Sometimes during the day the child looks quite healthy: he is cheerful, cheerful, and has absolutely no cough. Everything changes dramatically as night falls. It is at this time of day that sudden coughing attacks begin, which cause natural anxiety in the child’s parents.
If all the measures taken to get rid of the disease do not produce positive results, it is necessary to call a medical professional at home, and in emergency cases, an ambulance. Only a specialist can determine the exact reason why a child coughs when he goes to bed. Remember: most often, coughing at night is a consequence of some pathology. But it may happen that such a phenomenon is a simple and elementary cleansing of the bronchi from accumulated secretions (that is, dust and microbes). Each individual case must be examined individually.
Why do attacks occur at night?
Why does a child start coughing when he goes to bed? There are a number of factors that can provoke this phenomenon:
- The functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems is determined by the time of day. At night, the production of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol decreases significantly and, as a result, some narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi occurs. Which leads to difficult sputum discharge and, naturally, to coughing.
- When the baby is in a horizontal position, the discharge of sputum from the lungs and their blood supply deteriorate significantly due to the fact that at this age the pulmonary apparatus is not entirely perfect (that is, the breathing tubes have a rather small lumen). As a result, the child begins to have a coughing attack as soon as he goes to bed. That is, everything is natural.
- If the baby has rhinitis, then at night mucus can flow down the larynx and cause coughing, sometimes leading to vomiting.

Possible causes of coughing in children at night
Why does a child start coughing when he goes to bed? There can be a great many reasons for this manifestation:
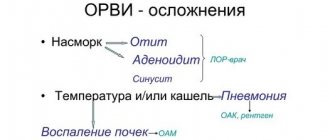
- Pathologies of the acute respiratory infections group.
- Tracheitis.
- ARVI (for example, influenza or parainfluenza).
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the lungs (i.e. pleurisy).
- Bacterial sinusitis.
- Foreign body in the respiratory tract.
- Allergy.
- Inflammation of the lung tissue (i.e. pneumonia).
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, gastric reflux).
- Helminths.
- Whooping cough.
- Bronchial asthma.
- ENT diseases of a chronic or acute nature (for example, sinusitis, laryngitis, adenoiditis or rhinitis).
Important! If a child develops symptoms such as chest pain, body temperature above 38 degrees, convulsions, swelling of the face (or neck), and difficulty breathing, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Let's look at some points in more detail.
Should you see a doctor?
The help of a specialist is necessary if the corresponding symptoms of an infectious disease appear.
- The child often wakes up at night and complains of chest and abdominal pain.
- When coughing up, the little man wheezes and whistles. His breathing is labored.
- The baby looks pale and sweats often.
- You can see blue discoloration in the area of his lips and nails. Sputum is green, yellow, red, or brown (infection develops in the body).
We recommend: Severe barking cough in a child without fever
Whooping cough
What is the reason that the child went to bed and started coughing? Perhaps this is a serious disease of the respiratory tract of an infectious nature, which is characterized by severe spasmodic coughing attacks, that is, whooping cough. It often occurs in children under two years of age. Infection occurs only by airborne droplets through direct contact with an already sick person, and the incubation period lasts about one to two weeks. For one month (starting from the moment the first signs of the disease appear), a child infected with whooping cough is dangerous to everyone around him. Therefore, every precaution should be taken.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Lack of appetite.
- Sometimes the presence of irritability.
- There is general weakness and malaise.
- In rare cases, body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees.
- At the early stage of the disease, lacrimation, sore throat and runny nose are observed.
- During the crisis period of the disease, inflammatory processes of the bronchi, trachea or throat occur.
- At the end of the second week after the onset of the illness, the child coughs heavily when falling asleep. Moreover, it is impossible to stop this wet cough, characterized by copious sputum production, with almost any medication, even potent medications.
- Attacks are accompanied by excitement, redness of the face, swelling of the veins in the neck, protruding of the tongue from the mouth (this often causes injury to the frenulum), possible cessation of breathing and even the development of suffocation.
- At the moment between cough shocks (their number ranges from five to ten), a deep breath is observed with a characteristic whistling sound (that is, reprise), which is again followed by a series of convulsive manifestations. The number of such cycles can vary from two to ten (and sometimes more).
- At the end of the attack, viscous sputum (vitreous) is released.
- Nausea and vomiting are possible.
- Coughing attacks bring the child to exhaustion. Sometimes there is a fainting or convulsive state.
Important! In babies, sputum may be discharged through the nasal cavity. Hospitalization of a patient whose condition is severe or moderate is mandatory.
The recovery period after an illness, which can be several months, depends on the severity of the disease and the protective forces of the patient’s body itself.
There is no innate immunity to this disease. It can appear only after a person has had this disease. Moreover, this acquired immunity persists throughout life. If a person is vaccinated against this disease, the effect is short-term and after a certain time (established by the vaccination calendar), revaccination must be carried out. And one more point that is worth mentioning: in children who have been vaccinated, whooping cough occurs in a milder form and with virtually no complications (compared to those who are not vaccinated).
What does a cough after a night's sleep mean in a child?

In any case, the parent should pay attention to the morning cough, and then to other symptoms - in order to compare them and promptly identify the disease that caused it, if it exists. However, you should not immediately rush into worries and invent diagnoses, as well as self-medicate.
Perhaps the child simply suffers from a dry throat in the morning and stops experiencing discomfort immediately after brushing his teeth or eating breakfast. Young children may fake coughing because they see it as getting parental attention. Cunning and older children can use a cough as an excuse not to go to kindergarten or school.
Cold
The most common and common cause of cough is the consequences of hypothermia. The child might have gotten his feet wet on the way home, or you might have forgotten to close the window at night. Children quickly catch colds because they have weak immunity.
You should not send a child with a cold to kindergarten or school - even if it is not contagious, the symptoms can be severe for the child and he will spend the day suffering from fever and runny nose.
A cold cough is accompanied by rhinitis, sometimes with a slight fever. At first glance, it is difficult to distinguish a cold from a more serious illness, so you should not ignore the child’s condition. If symptoms continue for more than 1-2 days in the presence of isolation at home and the availability of warm drinks, take the baby to the doctor or call him at home.
Allergy
This factor should be taken into account if a child has a dry cough in the morning during the warm season. Allergies are characterized by a dry cough, even if there are no other symptoms. At night, the child is mainly in one position and steadily inhales the air in the room. It is possible that you open the window in the nursery for air circulation, because plant pollen and other allergens are constantly entering the room.
ARVI
Typical childhood diseases that any parent inevitably faces. They are caused by contact with other carriers of the disease, which necessarily happens if the child goes to kindergarten or school.
Other signs of ARVI:
- pain and sore throat (long lasting);
- increased body temperature;
- runny nose;
- lethargy and weakness.
The cough during ARVI is not paroxysmal - the child will constantly cough with varying strength. even while sleeping. The first actions of a parent are to isolate the child at home, take preventive measures for themselves and prevent the baby from hypothermia. ARVI does not in any way interfere with the development of a cold, and these two diseases can develop simultaneously.
On this topic:
Why wheezing cough occurs in children and what can help in treatment
Pneumonia
Pneumonia or pneumonia is not the most common reason why a child usually coughs in the morning, but not to miss its development is one of the most important tasks for a parent. Pneumonia is incredibly dangerous for a child. The disease requires hospitalization and, if completely untreated, can be fatal even in adults.
The most important symptom by which you can distinguish pneumonia is a wet, productive cough, lingering and severe in nature. The disease does not occur with a dry cough.
The symptoms of pneumonia resemble ARVI, only in a more severe form:
- chest pain during coughing (an important difference in which ARVI can be excluded);
- a strong increase in temperature (from 39 degrees, depends on neglect;
- sweating;
- weak and lethargic state, constant desire to sleep;
- cough with phlegm;
- decreased appetite and pale skin.
If pneumonia is suspected, the pediatrician will definitely refer the child for additional examinations, after which it will be possible to say for sure whether the fears are confirmed. Pneumonia can be either unilateral or bilateral.

Bronchitis
Bronchitis is considered a “mild” disease compared to the previous one, but children endure it hard and for a long time - the disease can not only weaken the baby and force him to endure more than one unpleasant week, but also confuse parents with a long leave to care for the child.
The main danger of bronchitis is that it progresses. If your child's morning cough has signs of a bronchial cough, contact your pediatrician immediately - warm drinks and cough drops will not help.
Symptoms of bronchitis:
- lethargy, weakness, low energy in the morning;
- shortness of breath is added to pain in the sternum (behind), which is evidence of already developed bronchitis;
- a characteristic prolonged chill is added to the elevated temperature (up to 39 degrees);
- The cough itself not only causes pain, but also interferes with breathing.
It is very difficult not to notice bronchitis; parents often confuse it with pneumonia or ARVI in the early stages. If it comes to chest pain, then bronchitis is advanced - when going to the pediatrician, be prepared for possible hospitalization.
Asthma
Few people know that asthma, which has been a fear for parents for decades, is just a type of allergic reaction. Unfortunately, this reaction is so dangerous that in the absence of proper treatment and constant monitoring of the child, death is possible.
On this topic:
How and with what to treat a simple cough in a child: effective methods
Asthma doesn't just appear. Most often it occurs as a result of advanced respiratory tract disease (for example, bronchitis). The standard type of the disease, known to everyone because of asthma attacks, has nothing to do with this - a dry cough in the morning in your child is caused precisely by the “cough” subtype of asthma. Children forced to live with this disease cough almost constantly and need different therapy than standard therapy.
If your child has allergies and you suspect that what is happening to him may be a symptom of bronchial asthma, pay attention to the following signs:
- breathing is difficult, but the child is not completely suffocating (similar to bronchitis);
- dry, barking and paroxysmal cough;
- breathing, even when not difficult, comes out with a characteristic whistle;
- the child feels something in the chest between pain and a feeling of constriction.
If asthma is confirmed in a child, it is necessary not only to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment, but also to register the child. It is unknown whether the disease will remain with him in adulthood, but it is definitely not worth risking his health.
Allergy
The child is perplexed: “Why, when I fall asleep, do I start coughing?” Parents are also trying to find an answer to this question. Perhaps this is an allergic cough, which lasts for quite a long time and is accompanied by a runny nose and lacrimation. This illness usually occurs without fever (unlike colds). Sometimes a child experiences a sore throat and itching.
Most often, such a cough begins suddenly and is characterized as barking and booming. May be dry or combined with clear mucus.
If in the evening and especially at night the symptoms begin to worsen (sometimes they can reach real attacks of suffocation), then most likely the source (that is, the allergen) of the cough is either in the child’s bed or somewhere nearby. It can be anything:
- Pajamas or bedding made from low-grade raw materials.
- Toys located in close proximity to the child.

- Pieces of furniture filling the children's room.
- Perhaps the child coughs a lot when he goes to bed because of the poor-quality detergent in which the baby’s bedding and clothes were washed.
Advice! To determine the source of an allergic cough in a child, begin gradually, item by item, isolating them from the baby and observing his condition. And also, maybe it’s worth changing not only the brand of washing powder, but also the manufacturer of bed linen.
If a child goes to bed and starts coughing, parents should give the child an antihistamine at the very beginning of the attack to alleviate the condition and prevent the development of possible complications. In emergency cases, call emergency services. Allergies are not as harmless as they seem.
When to start worrying
Attentive parents with the minimum necessary amount of medical knowledge are confident that a one-time attack cannot be a symptom of a serious illness. The wait-and-see tactic is to monitor the condition. To do this, during the day you need:
- watch the child;
- record negative manifestations if they occur in the morning and afternoon;
- Measure your temperature several times (preferably in the morning and evening).
Against this background, a primary picture of the disease can be drawn up.
- At what time and how regularly does the cough reflex appear?
- Under what specific conditions does it manifest itself?
- Does the child have temperature fluctuations and feverish conditions?
- Does it start only in bed or does it happen in other body positions, as well as in another room.
- Are there any objective prerequisites to suggest the presence of a disease - suffocation, excessive sputum, weakness, headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea or constipation.

Three of the listed reasons for which a child goes to bed and immediately starts coughing are a signal to see a doctor and get treatment. More than three - the appeal must take place immediately. All of the listed signs in a child - cough after sleep, and in the evening the child cannot fall asleep due to cough - indicate illness.
This periodicity has become a habitual state, and continues during the day - a visit to the doctor should take place immediately. The family doctor and nurse at the children's clinic will probably want to know the reason for the urgent call. In order to give the necessary information, you need to carefully listen to your breathing, find out the condition of the nasopharynx, and look at the throat.
Bronchial asthma
If a child complains: “I fall asleep and start coughing,” do not ignore his complaints. A possible reason for this manifestation is bronchial asthma, the symptoms of which only intensify with overexcitation, stress or anxiety. The disease, which is characterized by pain in the sternum (in the area of the heart muscle), can be provoked either by infectious pathogens or certain allergens. What can cause a cough:
- dust;
- dry air in the room in which the child sleeps;
- pollen of various plants;
- animal hair;
- a glass of warm milk drunk before bed if the child suffers from a hidden allergy to dairy products;
- washing powder;
- fillings for mattresses and pillows.
Important! If you have installed an air humidifier in your child’s room, remember that the use of this device contributes to the circulation of pathogenic microbes and allergens in the room.
At an early stage of its development, asthma manifests itself exclusively as attacks at night due to spasmodic reactions in the lungs to internal and external stimuli. The acute form of this disease makes itself felt in the morning hours.
As a result of the protracted course of the disease, the baby may experience shortness of breath. Therefore, at the first signs of this dangerous disease, you should not put off going to an allergist and pediatrician for a long time.
Causes of cough in a child during sleep
We list the main causes of cough in a child during sleep:
- Infections - viruses, bacteria, fungal microorganisms;
- Stomach problems;
- Whooping cough vaccinations;
- Allergy;
- Dry or too humid air in the bedroom;
- Quarrel or stress;
- Heart problems;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Teething;
- Foreign body.
By the way, with asthma, a child’s cough during sleep manifests itself mainly at night or in the morning. In addition to coughing, the disease can be indicated by wheezing and whistling that occurs during sleep.
Also, night cough is a common occurrence with cerebral palsy . In this case, its cause may be a pneumonia pathogen that penetrates the weakened body of a sick child.

In addition, coughing during sleep can be associated with psychosomatic disorders. For example, provoking factors may be stress, overly strict upbringing, or, conversely, lack of parental attention.
Let's look at several causes of cough.
Infections
A dry cough in a child during sleep primarily indicates infectious diseases. Determining whether a cough is infectious or not is quite simple. He will certainly be accompanied by a runny nose, sore throat and other cold symptoms. Thus, by eliminating the underlying disease, you can relieve the child of cough.
Digestive tract problems
The main problem associated with the stomach that causes severe coughing during sleep in a child is reflux . With reflux, acidic stomach contents back up into the esophagus and can reach the upper respiratory tract. As a result, the latter become spasmed, which leads to severe coughing.
Reflux usually worsens after a heavy meal. Therefore, in order to prevent the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, it is not recommended for the child to eat at night.

Allergy
Night cough associated with allergies appears in spring and early summer, when many plants begin to bloom. To reduce the frequency of coughing attacks, the child should be given antihistamines . They will help cope with allergies and prevent coughing at night. Please note that all allergy medications are prescribed by a qualified doctor during an in-person consultation.
If your child has not previously suffered from allergies, it is not a fact that he has not developed one now. If you suspect it, remove all provoking factors from the bedroom. For example, replace bedding, pillows and pajamas with their hypoallergenic counterparts. After this, the cough should go away. If this does not happen, the cause of the cough should be sought elsewhere.
Skin rashes combined with a runny nose and night cough definitely indicate an allergy.
Moist or dry air in the bedroom
Humid and dry air disrupt the functioning of the respiratory system, which leads to a night cough. In this case, it is important to know the air humidity in the children's bedroom. By the way, it can be determined without devices. With high humidity, a damp smell appears, and things in the room seem damp to the touch. In addition to this, breathing in a room with high humidity can be difficult: the air literally becomes heavier.
Being in a room with low humidity quickly dries out the nasopharyngeal mucosa, which disrupts the breathing process. And as a result, a cough occurs during sleep.
If you find that the air in the room is humid, ventilate the room more often . This will reduce the moisture content in the air and reduce the risk of a child coughing at night.
In the case of dry air in the bedroom, it is recommended to buy an air humidifier. The device automatically sprays moisture around the room at a certain frequency. This increases the humidity in the bedroom.

Teething in babies
This unpleasant process often provokes a cough in a child during sleep. In addition, during the period of active dental growth, the child often experiences fever, sleep disturbances, bruxism and decreased appetite.
Causes of night cough during teething include a runny nose, increased activity of the salivary glands and regular crying. In each of these cases, the child’s body loses relatively a lot of moisture. As a result, the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and upper respiratory tract become dry. Actually, this is the main cause of a dry cough in a child’s sleep.

Foreign body
Parents cannot always keep track of what their children put in their mouths while playing. However, we all know how such experiments can end. Therefore, if your child has a severe cough during sleep, carefully examine his mouth . Found something foreign? Take the following measures immediately
- Tilt the child head down and pat his back with your hand.
- If the foreign object does not come out, place the baby on his back and place his hand, palm down, in the area between the navel and solar plexus. Afterwards, press on this area several times, as if you were doing an indirect cardiac massage. Try to keep your movements neither too weak nor too strong. In the first case, the foreign body may not come out, in the second, you are likely to harm the child even more. If the child’s breathing is not difficult, it is better to call a medical team ; specialists will remove the foreign object without harm to health.

Parasites are the cause of cough at night
Why does a child cough when he goes to bed? Perhaps these are helminthic infestations. For example, parasites such as giardia and roundworms can cause a dry cough in children at night. The fact is that the larvae of these helminths, migrating through the human circulatory system, can enter the trachea, bronchi or lungs. This causes irritation of the receptors and, as a result, a coughing attack, which is accompanied by such symptoms as stool upset, pain in the abdomen, dizziness and nausea.
When a person is infected with helminths, symptoms such as fever, chills or sore throat are usually not observed.
In order for a doctor to be able to diagnose the presence of helminths in the body, which could cause the child to cough when falling asleep, the usual general clinical tests are not enough. By the way, their results will be ready after only 10-12 days (not earlier). It is often necessary to prescribe an additional test such as ELISA (that is, enzyme-linked immunosorbent test).
Types of cough
Modern medicine is inclined to think about the appearance of cough in a room where there is a potential allergen (dust, fluff, or animal hair), excess heat, cold air or insufficient humidity. The child coughs in the morning after sleep and after a change from a sleepy state to wakefulness, when the frequency and rhythm of breathing changes. But the symptom of cough after sleep in a child easily turns from a simple and natural state of a sleepy body into a pathological and dangerous one if that very notorious excuse appears.
A cough in the morning and evening in a child is probably a sign of a pathological condition in which secretory secretions, copious sputum or an allergic component in a pathological manifestation are present.
It leads to irritation of the nerve endings located in the pharyngeal segment, leading to the appearance of a reflex reaction.
If a child coughs when he goes to bed and cannot fall asleep because this happens again and again, it is logical to assume pathological causes that negatively affect the mucous membrane or respiratory tract with a new change in body position. In such cases, you shouldn’t immediately panic and sound the alarm, and even more so, don’t rush to the home medicine cabinet, scooping out all the medications in a row. For a dry cough, medications are recommended that transform it into a productive one. When wet, on the contrary, they depress the cough center. Incorrectly used medication can only aggravate the condition and make the cough protracted.
Gastroesophageal reflux
“I cough when I fall asleep,” this is how the baby sometimes complains to his mother in the morning. What could it be? This may be gastroesophageal reflux, which is characterized by a sore throat, dry cough and sometimes vomiting (usually without fever).
The child's condition may be aggravated by daytime heartburn, which recurs periodically. This may indicate inflammatory processes in the stomach or esophagus; congenital pathologies or elementary overeating immediately before bedtime.
What is reflux? This is the movement of stomach contents back into the esophagus. This is the “food cycle in the body.” As a result of these movements, due to the acidic environment of the stomach contents, irritation of the walls of the esophagus occurs and, as a result, cough.
Pathological morning cough
Often a cough can be a consequence of a pathological process in the body. In order to avoid complications and detect the disease in time, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination by a doctor.
When a child has a cough in the morning, this can happen for the following reasons:
- ARVI. The cough in the first days of the disease is dry, accompanied by other catarrhal symptoms.
- Reflux esophagitis. The cough reflex increases after eating due to the entry of stomach contents into the esophagus.
- Allergic reactions. Contact with an allergen often causes morning cough in children.
- Bronchial asthma. The coughing attacks are dry, but at the end of them a wet cough appears with a small discharge of sputum.
- A deep, wet cough is a sign of an inflammatory process in the respiratory system.
- Whooping cough. It is characterized by paroxysmal and severe cough with sputum production.
These symptoms require immediate treatment. If you let the disease take its course, a number of complications may arise.

Coughing attacks in an infant
Why does a child cough when he falls asleep? The causes of cough in babies who are not yet a year old can be:
- The first baby teeth appearing. In this case, a large amount of saliva is formed, which, flowing down the larynx, becomes a provocateur of the cough reflex.
- In addition, the baby is bothered by pain in the gums. As a result, it becomes difficult for him to swallow saliva and coughing occurs.

- Baby's diet. An insufficient amount of iron in his diet can cause inflammation of the throat and, as a result, coughing attacks. To avoid this, you need to add microelements to your food.
On a note! So that the problem of your child coughing when he goes to bed no longer bothers you, you should put the baby to sleep on his side (only 2-3 hours after eating), placing a small pillow under his head (so that he cannot choke on saliva).
Medications for the treatment of night cough in children
The child coughs when he goes to bed. What to do in this case? You can give one of the following medications:
- “Bronholitin” or “Stoptussin”, which have a combined effect (antitussive and bronchodilator).
- If a child goes to bed and starts coughing, give him syrup “Breast Elixir”, “Doctor Theiss”, “Doctor Mom”, “Pertussin”, “Bronchicum”, “Mukaltin”, “Linkas” or ammonia-anise drops. These herbal preparations have a good expectorant effect and will help in the fight against tracheitis and bronchitis.
- For sore throat, cough lozenges and lozenges can help, as they have a soothing effect on the throat. They are recommended for use by children over four years of age (“Septolete”, “Anti-angin”).
- To combat dry cough in children, medications such as Tusuprex, Glaucin, Libexin, Levopront, Sinekod, Glauvent or Sedotussin are suitable, which help suppress attacks. Important! All medications that suppress cough can be used only as prescribed by a doctor and in accordance with the age of the child.
- "Terfenadine" or "Erius". Each of them is recommended as an antihistamine for allergies.
- Does your child cough when he goes to bed and wakes up? To combat attacks of wet cough, medications such as Bromhexine, Ambroxol, Ambrobene, Flavamed, Lazolvan and ACC are suitable, which help thin the mucus and remove it from the lungs and bronchi.

- The formation of snot, as a rule, is a concomitant manifestation of coughing attacks. Vasoconstrictor drugs and nasal sprays (for example, Vibrocil, Galazolin, Naphthyzin, Tizin Xylo, Nazivin or Otrivin) will help get rid of them. Important! You should not use such medications for more than a week. Otherwise, excessive drying of the mucous membrane may occur.
- If there is a cough in children under one year of age, whose bronchi are still poorly developed, drugs such as Prospan or Gedelix are recommended. These medicines contain ivy extract as an active ingredient.
Medicines to treat serious conditions such as asthma, pneumonia, and gastroesophageal reflux should be prescribed by your doctor. As, indeed, all other medications for the treatment of other ailments. Remember: self-medication is dangerous.
Recommendations from a pediatrician
Many pediatricians are confident that coughing is just the body’s protective reaction to a certain pathology, which should be identified and treated. But we should not forget that attacks cause some discomfort to the patient. You can get rid of them quite simply: you just need to drink a lot (for example, warm tea, fruit juice, compote or water) and ventilate the room often. In addition to this, you need:
- Carry out wet cleaning of rooms in the apartment as often as possible.
- If a child goes to bed and starts coughing, what should you do? Avoid any contact of the baby with allergens, that is, with objects that smell strongly or irritate the respiratory tract (for example, a toy, a piece of furniture, household chemicals, a pillow or tobacco smoke).
- Use a humidifier. In this case, the optimal temperature in the room should be about 20-22 degrees.
- For children aged 1 year or older, we recommend inhalations from decoctions of medicinal herbs, a mixture of soda and water, as well as saline solutions. However, such manipulations are contraindicated for infants.
- To make it easier for babies who are not yet a year to sleep at night, their position in the crib should be changed. These manipulations help prevent the accumulation of mucus in the nasal cavity.
- Does your child cough when he goes to bed and wakes up? You can avoid this if you clean your baby’s nose every evening, just before bed, using a solution of salt and warm water for this purpose. After the procedure, the patient should blow his nose well.
- The kid is surprised: “Why do I cough when I go to bed?” You can ease his suffering if you make a foot bath (water temperature should be 42-43 degrees).
Important! When treating coughing attacks, you should never give your child antibiotics without a prescription from a specialist. Also, if there is sputum, you should not use antitussive medications, and if you have dry coughing, you should not use drugs with an expectorant effect.
Main reasons
Cough in the morning can occur due to the following physiological and pathological conditions:
- accumulation of mucus or saliva in the throat;
- increased dryness of the air in the room where the child sleeps;
- milk entering the respiratory tract due to incorrect positioning of the infant during feeding;
- infectious diseases of the bronchi and lungs;
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to irritation of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and a reflex cough;
- allergic reactions;
- psychosomatic reasons.
In order to determine what is the cause that provokes this symptom, you need to pay attention to how the child feels outside of a coughing attack. If throughout the day the child is active, cheerful, and easy to communicate with, then this speaks in favor of the physiological causes of morning coughing.
It is also necessary to constantly monitor body temperature and pay attention to whether the act of swallowing causes discomfort to the child. Fever, redness and sore throat are signs of a cold and indicate that the cough is most likely caused by an infectious agent.
If possible, it is necessary to replace the materials that the child comes into contact with during sleep with hypoallergenic ones and control the level of air humidity in the room.
Physiological
A physiological cough is a natural reflex reaction of the body to irritation of the mucous membranes by foreign bodies or liquid entering it. It can be either dry or wet (with the discharge of a small amount of clear sputum). This cough is neither long nor too strong. The child should feel normal throughout the day, as well as have good sleep and no other signs of infectious diseases (sore throat, snot, fever, skin rash).
Physiological reasons that can lead to morning cough in children:
- inhalation of particles of milk or formula while feeding a baby (occurs due to improper attachment to the breast and feeding in the wrong position);
- hypersalivation (increased salivation), which appears during the eruption of baby teeth and leads to the accumulation of a significant amount of saliva in the throat during the night, and after waking up the baby is forced to cough it up;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx, which leads to soreness and discomfort and causes the child to want to cough (can occur when the normal microclimate is disrupted, especially in winter when heating with artificial heat sources);
- coughing can be a psychosomatic manifestation of lack of attention (the child will stop coughing as soon as the parents show interest in him).
Pathological
To suspect that a child’s cough is caused by some disease is the presence of the following accompanying symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- pain, sore throat, discomfort when swallowing;
- rash on the skin (exanthema) or mucous membranes (enanthema);
- disturbance of sleep and behavior of the child;
- complaints of heartburn, sour belching;
- history of frequent allergic reactions.
Parents should also be concerned about a cough that is protracted, paroxysmal in nature and leads to vomiting.
Do not forget that this symptom may be a residual phenomenon after previous diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
A morning cough in a child may occur in the presence of the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI) (if a child has a cold, the cough can bother him not only in the morning, but at any other time of the day);
- pneumonia is a serious illness that requires immediate medical attention (characterized by a severe general condition, a sharp increase in temperature, sputum may be purulent);
- whooping cough is an infectious disease characterized by the appearance of periodic bouts of barking cough, ending in reprises (noisy whistling inhalation);
- allergy to materials with which the child is in contact throughout the night (may also cause itching, rash and asthma attacks);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition that is characterized by the pathological reflux of acidic gastric contents into the overlying sections, while gastric juice can enter the pharynx and trachea and cause coughing attacks.
Folk remedies to combat symptoms
Many parents are concerned that their child coughs when he goes to bed. At the same time, they are adherents of unconventional methods of treatment. Here are a few methods from the arsenal of traditional medicine:
- Warm milk copes well with coughing attacks. You can add either butter (a small piece per cup), or baking soda (1/4 teaspoon per 100 ml of dairy product), or honey (about 6-8 ml), if you are not allergic to this product. Keep in mind that milk and soda can only be given to children over 5 years old. It's not worth it before.

- Does your child go to bed and start coughing a lot? Warm compresses of potato cakes applied to the chest (or back) may help. That is, they need to be alternated. The algorithm for the procedure is as follows: boil several potatoes (with their skins on), knead them, wrap them in cotton fabric and place them on the sternum or back. Wrap the top with a warm woolen scarf. The duration of the procedure is 2-3 hours. Several such procedures - and the problem of the child falling asleep and starting to cough will be solved. Before placing the tortillas on your chest or back, check that it is not too hot. Otherwise, burns may occur.
- Slowly dissolve honey (preferably buckwheat) immediately before bed. If a child has an allergic reaction to honey, then this method should be abandoned.
- Immediately before bedtime and immediately after it, give your child warm tea with raspberries, fruit and berry juice, as well as plain boiled water.
- Chest collection number 1, which helps remove mucus and reduces the inflammatory process. The main components of this herbal collection are licorice root, coltsfoot and oregano.
- Breast preparations numbered 2 and 3, which have emollient, expectorant and antiseptic properties. Intended for the treatment of bronchitis, pneumonia and prolonged cough.
- Breast collection number 4, which includes herbs such as wild rosemary, calendula, chamomile, peppermint, licorice and violet.
- In some cases, burnt sugar can help cope with a coughing attack. We prepare it as follows: pour sugar (1 tablespoon) into a metal container and begin to heat it on the stove until it dissolves and acquires a brownish color. After removing from the heat, cool it and give these “lollipops” to the child to suck. You can also add sugar that has not yet hardened into warm milk.
On a note! All fees can be purchased at the pharmacy network. Moreover, numbers 1, 2 and 3 are intended to combat the disease in children over six years old, and number 4 can be given even to a child aged two years.
Therapeutic diet to improve immunity
Does your child go to bed and start coughing a lot? The reason for this phenomenon may lie in the weakened immunity of the baby. What can be done in this situation? A special therapeutic diet can help improve the functioning of the immune system and significantly increase vitality. Here is what is recommended to be included in the daily menu:
- A decoction made from rose hips.
- Drinks from lingonberries or cranberries.
- A puree made from potatoes using warm milk.
- Freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices. Grape is especially recommended (as are the grapes themselves).
- Hercules porridge with butter, cooked in milk.
- Fruits rich in vitamin C (preferably citrus fruits).
- Salads of fresh cabbage with olive oil or radish with sour cream.
- Honey (in the absence of an allergic reaction to this product).
Prevention of the disease
Preventive measures to prevent coughing attacks at night are sometimes of great importance. What to do:
- Prevent any contact with potential carriers of allergens.
- Try to do wet cleaning in your apartment (or house) every other day.
- Sixty minutes before bedtime, the room should be well ventilated.
- Aromatherapy is a good help in preventing coughing attacks (for example, peppermint, eucalyptus or laurel oil).
- Ensure that the child leads an active and healthy lifestyle (that is, spends less time in front of the computer in a stuffy room, and more physical exercise in the fresh air).
- It is necessary to provide the child with a balanced diet, which should contain foods high in ascorbic acid.
Don't forget that your child's health is in your hands! Pay attention to the symptoms of illnesses in a timely manner and seek help from specialists.
Prevention measures and treatment features
Cough in the morning in a child is best prevented than treated. Of course, it will not be possible to completely avoid colds in childhood. The young body does not yet have a strong immune system, therefore, children often pick up viral infections. If your child attends daycare centers or has frequent contact with children, he or she is at risk. The best solution would be to carry out proper prevention. If a seasoned baby develops a cold, you can cure the illness much faster.
For preventive purposes, Dr. Komarovsky recommends doing the following:
- Use humidifiers if there are heaters in the house.
- Do not allow the child to come into contact with the allergen.
- Do not place your baby's crib in a draft or near an air conditioner.
- Monitor your child's diet.
- Walk outdoors with your baby regularly.
Preventative measures will help you keep your child healthy. With these simple methods you can avoid colds, which are sometimes difficult to cure a baby.