The function of leukocytes in the body and what causes the increase in their rate in children’s urine
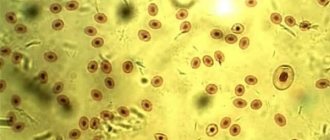
Leukocytes are formed in the bone marrow to protect the body from pathogenic microflora and maintain homeostasis.
This important component of blood is divided into several groups, each of which copes with certain tasks:
- neutrophils - fight bacterial infections;
- eosinophils – regulators of allergic reactions;
- lymphocytes – produce antibodies;
- monocytes - through phagocytosis (absorption and digestion), destroy microbes and foreign substances.
Consequently, the number of leukocytes increases rapidly during inflammatory processes, allergic reactions or the development of infectious diseases.
The number of leukocytes is a very important indicator and parents should discuss any deviation from the norm with a doctor who, if necessary, will prescribe adequate treatment. Timely diagnosis is the basis for effective therapy and recovery. Therefore, urine tests in children should be performed regularly.
Urinalysis in children under one year of age
Why was my baby given a urine test?
A pediatrician may refer an infant for OAM for several reasons:
- It's time for a scheduled examination. It is carried out three times: at 1 month, at 6 months and a year.
- Before vaccination (to identify contraindications).
- If you suspect any pathologies.
- Before the child is admitted to the hospital.
- After the baby has suffered a particular disease (to track the healing process).
How to collect urine from a baby?
Only fresh urine can be submitted to OAM. It needs to be collected in the morning, when the baby wakes up and has not yet had time to eat. Otherwise, the analysis results will be erroneous.
Before the baby pees in the jar, he needs to be washed with baby soap. This is necessary to prevent impurities from getting into the urine.
You cannot take tests if your baby has recently taken any medications, especially those containing dyes.
Urine is collected in a clean container, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. The material should not be poured into a jar from a pot or the contents of a diaper should be squeezed into a container.
How to take urine from a boy?
Place the baby on the swaddle. Take off his pants and diaper. When the baby begins to write, place a clean test tube under the stream to collect the analysis. For OAM, it is enough to collect 50 milliliters of material.
How to take urine from a girl?
Buy a urine collector with sticky edges from the pharmacy. Place the baby on the diaper and secure the urine bag in the crotch with Velcro. When the girl pees, remove the container and pour its contents into a clean container.
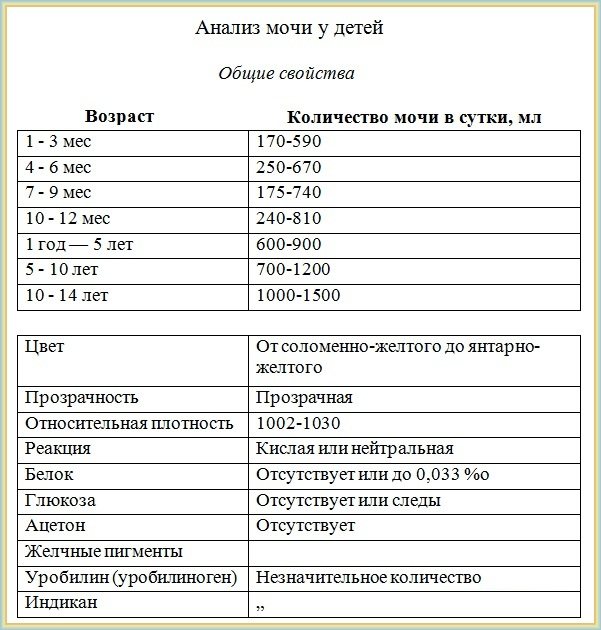
Urine analysis in children under one year of age: norm and interpretation
Normal TAM indicators for infants are:
- Color – light, amber
- Transparency – high
- Specific gravity – 1000-1005
- Acidity – 4,4-7,3
- Glucose - not detected
- Ketones – not detected
- Salts – not detected
- Bacteria – not detected
- Epithelium – 0-2 cells
- Mucus – none / in small quantities
- Leukocytes – 0-3 cells
- Red blood cells - not detected
- Protein – up to 0.002 g/l
- Bilirubin – not detected
- Urobilinogen – up to 10 µmol
If the test results match these indicators, your baby is healthy.
Deviations from the norm: how to understand them?
If you collected urine according to the rules, took it to the clinic on time, and the analysis recorded certain abnormalities, this may indicate that the baby has various pathologies:
- Color Brown or red-brown urine is a sign of kidney disease, cloudy or white urine is a sign of diabetes. In the first 10 days of life, the color of a baby’s urine can change from clear to brick-colored. This is not a deviation and is associated with the developmental characteristics of the baby. If your baby ate foods with dyes before the test, his urine may also change color.
- Odor Healthy babies have very little odor in their urine. Strong odors are caused by infections or diabetes.
- Transparency If a baby pees with a cloudy liquid, this is one of the signs of diathesis.
- Specific gravity Increased values occur with dehydration and temperature. Decreased levels are extremely rare and indicate a specific disease - diabetes insipidus.
- Change in acidity High pH occurs with inflammation and kidney failure. Low acidity is a sign of dehydration, intestinal disorders, tuberculosis or diabetes.
- Glucose There may be some sugar in a baby's urine, and this is normal. If the glucose level is elevated, you will be prescribed an additional test. The baby may have diabetes.
- Protein If its amount exceeds the norm, we are talking about inflammation of the urinary tract, kidney disease or other, rarer pathologies.
- Epithelium Enters the urine during inflammatory processes (for example, cystitis).
- Bilirubin may appear in the urine due to an improper diet (abundance of carbohydrates) or with liver disease or kidney stones.
- Ketones Appear due to severe stress, malnutrition, lack of carbohydrates, diabetes and infections.
- Urobilinogen If its content in the urine is exceeded, this is a sign of liver failure or intestinal inflammation.
- Red blood cells enter the urine during renal colic, cystitis or urolithiasis.
- Leukocytes Appear during inflammation.
P. _ S .: Pay attention to the color and smell of baby urine. If it darkens, becomes cloudy or smells unpleasant, contact your pediatrician immediately. A timely diagnosis will keep your baby healthy.
The normal content of white blood cells in children's urine, depending on gender and age - table
Leukocytes in the urine of a child without pathogenic disorders in the genitourinary system should not exceed 10 units in 1 μl of urine. Gender, age and physical parameters of the baby’s body directly affect the white blood cell count.
The body of a newborn is not able to ensure proper functioning of the kidneys. Consequently, an increase in the norm of leukocyte cell content to 15 units is typical. According to the leukocyte formula, this phenomenon is designated as the initial physiological crossover.
A constant or increased level of leukocytes indicates pathogenic disorders. The normal level for boys under 1 year of age is no more than 1-1 units. In female infants, it is possible that white blood cell limits may be exceeded by up to 5 units.
The leukocyte rate in young patients is higher than the normal rate in adults. In children over 1 year old, 1-8 units is considered a safe amount. The normal indicator for the number of leukocytes in urine depends on the age and gender of the child.
The table below will help you understand this issue more easily:
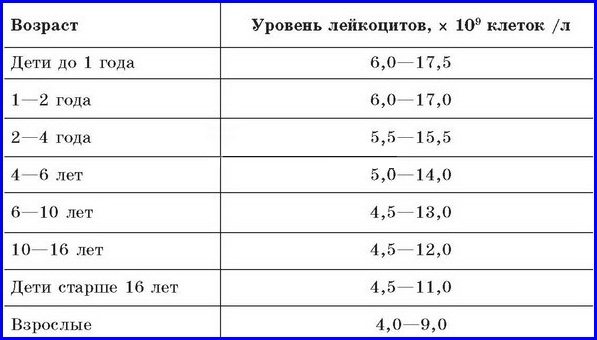
| Child's age | Normal indicator units. leukocytes in the field of view, during a general urine test | |
| in boys | in girls | |
| From birth to 1 year | 8-9 | 5-6 |
| 1-7 years | 0-3 | 0— 1 |
| 7-18 years | 0-3 | 0-6 |
| Limit value | 9-10 | 6-7 |
Leukocytes in a child's urine exceeding the above normal values are reported as leukocyturia. If white blood cells are significantly elevated and cloudy urine is observed, then this condition is characterized by pyuria (discharge of pus along with urine).
Other causes of elevated white blood cell levels
In addition to infections of internal organs, the cause of abnormalities in urine analysis may be damage to the external genitalia. In particular, an increase in the concentration of leukocytes in the urine is observed with inflammation of the mucous membranes of the urethra, which is a common pathology in both boys and girls.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Itching and burning in the genitals
- Severe pain syndrome
- Presence of blood in urine
- Change in odor and color of urinary fluid
- Increased urination
Treatment of infections of the external genitalia is complicated by the fact that the symptoms and manifestations of the disease are almost identical to infections of the urinary system. An accurate diagnosis is made through the use of various diagnostic procedures. One of the most radical is bladder catheterization. With such an examination, a normal level of leukocytes is noted, while the indicator in a conventional urine test indicates a deviation from the norm.

In infants, the cause of increased white cells in the urine may be due to the presence of diaper dermatitis. This disease occurs due to prolonged use of diapers, which retain urine and feces and come into contact with the baby's skin. A concomitant factor in the development of diaper rash is the presence of food allergies.
The disease manifests itself in the occurrence of swelling in the groin area and severe redness of the skin. In this case, there are no symptoms of infectious infection.
Another reason for the increase in white blood cells in the urine is allergies. The pathology is provoked by a sharp jump in the concentration of eosinophils in the blood. An increase in the number of leukocytes in this case is a response of the child’s body to the action of the allergen. The intensity of white blood cell production depends on what substance causes the allergy and the presence of concomitant diseases.
There are various reasons for an increase in the level of leukocytes in the urine of a child, which are not associated with infectious lesions of the internal urinary organs.
Reduced white blood cell count
The normal content of white blood cells in urine is considered to be their complete absence or a small amount. Therefore, the presence of pathologies is indicated exclusively by an increased level of leukocytes - leukocyturia.

Leukocytes in a child’s urine in small quantities indicate favorable tests, and parents should not be alarmed. If there are no white bodies in children's urine, the organs of the urinary system are not inflamed and function normally.
An increase in the concentration of white blood cells in urine leads to radical changes in its chemical composition. In case of unfavorable test results, it is important to promptly determine the reasons for the increase in leukocyte counts.
Why are leukocytes elevated?
An increase in white blood cells in the urine may be associated with several factors, and not all of them are pathological, that is, they are not considered in the context of diseases of the urinary system.
For example, in girls, sometimes leukocytes can come from the vagina or intestines, which is due to the close proximity of the latter to the urethra (urethra). However, it should be noted that in this case the result of the study will not be high, but will only deviate slightly from the norm.
If, after a repeated urine test, the indicator is at the same level, then an inflammatory process may be occurring in the child’s body. Then it is necessary to conduct a full examination to confirm or refute this assumption.
Reference! In case of severe leukocyturia (the presence of leukocytes in the urine), even if there are no accompanying symptoms, a comprehensive diagnosis is mandatory.
Because, most likely, we are talking about a serious inflammatory process of an infectious nature. So, an increase in leukocytes in the secreted fluid in a child may be a consequence of pathologies such as:
Leukocytes and bacteria in a child’s urine
- allergic reactions, diaper rash;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- urinary tract infection;
- an inflammatory process localized in the external genitalia;
- growth of microflora during prolonged artificial urinary retention;
- pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis, occurring in the acute stage, developing against the background of acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections.
The last mentioned diseases, pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis) and glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney) are very serious pathologies, and are often accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture.
Laboratory indicators of urine also change significantly; for example, leukocytes can reach 75 cells in the field of view of a microscope or be completely in the urine. While the other listed possible reasons for the increase in the coefficient, in most cases do not lead to an increase in it above 25 units in the sample.
Causes of elevated levels of leukocytes in urine
Leukocytes with an observed excess of their content in the urine are often caused by inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system in a child, sometimes by factors not related to dysfunction of the body.
Causes of a pathological nature
The presence of various types of leukocytes in a child’s urine may indicate the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis. The disease is characterized by acute specific inflammation of the kidneys with multiple contents of mononuclear white bodies - monocytes - in the urine;
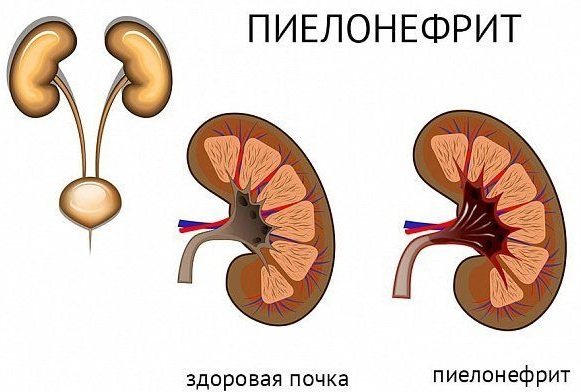
- glomerulonephritis. Renal failure, occurring in acute or severe form. It may be caused by a morphological disorder of the kidneys or infectious inflammation. In urine there is an increased concentration of white blood cells of the granulocytic type;
- cystitis. Defined as inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. It is diagnosed mainly in girls. Often the etiological factors of the disease are associated with stagnation of urine;
- Urolithiasis Urolithiasis, which develops against the background of stone accumulations in the organs of the urinary system. The formation of large stones in the kidneys leads to blockage of the ureter and a deterioration in the outflow of urine. Stagnant urine becomes a favorable environment for the development of bacteria;
- Koch infection. Well-known tuberculosis affects the kidneys, liver and other vital organs. An increase in leukocytes in urine is observed exclusively in renal tuberculosis;
- allergy. Immunological disruptions provoke allergic inflammation, in which the level of esinophilic granulocytes in the urine increases;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organs of the reproductive system . Often occur as a result of poor care of the child’s genitals. There is damage to the mucous membrane caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms that stimulate increased production of lymphocytes. Accordingly, the analyzes record an increased content of white cells.
Causes of leukocyturia not related to pathogenic factors
As a rule, unfavorable indicators are preceded by inflammatory processes.
Less commonly, the cause of leukocyturia is improper preparation of the child for testing, including:
- consuming a high-protein meal before sample collection;
- taking a hot bath the day before urine collection;

- collection of urine from poorly washed genitals in children.
When collecting urine, the sterility of the container is strictly observed. Otherwise, bacteria may get into the tests, and the results of the study will be incorrect. Therefore, doctors recommend collecting biological fluid in a specially prepared container, opening it only before urinating and after collection, and immediately closing it tightly with a lid.
What can an increased level of leukocytes in a child’s urine tell about?
Leukocyturia (increased levels of leukocytes in the urine) indicates the presence of an internal inflammatory process. This may be chronic or acute kidney disease, urinary tract infection, or some systemic or endocrine diseases.
It is important that leukocytes can appear in the urine even if the baby does not have a fever or other signs of an acute process. In this case, leukocyturia will be the first symptom of a developing disease. It is necessary to start treatment in time, before the disease becomes chronic and leads to serious kidney damage.
A significant increase in leukocytes in the urine can be noticeable without laboratory tests. The urine becomes cloudy, sometimes there are white flakes, and the smell changes. This is an extremely alarming symptom. If you notice such changes when emptying your child's potty, contact your doctor immediately!
The pediatrician explains how to make or exclude the diagnosis of leukocyturia and determine the extent of the disease.
Signs of increased white blood cell count in children
Visual signs of a violation of the chemical composition of urine indicate immediate testing.
With an increased level of white blood cells in a child’s urine, characteristic symptoms appear:
- pain in the bladder localized in the lower abdomen, lumbar region;
- cloudy urine color (mucus, blood, visible protein flakes, sand, purulent discharge appear in the urine);
- poor health, syndromic pain, hyperthermia, combined with discolored urine;
- difficulty urinating with pain when passing urine;
- fever, accompanied by a state of chills, weakness, lethargy, swelling of the limbs and in the eye area (the child's eyelids often swell).
You should also think about submitting a urine sample for analysis if your baby is worried. At the same time, along with the changed appearance of urine, pathogenic disorders are indicated by the baby’s anxiety, moodiness, crying, and refusal to accept breast milk.
Rules for collecting urine for analysis
For children under 1 year of age, a general urine test is recommended to be performed every trimester. As the child gets older, the frequency of testing decreases. The pediatrician prescribes tests if the child complains of pain in the back, cutting pain when urinating, or difficulty passing urine with blood.
To avoid erroneous results and the need for a repeat test, parents should adhere to the following rules:
- Limit your child's intake of foods high in protein and vitamin C during the day.
- Bathing a child in hot water is prohibited; intense physical exercise is contraindicated for children of school and preschool age.
- Urine collection is carried out in the morning between 7 and 10 o'clock. The material is collected in a special container purchased at the pharmacy with a tight-fitting lid.
- An average portion of urine, amounting to 50 ml, is collected in a container (when urinating, the initial and final portions are drained into the toilet). During the procedure, do not touch the inside of the container with your fingers.
- Before urinating to remove a sample, the child should wash thoroughly with soap and dry the genital area with a clean towel.
- The sample is delivered to the laboratory within — — 1 hour from the start of biomaterial collection. The liquid must not be stored in a place that is too cold or warm.
Collection of urine from infants
In infants, urine collection in an amount of 10 ml is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, with the obligatory observance of all hygiene standards. The biomaterial is collected through a urinal. A special reservoir is attached to clean, dry skin in the groin area, around the urethra.
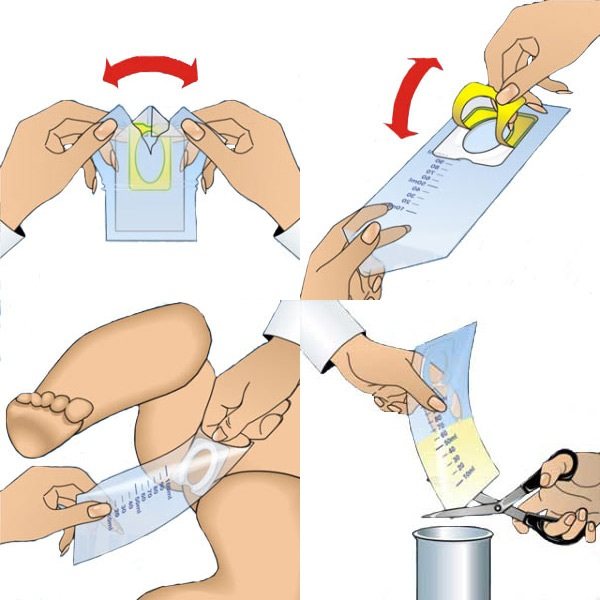
The urine bag is a plastic bag with a protruding neck at the end. The tank for boys has a round neck, and when urine is taken, the penis is inserted into it. In the version for girls, the neck shape is oval (in the form of a willow leaf) and is attached to the crotch.
Before collecting biological material, you should not feed your baby unfamiliar foods (breastfeeding mothers should not eat them). It is not recommended to give your baby vegetables and fruits that change the color of urine.
What determines a general urine analysis
A general urine test determines many different parameters, including the number of red and white blood cells, which are important in the diagnosis of many diseases. The first OAM is performed on an infant. The internal state of the baby's body is determined by the number of white blood cells contained.
In addition to the quantitative indicator of white blood cells, OAM helps determine:
- biofluid density;
- presence of sediment (transparency);
- the presence of foreign impurities (protein, sugar);
- shade;
- saturation with organic substances;
- acidity level.
A urine test is one of the main laboratory tests that allows you to check how well the child’s genitourinary system is working.
Urine examination allows us to identify diseases of such organs as:
- kidneys;
- ureter;
- bladder;
- urethra (urethra);
- adrenal glands;
- liver.
In addition, urine analysis is the main diagnostic test for suspected diabetes, allowing the doctor to check the effects of medications and diet. You should remember to take the sample correctly so as not to affect the reliability of the result.
The norm of leukocytes and other substances in a child’s urine
Leukocytes in a child's urine increase significantly with inflammatory diseases in the genital and urinary system. Therefore, for symptoms indicating pyelonephritis, urethritis, cystitis, glomerulonephritis, a urine test is required.
The length of time you wait for OAM results depends on the urgency of receiving them. If the doctor needs the indicator data urgently, the study is carried out within 1-3 hours. In standard situations, the result can be obtained within 1 day.
Leukocyturia
An increase in leukocytes above the norm (from 20-25 units) is called leukocyturia, everything above 60 is called pyuria.
In the analysis form, the result of leukocytes is written as follows:
- Leukocytes 0-2-3, 3-4,4-5, 5-8, 7-10 in the field of view. The doctor sees from 0 to 10 leukocytes in the field of view
- Leukocytes 10-15, 15-20, 20-25, 30-40, 25-50 and more in the field of view. This is a high level that is not the norm.
- Accumulation of leukocytes in the urine. They form groups in the field of view.
- A laboratory representative may conclude “all white blood cells.” Entirely means that there are so many of them that they cannot be counted. This is one of the worst results and indicates serious inflammation. When it reaches 60 or more, urine becomes cloudy in color and sediment is possible.
When are repeat tests needed?
The cause of leukotcuturia is not always a pathological factor. Erroneous results are often due to the non-sterility of the container for collecting biomaterial, violation of hygiene standards and the procedure for collecting the average portion of urine. In these cases, the doctor prescribes a repeat laboratory test.
If leukocyturia is detected in a child after repeated OAM, clarifying tests are performed, including additional diagnostic methods.
To confirm the true causes of elevated leukocytes, the doctor prescribes:
- repeated general examination of urine;
- urine examination using the Nechiporenko method;
- Amburge test;
- analysis of the content of living leukocytes;
- Kakovsky-Adissa analysis.
A secondary general analysis is carried out taking into account all the rules for collecting urine, including:
- preparation of sterile containers;
- strict adherence to hygiene standards for the child’s genital organs before collecting the sample;
- collecting an average portion of urine in a container tightly closed with a lid;
- compliance with the rules for storing biofluids (collected material is stored for no more than 1 hour, during which it must be delivered to the laboratory).
To clarify the diagnosis of pathogenic disorders in the genitourinary system, leukocytes, erythrocytes (red blood cells), and cylinders are counted. To do this, the methods described below are used.
Urine analysis according to Nechiporenko
If there are observed deviations from the norm in the content of leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders, after OAM, a more accurate analysis of urine is carried out using the Nechiporenko method. It allows you to obtain a final diagnosis, based on which effective treatment is prescribed.
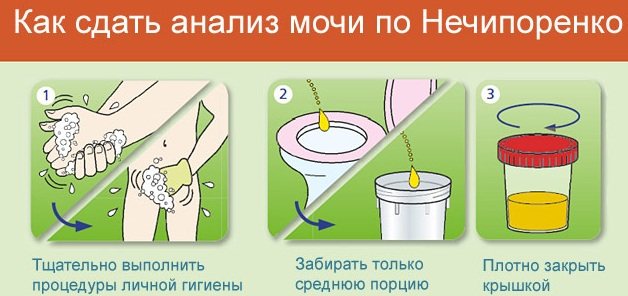
This method was first proposed by the Soviet doctor A.Z. Nechiporenko. The analysis is mainly aimed at diagnosing pathological processes in the urinary tract. For analysis, a portion of urine of 50-100 ml is collected.
The study of biological fluid is carried out in stages:
- The urine collected in a container is shaken and 10 ml of liquid is poured into a graduated test tube.
- The test tube containing the biofluid is centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 3 minutes.
- Using a pipette, the top layer of urine is removed until 1 ml of liquid with sediment remains in the vessel.
- The remaining urine with sediment is shaken well and poured into a special counting chamber, in which leukocytes, erythrocytes and cylinders are counted separately. The calculation is carried out in 1 mm3 of liquid sediment.
Preparation of urine collection for research using this method is identical to the collection of biomaterial for a general urine test. The normal indicator of leukocyte concentration according to Nechiporenko is no more than 1000 units per 1 ml of urine. In terms of time, this research method takes no more than 15 minutes. Therefore, parents can pick up the result in just 5-7 hours.
Urine analysis according to Kakovsky - Adiss
It is a quantitative analysis of urine excreted per day. The sample is taken to the laboratory and centrifuged. Then the top layer is selected. The remaining sediment (1-0.5 ml) is examined in a Fuchs-Rosenthal counting chamber, where leukocytes, erythrocytes, and cylinders are counted separately.

This method is intended for differentiated diagnosis of pathologies of the genitourinary apparatus, especially such as:
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease.
According to Kakovsky-Adiss, the normal indicator of the number of different types of blood cells in urine excreted per day is: leukocytes - 1000, erythrocytes 1000 and up to 10 hyaline casts.
Research by the Amburger method
The method of examining urine, invented in 1954 by a scientist clinician who studied kidney diseases, J. Amburger, effectively determines the imbalance of formed elements in the minute volume of urine. It is a modified Kakovsky-Adis test and is relevant in modern practical medicine.
The study of biomaterial according to Amburge is carried out in laboratory conditions using a centrifuge.
The procedure is performed according to the algorithm below:
- Urine is collected over a 3-hour period and 10 ml is taken from it.
- The sample is placed in a centrifuge apparatus and rotated for 5 minutes at a speed of 100 rpm.
- The top layer of liquid is removed until 1 ml of sediment remains.
- The counting of leukocytes and erythrocytes in 1 ml of sediment is carried out in a counting chamber.

The Amburge test is considered positive if the blood cell count is: 1000 red blood cells, 1000 white blood cells. The test itself takes 30 minutes. Results are usually ready the next day.
To treat diseases that cause leukocyturia, conservative methods of therapy are used. If the causative agent is inflammatory processes, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive course of medications to eliminate the bacterial microflora obstructing the ureter.
How to normalize white blood cell counts in a child’s urine
Using modern diagnostic methods, a medical specialist identifies an infectious agent that has entered the urinary system or genitals. D
To select the most effective drugs, before prescribing antibiotics, tests are carried out to determine the susceptibility of pathogenic microbes to the action of various medications. Then, taking into account the harmful effects of drugs on bacterial microflora, an appropriate course of treatment is prescribed.
Drug therapy
When prescribing antibiotics, the age of the child is taken into account. Drugs are selected based on their activity before being removed from the body. To eliminate inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system (kidneys, urethra, bladder) caused by infectious pathologies, the following are prescribed:
- Ampicillin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Bactoclav;
- Solutab and other drugs similar in composition and action.
For inflammation of an immunoallergic nature, treatment is prescribed not only by a urologist, but also by an allergist, who will select the optimal medication course, including antihistamines.
Herbal medicines will effectively help normalize the outflow of urine, eliminate congestion, stabilize hemodynamics in the kidney tissues, reduce irritation of the urinary mucosa.
Children over 6 years of age are treated with Canephron tablets based on yarrow, lovage, and rosemary. Young patients aged 1 year and older are prescribed Urolesan (a combined herbal medicine in the form of syrup).
For infants, selecting medications is more difficult. This is due to the contraindication of antibiotics for infants. The course of treatment is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
For infants, injections are rarely prescribed; tablets are mostly prescribed. Before taking the medicine, the tablets are crushed and mixed with water, breast milk, or formula.
Folk remedies and diet
In addition to the medication course, a proper diet is followed, excluding foods that irritate delicate tissues. For infants and older children, herbal decoctions with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed. Doctors especially recommend infusions of chamomile, currant, and rosehip leaves.
For urinary tract infections, avoid the consumption of fried foods. It is necessary to increase the amount of fluid consumed - the child needs to drink more clean water and healthy cranberry juice.

Older children are prescribed diet table No. 5, which provides nutrition low in fat, but with complete calories and the inclusion of a large amount of vegetables and fruits in the diet.
In cases of acute forms of inflammatory processes, the child requires bed rest. If the disease manifests itself in a severe form, the minor patient is treated in an inpatient setting until the acute symptoms completely disappear.
White blood cells exceeding the norm in the tests of a small patient are a signal to parents to immediately visit a pediatric urologist. Often, elevated levels of white blood cells in the urine indicate inflammatory diseases that occur without their inherent symptoms. It is important to neutralize the disease at an early stage of development, preventing the pathology of the genitourinary organs in the child from becoming chronic.
Author: Breiman Andrey
Article design: Vladimir the Great
When does protein and leukocytes appear in the urine?
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Urine testing is a common laboratory procedure that is prescribed for all visits to a doctor with health complaints. Protein and white blood cells found in the urine are often a cause for concern.
The results of laboratory tests of urine provide the doctor with initial information for the correct diagnosis. Most of the substances that enter or are produced by the human body are eliminated with its help. After analyzing changes in the level of salts, cell elements, and substances of organic origin in this liquid, we can draw a conclusion about the state of the internal organs and the state of the body’s immune system.
Indicators for the presence of protein and leukocytes are standard items in the diagnostic urine test form. An increase in values is often a symptom of diseases that require serious medical intervention. Parents should know the reason for the increase in such indicators in order to correctly assess the child’s health status.
What do protein and leukocytes in urine mean?
Indicators of the presence of protein in the urine and leukocytes in it signal various conditions and are often caused by various reasons. A high concentration of protein compounds in urine is referred to as proteinuria; if the concentration of white blood cells is higher than normal, it is referred to as leukocyturia.
Protein indicator
Proteinuria is one of the main indicators for identifying kidney disease. A slight increase in the level of protein compounds in the secretions (this condition is called physiological proteinuria) occurs in people who do not have pathologies. This can happen with significant physical effort - in this case, the excretion should not exceed 0.08 g per day at rest and 0.25 g per day during prolonged exercise (stress, or marching proteinuria).
Protein in the urine of healthy people appears due to excessive nervous stress or severe hypothermia. In adolescence, increased protein in the urine may occur (so-called orthostatic, determined when the child’s body is in an upright position). If protein appears in the urine, what does it mean? This phenomenon is provoked by:
- Glomerulonephritis;
- nephrosclerosis;
- kidney damage caused by diabetes;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- disturbances in the functioning of the renal tubules in certain conditions;
- neoplasms;
- impaired renal function due to cardiovascular failure;
- infection of the urinary tract.
White blood cell level
A high level of leukocytes detected during analytical urine tests is a sign of kidney pathology, which is often accompanied by inflammation of the urinary tract. With high numbers of leukocytes, it changes in appearance and becomes cloudy. It should be noted that the level of leukocytes can often be caused by gynecological inflammation, poor personal hygiene, and improper collection of urine for research.
Exceeding the level of white blood cells in urine is provoked by:
- all forms of pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- acute and chronic prostatitis;
- inflammation of the bladder and urethra;
- kidney stone disease;
- nephritis;
- lupus nephritis;
- failure to accept a kidney transplant.
How are protein and leukocytes determined?
Urine is a liquid that is constantly formed in the kidneys and flows down the ureters into the bladder. After filling the organ, it is removed by the act of urination. The human body produces up to 2 liters of urine per day. Its composition is a variety of organic and inorganic compounds dissolved in water (mineral salts, amino acids, enzymes, etc.).
Urine is the optimal material that makes it possible to determine the presence of diseases of the prostate, kidneys and their tracts, and other systems of the human body. Therefore, urine analysis is used as an object to obtain diagnostic information.
To obtain objective data on the composition of urine and the presence of traces of protein and leukocytes in it, several methods are used. Often, the indicators of such studies are the basis for making a diagnosis, determining the severity of the patient’s condition, and based on them, a treatment regimen is determined.
For correct analysis results, the starting material must be correctly collected from the patient.
Requirements for collecting urine for analysis
Urine tests are divided into planned and special. Planned ones are carried out at the initial visit to the doctor and during treatment, special ones - exclusively for medical indications.
To properly collect liquid you should not:
- drink diuretics of any origin;
- drink plenty of fluids;
- eating foods that change the color of discharge;
- take medications that change its composition;
- drinking alcohol;
- give it to women during menstruation;
- Collect fluid sample after cystoscopy for up to 7 days.
Necessary:
- donate morning urine collected after the night or part of the daily urine;
- separate the first part and send the remaining liquid for analysis;
- collect the liquid in a standard sterile container;
- Before collecting fluid, wash the genitals thoroughly;
- transfer the liquid to the laboratory within two hours after collection (urine stored in the evening becomes unusable due to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and salt precipitation)
Methods and types of urine analysis
The main types of urine tests, on the basis of which a conclusion is made about changes in the level of leukocytes and protein in the urine, is
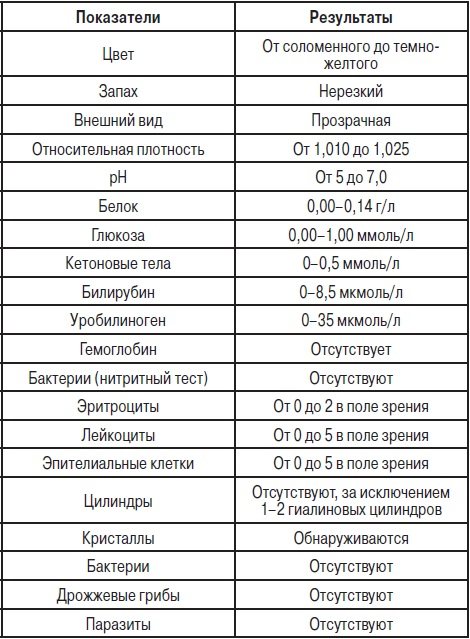
General clinical urine analysis is the most commonly used, but informative method that does not impose special requirements for collecting fluid. The result is the definition:
- transparency;
- colors;
- density;
- the presence of protein in the urine;
- Sahara;
- the presence of leukocytes, epithelial cells, erythrocytes;
- level and composition of salts.
Based on the general analysis, we can determine:
- diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract (nephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrosclerosis, stone disease, cystitis; neoplasms;
- prostatitis and urethritis.
The Nechiporenko study allows you to determine the presence of inflammation in the body’s urinary system and kidneys, technically it is a count of cells in a unit of urine volume measurement. Used to diagnose bladder inflammation and pyelonephritis, the middle part of morning urine is examined.
Determination of protein levels is used to monitor the ability of the kidneys to function. The presence of such compounds that cannot be absorbed by the tubules indicates the presence of infections and inflammations, poisoning and other pathological conditions. The study is carried out on the basis of average daily urine. In some cases, if the result makes the doctor doubt its correctness, the material is re-sampled or the study is carried out using a different method.
Normal levels of protein and leukocytes
Analysis indicators are considered normal when:
- no more than 3 cells are visible in male urine;
- in women's - up to 7;
- in the nursery - until 7.
Exceeding the norm and reaching an indicator of 7 to 10 cells indicates a health problem; if the number is more than 10, it is a sign of kidney disease. In this case, a urine test according to Nechiporenko may be prescribed. Its pathology indicators for:
- adults start at 2000 units. per 1 ml. draft;
- children - from 4000 units.
Protein is normally absent in urine, the minimum detectable amount is 0.03 grams per liter.
The appearance of protein, causes and treatment
The appearance of proteins in the urine (albumin and globulins) indicates damage to the kidneys and their tissues.
If an increased protein content is detected, an additional daily test is prescribed. This is due to the fact that the composition of urine changes throughout the day, and the indicator can be further clarified, and distortion of the indicator due to hygiene violations is also excluded. The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Causes
Protein in the urine appears due to pathologies in the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Typically, a significant proportion of them does not pass through their membrane due to the bulk of their molecules and structure. In pathology, low molecular weight proteins (usually albumin) are released, which leads to the development of a pathological condition with its excessive loss.
If the pathology is large enough, large protein molecules may enter the urine:
- part is produced by the kidney tubules;
- the indicator can manifest itself when parts of the urinary system are infected, its tumors or progressive inflammation.
Exceeding the physiological norm of protein in the urine (proteinuria) can be:
- prerenal;
- renal;
- postrenal.
The prerenal form of increased levels is caused by the detection of pathogenic proteins and is associated with the beginning of the process of tissue destruction in the body.
A renal increase in the level is associated with kidney diseases, traces of it are detected in day and night urine, a postrenal increase is associated with diseases of the excretion pathways.
Increased protein in the urine is often regarded as an indirect symptom of kidney disease.
Proteinuria caused by changes in kidney function is:
- glomerular origin, provoked by a violation of the action of the membranes of the glomeruli of the kidneys, with a value of more than 3 g/l;
- tubular - caused by impaired protein absorption in diseases of the tubules (indicator less than 0.14 g/l).
Malfunction of membranes and the appearance of protein in the urine is caused by:
- one-time strong or constant nervous tension;
- a large share of meat dishes in the diet;
- excessive physical activity;
- constant or one-time hypothermia;
- cystitis and urethritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- endocrine system disorders.
In pregnant women, increased protein in the urine causes the following conditions:
- fatigue and poor health;
- hypertension;
- swelling.
An increase in protein in the urine of women in this condition may indicate the body’s preparation for imminent childbirth and inflammatory processes in the body.
In children, protein in the urine may appear due to kidney disease and
any inflammatory processes in the body.
The risk group for increased protein content in the urine is children, obese people and people over the age of 6 years.
Symptoms indicate a disorder:
- increased blood pressure;
- hypertension;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- nausea and vomiting;
- joint pain;
- weakness, fatigue;
- dizziness and fainting;
- swelling.
Additional signs of increased protein in the urine will be a change in color due to the entry of red blood cells into the blood, foaminess of the urine during separation. Proteinuria is classified according to the amount of protein excreted:
- weak - with a protein volume of up to a gram per day;
- medium weight – up to 3 grams;
- severe, when the volume exceeds 3 g per day.
In adolescence, a form of physiological proteinuria is identified, associated with the active growth of children or the transmission of infections, and disappears when the symptoms of inflammation are eliminated or the load disappears.
Treatment
Elevated levels of protein in the urine can be eliminated by treating the underlying disease that caused it. The diagnosis is made exclusively by a doctor based on additional instrumental and hardware diagnostics. Sometimes drugs can be prescribed on the basis of a preliminary diagnosis before a final diagnosis is established (antibiotics, hormonal agents, diuretics).
If protein is present in the urine due to inflammation of the urinary system, the patient is prescribed bed rest.
Traditional medicine offers self-prepared or pharmacy diuretics for the treatment of proteinuria:
- from thyme and chamomile;
- horsetail and birch buds;
- lingonberry leaves.
Taking powder from ground pumpkin seeds has a good effect on your general condition.
To correct the condition, be sure to prescribe a diet that excludes pork and beef, salt, fat, mushroom and meat infusions. Shown are fruits, vegetables, legumes, chicken and fish.
Elevated white blood cells, causes and treatment of the condition
Exceeding the norm of white blood cells in the urine is designated as leukocytonuria, and indicates inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary system. Visually, in severe inflammatory processes, there is an accumulation of pus and traces of blood.
The disease is not diagnosed based on the number of leukocytes alone in a urine test; for this purpose, these data, blood test indicators and the results of hardware tests are considered in combination. If there is inflammation in the body, an increased level of leukocytes will be shown in a blood test.
The appearance of a large number of leukocytes (white blood cells) in urine is explained by their essence - these cells are designed to act as blockers of pathogenic agents that penetrate the body. Leukocytes, penetrating through the capillary walls into the space between the cells, immobilize infectious agents and, having destroyed them, destroy themselves. Externally, pus and redness appear at the site of inflammation.
With inflammation of the genitourinary system and kidneys, a large number of leukocytes appear on the mucous membranes to stop the infection. When excreted, urine is washed away and excreted by the body through the urinary tract.
Symptoms of inflammatory diseases and suspected leukocytonuria are:
- general weakness;
- temperature increase;
- pain in the lower back and abdomen.
- discomfort when urinating.
In some cases, an excess of white blood cell levels is associated with specific treatment:
- anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibiotics of some groups;
- diuretics.
If there is no acute infection, but an increased level of leukocytes in the blood is observed, it is necessary:
- stop using antimicrobial gels and soaps, which kill your own microflora and provoke vaginitis;
- adhere to sexual hygiene;
- reduce the consumption of sweets to suppress the growth of fungi, which provoke an increased content of white blood cells;
- regulation of drinking regime;
- increasing the menu of vegetables and fruits as carriers of vitamin C.
When determining the inflammatory diseases that cause leukocytonuria, treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor, prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, diuretics, and pain relievers.