Fetal fetometry by week and a table that describes the dynamics of the child’s development are not absolutely accurate. Figures that differ from the statistical average may be a diagnostic error. After some time, the obstetrician-gynecologist will prescribe a repeat ultrasound screening.
Often the parameters of the fetus reach the desired value after a while.
Key points of fetometric research
The key data of a fetometric study are the following indicators:
- DB - thigh length;
- BPR - biparietal size;
- DP - shoulder length;
- KTP - coccygeal-parietal size;
- DN - nasal bone length;
- LZR - fronto-occipital size;
- OG - head circumference;
- DG—tibia length;
- AB—abdominal circumference;
- TVP is the thickness of the collar space.
A decoding of the designations of the studied parameters is provided, since the fetometric data is written in the table in Latin.
A video about the stages of ultrasound was presented by the 1st Medical Quarter of Crede Experto on Taganka.
Child's weight
By the 12th week, the baby’s body weight is normally only 19 g; by the middle of pregnancy, the baby will weigh about 345 g, and by the 32nd week - almost 2 kg.
If you promptly pay attention to the problem with the discrepancy between the fetal body weight and the standard, and take preventive measures, then it will be possible to correct the situation relatively easily. The rate of weight gain is greatly influenced by genetic factors. The gynecologist makes sure that the dynamics are positive.
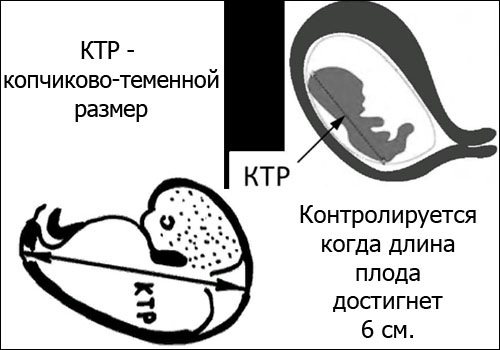
KTR (CRL, coccygeal-parietal size)
KTR (Latin analogue of CRL) means coccygeal-parietal size, that is, the height of the child. It is calculated from the crown to the end of the coccyx.
If this indicator differs slightly from the norm, then the fetus is not in danger. An increase in CTE over several weeks by the same value indicates that the fetus is relatively large in size.
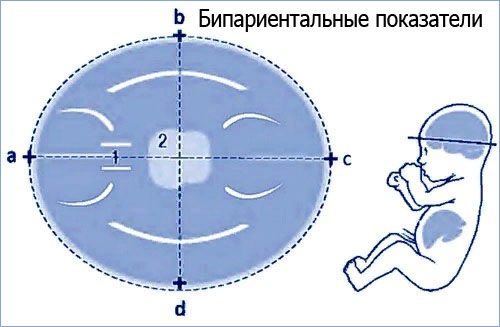
BPD (BPD, biparietal and fronto-occipital head sizes)
The letters BPD indicate the width of the fetal head. This is the maximum distance between the parietal bones. The size can be determined by taking measurements along the smallest axis of the circle between the child's temples. BDP allows you to determine the exact duration of pregnancy.
The parameter of biparietal fetal head size (BSD) helps to identify developmental abnormalities already during the first trimester. The data obtained characterize the state of the fetal nervous system.
The LZR or fronto-occipital size is calculated between the most distant points of the forehead and the back of the head.
OG (chest circumference)
The volume of a child's chest is determined by calculating the diameter of its circumference. A size that does not correspond to the norm should not cause any particular concern; most likely, this is a genetic feature. Perhaps the baby will simply be born large. It is necessary to take into account the physical characteristics of the mother and father.
AB (abdominal circumference)
Abdominal circumference is measured at 20 and 32 weeks of pregnancy. The parameter is calculated along the line of the liver, stomach and umbilical vein. When the difference in indicators exceeds the permissible norm, the doctor will diagnose intrauterine growth retardation. However, to confirm it, the size of the coolant is calculated in relation to other parameters - the size of the head, femur, and BPR. If most indicators are normal, then this indicates a delay in the development of the asymmetric form.
DB (femur length)
If a discrepancy in the thigh length is detected, this also does not indicate the presence of pathology. Much depends on individual characteristics. For example, when the length of the femur and shin bones is longer than normal, it means that the parents of the unborn baby or other relatives have a long leg.
PMP (PVP)
PVP is the estimated body weight of the fetus. During an ultrasound examination, there is a possibility of an error in weight. To eliminate errors, this figure is calculated using various medical formulas.
Calculation methods:
- Zhordania (Lebedeva) - PMP = height of the uterine fundus × abdominal circumference.
- Bublichenko - PMP = 1/20 of a woman’s weight.
- Lankowitz - PMP = (height + maternal weight + abdominal circumference + uterine fundus height) × 10.
- Jones - PMP = (height of the uterine fundus - 11) × 155. The value 11 is a conditional coefficient for a pregnant woman weighing up to 90 kg.
- Yakubova - PMP = (abdominal circumference + uterine height) × 100/4.
Calculations are made after 38 weeks of pregnancy.
The Family TV channel presented a video about performing an ultrasound in the third trimester.
Key indicators of fetometric research
Fetal fetometry by week (a table of measured values and accepted norms, which is attached to the research responses, allows you to independently decipher the results) and a biochemical blood test are a full-fledged set of studies that complement each other.
Thus, ultrasound screening alone, carried out even with the most innovative devices, is not informative until the 11th week due to the short length of the fetus. That is why the doctor prescribes examinations only at certain times.
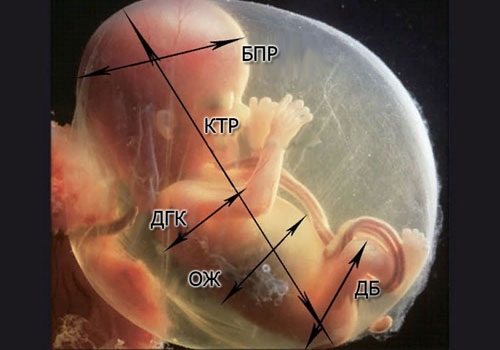
The main parameters of fetometry are:
- Weight . This parameter is monitored throughout pregnancy. It characterizes the health and vitality of the child, and is also one of the decisive factors for choosing the type of birth. On average, healthy children gain weight from 10 to 100 g weekly. But here, too, slight deviations are possible due to the genetic characteristics of the child.
- OB - abdominal girth or circumference. It is not measured if the fetal weight exceeds 4 kg. It determines the formation of internal organs.
- KTP - size of the coccygeal-parietal. This is the length of the fetal body without taking into account the size of the head: from the fontanel to the coccyx. It is used to determine the gestation period until the embryo reaches 6 cm.
- BPR —bipariental size. This is the circumference of the embryo's head. It is measured between the temples. According to it, the obstetrician-gynecologist monitors the formation of the brain and sets the gestation period with a certainty of 10 days.
- DB - thigh length. This indicator is used to check the child’s skeleton, or rather the absence of joint dysplasia. DB is measured only in the absence of BPR measurements. It helps to find out the date of conception and time of gestation.
- OG (DHA)—breast diameter. After 23 weeks, this parameter ceases to be informative. It is used only to analyze the overall health of the child in combination with other characteristics.
If necessary, measure the following parameters:
- occipital bone size;
- nose size;
- width of the neck fold;
- half abdominal circumference: from the umbilical cord to the spine;
- contours and size of the fertilized egg;
- shoulder size;
- head size and shape.
This is not a complete list of measured parameters during fetometry.
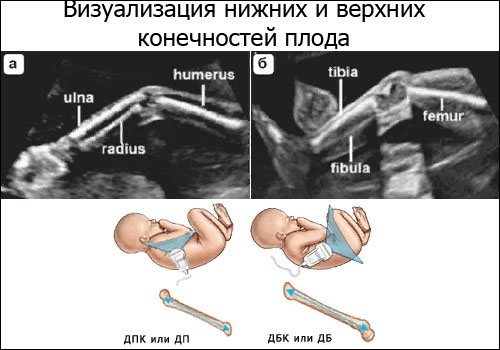
This also includes bone measurements:
- tibia;
- tibia;
- ray;
- elbow;
- brushes;
- Feet.
These parameters have no significance for identifying various anomalies and are defined only for the sake of additional information.
Tests and examinations in the third month of pregnancy
As a rule, it is in the third month that a pregnant woman is registered: during the first examination, a new medical record will be created, into which all the results of tests and regular examinations will subsequently be entered. And now the list of these same tests and examinations is quite impressive: doctors need to make sure that the pregnancy is progressing according to indications, the baby in the mother’s tummy is in perfect order, and there are no diseases or conditions that threaten pregnancy. And if, nevertheless, some problems are observed in the body, tests and examinations in the third month of pregnancy will give specialists the opportunity to decide on a further plan of action.
When registering, a woman's height, weight and blood pressure will be measured. An examination on the chair is also required, during which the doctor will take a gynecological smear (to identify possible sexually transmitted infections) and a cytological smear (determining the structural features of the cells of the surface and canal of the cervix). In addition, during a manual examination, the gynecologist determines the structural features of the internal genital organs and determines whether the size of the uterus corresponds to the gestational age.
Now it is also necessary to take a clinical blood test and a general urine test. A blood test is also indicated for HIV and ToRCH infections (toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, herpes, syphilis, hepatitis B and C and some others), which threaten the fetus with pathologies and developmental anomalies. The pregnant woman is also recommended to undergo a biochemical blood test, which allows assessing the functioning of many internal organs, as well as a blood clotting test.
A consultation with a therapist, ophthalmologist, dentist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, or an electrocardiogram session would not hurt.
At the end of the third month of pregnancy, at 11-12 weeks, the first planned ultrasound occurs, during which the specialist will determine the gestational age and estimated date of birth, eliminate the possibility of multiple pregnancies, and assess the degree of risk of genetic abnormalities and malformations of the baby.
Baby's weight
This measurement is of great importance for the developing and growing embryo. With its help, the obstetrician-gynecologist monitors the child’s condition and assesses the likelihood of abnormalities. With timely detection of abnormalities, the development of many intrauterine diseases can be prevented.
The increase should be up to 100 g weekly, and several kilograms between screenings. It must be remembered that the individual characteristics of the child’s body can shift the size of the increase up or down from the table values.
The main thing when monitoring fetal weight is the dynamics of weight gain, not its decrease.
Sex in the third month of pregnancy
Sexual intercourse is not a contraindication or prohibition at the end of the first trimester. On the contrary, being in a euphoric state increases libido and desire for intimacy.
Sex does not harm the baby and does not affect the process of the gestational period.
The ban on intimacy applies if there is a risk of miscarriage or the pregnancy is complicated by other pathological reasons (chronic diseases, hypertension).
KTR
The results of the distance from the crown to the tailbone of the fetus are entered into the table of the results of the first screening. This is the main parameter when conducting research in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is strictly controlled until the child reaches a length of 6 cm.
Based on the coccygeal-parietal size, the date of conception and gestational age are determined with an accuracy of 7 days.
The CTE indicator is not informative in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy , since fetal growth during this period is determined by heredity. Jumps in this parameter may go beyond normal values, so in the second screening the main parameter is the distance between the parietal bones.
If the CTE indicator increases for a couple of weeks, a repeat examination of the mother is prescribed to identify pathologies such as:
- diabetes;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- tumors.
In the absence of these problems with the mother's health, an increase in the distance between the crown and the tailbone indicates a large size of the fetus. At the time of birth, he may weigh more than 4 kg.
When carrying particularly large children, it is necessary to take various medications carefully and under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist, especially vitamin complexes and nutritional supplements. Abuse of such drugs can increase the baby's weight up to 5 kg , which will provoke a difficult birth.
A decrease in CTE may also be normal, or may indicate a pathology of fetal development.
This result when measuring CTE is considered normal if late ovulation and late fertilization have occurred. No modern ultrasound machine can detect such a difference in timing. In this case, the time of conception shifts and does not coincide with the time calculated from the woman’s menstrual cycle.
To clarify the situation, the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes repeat fetometry after 7 days.
A decrease in the distance from the crown to the tailbone may indicate pathologies:
- Weak production of progesterone. After additional tests, the attending gynecologist prescribes a hormonal treatment regimen. If its recommendations are not followed, spontaneous miscarriage may occur.
- Infectious diseases of the mother or infection of the fetus. These include sexually transmitted diseases. They not only interfere with the child’s normal weight gain, but can also cause serious abnormalities. The attending physician prescribes the necessary blood, urine and stool tests to determine the type of infection. After this, he prescribes the required and effective treatment.
- Damage to the uterine mucosa. Erosion, fibroids or a previous abortion injure the mucosal tissue. Because of this, the fertilized egg is not able to firmly attach itself to the walls of the uterus, which threatens spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Genetic diseases. These include Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome and others. To confirm them, a genetic examination is required. Severe forms of pathologies end in miscarriage.
- Non-developing pregnancy (frozen). This pathology provokes the death of the fetus and threatens the mother:
- opening of bleeding;
- infertility;
- anaphylactic shock;
- fatal.
If this diagnosis is confirmed, the woman requires immediate surgery. This pathology is excluded by listening to the child’s heartbeat on an ultrasound.
Alarming symptoms

At week 10, white, odorless discharge is normal. With a weakened immune system, the expectant mother may develop thrush. The disease is characterized by itching and burning in the vagina.
If the discharge has acquired a greenish or yellow tint, flakes are observed and an unpleasant odor is felt, it is important to urgently find out the cause. Infection is indicated by pain and burning when urinating.
The greatest danger is bloody or brown discharge. They usually appear along with contraction-like pain. Such symptoms may indicate the onset of a miscarriage. In such a situation, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Discharge with blood occurs during an ectopic pregnancy - when the fetus is fixed in the fallopian tube. This condition is characterized by increased danger. If it is not diagnosed in time, the grown egg will damage the fallopian tube. A rupture poses a threat to the life of the pregnant woman, so immediate surgery is required for an ectopic pregnancy.
At the 10th week of pregnancy, spotting may appear after sex, a careless examination by a gynecologist, or during erosion of the cervix - characteristic ulcers appear on it. Discharge in such cases is not accompanied by nagging pain in the abdomen. A visit to a specialist is mandatory even if blood clots appear for a short time.
BPR
Biparental indicators are the main parameter in mid-pregnancy. It shows the maturity of the brain and the compliance of the fetus with the gestation period. BPR is measured between the temples along the eyebrow line. Sometimes, together with it, the distance between the forehead and the posterior fontanelle is determined along the outer borders of the frontal and occipital bones (LZR).
BDP indicators help to determine the degree of safety of childbirth for a woman and her child. If BPR values are higher than normal, the pregnant woman is prescribed a planned cesarean section. The combination of the BPD and LZR parameters determines the development of the child’s nervous system and brain.
A distinctive feature of these characteristics is a decrease in growth rate with increasing gestation period.
As with KTR, jumps in BPR and LZR relate to both normal and pathological development of the fetus. A deviation of all values by 4 weeks is considered normal when the child weighs more than 4 kg, since his growth is uneven. To confirm a positive result, the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes a repeat ultrasound in a few weeks.
Increased biparental indicators can also be a pathology and indicate the presence of abnormalities of bone tissue and brain:
- neoplasms;
- hernias;
- hydrocephalus;
- accumulation of fluid in various parts of the brain.
If these pathologies are confirmed, the obstetrician-gynecologist will give recommendations to the pregnant woman:
- in case of hernias and neoplasms - termination of pregnancy, since the fetus with such complications dies at a later stage;
- for hydrocephalus or dropsy - treatment with antibiotics, and negative results are advised to terminate the pregnancy.
A decrease in BPR and LZR always indicates pathologies:
- Underdevelopment of the brain structure or its complete absence. In this case, the woman is immediately operated on, regardless of the gestation period and the stage of the complication.
- Deviation from the timing of development. In this case, medical intervention and correction of the fetal condition are necessary. In their absence, the fetus dies.
Together, the BPR and LZR determine the shape and circumference of the fetal head.
Belly at 3 months pregnant
The baby is growing, and your belly is expanding along with its size. The uterus is located in almost the entire pelvic region. It has reached such a size that a woman can feel it herself. And by the end of the 12th week you will already feel it above the pubic bone. The belly is not yet big enough to start a whole wardrobe change if this is your first pregnancy. But for those who already have at least one child, it usually appears earlier and the usual clothes become small.
During this time, your weight may not have changed, or it may have increased by a couple of kilograms - if the increase is from 2 to 4 kg, this is quite normal.
Belly at 3 months pregnant: photo
The tummy becomes rounded, but this depends, rather, on the build of the expectant mother. It may be more noticeable in thin women than in curvy women.
photo: babycenter.com
- Your child already has fingerprints. This is impressive as its tiny body is only about 7-8 centimeters long and weighs only 10-13 grams.
- If it is a girl, then now she already has more than 2 million eggs in her ovaries.
- The body catches up with the head. The head now makes up a third of her body, rather than half.
- Your risk of miscarriage is now much lower. In addition, many women notice an increase in libido during this period.
Ultrasound at 3 months of pregnancy
At 11-13 weeks, an ultrasound examination is mandatory for every expectant mother registered at the antenatal clinic. The specialist will once again clarify the duration of pregnancy and expected birth, rule out or confirm the presence of multiple pregnancies. But the important thing is that already at this stage the doctor will be able to diagnose the correct development of the fetus and monitor the risk of genetic abnormalities.
Determination of thigh length
Measuring the length of the thigh is an equally important indicator. It determines the possibility of underdevelopment of the skeletal system . An ultrasound specialist takes a measurement of the femur if the device was unable to display the BPR parameter or the shape of the fetal head has changed significantly.
The length of the femur determines the gestation period to within a week. Determining the size of other bones to determine the gestational age is not highly accurate.
Abdominal circumference
If the child weighs more than 4 kg, this parameter is not determined. The volume of the abdomen characterizes the development of the internal organs of the fetus: stomach, ductus venosus, intestines, gall bladder, and so on. Using an ultrasound, an obstetrician-gynecologist monitors the formation and growth of internal organs.
Abdominal girth is not as precise as femur size, but is used as a key indicator when suggesting intrauterine growth retardation.
How does measuring abdominal circumference by week help identify fetal development abnormalities?
If the fetal abdominal circumference lags behind the standard size by 2 or more weeks, doctors may diagnose the child with intrauterine growth retardation syndrome (IUGR, malnutrition). When making this diagnosis, it is not the parameter itself that is assessed, but the relationships: OH/CO, BPR/CO and DB/CO, etc.
The first signs of the syndrome can be seen as early as 24-26 weeks. Usually at this time the doctor identifies a symmetrical form of malnutrition, when the baby lags behind the norm in all measurements. This type of syndrome is rare.
More often there is an asymmetric form of fetal growth retardation. At the same time, the baby’s head and skeleton grow normally, but the internal organs are reduced. In other words, the head circumference, biparental size and thigh length correspond to the gestational age, and the fetal abdominal circumference is reduced. In this case, the ratios of exhaust gas/coolant, BPR/coolant and DB/coolant will be below normal. But only a doctor can make a final diagnosis
!
Chest volume
Breast diameter is a highly informative parameter in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy , but other parameters are studied along with it to assess the condition of the fetus. Based on the volume of the chest, the obstetrician-gynecologist determines the development of the chest organs: heart, lungs, thymus and trachea, and also assesses the risk of developing skeletal dysplasia.

Chest circumference is not always measured; it is only informative if other parameters are available and cannot serve as a basis for making a diagnosis.
Analyzes and research
At this time, registration takes place, so the range of tests, hardware tests and examinations has been increased.
So, the tests and examinations carried out:
- History taking and external examination:
- measurement of weight and height parameters;
- blood pressure measurement;
- collection of gynecological history;
- examination on a gynecological chair using mirrors.
- Laboratory blood tests:
- general or detailed blood test with mandatory leukocyte and platelet counts;
- biochemical blood test: glucose, urea, protein and transaminases;
- blood group and rhesus affiliation;
- coagulation system with determination of D-dimer;
- enzyme immunoassay for the level of female hormones;
- blood for TORCH infections;
- study of general urine analysis and urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- vaginal smear for flora and atypical cells.
- Consultations with specialized specialists: endocrinologist, dentist, ophthalmologist, nephrologist, cardiologist.
- ECG, echocardiography and ultrasound of the fetus.
It is especially important to carry out prenatal screening to diagnose fetal abnormalities and terminate the pregnancy if necessary.
The screening test consists of two parts:
- Fetal ultrasound;
- enzyme immunoassay of progesterone, estrogen and hCG.
The data obtained determine the possibility of developing chromosomal mutations and genetic damage.
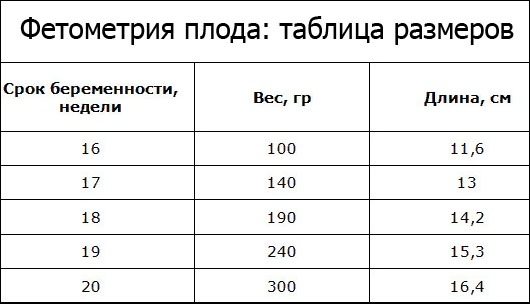
Table: norms of fetal photometry by week
After undergoing screening in each trimester of pregnancy, parents want to make sure that the child is developing normally. To make it easier for parents and doctors to navigate the measurements taken, there is a general system of standards.
Fetal fetometry by week: table of limit values of key parameters.
| Week of pregnancy, obstetric | KTE, mm | Weight, g | BPR, mm | DB, mm | Coolant, mm | DHA, mm |
| 12 | 42-73 | 13-25 | 22-24 | 7-11 | 50-71 | 21-25 |
| 13 | 51-87 | 25-37 | 25-27 | 10-14 | 58-79 | 22-26 |
| 14 | 87-150 | 37-60 | 28-30 | 13-19 | 66-91 | 24-28 |
| 15 | 140-159 | 60-88 | 31-33 | 15-20 | 85-103 | 26-30 |
| 16 | 153-172 | 88-130 | 34-37 | 17-23 | 88-115 | 28-36 |
| 17 | 170-195 | 130-180 | 38-41 | 20-28 | 93-130 | 36-40 |
| 18 | 195-212 | 180-230 | 42-47 | 23-31 | 105-144 | 39-43 |
| 19 | 215-238 | 230-290 | 48-49 | 26-34 | 114-154 | 42-46 |
| 20 | 238-250 | 290-382 | 50-53 | 29-37 | 125-163 | 46-50 |
| 21 | 250-275 | 382-458 | 54-56 | 35-39 | 137-177 | 48-52 |
| 22 | 275-290 | 458-552 | 57-60 | 37-43 | 148-190 | 51-55 |
| 23 | 293-320 | 552-630 | 61-64 | 40-46 | 160-201 | 54-58 |
| 24 | 310-322 | 630-754 | 65-67 | 42-50 | 173-223 | 57-62 |
| 25 | 322-335 | 754-870 | 68-70 | 46-50 | 183-228 | 60-64 |
| 26 | 335-345 | 870-990 | 71-73 | 49-58 | 194-240 | 62-66 |
| 27 | 345-360 | 990-1200 | 75-76 | 53-60 | 206-253 | 67-71 |
| 28 | 359-385 | 1200-1350 | 77-79 | 54-61 | 217-264 | 71-75 |
| 29 | 382-396 | 1350-1500 | 80-82 | 55-62 | 228-277 | 74-78 |
| 30 | 396-405 | 1500-1690 | 83-85 | 56-62 | 238-290 | 77-81 |
| 31 | 400-428 | 1690-1800 | 86-87 | 59-65 | 247-300 | 79-83 |
| 32 | 425-437 | 1800-2000 | 88-89 | 60-66 | 258-314 | 81-85 |
| 33 | 432-440 | 2000-2200 | 90-91 | 63-69 | 267-334 | 83-87 |
| 34 | 438-450 | 2200-2320 | 92-93 | 64-69 | 276-336 | 86-90 |
| 35 | 446-460 | 2320-2600 | 94-95 | 65-71 | 285-344 | 89-93 |
| 36 | 458-470 | 2600-2700 | 96-97 | 67-72 | 292-353 | 92-96 |
| 37 | 469-480 | 2700-2885 | 98-98 | 68-74 | 300-360 | 95-99 |
| 38 | 478-498 | 2885-3000 | 99-100 | 70-76 | 304-368 | 97-101 |
| 39 | 493-510 | 3000-3223 | 101-102 | 72-78 | 310-375 | 99-103 |
| 40 | 505-538 | 3223-3400 | 103 | 74-80 | 313-380 | 101-105 |
There is also a separate table of accepted CTE values, since this indicator is most informative only in the first weeks of gestation until the fetus reaches a size of 60 mm.
| Week of pregnancy, obstetric | Fruit size, mm | KTE, mm |
| 5 | 03-1,0 | 1-4 |
| 6 | 0,9-1,3 | 3-8 |
| 7 | 1,0-1,5 | 7-12 |
| 8 | 1,3-2,0 | 11-18 |
| 9 | 2,1-2,7 | 17-23 |
| 10 | 2,7-3,8 | 24-40 |
| 11 | 3,5-4,5 | 26-53 |
Is research harmful?
The ultrasound procedure is completely harmless. The waves produced during the test are high-frequency sounds that are not detected by the human ear.
Ultrasound:
- does not affect the condition of the skin;
- not capable of causing pathologies of internal organs;
- does not affect the course of pregnancy.
The high frequency of the waves causes slight vibrations in the tissues, which do not change their structure in any way. Also, the effect of ultrasound does not have a cumulative effect, which has been proven by scientific research. When conducting fetal photometry, several factors are taken into account: the course of pregnancy and the woman’s health.
It is worth remembering that each child’s body is individual and hereditary characteristics can affect the values obtained. Because of this, they may differ from the table parameters. To confirm the normal development of the child, it is necessary to undergo a screening ultrasound after a few weeks.
Author: Shalunova Anna
Article design: E. Chaikina
What happens in a woman's body
The female body undergoes many changes. Hormonal levels change, and toxicosis often develops for this reason.
There are no external signs, but sometimes a slight rounding of the abdomen is possible (more often in thin representatives of the fairer sex).
Hormone production occurs at an accelerated pace to prolong pregnancy and normal intrauterine development of the fetus.
At the end of 3 months, mandatory prenatal screening is carried out to detect possible developmental pathologies of the baby.