Main features of the examination technique
Ultrasound examination is considered one of the most popular methods for diagnosing various pathologies. The examination is not difficult, does not require significant financial costs, is safe for patients, and allows one to obtain accurate information.
Ultrasound of the brain is performed in children, and not in adults, because with age, fontanelles grow between the bones of the skull, ultrasound radiation does not penetrate the brain, and sensors do not pick up signals.
This examination method is called echography because, when passing through soft tissue, signals in the frequency range from 0.5 to 15 MHz are reflected in different ways from substances with a different structure. Based on an analysis of existing reactions after comparison with normal results, doctors make a diagnosis.
The brain is examined in this way only in infants. The maximum age at which an ultrasound of the brain vessels of a child is performed is 1.5 years . The sensor is located between the frontal and parietal bones of the baby, but fontanelles are still present in the area of the temples and the back of the head, and later they heal.
Is ultrasound of the brain harmful for children under one year old?
Parents are often concerned about how harmful it is for young children to undergo a brain ultrasound. However, they do not need to worry - neurosonography is an absolutely painless procedure, during which the condition of the nervous tissue is assessed by exposing the area under examination to ultrasound waves of a certain frequency. It is performed non-invasively, in real time and without the use of anesthesia. In addition, ultrasound does not require special preparation and can be performed repeatedly in a short period of time.
The advantage of using brain ultrasound over other methods of examination is obvious even to a person ignorant of medicine: firstly, it does not require large financial costs to examine the internal state of this organ of a newborn and is available free of charge with a referral from a specialist under the compulsory medical insurance policy. Secondly, it does not require special preparation and administration of medications the day before.
One of the advantages of brain ultrasound in children under one year of age is the immediate receipt of examination results, while the decrypted data contains all the information necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
However, despite all the advantages, modern ultrasound equipment does not allow a full assessment of the internal state of brain tissue, therefore, if a serious illness is detected, the baby may be referred for additional examination.
What is the procedure?
Neurophysiography means performing an ultrasound examination of the brain in newborns and children under 1 year of age. High-frequency vibrations are reflected from the brain and display its outline on a digital display.
The procedure is safe, does not cause pain, and allows you to obtain a lot of information. These circumstances make it possible to carry it out regularly. There is no need to administer anesthesia to the patient ; it is enough to keep the child immobile or wait until he falls asleep. Crying or screaming has no effect on the results.
This method of examination is considered most suitable for infants. It is carried out until the fontanel between the bones of the skull is overgrown.
Ultrasound of the brain in newborns makes it possible to familiarize yourself with all the individual structures of the organ. During a short procedure, doctors will be able to analyze brain processes and the general dynamics of their flow.
When is an ultrasound of the brain prescribed for newborns?
Ultrasound of a newborn’s head is prescribed in a number of cases:
- premature birth (36 weeks or more);
- there are signs of damage to the child’s central nervous system;
- the body weight of the newborn does not exceed 2800 grams;
- bulging fontanel;
- cerebral hernia;
- multiple external developmental defects; • birth injury.
Also, ultrasound of the brain in newborn children is performed after transfer to intensive care, in case of too rapid and protracted labor, in case of complications during the birth process, if the child did not cry immediately after birth. In addition, the examination may be prescribed for other indications, including if specialists suspect an intrauterine infection. From a month to three months, ultrasound of the brain is performed on children if there is a suspicion of neurological diseases. An examination may be required if there is psychomotor retardation, muscle weakness, or seizure activity. To diagnose possible pathologies in the development of a child’s brain, ultrasound of the head is recommended for newborn children from one month to one year of age. It is recommended to carry out several procedures at intervals of a month or more.
Indications
For a child in the first year of life, there are many indications for an ultrasound examination. This could be pregnancy and childbirth, suspicions of various diseases, congenital defects, etc. Determining pathology in the primary stages of development gives a better chance of recovery.
The procedure lasts a maximum of 15 minutes. To examine the head, a specialist attaches sensors to the anterior fontanelle and temple area. In rare examples, the occipital areas are examined. An ultrasound is performed in order to obtain reliable information about the state of the newborn's brain .
The displayed data is compared with the normal state and a diagnosis is made. A total of 12 common diagnostic indicators are used. The neurologist takes into account the examination results when determining the therapeutic technique.
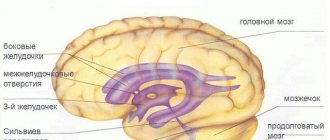
The doctor determines the condition of the wide blood vessels of the brain, identifies deformation of the walls, damage, plexus, neoplasms, and analyzes the structure of the tissues. The main parameters to study are the volume of the ventricles. Excessive indicators indicate violations.
What is brain ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the brain of newborns, or, as it is also called, neurosonography, is an absolutely harmless method for studying brain tissue, the cerebral cortex, blood vessels and other structures located inside the skull. This diagnostic method is based on the principle of echolocation. The ultrasound pulse sent by the device penetrates the brain tissue and is reflected from it. The reflected signal is captured by the sensor and displayed on the monitor as an image.
The entire examination procedure is absolutely safe, has no side effects and does not take longer than 15–20 minutes. In this case, diagnostics can be carried out even while the child is sleeping. And if the sleep is deep, then the baby will not even wake up. But both the doctor and you will receive complete information about the health of the baby’s brain.
Ultrasound of the brain in children
Neurosonography indicators are determined by the week in which the baby is born. We list the normal indicators of ultrasound examination:
- The grooves and convolutions in the brain should be located symmetrically, the ventricles and cisterns should be clearly visible.
- The echogenicity index of the subcortical nuclei is normal.
- The anterior horn of the extreme ventricle is approximately 1-2 mm deep. Its size should not exceed 4 mm.
- There is no fluid in the gap between the hemispheres of the brain. The normal width is 2 mm.
- The choroid plexuses in the area of the ventricles are homogeneous.
- The size of the 3rd ventricle is 2-4 mm.
- The stem structures are located in their place.
- The length of the large tank is 3-6 mm.
A neurologist interprets the ultrasound results. He can prescribe the correct therapeutic technique for the baby. Monitor and determine trends in the development of brain tissue, identify possible diseases. The neurologist needs to evaluate the neurophysiography data and compare them with the identified symptoms.
What disorders can a brain ultrasound detect?
Ultrasound of the brain in children allows us to identify a wide variety of diseases, structural changes, tumors, hemorrhages and the consequences of even minor birth injuries. During diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the following parameters:
- Sizes and contours of the ventricles of the brain. As well as the surface area of these cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
- Condition of large vessels of the brain and their interweavings.
- Structure of brain tissue, etc.
Based on the data obtained, a transcript of the ultrasound of the brain of newborns is being prepared. It must indicate all deviations from the norm. So, for example, an increase in the ventricles of the brain indicates the presence of hydrocephalus, and expansion of the walls of large blood vessels (arteries) indicates the presence of an aneurysm. Also, during the examination, the doctor can determine whether there was a cerebral hemorrhage during childbirth, whether intracranial pressure is increased, or whether there are structural changes.
It makes no sense to dwell in detail on each disease, as well as on a complete transcript of ultrasound data. All the same, only a doctor can give an accurate answer to the question - is everything okay with the baby? Yes, and only a highly qualified medical professional should determine the degree of damage, as well as prescribe treatment.
But don’t be too scared if after an ultrasound you and your baby are sent to a neurologist. In many clinics, it is this doctor who makes the final conclusion. In addition, minor consequences of birth injuries, small cysts and other misfortunes can be easily treated in infancy.
Decoding
Often the transcript shows such diseases. Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain occurs if their depth is higher than normal. This is a characteristic sign of hydrocephalus. Externally, in a newborn, this disorder is visible to the naked eye.
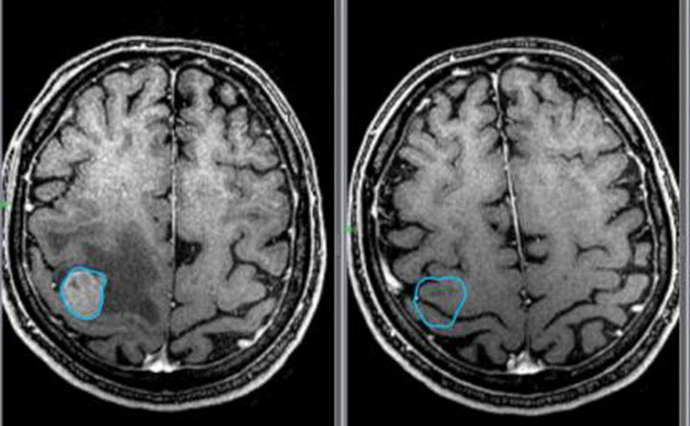
The head increases in size, the forehead protrudes forward, moles become larger. Hydrocephalus is diagnosed after bleeding or infectious processes, problems with the development of the child. The child often has migraines, fatigue, undeveloped physical development, and has mental problems.
An increase in the subarachnoid space of more than 3 mm is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a deterioration in appetite. This may indicate meningitis. The disease can develop as a result of hydrocephalus.
A cyst of the plexus of blood vessels is cells of the ventricular mucosa that secrete cerebrospinal fluid. A cyst is formed in the form of a cavity filled with something. They often do not manifest visual symptoms in the child. Such formations do not require treatment, since they resolve over time.
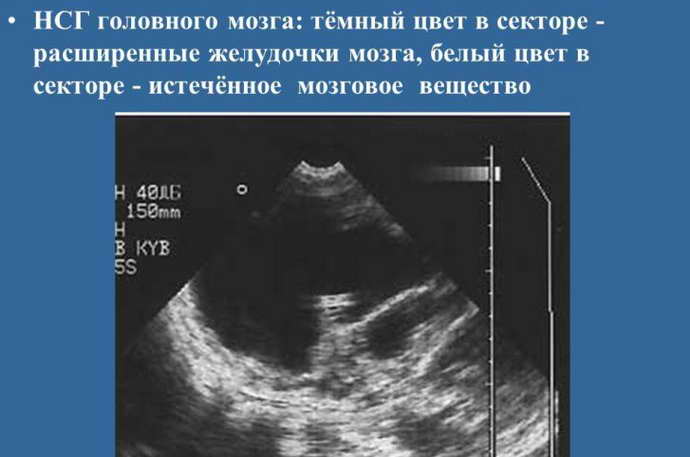
Ischemic disorders in the head. Blood vessels don't do their job well. If these areas are highly dense, brain cells atrophy in fragments, and crust formation is distorted.
If the examination results show the presence of diseases, the neurologist will prescribe prophylaxis or select an appropriate therapeutic technique. Medicines will help accelerate the closure of fontanelles.
If you have high ICP in a newborn, you should not use Aquadetrim. If there are too many abnormalities in brain development, the child will be hospitalized and complex therapy will be prescribed. Children who develop brain diseases should not be vaccinated.
Decoding the results
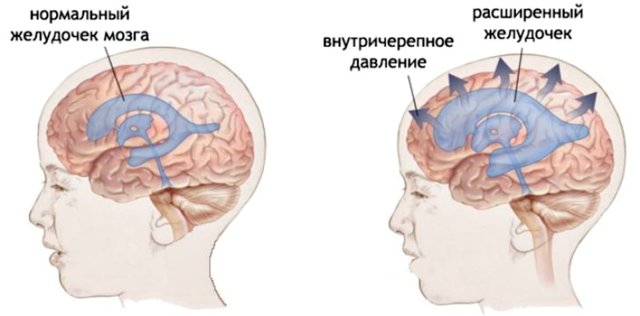
With increased ICP, the device can show dilated ventricles of the brain
The decoding is carried out by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. The normal ultrasound scan of a child’s head from birth to one year depends on age, the state of the nervous system, and the characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth.
Mandatory indicators that are the norm:
- the pattern of convolutions and grooves is distinct;
- brain structures are symmetrical;
- the thalamus and subcortical nuclei have a homogeneous structure, average echogenicity;
- absence of fluid in the interhemispheric fissure, its size should not exceed 2 mm;
- the cisterns are anechoic, the ventricles of the brain are without inclusions, homogeneous;
- body of the lateral ventricle no more than mm deep;
- the choroid plexuses should have smooth contours and be homogeneous;
- stem structures are not displaced;
- the depth of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle is 1-2 mm;
- large tank within 3-6 mm;
- third ventricle 2-4 mm.
You should not pay special attention to the numbers indicated in the conclusion if it is stated that the baby is healthy. Sometimes a deviation in one of the indicators is normal, for example, for premature babies and children who experienced acute hypoxia during childbirth.
The doctor conducts a comprehensive assessment of the results. Only a combination of factors can indicate hypoxia, hydrocephalus, ischemic foci, etc. If the data shows the presence of a serious pathology, additional research methods are prescribed, for example, MRI or CT.
What does ultrasound reveal?
An ultrasound of a child’s head allows you to examine:
- Ventricles of the brain . In the process of visualizing their volume and contours, the specialist identifies hemorrhages, cysts, dropsy, and processes that contribute to the development of rickets. If diseases are eliminated in time, pathologies of intellectual and physical development will be avoided.
- Condition of wide vessels . Aneurysms are detected in the form of enlargement of arterial walls. As a result, blood flow to the brain becomes difficult.
- Hemorrhages caused by prematurity. This problem needs to be monitored as closely as possible, as the result may be the death of the baby.
- Infections that cause meningitis. If the disease is detected in time, the child can fully recover.
- Oncology is detected in rare cases.
How is it carried out?
It is possible to perform an ultrasound of the child’s brain only until the age when the fontanelles close. The examination is carried out through the anterior, lateral fontanelles or foramen magnum at the base of the child’s neck.
During an ultrasound, the diagnostician moves a special sensor over the baby's head. The resulting pulses are sent to the device and displayed on the monitor in the form of images. This is a comfortable procedure that can be done in the clinic, even while the child is sleeping.
You can sign up for ultrasound diagnostics by calling the reception at (495) 951 87 63 or
In our center, infants undergo comprehensive diagnostics (NSH, ultrasound of the hip joints, EEG/video-EEG monitoring) and consultations with a neurologist, orthopedist, geneticist, and ophthalmologist.
Method of carrying out
Performing an ultrasound of a child's head does not require prior preparation. It is necessary for the baby to be in a calm state, it is better to let him sleep. In such a situation, he will not have any discomfort; you can use a toy to distract his attention.
An ultrasound of a child’s brain involves performing the following steps:
- The baby is placed lying down and held in the correct position. The procedure is performed within 10 minutes. The patient needs to be calmer during this period.
- Newborns are not given anesthesia. You need to hold the head so that it does not move.
- The baby's head is smeared with a gel that differs in composition from the product used for ultrasound in adults. This substance is hypoallergenic and strengthens the sensor signal by eliminating air between the device and the skin.
- A sensor device is applied to the treated area. The specialist moves them around the head, reads data from organs and tissues.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the brain
No special preparation is required to perform an ultrasound of the brain in newborns. The only thing that won’t hurt is to ensure that the child is in a good mood. Therefore, try to visit the ultrasound room first if you have to “run around” several doctors.
You can also grab a bright toy or a bottle of your baby’s favorite drink. By ensuring your baby is in a good mood, you reduce the examination time. Keep this in mind when planning your diagnostic visit!
Safety of the procedure
When performing an ultrasound of the brain in newborns, the safety of the procedure must be taken into account. A child's fragile body can easily get injured . Similar studies have been carried out frequently for children recently.
Previously, procedures to study the state of the brain were carried out less frequently. Equipment for MRI using anesthetics has performed well in practice. It is easy to understand that this type of diagnosis is complex and can provoke negative consequences.
New methods have made the work of doctors and the lives of patients much easier. The procedure makes it possible to identify various brain diseases in children.

Types of brain ultrasound for children
In neurosonography, the sensor is located in different areas of the head. Due to its position, there are several types of brain ultrasound for children: transfontanelle
,
transcranial
, combined and examination through bone injuries. Transcranial ultrasonography is performed for children older than one year, since due to overgrowth of the fontanelles, it is necessary to conduct an examination through the temporal or parietal bone. A combined method is used to obtain the most detailed image of the brain from various angles. The examination combines the position of the sensor with a transcranial transfontanelle examination.
Neurosonography
With neurosonography, the examination is carried out through non-ossified areas of the skull - the fontanelles. Their overgrowth occurs by one year, less often by one and a half years, so an ultrasound of the head through the fontanelles is performed on a child up to one year old.
Possible harm from ultrasound of a child's brain
The procedure is harmless and always brings good results. Allows you to identify pathologies at the primary stage of development and improve the baby’s health using conservative methods without traumatic surgical interventions.
When there are indications, ultrasound of the brain in children must be performed . Parents often do not consent to such procedures; as a result, it is not possible to determine in advance the development of dangerous pathologies. Such negligence often leads to negative results.
To make a correct diagnosis and identify the problem in time, a simple external examination of the child is not enough. In some cases, it is necessary to use ultrasound equipment for examination.
Benefits of brain examination using NSG
NSG has many advantages:
- high information content;
- relative cheapness;
- accessibility, painlessness and safety of the procedure (ultrasound of the child’s brain can be performed several times in a row without fear of undesirable consequences);
- quick results;
- the ability to control the dynamics of the disease (if present).
Probably the only disadvantage of neurosonography is the impossibility of performing it in children after one year.