Logical thinking is one of the most complex forms of thinking, developing only at the beginning of the school period of development (6-7 years). It is based on imaginative thinking, the skills of which should already be quite well formed by this period.
Development of logical thinking with the help of educational games
The development of logical thinking operations in children aged 6–7 years is a complex and multi-stage process. Its achievement poses many challenges for the child, including:
- Enriching ideas about the world around us.
- Understanding the patterns that unite objects and phenomena.
- The ability to identify the most common and significant features of objects.
Thanks to the proper level of development of logical thinking, a child at the age of 6 will be able to more successfully master the school curriculum and acquire knowledge, skills and abilities that are significant in the future.

In particular, this will contribute to the internalization of many mental processes (including the development of mental arithmetic and internal speech).
Stages of development of logical thinking of a preschooler
The development of the foundations of logical thinking in children aged 6–7 years is carried out in several stages.
- The child learns the basic properties, quantitative and qualitative characteristics of objects, and also learns to use them in his daily life.
- Implementation of thinking operations with the replacement of real manipulation of an object with verbal reasoning.
- Replacement of verbal active accompaniment of activity with internal mental operations.
Jigsaw puzzles for 6-7 years old
Requirements for the logical development of a child
By the age of six or seven years, a child should successfully cope with the following thinking operations:
- The child must be able to find patterns that unite groups of objects according to one or another attribute, and also continue logical series independently, without using hints and leading questions.
- Find an extra item from the 5 offered to him.
- Compose stories independently from pictures and come up with a logical conclusion.
- Divide objects into groups, while specifying which feature was taken as a basis.
If the child has not yet acquired these skills by the right age, competent development of thinking in children from 6 to 7 years old can solve this problem.
How to develop logic and thinking in children 5, 6 and 7 years old
At the age of 5-7 years, children spend most of their time in kindergarten. Therefore, all classes are conducted by a teacher in the classroom.
Children of primary preschool age can develop thinking in the following ways:
- conducting conversations and discussions. Children of this age can not only perceive information, but also express their opinions and make simple conclusions;
- conducting didactic games and performing exercises with logical content, solving puzzles. Assignments may be in printed form;
- games that involve both creativity and logic. A child will remember best what he created with his own hands. Therefore, he can be asked to complete the following tasks: complete the missing part of a geometric figure, give the missing items: a fishing rod to a fisherman, a car to wheels, etc. It is necessary that the child can explain his choice;
- using the “intentional error” technique. At the age of five, a child has already formed ideas about humor and their thinking is sufficiently developed not to take on faith everything that adults say. It is possible to use an intentional error in any class, the main thing is that the material is familiar to the children;
- use of substitute items. This technique, by transferring some properties of an object to a replacement one, develops thinking, imagination, and creative abilities. Children are able to imagine imaginary properties of objects;
- use of signs and pictograms. In the fifth year of life, the baby becomes familiar with numbers. By studying them, the child develops abstract thinking. Using numbers, the child should be able to collect identical objects into a group and indicate their number. First, simple tasks are offered: objects are arranged in a row. The child must determine their number by pointing to a certain number. Then the task becomes more complicated: objects of two types are laid out randomly (for example, 3 apples and 2 pears). The child must be able to determine the quantity of each item and point to the corresponding number;
- pictograms are images of objects in a simpler form. They convey the main and recognizable characteristics. Pictograms promote the development of analysis and synthesis skills. Having studied the pictogram, the child first expresses an opinion about what object is depicted, then highlights its main features. After this, together with an adult, he makes a conclusion whether the guess was correct.

Example of an icon
At six or seven years old, practical training is important. Independent work is important here. Older preschoolers explore the proposed objects. They compare their properties, color, shape, size. They should receive information not in ready-made form, but with the help of leading questions.
Preschooler thinking: types and methods of development
For older preschoolers, you can conduct various experiments and experiments, as well as arrange presentations. Children must observe their progress and record data in a special journal. Then, looking through the log, they must explain how the stages of the experience are interconnected: what happened at the beginning and what happened at the end. Practical techniques are closely related to verbal ones. The child must be able to explain why it happened this way.
Important! It is necessary to enter into a playful argument with preschoolers, encouraging them to express their point of view. Everyone should be able to defend their opinion.
Basic logical operations
The operations of logical thinking that a child should master by this age include:
- analysis;
- synthesis;
- comparison;
- classification;
- proof.
Mastering logical operations allows the child not only to successfully carry out most types of activities, but also:
- improve attention characteristics;
- think clearly and specifically, avoiding the most common mistakes at this stage;
- develop the ability to focus on solving a problem;
- master the art of coherent speech and persuasion.
Labyrinth for children 6-7 years old
Exercise 5. Danetki
A logic game that got its name due to the condition: when guessing a word, you can answer the questions of the second player only “yes” or “no”. And the second player’s task is to select questions that will bring him closer to solving the word.
The game also trains imagination, attention and the ability to remember, since keeping all the conditions in memory is not an easy task. What else contributes to the development of a child’s logical thinking?

However, often the child is not able to study them due to unformed logical thinking, which results in a vicious circle. Then interest comes to the rescue. And programming. Through play, the child will be able to master it on the Codewards course.
(since the age of 7!).
Read more about computer courses at Unium in this article
. Programming is a strong foundation that will help make a child’s thinking more structured, systematic and logical from an early age.
Author of the article: Alina Repetskaya is a teacher at Yunium on mnemonics.
.
Types of games to develop logical thinking in children
Currently known games and tasks for the development of logical thinking in children can be divided into the following categories:
- Graphic games are aimed at improving fine motor skills and basic preparation of the hand for writing.
- Mathematical - games and puzzles, which are based on teaching a child to count, logic and abstract thinking.
- Speech games – contribute to the development of a child’s active vocabulary.
- Puzzles and board games teach a child to think consistently and strategically. In addition, they strengthen the child’s ability to work in a team and express themselves in joint activities.
Test tasks for the level of logical thinking
Games and exercises to develop a child’s logical thinking
The logical development of children aged 6-7 years is impossible without specially organized activities aimed at achieving a given result. Thematic games and exercises can provide considerable assistance to parents in this regard.

Logic games from the store
"I made a wish"
The parent thinks of an object in his mind. The child’s task is to guess it using clarifying questions. It is advisable that the child learns to correctly formulate leading questions, allowing him to identify the key features of the objects being guessed.
"I'm taking it with me"
To play you will need cards with images of a variety of objects. The child is invited to choose those that will be useful in a given situation (for example, outdoors, at the theater, visiting, at school, etc.). It is advisable that among the drawn objects there be a variety of objects - including those that may be useful in several situations at once or not useful at all.
The child takes out cards one by one and explains whether he will need this or that item, giving reasons for his decision.

An interesting game for logical thinking
"Seated in rooms"
Cards with images of people of different genders, ages, hair colors, eyes, etc. are laid out in front of the child. And also a sheet of paper divided into four equal rectangles (symbolic “rooms”). Its task is to “settle” people into rooms depending on one quality or another. And then answer the questions proposed by the parent (for example, which of the drawn people can enter two or more rooms, who is not suitable for any room and why).

Game extra object - complicated version for 6-7 years old
Comparison problems
The child is asked to compare, comparing several objects or phenomena with each other. For example:
- Birch is taller than oak, and oak is taller than pine. Which tree is the tallest and the shortest?
- Olya's hair is darker than Masha's, and Katya's is darker than Olya's. Which girl has the darkest hair? etc.
It is necessary to take into account not only the children’s answers, but also their reasoning for their choice.
Logic exercises
Tasks that are aimed at developing logical thinking encourage thinking and analysis.
Mathematical
Mathematical tasks that are aimed at developing logic for children 5 years old can be as follows:
- Masha took three apples, and Kolya took 1 more than Masha. How many apples did Kolya take?
- Kolya drew 4 boats, and Maxim drew 3 more boats. How many boats did Maxim draw?
- Gleb is 9 years old, and his brother is 2 years younger. How old is Gleb's brother?
- Anya drew 10 houses, and Ilya drew half as many. How many houses did they draw together?
For children 6 years old:
- The gardener was processing the rose bushes. On the first day he processed 5 bushes, and on the second day 3 fewer bushes. How many bushes did the gardener process in two days?
- The brothers decided to build a house out of cubes. Sasha brought 5 cubes, and Andrey brought 3 cubes more. How many cubes are there in total?
- There are 6 berries in the jar, and half as many in the plate. How many berries are on the plate?
Board logic games
Board games are aimed at finding a way out of a game situation, which is presented in the form of a visual aid. This game can be printed at home on a printer. Board games include: lotto, checkers, dominoes, educational games, etc.
For children 5-7 years old, you can offer to play the following games:
- “What does a doctor need?” The main goals of the game: to develop knowledge about the profession of a doctor, about what tools he needs for work. This game also develops fine motor skills, speech and the ability to express one’s thoughts logically. For the game, pictures are printed with different tools: those that the doctor uses for work, and those that do not. The child must select the tools necessary for the doctor, explaining his answer as to why he needs them.
- “When might this be?” This game reinforces children's understanding of the times of day. It also cultivates patience and attention. It is necessary to arrange pictures with different times of the day. Children must explain what time of day is shown in the picture and explain why they think so.
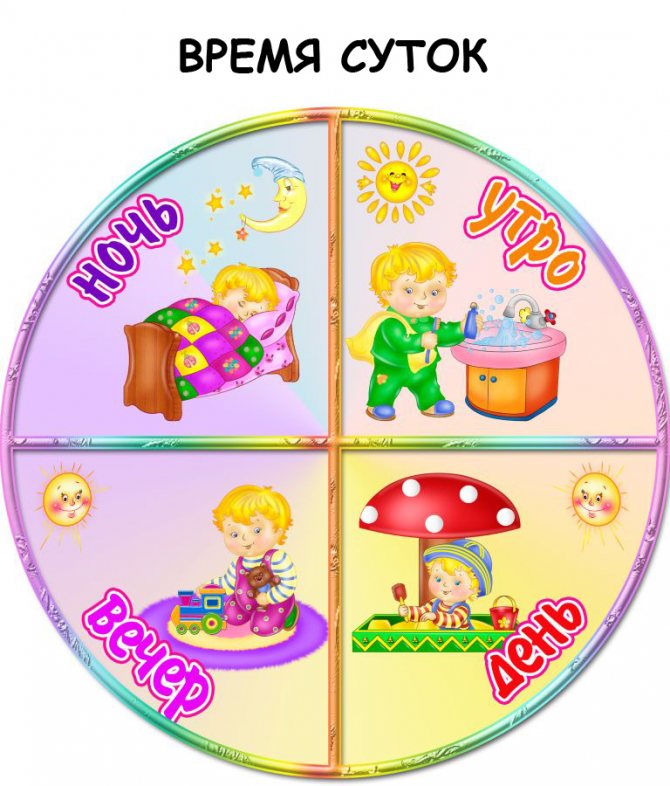
Pictures with images of times of day
Computer games and programs
Computer children's programs have many advantages over traditional teaching methods. These programs are available online. They form skills, educational and practical activities.
Calendar plan in the preparatory group for each day according to the Federal State Educational Standard
Examples of programs that develop logical thinking: “Logic for Kids”, “Baby Logics”, “Cifiri”, “Funny Pictures”. These programs are a tool package for creating and solving problems that involve assembling on the screen many objects of text and graphic structure.
Children will especially like the more colorful programs “From the Screw” and “Air-Race”. Here, control occurs by pressing certain keys or moving the mouse cursor in a certain direction.
The “MathMatic” and “Fun Arithmetic” programs will develop counting and reading skills. This program can be used for children 7-8 years old.
Comic
Solving humorous problems develops attention, intelligence, and encourages reasoning.
Card index of joke tasks for ingenuity:
- Who can swim faster: a duckling or a chicken?
- Will the bird or the caterpillar reach the flower faster?
- Two crocodiles flew over the forest. One was red and the other was yellow. Who will fly through the forest faster?
Tips and recommendations for parents on conducting developmental activities
The development of logic in children aged 6-7 years should be carried out in the most relaxed and comfortable environment possible. The more actively game teaching methods are used in classes, the more effective they will be.

By the age of 6, a child should be able to play chess
Taking into account the rapid fatigue of children, it is advisable to calculate the duration of the lesson so that it does not exceed 20-30 minutes.
It is very important that the child not only gives answers to the proposed questions and finds solutions to tasks, but also explains his answers in as much detail as possible. This will make sure that the child really sees logical patterns and understands them.











