Among all kinds of troubles that can happen during pregnancy, Rh conflict occupies a special place. It happens when a pregnant woman is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh positive. What actions should be taken in this case?
Since school, we know what an important role red blood cells - erythrocytes - play for humans. When red blood cells were studied in sufficient detail, it turned out that these red blood cells carry a huge amount of proteins on their surface. We are very familiar with some of these proteins - they determine the type of blood group. Let's get acquainted with one more thing - the so-called Rh factor.
It is the Rh factor that determines whether a person will be Rh positive or Rh negative. What does this mean? It's simple: the fact is that not all people have the Rh factor, so in cases where it is absent, they say that the blood is Rh negative. Accordingly, when the Rh factor is present, the blood is Rh positive.
This is interesting! The ratio of Rh positive to Rh negative people is strongly influenced by race. So, if among Europeans 85% of the population has the Rh factor, then among Africans this figure is 93%, and in Asian countries the proportion of the population with Rh-positive blood is close to 99%, i.e. For these regions, the problem of Rh conflict is not as pressing as, for example, for us.
Why is blood different in people?
There are dozens of different systems, each of which describes differences in the blood of different people in its own way. The most popular of them are the ABO system and the Rh system.
AVO system
On the cell membrane of the erythrocyte there are antigens A and B. In the blood plasma in which the erythrocytes are located, agglutinins (antibodies) α and β are present. As a result, four combinations of antibodies and antigens are possible. Each of these combinations determines a person’s blood type.
- If there is a combination that includes α and β, the person’s blood is of the first group or zero – 0 (I).
- The combination of A and β gives the second group - A (II).
- The third group is formed when B and α – B (III) are present.
- The fourth group is obtained from the combination of A and B - AB (IV).
Why are only these combinations possible? Because antibodies and antigens of the same name, for example, B and β, cannot be found in human blood. They come into contact with each other, which leads to the death of red blood cells.
Rh system
Rhesus in the coordinates of this system is the D antigen (protein) located on the cell membrane of the erythrocyte. People who have this protein have Rh positive blood. It is usually denoted Rh+. When the protein is absent, the status is Rh negative (Rh-).
How does a child inherit blood?
AVO system
There is a common misconception that a child will have either the mother's or the father's blood type. Tables are published with the help of which it is supposedly possible to find out the group of the child based on the groups of the father and mother. However, they do not describe a pattern, but a probability. In fact, it could be any group.
Rh system
An accurate prognosis is only possible when both parents are Rh negative. The child will have Rh negative status. In other cases, Rh can be either positive or negative.
Two types of conflict
Rh blood group conflict is possible during pregnancy only when the mother has Rh- blood. How many people are there in the world with negative Rh factor? Much less than Rh-positive (Europeans - 15%, Africans - 7%, Asians - 1%). Therefore, conflicts due to different Rh factors do not occur often.
Conflict between the blood group of mother and child is a dangerous phenomenon. However, it should be noted that Rh conflict has more severe consequences for the child than blood type conflict.
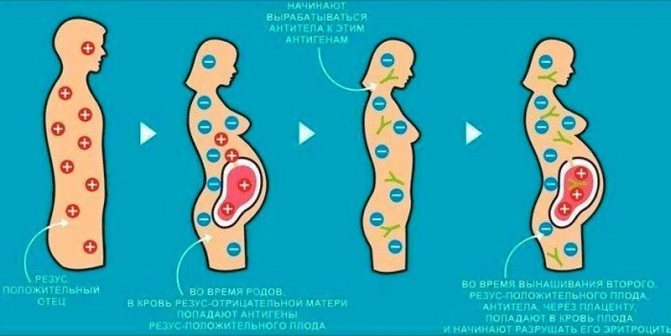
The mechanism of occurrence of Rh conflict
In the case of Rh conflict, upon contact, the red blood cells of the fetus and the woman stick together, which leads to complications. It is worth noting that Rh-positive blood tolerates this more easily. For this reason, a woman with Rh+ does not experience a Rh conflict during pregnancy with a fetus with Rh–. The mother's blood does not react to the child's Rh, so protective antibodies are not formed.
A dangerous condition is a negative Rh factor in a woman during pregnancy with a Rh-positive fetus. This is observed when a baby inherits Rh from a father with Rh+.
In this case, the following processes occur:
- The meeting of the blood of the mother and the fetus occurs in the space between the placenta and the uterus.
- An exchange takes place there: nutrients and oxygen are supplied to the baby, and waste products are supplied to the mother.
- Against this background, some of the positive red blood cells of the fetus enter the blood of the pregnant woman, and her negative red cells enter the blood of the child.
- In the same way, antibodies penetrate the baby, which are produced in response to genetically foreign material - fetal red blood cells.
Regardless of how often a woman is pregnant, the entry of positive red blood cells from the fetus into the blood of a mother with negative Rh occurs in several other situations. Main cases:
- Pregnancy, which is accompanied by gestosis, threat of miscarriage or serious illness of the woman.
- Premature placental abruption or manual separation.
- Delivery by caesarean section.
- Cordocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy, amniocentesis are studies that are carried out during pregnancy.
- Mother's Rh-positive blood transfusion.
- Miscarriage, induced abortion or surgery for ectopic pregnancy.
Article on the topic: Adrenaline as a mediator in the biological and chemical processes of the body
How to determine the Rh factor in a child
Families with negative Rhesus should not worry, although this is rare. Only 3% of men have Rh-. According to the laws of genetics, inheritance comes from the father or mother. Rh transmission principles:
| Mother's Rh | Father's Rh | Rh child | Risk of conflict |
| – | – | «–» | Absent |
| + | – | «+» – 50%; «–» – 50%. | Absent |
| – | + | «+» – 50%; «–» – 50%. | 50% |
| + | + | «+» – 75%; «-» – 25%. | Absent |
Blood group conflict during pregnancy (table)
A conflict with the fourth blood group during pregnancy, as the table shows, is impossible when the expectant mother has it. In all other cases, conflict is likely. Blood type incompatibility between mother and child is most pronounced when women with the first group carry a fetus with the second or third group.
| mother | child |
| 0(I) | A(II) |
| 0(I) | B(III) |
| 0(I) | AB(IV) |
| A(II) | B(III) |
| A(II) | AB(IV) |
| B(III) | A(II) |
| B(III) | AB(IV) |
What can be done if there is a conflict between mother and child based on blood type?
The expectant mother does not feel the changes occurring in the fetus. An unusual process will be indicated by high antibody values. That’s why testing needs to be done on time and preparation done responsibly so as not to get a false result.
If a pregnant woman’s hemolysins are higher than normal and steadily continue to increase further, the gynecologist offers the woman the following options for getting out of a dangerous situation:
- If the term is long, you can cause premature birth. The baby is removed from the mother's belly and placed in a special device that keeps him healthy and alive. No one can give accurate forecasts or guarantees for 100% survival.
- Intrauterine blood transfusion to the fetus.
Doctors advise pregnant women with blood type 1 to be on alert and tell the gynecologist about this feature early in pregnancy.
How does conflict between the blood type of mother and child work?
When fetal blood enters the mother’s blood, her body begins to react to the detected foreign antigen, that is, to the one that the child has, but not the mother. The reaction is that antibodies begin to be produced according to the blood type during pregnancy, designed to destroy foreign antigens and thereby protect the mother’s body.
Maternal antibodies enter the fetal blood and begin to destroy red blood cells. A lack of red blood cells results in oxygen starvation for the child. When red blood cells die, toxins are formed. These factors negatively affect the fetus’s body and give rise to hemolytic disease.
The mechanism of Rh conflict
During pregnancy, the Rh factor from the red blood cells of the Rh-positive fetus enters the blood of the Rh-negative mother. It is perceived as a foreign substance - and the mother’s body gives the signal “Attention, we are under attack!” to the production of antibodies to the Rh factor, as a result, the child’s red blood cells disintegrate. Their breakdown leads to damage to the liver, kidneys, brain of the fetus, and the development of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
If this is your first pregnancy
As a rule, the difference in the Rh factors of the expectant mother and child during the first pregnancy during its normal course is not significant. As long as the baby's red blood cells do not enter the mother's Rh-negative blood, everything is fine. The natural barrier is usually the placenta, which reliably protects the woman’s blood vessels from such penetration.
If pregnancy is second
Antibodies are typically used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects—such as bacteria and viruses. In Rh-negative women, antibodies begin to be produced during the first birth, abortion and miscarriage. This process is called sensitization, and its intensity increases when even a small amount of the baby's blood enters the mother's bloodstream. During the first birth, antibodies do not have time to harm the baby.
Carefully!
In subsequent pregnancies, antibodies can pass through the placenta into the blood of the fetus and the baby can become seriously ill.
Almost all women know that abortion is dangerous. The medical institution where they are produced may not check a woman’s blood for the presence of the Rh factor. It is possible that it will turn out to be negative. And if a woman with Rh-negative blood wants to get pregnant again to give birth to a child, she can expect big problems.
When does blood type conflict occur?
It is possible during pregnancy itself, during childbirth and while breastfeeding a child.
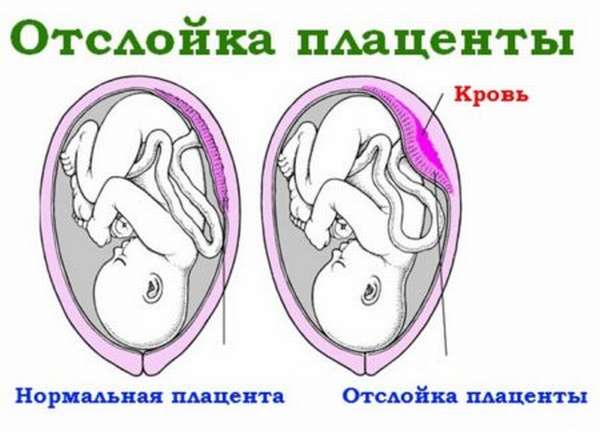
During pregnancy
If the pregnancy proceeds normally, mixing of the blood of mother and child does not occur, since there is a placental barrier. The essence of this barrier is that a healthy placenta has the ability to pass some substances from mother to child, but not others.
But sometimes the blood mixes, and a blood group conflict occurs during pregnancy. This happens, for example, with placental abruption.
Symptoms of placental abruption look like this:
- bleeding from the genital tract,
- tense state of the uterus and pain on palpation,
- disruption of the child's heart.
The danger to the baby’s health depends on the degree of pathology. If one-third to one-half of the placenta detaches, the baby dies. At the slightest suspicion of placental abruption, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a doctor.
The most significant conflict in the group occurs in the early stages of pregnancy. Prolonged release of antibodies causes more damage to the baby than when it occurs later in pregnancy or during childbirth.
During childbirth
During childbirth, the placenta is naturally destroyed and the blood of the mother and baby comes into contact.
- The risk of unwanted complications in the form of hemolytic disease is low if childbirth occurs according to a normal scenario.
- However, if they become protracted, after a certain period of time the newborn may develop hemolytic disease.
If a woman with the first group or with a negative Rh factor gives birth, blood must be taken for analysis from the umbilical cord vein to find out the child’s group, its Rh status and bilirubin level.
A high level of bilirubin indicates that there is increased destruction of red blood cells in the baby’s blood. If the bilirubin level is not normal, repeat tests are performed during treatment.
When feeding
Modern medicine believes that hemolytic disease can appear during breastfeeding in very rare cases, since maternal antibodies die in the child’s stomach. But twenty years ago, mothers with the first group or with a negative Rh factor were prohibited from feeding their children for several days. Doctors believed that during this time the mother's body stopped producing antibodies.
How to avoid problems
Sensitization both during and after pregnancy can be avoided. Then the risk of complications when carrying a child again will be significantly reduced. To do this, immediately after childbirth, abortion or miscarriage, you need to be tested for antibodies. If they appear, you need to get an injection of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. It prevents the production of antibodies. For bleeding during pregnancy, immunoglobulin must be administered. With the help of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin, it is possible to reduce the risk of hemolytic disease in children by almost 10 times.
Prepared based on materials from the magazine “Women’s Health”
What factors increase the risk of conflict?
The risk is lowest when a woman gives birth for the first time.
- The risk of conflict increases if the woman has undergone a blood transfusion.
- Abortions or miscarriages are also considered negative factors.
- Another factor is the second, third and subsequent pregnancies.
- If a woman has already given birth, and the children had various kinds of health problems, for example, hemolytic disease of the newborn, mental disorders, then there is a serious threat of conflict in the group.
How does Rh conflict manifest in a child?
From the first hours of life, the baby develops and continues to develop symptoms of hemolytic disease of the newborn. Its severity, and therefore possible complications and consequences for life and health, directly depends on the aggressiveness of the intrauterine Rh conflict and on the amount of anti-Rh antibodies accumulated in the child’s body. In any case, without active monitoring by doctors and without adequate treatment, this disease is life-threatening or can lead to disability.
When does Rh conflict occur during pregnancy?
The first and main condition is that a Rh-negative mother must bear a Rh-positive child who has inherited the protein composition of red blood cells from her father. Moreover, according to statistics, half of these fathers pass on the Rh factor to all their children, and the second half - in approximately 50% of cases. That is, only 25% of babies are born Rh-negative, which means without an immunological conflict.
The second condition is the meeting of the mother’s body with the Rh protein that occurred before pregnancy with the formation of immunological memory cells. It happens:
- with transfusion of Rh-positive blood or red blood cells;
- with previous abortions or miscarriages, if the fetus was Rh-positive;
- after a previous spontaneous birth or cesarean section, if that child inherited the father's Rh factor.
The third condition is a violation of the barrier properties of the placenta. During a normal pregnancy, the blood of the mother and fetus never mixes. This can happen with intrauterine infections, with partial placental abruption or trauma, as well as with amniocentesis and cordocentesis.
Very rarely there are casuistic cases when a Rh conflict develops already during the first uncomplicated pregnancy in a woman who has not had blood transfused.
The likelihood of developing Rh conflict during the first and subsequent pregnancies
During the first pregnancy, Rh conflict develops in no more than 10% of expectant mothers with Rh negative blood. These are women who have previously received blood transfusions. Each subsequent pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus, especially with a short time interval, increases the risk of this condition.
How can you find out about a conflict in advance?
If conception is not accidental, before it it is advisable to find out the compatibility of the group and Rh factors that the potential mother and father have. Tests can be taken at public medical institutions and private clinics, for example in the Invitro network. Requirements for preparing for the test for the group and the Rh factor are somewhat different.
- When determining the group, it is recommended not to eat for four hours before starting the analysis.
- The requirements for preparing for the Rh factor test are stricter. In particular, it is forbidden to eat fatty foods the day before taking a sample and not to smoke half an hour before.
You can take two tests at once. Blood is taken either from a finger or from a vein.
Knowing the group and Rh factors of both parents, it is possible to determine risky combinations with a certain degree of accuracy.
Risk information can be obtained from the following table.
| mother | father |
| 0 (I) | A(II), B(III), AB(IV) |
| A(II) | B(III), AB(IV) |
| B(III) | A (II), AB (IV) |
However, it is worth paying attention to the relative reliability of these combinations. They indicate that the risk of conflict within the group is probable, but not obligatory.
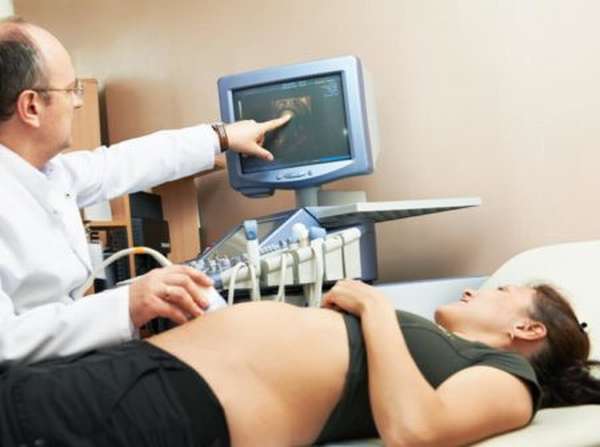
Preventive measures
The conflict between mother and fetus based on blood types is dangerous because the woman may not be aware of it. Its presence does not worsen her well-being. Therefore, you need to monitor the level of antibodies (titer) in it.
The standard analysis schedule is as follows:
- up to 32 weeks – once a month:
- from 32 to 36 weeks twice a month,
- after this period - every week.
However, in case of deviations from the norm, it is necessary to take tests more often; if the titer is determined to be high, then the pregnant woman will be admitted to the hospital for a thorough examination.
- It includes ultrasound examination of the placenta, amniotic fluid, and the condition of the fetal liver and spleen. Excessive amount of amniotic fluid, abnormally enlarged liver and spleen of the baby, thickened placenta indicate the development of a conflict regarding the blood type and Rh factor.
- In certain situations, when the safety of the fetus is of concern to doctors, a procedure called amniocentesis (analysis of amniotic fluid) may be performed. The high density of amniotic fluid indicates the process of destruction of red blood cells. Amniocentesis allows you to accurately determine the baby’s blood type and the number of antibodies.
- Another procedure is cordocentesis. During this procedure, blood from the umbilical cord is taken for analysis. The procedure is done using a needle, which is inserted into the uterus through a puncture in the anterior abdominal wall. This analysis allows you to assess the severity of hemolytic disease.
- If there is a conflict regarding the Rh factor, a Rh immunoglobulin vaccination is performed.
What factors develop conflict?
Blood type conflict is regulated by the placenta, which protects against mixing of different bloods. But this is only possible if the placenta is healthy. If there is a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels of the placenta, it exfoliates, or diagnostics has established other deviations from the norm, the baby’s cells enter the bloodstream of the pregnant woman.
This causes an active process of formation of antibodies that penetrate the fetus and attack its cells. Hemolytic disease occurs. The situation is aggravated by the toxic bilirubin produced. It causes irreparable harm to the child, changing the structure of his internal organs. The brain, liver, and kidneys are the first to suffer. It is impossible to predict whether a newborn will be born physically healthy or not.
Therapy for conflict
What may be included in the course of treatment?
- Intravenous administration of vitamins and glucose is performed. Immunoglobulin injections are prescribed.
- Plasmapheresis may be used to reduce the number of antibodies in pregnant women. During this procedure, blood is drawn from a vein (250-300 ml). Then the cell mass is separated from the plasma, diluted with special solutions and returned back into the vein.
The first disadvantage of plasmapheresis is that no more than a fifth of harmful substances are removed in one procedure, so several sessions have to be done.
The second disadvantage is that useful substances (immunoglobulins, fibrinogen, prothrombin) are removed along with antibodies and other undesirable components.
Plasmapheresis is contraindicated in cases of poor blood clotting and low protein content.
- When the titer increases, a purification method known as hemosorption is also used. In this case, the blood is purified with sorbents that retain toxic impurities, including antibodies.
What you need to know about hemolytic disease
If, despite all the measures taken, the child is born with it, parents should not panic.
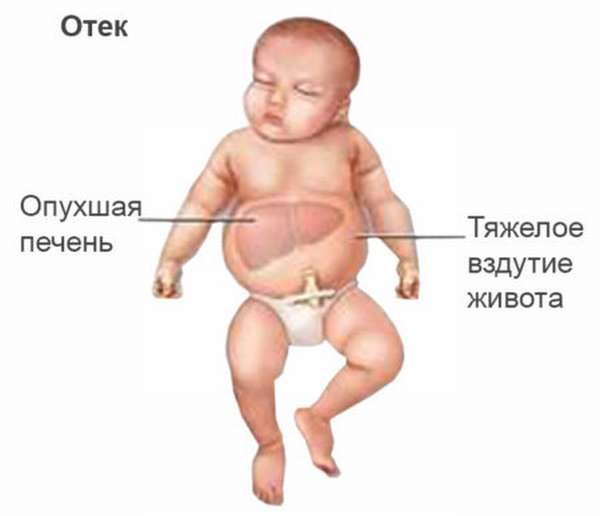
Clinical forms
There are three forms of this pathology:
- edematous,
- icteric,
- anemic.
- The first form is rare, but has the most severe consequences. It is called this because the child is born in very poor condition, with severe swelling and severe anemia.
- In the second form of the disease, an increased level of bilirubin in the baby’s blood gives it a yellow color (newborn jaundice), which is observed, for example, with hepatitis A.
- The disease progresses most easily in the anemic form. There are no external signs, or they are mild, diagnosed with a laboratory blood test.
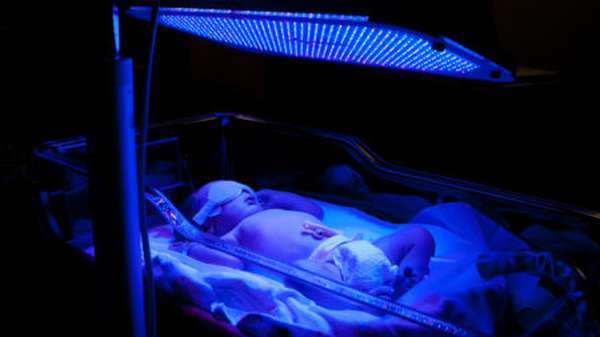
Dangers for the baby
If the number of antibodies in the mother's blood is small, they cause a mild form of anemia in the baby. When their number increases, the fetal body does not have time to produce new red blood cells. Then the child’s anemia occurs in a more serious form. Hemolytic disease of the fetus may occur, in which the functioning of the liver and spleen is disrupted and the organs themselves increase in size. As more severe manifestations of the disease, swelling of the tissues and brain may occur. Whether a child with positive Rh blood will get sick depends not only on the quantitative composition of the antibodies in the Rh negative mother, but also on their quality. Not all of them are able to penetrate the placenta and cause harm to the fetus. Then the child is born healthy or with a mild form of the disease.
Ultrasound control
In our center, hemolytic disease of the fetus is determined in the womb using ultrasound examinations. If the baby's liver is enlarged already at 20 weeks of pregnancy, additional diagnostic tests are performed. Then an intrauterine blood transfusion is performed. And at 28 - 30 weeks, children with severe forms of hemolytic disease are born by cesarean section. They are being cared for in the pediatric intensive care unit. In particularly severe cases, a replacement blood transfusion is performed. It is done only when it comes to preserving the life of a child. It happened that a newborn needed up to six such transfusions.