The Mantoux test is a research method with which doctors evaluate the body’s response to the entry of the tuberculosis pathogen antigen into it. The Mantoux test is used to confirm the diagnosis of tuberculosis and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. At the Yusupov Hospital, only tuberculin preparations registered in the Russian Federation are used for the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is performed by a specially trained nurse, and the results are assessed by a doctor who has undergone special training.
Sometimes people call the test “Mantoux vaccination”. This is an incorrect term, since after tuberculin is administered, the patient’s body does not produce antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Doctors evaluate the body's response to the injection.
Tuberculin is a filtrate of a heat-killed culture of human and bovine Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is purified by ultrafiltration or other means, precipitated with trichloroacetic acid, treated with ethyl alcohol and anesthetic ether and dissolved in a stabilizing solvent. The drug is a colorless transparent liquid that does not contain sediment or foreign impurities.
The active substance of the drug (allergen-tuberculoprotein), when performing an intradermal tuberculin test, causes a specific delayed-type allergic reaction in the body vaccinated with BCG or infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the form of a local reaction - infiltrate (papules) and redness.
Why is Mantoux test done?
The Mantoux test is done to identify individuals newly infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with hyperergic and intensifying reactions to tuberculin, and to determine epidemiological indicators for tuberculosis. The purpose of the study is to select groups for anti-tuberculosis vaccination with the BCG-M vaccine in children aged two months and older who did not receive vaccination in the maternity hospital, and for revaccination with the BCG vaccine, for the early diagnosis of tuberculosis in children and adolescents. For mass tuberculin diagnostics, a single intradermal Mantoux tuberculin test is used with two tuberculin units (TU) of purified tuberculin in a standard dilution.
Individual tuberculin diagnostics are carried out to determine post-vaccination and infectious allergies to tuberculin, diagnosis and differential diagnosis of tuberculosis and other diseases, determine the “threshold” of individual sensitivity to tuberculin, the activity of the tuberculosis process, and assess the effectiveness of anti-tuberculosis treatment. How to replace Mantoux? For individual tuberculin diagnostics, in addition to the Mantoux test with 2 TU of purified tuberculin in a standard dilution, Mantoux tests with various doses of tuberculin, a graduated Pirquet skin test, and determination of tuberculin titer are used. To carry out individual tuberculin diagnostics, purified tuberculin in standard dilution and dry purified tuberculin are used.
What side effects are possible?
From the moment of tuberculin administration until the result is assessed, 72 hours must pass. Usually this period proceeds easily, without any worries. However, in some cases, side effects are possible, so parents need to pay special attention to the child during this period of time and monitor the general condition of the child.
In some cases, there may be unpleasant sensations that can cause discomfort. We are talking about redness and itching of the skin at the site of tuberculin injection, sometimes there is slight swelling of the tissue.
The following reasons cause this reaction:
- individual intolerance to tuberculin, severe allergic reaction to the drug;
- unaccounted for contraindications for the test (the test was carried out against the background of an existing infection, or not enough time has passed since the illness);
- infection through an injection wound (when the test site was subjected to excessive mechanical stress - friction, scratching).
To reduce an excessive allergic reaction, the child can be given an antiallergic drug.
To prevent infection, you need to convince the child not to touch or scratch the injection site. Of course, a teenager will listen to advice in this regard, but if the baby is a year or two old, it is extremely difficult to explain this to him. In this case, an adult needs to pay special attention to the baby to prevent any impact on the hand. Long sleeves will also help with this.
If antiallergic drugs do not help, the symptoms do not go away, but, on the contrary, worsen, the child feels unwell, the temperature rises, the baby complains of pain in the arm on which the test was performed, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
Contraindications to the Mantoux test
There are no absolute contraindications to performing the Mantoux test. When carrying out this reaction, inactivated tuberculin is used, which does not contain live pathogens. It cannot cause harm to health. The dose of the drug is so small that it cannot cause life-threatening allergies. For this reason, the Mantoux test still remains one of the most common methods for mass diagnosis of tuberculosis, although it is quite inaccurate.
The Mantoux test is not performed on children under twelve months of age. Their immunity has not fully developed, so it is impossible to judge from the test results whether the body is infected with tuberculosis. The reaction will be false negative if the child is sick. The Mantoux test is carried out no earlier than four weeks after vaccination, since any vaccinations can affect the results and the reaction very often becomes false positive.
The Mantoux test is not carried out in children's groups where quarantine has been declared, even if individual children are healthy. In this case, it is postponed until the quarantine is lifted. The Mantoux test is not performed on patients with infectious diseases or during exacerbation of chronic diseases until their symptoms completely disappear. Doctors also include seasonal allergies, which manifest themselves as skin rashes and signs of rhinitis or other symptoms, as chronic diseases. The Mantoux test is postponed until the patient recovers in the presence of skin diseases, allergic conditions (bronchial asthma, idiosyncrasy with pronounced skin manifestations, rheumatism in the acute and subacute phases). The test is not given to patients suffering from epilepsy, or if there is a severe allergic reaction to the components of the drug or a severe skin reaction has occurred during a previous Mantoux test.
When and why is the vaccine given?
Mantu is made for children from one to 14 years old. This is not a vaccination in the full sense of the word, but a method of screening for a disease. Based on the results of the procedure, doctors judge the possible presence of pathogens of a serious illness in the body. Newborns are vaccinated against tuberculosis with BCG while still in the maternity hospital. By the age of 7 years, the effect of the drug ceases. The test helps to find out whether the body still has immunity against infection.
Mantoux is made for the following purposes:
- Identification of those children whose reaction is strongly expressed. Additional examination is required, as there is a suspicion that they are sick.
- Monitoring dynamics over several years. It is used to judge that there may be pathogenic bacteria in the body and the development of tuberculosis has begun.
- Identification of persons who do not have an immune response to Mantoux (there is no lump or redness, only a trace of the injection remains in the form of a dot); such children must be vaccinated against the disease again.
You can find out information about tuberculosis prevention in the video from the Profilaktika Tomsk channel.
How is the Mantoux test performed?
A special substance, tuberculin, is injected into the skin below the elbow on the inside of the arm with a syringe. It is impossible to get this disease from it. After all, the drug is made from particles of pathogenic mycobacteria that are neutralized by heating. This vaccine is considered non-live. No preparation is required on the part of the patient for the procedure.
Contraindications
You cannot do the Mantoux test in the following cases:
- when a child suffers from epilepsy;
- there is an infectious or viral disease, flu, quarantine at school or kindergarten;
- there are skin diseases;
- for allergies of any origin;
- there are chronic ailments, especially in acute form.
Side effects and complications
Sometimes a child may experience adverse reactions to Mantoux:
- disturbance in the digestive system;
- lethargy and fatigue;
- increase in body temperature;
- skin rash;
- cough a week after the test was administered.
The occurrence of side effects in some children suggests that tuberculin contains a small amount of toxic components. They cause undesirable consequences.
Technique for performing the Mantoux test
Before performing the Mantoux test, the patient's temperature is measured and he is examined by a doctor. To perform an intradermal Mantoux test, the Yusupov Hospital uses one-gram disposable tuberculin syringes with thin short needles with a short oblique cut. Do not use syringes and needles that have expired. Before use, the nurse checks their release date and expiration date. The use of insulin syringes for tuberculin diagnostics is prohibited.
To perform the Mantoux test, the nurse uses the following materials:
- Bix size 18x14 cm with sterile cotton balls;
- Millimeter rulers 100 mm long, made of plastic;
- 50 ml bottle with ethyl alcohol;
- 50 ml bottle with ammonia;
- Anatomical tweezers, 15 cm long;
- Injection needles N 0840 for extracting tuberculin from a bottle.
The nurse carefully wipes the ampoule with tuberculin with gauze moistened with 70% ethyl alcohol. Then the neck of the ampoule is filed with a special knife and broken off. Using a syringe used for the Mantoux test and a needle N 0845, tuberculin is extracted from the ampoule. Takes two doses of tuberculin (0.2), inserts the needle of a tuberculin syringe, releases the solution to the 0.1 mark into a sterile cotton swab. After opening, the ampoule is stored under aseptic conditions for no more than two hours.
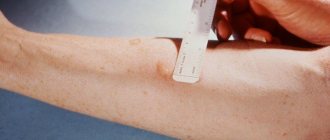
The Mantoux test must be performed on patients in a sitting position, since in emotionally labile individuals the injection can cause fainting. Treat the area of skin on the inner surface of the middle third with 70% ethyl alcohol and dry with sterile cotton wool. A thin needle, cut upward, is inserted into the upper layers of stretched skin parallel to its surface. After the hole of the needle is inserted into the skin, one dose of tuberculin (0.1 ml of solution) is injected from the syringe. What are the dimensions of the Mantoux test? A whitish papule in the form of a “lemon peel” with a size of at least 7-9 mm is formed in the skin.

Evaluation of the results of the Mantoux test with 2 TE
The doctor evaluates the result of the Mantoux test after 72 hours by measuring the size of the infiltrate (papules) in millimeters. Using a ruler with millimeter divisions, the nurse measures and records the transverse (relative to the axis of the forearm) size of the infiltrate. If there is no infiltrate, hyperemia is measured and recorded when taking into account the reaction to the Mantoux test.
When performing a Mantoux test, the reaction is considered:
- Negative – in the complete absence of infiltration or redness or in the presence of a reaction from the injection (0-1 mm);
- Doubtful - if the infiltrate is 2-4 mm in size or only redness of any size without infiltration is determined;
- A positive Mantoux test is considered in the presence of an infiltrate with a diameter of 5 mm or more.
Mantoux reactions with an infiltrate size of 5 to 9 mm in diameter are considered weakly positive, moderate intensity - in the range from 10 to 14 mm, pronounced - in the range of 15-16 mm. Hyperergic (large) Mantoux in children and adolescents is considered in the following cases: a reaction in children and adolescents with an infiltrate diameter of 17 mm or more, in adults - 21 mm or more, as well as vesicular-necrotic reactions, regardless of the size of the infiltrate with or without lymphangitis . An increasing reaction is considered to be an increase in infiltrate by 6 mm or more compared to the previous Mantoux test. A positive Mantoux test is visible in the photo.
False negative results can be obtained in the following cases:
- With age-related immune deficiency, unbalanced nutrition, renal failure, diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression by drugs (glucocorticoids);
- In patients with cancer, HIV infection, sarcoidosis;
- If you have severe forms of tuberculosis;
- If the patient has suffered from a viral infection (measles, chickenpox, mumps, influenza, infectious mononucleosis);
- In case of co-infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, HIV also results;
- After immunization with live vaccines (measles, mumps and rubella).
The interval between any preventive vaccinations and the Mantoux test should be at least one month. Routine vaccinations can be carried out after taking the Mantoux test after 72 hours. A false positive reaction during the Mantoux test can be caused by infection with non-tuberculous mycobacteria and previous BCG vaccination.
Sometimes after the Mantoux test, patients’ body temperature rises, general malaise and headache occur. These symptoms do not require intervention and go away on their own. Where to do a Mantoux test in Moscow? The Mantoux test can be done by calling the contact center. Patient reviews of the Mantoux test at the Yusupov Hospital are positive.
Author
How to check Mantoux results after the second vaccination
The normal indicator is the size of the “button” - 1 cm. At 9 years old it can reach 16 mm, and this will also be considered normal.
Starting from the age of 10, results are assessed taking into account previous indicators. The size of the papule should steadily decrease. At the age of 15, the test result in a healthy child becomes exclusively negative.
Any jump or excess of indicators during this time is grounds for immediately contacting a phthisiatrician and undergoing an examination. This is especially true for those children whose previous test gave a negative reaction.