Pathological cough
This cough is a consequence of the development of various diseases. If a physiological cough is of the same type, then a pathological cough can have a different nature and severity, depending on the specifics of the pathology that caused it. Assessing the characteristics of pathological cough is extremely important for the diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease. Pathological cough has a fairly large number of varieties, which will be described below.
Productive cough (wet)
Characterized by excessive sputum production. It can develop due to various pathologies, for example, bronchitis or pneumonia, as well as due to the accumulation of fluid in the respiratory tract that has entered them from the cavity of a ruptured cyst. The expectorated sputum may contain blood, mucus and pus.
Nonproductive cough (dry)
This cough does not go away for a long time unless the nature of its origin is found out and treatment begins. As a rule, it does not bring relief to a person. May occur due to:
- pneumothorax;
- development of the pathological process in tussigenic zones;
- development of diffuse processes in lung tissues;
- development of a disseminated process in the lungs;
- development of benign and malignant neoplasms;
- development of metastatic tumors;
- cancer development;
- development of tuberculosis.
"Barking" cough
This cough is often accompanied by hoarseness and attacks of aphonia. In most cases it occurs:
- when a tumor tumor compresses the trachea;
- with the development of inflammatory processes in the tissues of the vocal cords and larynx;
- during attacks of hysteria;
- with the development of whooping cough;
- with croup (true and false);
- with the development of laryngitis.
Bitonal cough
Most often it develops in childhood when the lumen of one of the bronchi narrows. As a result, the speed of air flow changes, which leads to a change in the pitch of cough tones.
Whooping cough
This type of cough occurs mainly at night. Characterized by frequent intense coughing impulses. In between there are deep and loud sighs. After attacks, vomiting may begin due to excessive irritation of the vomit.
Intermittent cough
This cough does not go away for a long time and appears with a certain frequency. Its presence is typical for smokers (mainly in the morning), as well as for the following pathologies:
- emphysema;
- ARVI;
- bronchial asthma;
- pneumonia.
Coughing
It represents short and weakly expressed cough impulses, indicating the prolonged presence of a cough receptor irritant. Often observed in the presence of:
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- circulatory disorders;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- obstructive bronchitis, which also occurs in a chronic form.
Silent cough
Coughing that is not accompanied by any characteristic sounds may indicate:
- about significant destruction of the vocal cords or their paralysis;
- about severe exhaustion of the body due to a long illness;
- about the development of syphilis;
- about the development of tuberculosis.
Spasmodic cough
This type of cough is characterized by the presence of laryngeal spasms and “wheezing” sounds during coughing impulses. In this case, the patient, in order to completely cough, must make a lot of effort. If such a cough occurs, it is recommended to take antispasmodic medications and call a doctor immediately.
Constant cough
Sometimes patients turn to doctors complaining that their cough has not gone away for quite some time. This may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system (poor blood circulation is noted), as well as the development of chronic diseases:
- trachea;
- pharynx;
- bronchi;
- larynx;
- lungs.
Sharp cough
This cough may appear with the development of the following pathologies:
- pleurisy;
- pneumonia;
- tracheobronchitis.
If the patient has a sharp cough that is not accompanied by a characteristic sound (silent), a tracheostomy may be occurring.
Whooping cough
This type of cough is often accompanied by vomiting. At the same time, trembling chest sounds are heard as you inhale. Although the sputum leaves, the patient does not feel any relief.
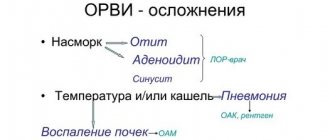
Symptoms accompanying a long-lasting cough
A cough, as a rule, is not the only signal warning of the development of a disease. It may be accompanied by the following symptomatic manifestations:
- hoarseness of voice;
- nasal congestion;
- discomfort in the nasopharynx;
- wheezing in the lungs;
- feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- belching;
- sputum production (possibly mixed with blood, mucus, pus).
Reviews from parents of young children
Irina Gubanova, 32 years old, 6-year-old child: “The cough kept me from sleeping, but there was no fever. The doctor prescribed inhalations with saline solution and Prospan drops several times a day. After 5 days of treatment, the sputum came out, but the cough did not go away, the child began to choke, and I noticed that my son’s cough began after buying a purebred puppy. I had to give the animal to my brother.”
Svetlana Epifantseva, 28 years old, child is 3 years old: “After a walk in the kindergarten, a cough started, we stayed at home, the local doctor prescribed us to drink Stodal syrup and take inhalations. Well, we bought a nebulizer in advance and treated ourselves at home. The inhaler was filled with steamed chamomile. Treatment began on time, and the son recovered quickly. A week later I went to kindergarten, but the cough recurred. I talked to a neurologist and it turns out that it’s stress from going to kindergarten. Now we are being treated by a psychotherapist.”
Galina Silicheva, 40 years old, third child, 5 years old: “We drank and ate a lot of medicine in two weeks, and then again I had a fever and cough with vomiting. I had to go to the hospital for pneumonia. I missed it somewhere, did it carelessly, we’re all in a hurry somewhere, we’re all in a hurry, we don’t have time.”
Prevention methods
Measures to prevent a prolonged cough are simple and familiar to everyone from childhood. But maybe that's why most people neglect them. And a frivolous attitude towards one’s own health does not remain without consequences. We take the liberty of reminding you of the measures that will prevent the disease from staying with you for a long time:
- give up bad habits, primarily smoking tobacco and electronic cigarettes;
- When working, people at risk must use personal protective equipment;
- avoid severe hypothermia of the head and legs;
- monitor the cleanliness, temperature and humidity of the air in the room;
- It is imperative to treat colds and viral diseases at an early stage - regardless of whether this is done using folk or traditional methods.
Important! If a residual cough persists for 3 weeks or more, be sure to consult a doctor again. . It is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it
And cough is no exception. Therefore, be more attentive to your health and take care of your respiratory system. After all, they supply the body with vital oxygen.
It is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. And cough is no exception. Therefore, be more attentive to your health and take care of your respiratory system. After all, they supply the body with vital oxygen.
Why does a cough persist for a long time in an adult?
A persistent cough is a dangerous symptom that indicates a serious illness. Common causes: gastroesophageal reflux disease, bronchial asthma, heart failure, respiratory problems, colds, viruses.
A prolonged cough is usually accompanied by other symptoms: severe shortness of breath, chest pain, lethargy, colored sputum (yellowish, greenish, etc.), whistling and loss of voice.
If the urge to cough does not go away for a long time, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe medication and draw up a therapeutic course.
After pneumonia
Residual cough after pneumonia, gradually fading, can persist for up to 1 month, which should not cause concern. A person who has had pneumonia continues to cough due to the slow recovery of lung tissue. In approximately 30% of those who have suffered the disease, the functional tissue is not restored at all: the affected areas become sclerotic, decrease in size, shrink, their blood supply is disrupted, and foci appear that predispose to the development of an infectious process.
If the cough does not go away after, the doctor draws up the last stage of the therapeutic course: prescribes medications that help eliminate the urge.
In adults, the urge to cough after pneumonia lasts longer than in children. In such cases, drugs of peripheral and central action are prescribed that suppress cough reflexes. Along with this, the specialist prescribes training exercises for the lungs, percussion massage, and inhalations.
If the cough does not go away for 1-3 months in an adult
If the symptom continues to bother you for a long period of time (from two weeks to a month), then the following diseases may develop: tuberculosis, asthma, bronchitis and other diseases.
Month
What to do if coughing does not go away for a month? If you are bothered by a long cough that does not go away within four weeks, you need to undergo an examination, determine the disease and listen to the symptoms .
The doctor will examine your throat and listen to your lungs. It would be a good idea to take tests to confirm the diagnosis.
To quickly get rid of a long-term cough, you need to drink plenty of fluids, eat a lot of fruits, do inhalations, and take medications prescribed by your doctor.
A cough without fever for a month does not disappear with smoking, as it complicates the healing process.
If a symptom does not disappear for 3 months in an adult after suffering from a cold, the following reasons are possible:
- the person has a weakened immune system;
- recovery is hampered by external factors: smoking, indoor air dried out by heating devices, alcohol consumption, dehydration due to low water and liquid intake;
- after an illness, another infection may occur, which leads to the development of pneumonia or bronchitis;
- in the worst case, a prolonged attack can cause the development of malignant tumors of the respiratory tract.
Before treating a cough that does not go away for up to 3 months, it is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence. If these are residual consequences of acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections, you should eat foods rich in vitamins, do inhalations, or ask your doctor to prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures.
Prolonged coughing may be due to heart disease. For an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a cardiologist.
With pneumonia, the patient’s condition improves for several days, then the temperature rises and a severe attack begins with sensations of chest pain. An X-ray of the lungs will help diagnose the disease.
2 months
Why has the cough not gone away for 2 months?
Coughing lasting more than 3 weeks can be called chronic. The cause of this cough may be a runny nose. Mucus flows down the nasopharynx and provokes a cough. If the patient has not treated the symptom for the entire time, then it will be more difficult to get rid of it.
The most common cause of persistent cough is asthma. Symptoms of asthma include:
- severe shortness of breath;
- feeling of congestion in the thoracic region;
- coughing with wheezing.
Read how to treat a severe cough with wheezing in an adult.
Causes of a dry, persistent cough
A dry or unproductive reflex almost always accompanies pathological processes. Contrary to popular belief, a cough that does not go away for several weeks or a month or more is not always the result of problems with the lungs and bronchi. What diseases are we talking about?
Hyperthyroidism with goiter
Goiter is a nodular or more often diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland, provoked by a number of exogenous and endogenous factors.
In this case, cough develops as a result of compression of the trachea and bronchi by an overgrown endocrine organ.
Excessive pressure leads to irritation of the lower respiratory tract.
The result is the formation of an intense reflex that will not go away until the operation is performed.
In this case, sputum production is not typical and is never observed. The release of exudate does not indicate a thyroid origin of the disease.
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the outer lining of the lungs. The pleura is a thin membrane of the bronchopulmonary structures; it primarily performs a protective function.
Pleurisy almost never develops as a primary pathology.
Most often we are talking about a secondary process, which is explained by inflammation of the pulmonary structures, bronchi, tracheitis (during the descent of pathogenic flora into the lower respiratory tract).
The disease is accompanied by nonspecific symptoms, primarily an intense, painful cough without phlegm that can last for months, chest pain and others.
Rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract
Paradoxically, it is possible to develop a cough even if the nasal passages and nasopharynx are affected. The reason is the flow of mucus and exudate, which is actively produced during a runny nose, into the lower respiratory tract.
Next, the mechanism goes through the standard path. The ciliated epithelium and its cilia perceive mucus and exudate as foreign objects that need to be expelled from the passages. A strong cough reflex develops.
In this case, there are practically no accompanying symptoms. This is a characteristic feature of the nasal nature of the cough.
Whooping cough
Childhood disease. It practically never occurs among adult patients, which is understandable.
This pathology develops with significantly reduced immunity, which is rarely observed in older patients.
The cough is intense, painful, clogging. It gets to the point where the patient begins to vomit from the force of the reflex.
Measles
Another inflammatory and infectious disease that occurs mainly in children and adolescents under 16 years of age. It is characterized by the same painful, long cough, although not always. Much depends on the strength of the infection.
Heart failure
Strangely, however, a cough can also develop as a result of congestive cardiac damage, which is explained by stretching of the ventricles of the heart.
It's all about disruption of gas exchange. When the heart muscle stops working as well as it should, the blood is less supplied with oxygen.
Shortness of breath begins, which leads to drying of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. The result is a cough, which is not always intense.
This is just one of the mechanisms for the formation of the reflex in heart failure. The disease is accompanied by many external symptoms. This dry cough does not go away for a month until the heart problems are eliminated.
Pharyngitis
It appears to be a disease in which inflammation of the pharyngeal mucous membranes and epithelial tissues occurs.
This unpleasant process is accompanied by sore throat, decreased swallowing activity of muscle structures, a dry cough, and voice disturbances (it becomes hoarse, hoarse, or disappears altogether).
Despite the discomfort of the current situation, pharyngitis extremely rarely produces complex and life-threatening symptoms. Although there is still a threat.
The cough has not gone away for a month: why?
The main reason for persistent cough is improper treatment of ARVI. At the beginning of the disease, spasms appear without signs of sputum production. The cough does not bring relief and provokes abdominal pain and heart rhythm disturbances. 4-5 days after the first signs of ARVI appear, the cough becomes wet. If the airways are not cleared of mucus, the process will be complicated by infection.
Other causes of dry cough include:
- Hyperthyroidism is a disease of the thyroid gland associated with diffuse enlargement of the organ. The cough reflex develops due to compression of the trachea and bronchi by the enlarged organ.
- Pleurisy is inflammation of the lining of the lungs. The pathology develops due to illiterate treatment of viral diseases and is manifested by severe pain in the chest. With pleurisy, a dry cough is observed for more than a month.
- Damage to the nasal passages. The main reason for the reflex is the flow of mucus into the throat. The epithelium of the lower respiratory tract perceives exudate as a foreign substance. Coughing clears the body of mucus. With sinusitis and rhinitis, other associated symptoms are rarely observed.
- Heart failure. Spasms in the chest are caused by stretching of the ventricles of the heart. A dry cough will not go away until problems with the blood supply are eliminated.
- Smoking. A common cause of prolonged cough is the use of tobacco products. The symptom is caused by irritation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory system by nicotine, carcinogens and harmful tars. Smokers' cough lasts for years.
- Harmful working conditions. Long-term symptoms are associated with occupational factors. To prevent health problems, people employed in hazardous work must use special protective equipment: masks, bandages, respirators. The problem affects people who come into contact with wooden, metal objects, and paint and varnish products. Small particles of materials enter the respiratory tract and provoke a lingering cough, which annoys the patient for 4 months or longer.
- Lung or throat cancer in humans. In pathologies, a nonproductive cough with a small amount of sputum is observed. In the final stages of cancer, streaks of blood will appear in the mucus.
- Infectious diseases of the throat: laryngitis, pharyngitis. The last type of disorder is associated with inflammation of the pharyngeal epithelium. It is accompanied by hoarseness, difficulty swallowing saliva and decreased muscle activity. Pharyngitis rarely provokes complications such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Laryngitis is swelling of the larynx and threatens asphyxia if medical attention is not received promptly.
Attention! A dry cough may be a sign of tuberculosis or whooping cough. The latter type of disease is more often diagnosed in children than in adults. It is manifested by suffocating attacks, fever up to 40 degrees and bouts of vomiting. With whooping cough, an adult’s cough does not go away for 3 months. Tuberculosis develops gradually. Its distinctive symptom is the presence of blood streaks in the sputum.
A cough that does not go away for 2 months may be associated with allergies or chronic problems in the body. It is not possible to completely cope with a chronic cough. The intensity of spasms will increase during the acute stage and decrease during periods of recovery.
On this topic:
Treatment of dry cough in an adult at home

A productive (wet) cough is caused by dozens of reasons. If the symptom does not go away for more than a month, then we are talking about the transition of the problem to the chronic stage of its course. Factors that provoke the problem include:
- ARVI or acute respiratory infections, accompanied by fever, heavy breathing, and headaches. Viral diseases are complicated by tracheitis and bronchitis, in which there is sputum production from the lower respiratory tract.
- Bronchitis is damage to the bronchopulmonary tract by infectious pathogens. The pathology is accompanied by copious or insignificant amounts of sputum, chest pain, and weakness. In chronic bronchitis, an adult has a cough that lasts for a month.
- Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs. Pathology is not always manifested by the lower respiratory tract reflex. Sluggish forms of pneumonia cause coughing for more than a month.
- Tracheitis is a lesion of the trachea. The structure is rich in nerve endings, so the inflammatory processes occurring in it are accompanied by intense spasm for 2-3 weeks.
- Bronchial asthma is a problem associated with a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi. The reflex from the respiratory tract manifests itself in paroxysms and requires immediate action on the part of medical personnel or the patient himself. Advanced bronchial asthma leads to suffocation.
- Reflux is esophagitis associated with the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. A spasm in the chest will haunt the patient until the digestive problem is resolved.
Sometimes a wet cough is associated with several reasons at once: bronchial asthma and bronchitis, in which pathogenic flora penetrates the lungs. The symptoms of each disease become more pronounced.
What to do if the cough does not stop for a week
Cough is an involuntary expiratory reflex that occurs as a result of irritation of the mucous membrane of the larynx, bronchi or throat and lung tissue. Thanks to this symptom, the airways are cleared of foreign bodies, harmful microorganisms, mucus, dust and sputum.
The reasons that provoke a prolonged cough include:
- colds;
- allergies;
- emotional overstrain.
Moreover, the cough can be wet or dry, night, daytime, periodic, paroxysmal, etc.
Treatment of weekly cough
If the cause of a week's cough is an acute respiratory infection.
then the doctor prescribes antitussives, but you cannot take antibiotics, since they only affect bacteria. But antibacterial agents may be appropriate for bronchitis and pneumonia, which are accompanied by symptoms such as fever and severe cough. In addition to antibiotics, if a severe cough does not go away for a week, expectorants based on medicinal plants are prescribed. In addition, the doctor can prescribe immunomodulatory drugs that activate the body's protective functions and reduce the effect of antiviral drugs.
It is worth noting that if the cough not only does not go away for more than a week, but is also accompanied by chest pain, high temperature (38 or more), and when coughing up bloody, green or yellow sputum is released, then you cannot self-medicate, but you must quickly contact doctor.
There are some recommendations that are important to follow when treating a persistent cough in an adult. To prevent your throat from getting dry, you need to drink plenty of fluids.
For this purpose, you can drink warm milk with honey every evening.
Fruit drinks and juices are no less useful. In addition, if a dry cough does not go away for more than a week, you should drink fresh black radish juice (1 tablespoon three times a day).
Diagnostics
If an adult’s cough does not go away for more than a month, then he needs to contact his local physician for a comprehensive examination. Standard diagnostics include a complete blood count and chest x-ray. If the therapist cannot determine the cause of the disorder, the patient will be referred to a specialist doctor - a pulmonologist.
Important! Independent selection of medications without professional diagnostics is not recommended. An illiterate fight against the protracted reflex leads to aggravation of the symptoms of the underlying disease and its transition to a difficult-to-treat form.
X-rays play an important role in the diagnosis of diseases accompanied by cough. If the images do not reveal pathological changes in the structure of the respiratory organs, then the patient is prescribed additional diagnostic procedures:
- examination of sputum for bacterial flora;
- thoracoscopy - a method for assessing the condition of the respiratory system through a puncture in the chest (used for suspected pleurisy, lung cancer, tuberculosis);
- spirometry - examination of external respiration using a special apparatus;
- tossography - determination of the intensity and frequency of the cough reflex;
- bronchoscopy – examination of the respiratory tract using a miniature device (bronchoscope).
On this topic:
Why does chest pain occur when coughing?
Patients will not be able to determine their preferred diagnostic method on their own. A specialist will help you choose the best examination method. In one case, a comprehensive diagnosis will be required using instrumental examination methods (X-ray, ultrasound or MRI), and in the other, the use of a phonendoscope (a device for listening to the chest) is sufficient.

Types of chronic rhinitis
If the snot does not go away for a long time, you need to urgently look for the cause. It happens that the patient’s torment lasts up to six months. Purulent and constant congestion most often appear with various types:
- catarrhal;
- vasomotor;
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic.
Catarrhal
A runny nose that appears against the background of respiratory diseases is not uncommon. Inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx often lead to profuse nasal discharge. With a mild form of the disease, developed rhinitis goes away quite quickly. Usually a few days are enough for complete recovery.
If a runny nose does not go away for a week, two, three, this is evidence that the pathology has developed into a chronic form. This condition is characterized by periodic exacerbations and attenuation of the disease for six months or more. During the period of remission, mucous discharge may stop, but itching, sneezing attacks, and dry mucous membranes appear. The reason why a runny nose becomes chronic is most often due to improper treatment.

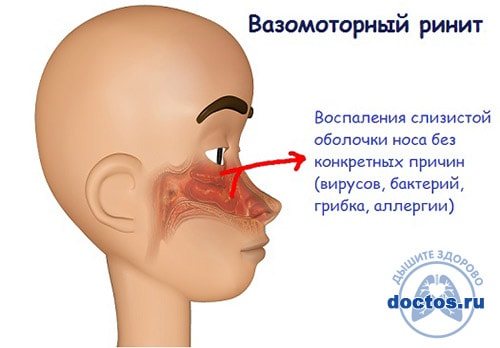
Vasomotor
If a runny nose does not go away for a month, it may be to blame. The causes of this pathology are still not fully understood. It is reliably known that this type of disease is not characterized by an inflammatory process in the nose. Most often, the problem develops due to poor circulation in the mucous membrane of the inferior nasal concha. As a result of excessive vasodilation, swelling develops and mucous discharge appears that does not go away for months.
Vasomotor rhinitis can be recognized by the color of the mucus. It is liquid, transparent and has no odor. Such snot lasts a long time and interferes with normal life. To alleviate their condition, patients have to constantly use vasoconstrictor drops, which is absolutely forbidden to do. As a result, instead of improvement, you can only get complications.
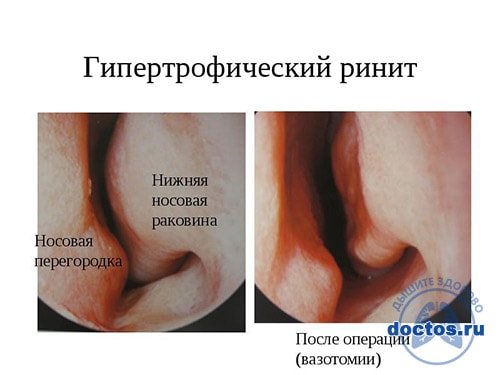
Hypertrophic
This occurs due to thickening of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. As a result, the normal mucous membrane is replaced by denser fibrous tissue, which leads to compression of blood vessels and poor circulation. A runny nose caused by this pathology can last up to six months.
Why does a runny nose not go away for a long time in such a situation? The cause is regular inhalation of caustic chemicals, for example, at work, as well as a deviated nasal septum due to injury. There is no specific treatment; the situation is resolved through surgery.
Atrophic
If a runny nose does not go away for a long time, the cause may be thinning of the mucous membrane. Patients complain of constant pain and a burning sensation, especially when instilled. This disease is often accompanied by bloody discharge and heavy bleeding.
Cough for more than 2 weeks
If a cough after an acute respiratory infection or bronchitis does not go away for more than 2 weeks, this means that the inflammatory process continues in the body. The cause of this residual phenomenon may be the addition of a secondary infection.
A patient whose immunity is weakened by a previous respiratory infection can easily become infected again. The cause of infection may be one’s own opportunistic microflora, which is suppressed by the immune system in a healthy person.
The cause of frequent coughing attacks may be an associated secondary external infection that occurs against a background of weakened immunity, for example:
- bacteria streptococci, staphylococci;
- mycoplasma;
- chlamydia;
- candida fungi;
- tuberculosis bacillus.
For no apparent reason, attacks of dry coughing tremors may occur due to allergies. The allergic cough reflex is caused by the presence of an allergen; the duration of this phenomenon depends on the concentration of the allergen and the reactivity of the immune system.
An allergic cough occurs in adults without fever, which distinguishes it from a cold, does not go away for a long time, and, if you treat it yourself, using herbal inhalations, is very dangerous. Self-medication can cause a powerful allergic reaction - anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema.
Treatment of cough with phlegm
To get rid of viscous and difficult to separate mucus, it is recommended to choose mucolytic agents that will not only make it more liquid, but also help the body get rid of it. After taking these medications, the cough goes away within a few days.
It is important to remember that these drugs should not be taken together with antitussive medications, as their actions contradict each other.
The most common mucolytic drugs are:
- Bromhexine. The product exhibits mucolytic and expectorant effects. The active substance is bromhexine hydrochloride. The dosage for different ages is indicated in the instructions. Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, intolerance and age under 3 years.
- Fluimucil. The drug is endowed with the ability to dilute sputum and remove it out. The active substance is acetylcysteine. The dosage is indicated in the instructions. Contraindications: intolerance, pregnancy and age under 18 years.
- Ambroxol. A mucolytic drug with many beneficial properties. The active ingredient is ambroxol hydrochloride. The dosage is given in the instructions. Contraindications: intolerance, pregnancy and liver failure.
What to do if your child’s cough won’t go away
If a child’s cough does not go away for a long time, the first thing to do is to identify the cause of this condition. If coughing bothers you after an illness (ARVI, influenza, bronchitis, etc.), then in this case the cough may be associated with the recovery period. Harmful microorganisms weaken the body, provoke inflammation and irritation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, and the body needs time to completely free the bronchi from mucus residues and restore the epithelium.
In this case, coughing does not pose a danger; usually the child coughs occasionally, and there may be a slight discharge of sputum.
It is worth noting that each body is individual, and the recovery process in each individual case proceeds differently and can sometimes drag on for months.
If the cough continues for more than three weeks, while the amount of sputum increases, the cough becomes stronger, it is necessary to show the child to the doctor, as in this case there may be a secondary infection, the development of complications or a severe allergic reaction.
Folk remedies for cough
If the cough does not go away for a long time, you can use folk remedies that will help soothe the irritated mucous membrane, improve the process of removing phlegm and speed up the healing process:
- Infusion of dill seeds - take 1 tsp. dill seeds, crush, pour 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 20-25 minutes. It is recommended to drink this infusion instead of water throughout the day until complete recovery.
- Serum with garlic – 2 tbsp. garlic pour 250 ml of cow's milk whey and put on fire, immediately after boiling, remove from heat and cool. This decoction should be drunk throughout the day.
- Honey – has unique anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects; with a prolonged cough, you can dissolve 1 tsp in your mouth. honey several times a day.
- Medicinal decoction - mix licorice, marshmallow root and elecampane in equal parts, take 1 tbsp. mixture and pour 200 ml of cold water, leave for two hours. Then put on fire and bring to a boil. Drink the cooled and strained broth in three doses during the day, the course of treatment is 10 days (it is recommended to prepare a new portion every day). If coughing continues, you can repeat the course of treatment after a week.
As already noted, coughing is a protective reaction of the body that helps clear the airways from small particles of dust, various contaminants, viruses, etc. If the cough does not go away for a long time, you need to determine the cause of its occurrence. It is worth remembering the residual effects that are observed during the period of recovery of the body and help cleanse the bronchi from mucus residues. Also, coughing may appear due to increased sensitivity of the receptors; in this case, coughing is disturbing after inhaling cold air, dust or the action of allergens.
Why does the cough not go away for a long time?
Very often, parents cannot understand why the child coughs for so long. What not to do and what are the main mistakes in treatment, due to which the unpleasant symptoms of the disease may not go away for a long time:
- Using expectorants to treat a wet cough (very often on the advice of a pharmacist at a pharmacy or a friend). Such an error in choosing a drug causes excessive formation of phlegm in the lungs, which the body does not have time to get rid of, and the child coughs non-stop. By the way, there is no evidence of the greater effectiveness of such remedies compared to drinking plenty of fluids and rinsing the nose.

- The indoor air is too dry and warm. Such a seemingly trifle can do a disservice in the treatment of any infection.
- Use of cough suppressants without acute indications. It is especially dangerous to take such drugs with a wet cough, because the body needs to get rid of the resulting phlegm.
- Warming up, hot inhalations, rubbing (especially during the acute period of the disease) should not be done. Firstly, no doctor would advise overheating a child who already has a fever. Secondly, even if the fever has long passed, the effectiveness of this treatment method raises many doubts. Instead of such procedures, doctors recommend using a nebulizer.