Just yesterday your little one was a cute baby, but today he suddenly started blowing bubbles. What happened, why is your mouth watering so much that you don’t have time to wipe it off? What should I do: call a doctor or is it not dangerous and will they go away on their own?
With the birth of a child, a mother has new questions every day. Before, there were no tears when I cried. Then you need to wipe your mouth, clean your ears, but it’s scary to get hurt. Now suddenly my mouth is watering, and for some reason so much... There are a lot of questions, let's consult a pediatrician.
What is the reason for such a phenomenon as drooling?
Parents notice that their babies start blowing cute bubbles in the third month of life.
It was during this period that the salivary glands had already formed. Therefore, it is not at all surprising that your child (3 months) leaves a wet mark on clothes and toys. Drool runs down the chin because the baby does not yet know how to swallow it well. A young mother may feel like there is too much moisture. Sometimes this process occurs earlier - when the child is 2 months old. Drooling is very common at this age. And this is considered a normal physiological phenomenon. It’s just that the glands of such babies formed earlier. And occasionally you can hear that even a month-old baby is drooling. Of course, this is not the norm, but each baby is individual. And if, apart from the fact that the child is drooling heavily, nothing else bothers him (his nose is breathing, drinking and eating milk as usual, etc.), then there is no need to worry about anything. Drooling is also often associated with teething, and rightly so.
Of course, this is too early for three months, but as was said earlier, each body is individual. In this case, there is no reason to sound the alarm if your child is 3 months old (drooling like a stream), and his gums are already swollen, which indicates the eruption of the first tooth. In this case, the child may be naughty and eat worse. But if everything else is fine (normal stool, no fever), then there is no need to worry. When the baby is teething, you can help if you give him special rings or toys to chew on, and in case of severe pain and anxiety of the baby, you need to lubricate the gums with an anesthetic gel (Cholisal, Kalgel, Kamistad Gel, etc.)
Excessive salivation in children two years of age and older
If the child is 3 years old and drooling, then in any case it is worth going to the hospital. Only specialists can answer the question of why this happens in a child at this age. They will determine whether drug therapy is needed in this case or whether this moment can be waited out.
When getting rid of these manifestations, it is necessary to compare treatment methods to the pathology itself. However, we cannot remain idle. Children with this problem may develop speech impairment
, because a large amount of clear liquid interferes with pronouncing words well. Subsequently, this can lead to delayed development and sociopathy.
By the age of 2, children usually already know how to swallow. If a child is drooling at 2 years old, and if it is not teething, a consultation with a speech therapist is necessary.
At this age, children may begin to erupt molar teeth. This may cause hypersalivation. As is the case with infants, the problem can arise due to ENT diseases, diseases of the digestive system, stomatitis, gingivitis, allergies. If the problem manifests itself mainly at night, then the baby may have a helminthic infestation.
.
What is saliva for?
Young parents often think about this when they take off another blouse from their child. It turns out that saliva is more important for infants than for adults.
Firstly, it helps digestion, as it contains enzymes, which promotes better breakdown and absorption of food. Saliva also softens and liquefies food, promotes the formation of a food bolus, which is especially important when the baby begins to try harder foods.
Secondly, saliva performs a protective function. It moisturizes the oral mucosa, protecting it from drying out and cracking, and also has bactericidal properties (thanks to the substances it contains - lysozyme, lactoferrin, mucin, etc.) These characteristics are especially important, because we all know how babies love to pull everything in your mouth.
Thirdly, saliva plays a buffering role because it can neutralize alkaline and acidic compounds in the oral cavity. It also has a mineralizing effect. Saliva contains compounds of fluorine, phosphorus, and calcium, which saturate tooth enamel with microelements. But these functions will be important during the period when the child already has teeth.
What should saliva be like normally?
In a healthy person, saliva appears clear or slightly cloudy and colorless, practically odorless. It is a little viscous; if you rub a drop between your fingers, you will feel it slipping. The viscosity is only slightly greater than that of water. The density of saliva varies depending on its composition and ranges from 1.002–1.12 g/ml.
One of the most important characteristics of saliva is acidity. Normally, it should be above 7 pH, that is, saliva is an alkaline environment. As acidity increases, salivary fluid loses its bactericidal properties. An acidic environment is perfect for the proliferation of pathogens.
The buffering capacity of saliva is a concept that characterizes the ability of salivary fluid to neutralize harmful substances that enter the oral cavity. The higher the acidity, the lower the buffer capacity. Acidity increases with prolonged consumption of carbohydrates. That is why parents forbid their children to eat a lot of sweets so that they do not have caries.
Parents should not be surprised if their beloved baby drools a lot. This is a normal physiological process intended by nature itself. Parents should be alerted to the side symptoms that accompany their increased secretion in toddlers. Therefore, you should know when such a physiological process should cause an alarming reaction, and when this is the norm and does not require any medical intervention.
Newborn
An increase in salivation can be observed in the first months after birth. In newborn children, this process is nothing more than a protective function.
In addition, saliva performs another important function in newborns, especially from 2 to 5 months. Thanks to special enzymes that are part of saliva, starch is broken down into sugar. This allows the gastrointestinal tract to adapt favorably to a new environment, promotes the proper digestion process, and normalizes intestinal function.
At 1 month
The swallowing reflex in a newborn is not yet fully developed, but the active work of the salivary glands stimulates the production of saliva. At 1 month old, the baby has not yet learned to swallow, although the young mother notices his swallowing reflex when breastfeeding.
Not understanding what he should do with the saliva in his mouth if he is already full, the logical action for him would be to release the saliva outward - and it seems to his parents that it is flowing in a stream down his chin. Mom and dad must ensure that the baby does not choke on saliva while lying on his back - it is best to place him on his side. Also make sure that the baby's chin remains dry, if possible.
At 2 months
How to care for a child with increased salivation?
If your baby is 3 months old (drooling profusely), then you need to change clothes as needed. You can use baby bibs, then there will be no need for continuous changes of clothes. It is also necessary, as necessary, to wipe the child’s face with sterile gauze or a soft (this is important, because the child has very delicate skin) ironed handkerchief. In this case, pay special attention to regular hand washing. Pouring boiling water over the baby’s toys and rings, which he constantly puts in his mouth, is the direct responsibility of the parents.
All these measures are aimed at ensuring that the baby does not have a rash, does not form “jams” (cracks in the corners of the mouth that can become inflamed) and maceration (this is when, under the influence of saliva, the skin on the child’s face is irritated and areas of inflammation form).
If, nevertheless, you notice macerations or “jams,” then in folk medicine it is recommended to lubricate them with olive, sea buckthorn, and linseed oil. You can wipe it several times a day with herbal decoctions: calendula, chamomile, sage. And after the procedure, it is necessary to blot the child’s face and mouth with a handkerchief. Among pharmaceutical preparations, pediatricians recommend Bepanten. You can also lubricate with baby cream.
But now there are so many kids prone to allergies that, if possible, it is better to consult a specialist.

How to help muscles?
Exercises for the speech apparatus are useless while the muscles are too relaxed or, conversely, tense. Therefore, before classes you should massage the facial, neck and shoulder muscles. First of all, these are light strokes; sudden movements cannot be made. Lay your baby down so that his head is on your lap, at right angles to your chest. Movements are made with both hands on both sides of the face simultaneously in the following directions:
- from the middle of the forehead to the temples;
- from eyebrows to hairline;
- from the middle of the forehead along the cheeks to the neck and shoulders;
- from the earlobes through the cheeks to the nasal wings;
- from the corners of the mouth, first to the middle of the upper lip, then to the middle of the lower lip, then to the wings of the nose.
If the muscles are very tense, then the movements should be very light all the time, but if they are relaxed, then vigorous kneading and gentle stroking should be alternated.
This is general advice for parents of children with dysarthria. Specific sets of games and exercises and medications, if necessary, are selected only by a speech therapist and a neurologist, based on the characteristics of the child’s condition.
Other causes of increased drooling in infants
One of the reasons is when stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane) develops in the oral cavity. With this disease, ulcers or white plaque are visible on the tongue, gums, and palate. There may be a high body temperature. Ulcers with stomatitis are very painful. Therefore, the child often refuses to breastfeed.
Another reason may be the onset of the disease, which occurs at the time when the child is 2 months old (drooling profusely). This may be a common acute respiratory infection. Then the baby’s nose is stuffy, he sneezes, and is restless. The temperature may also be elevated, and the baby refuses to eat or drink.
The child drools profusely even with helminthic infestation. Therefore, it is very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene. Increased salivation is usually observed at night. As a rule, marks remain on the pillow.
Also in infants, excessive salivation can be observed in diseases of the digestive system (enterocolitis, gastritis, hepatitis) and in some neurological and mental diseases (for example, cerebral palsy, autism).
Causes of drooling in a child
In newborn babies, drooling begins to appear at one and a half months; up to three months, salivation can be very strong; by the age of one year, it subsides. Both physiological and pathological factors can increase saliva secretion. It makes no sense to run to the pediatrician every time you notice drooling; you should know what these moments can mean.
Important! The drool of a 2 month old baby is quite physiological. At two months, this situation may not cease to appear even during sleep, which causes discomfort for both parents and baby.
A biological fluid called saliva is produced by the salivary glands and released into the oral cavity. 3 main glands are involved in the production:
- submandibular;
- sublingual;
- parotid;
- and many other, smaller ones.
What is drool for? If few of them are produced, then the mouth feels dry, unpleasant tightness, and thirsty.
Purposes of saliva:
- moistens the mucous surface;
- promotes the pronunciation of words and sounds, the latter the infant begins to pronounce a month after birth;
- the perception of the taste of food is facilitated because a piece of food dissolves, the taste buds of the tongue perceive the disintegrating molecules;
- helps chewed food stick together, making it easier to swallow later, and the baby will not constantly choke;
- the oral cavity is cleared of remaining food;
- bactericidal and disinfecting effects;
- Gums and teeth are protected from diseases.
The composition of saliva is 98% water, 2% consists of substances:
- mucin, which moistens the food bolus and sticks it together;
- lysozyme, which destroys microbial cells;
- enzymes amylase and maltase, which break down carbohydrates into saccharides.
Why does a two month old baby drool? This is due to the development of the child's body. They appear almost immediately after birth, and by three months their secretion increases.
Note! If a 2-month-old baby drools in bubbles, this does not always indicate pathology. Since the secretion of the glands begins to work more actively, salivation also increases.
Physiological causes of drooling:
- The swallowing reflex is not yet formed. Despite the fact that the child has already been born, many of his systems and organs still continue to develop. It is still difficult for a baby to swallow at two months, so the oral cavity is abundantly supplied with saliva. This makes it easier for food to penetrate into the esophagus and beyond. Since swallowing is still difficult, the baby cannot swallow all the drool, as a result of which he lets it out in bubbles.
- Protective barrier. The baby, having been born, learns a new, previously unknown world. He wants to know, see, open, examine and taste everything. Everything ends up in the mouth: toys, diapers, fingers and toes. During this period, the immune system is not yet working at full strength, but is just passing through the moment of formation, so it cannot fight back all the bacteria that are in the body; saliva copes with this.
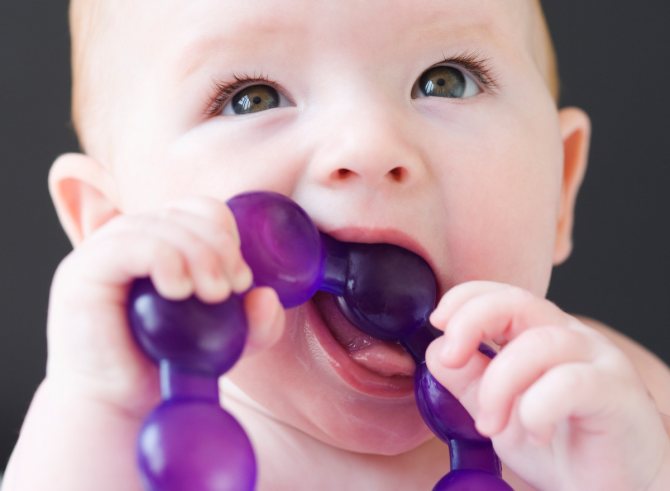

Baby holding a teether in his mouth
- Teeth are coming through. During this period, the baby may be very capricious, trying to put his fist in his mouth, as if he were hungry, in order to somehow relieve the unpleasant sensations. Teething begins between 3-6 months, accompanied by fever, pain, itching in the gums, and lethargy of the child. Saliva helps to disinfect the inflammatory focus and calm the pain a little.

The first teeth are being cut
Additional Information. Peak salivation is from three to five months. By six months, the swallowing reflex is usually fully formed. At one year old, the baby already begins to control swallowing, so bubbles and streams of drool do not end up on the chin.
Drooling bubbles
Excessive drooling and blistering in babies is a natural process. It is not always correct to suspect a disease or developmental anomaly in this, since the situation may indicate the maturation of the salivary glands or the beginning of teething.
Salivation bubbles
Immediately after birth, the baby does not need saliva - he drinks mother's milk or artificial formula, this is liquid food that does not require grinding.
As they grow older, salivation increases; by the end of the first month, the baby is increasingly blowing bubbles from his mouth. This indicates that the glands have begun active maturation, preparations are being made for future digestion of food and its assimilation. Since the baby does not yet know how to swallow well, he is not able to cope with such a flow of liquid, he cannot understand how to move his tongue, cheeks and throat to the required extent, so saliva comes out. The baby enjoys this and begins to play with it, making bubbles.
Note! Once the baby has learned to swallow, the period of teething may begin. The gums swell greatly, causing hyperproduction of saliva. A similar situation awaits at the time of introducing complementary foods. Here, salivation helps the baby get used to new foods that are unfamiliar in consistency to the baby.
In some cases, bubbles may indicate an allergic reaction in the baby. Allergic rhinitis is especially common. Then, in addition to drooling, you can see how the mucous membranes are swollen, the eyes are watering, the baby is crying, sneezing, waving its arms. The causes of rhinitis include dust, flowering plants, and pet hair.
If excessive salivation is a disease
If a baby is drooling profusely at 2 months, this may also mean hypersalivation (excessive salivation due to some illness). The symptoms here are pronounced: drool flows down the chin, chest, there is too much of it, a rash and irritation appear around the mouth.
What are the reasons:
- Stomatitis. Inflammation is found in the mouth, ulcers and aphthae form on the mucous membrane. Saliva acts on them and tries to neutralize the infection; its strong secretion is a consequence of the reaction to infection.
- Candidiasis is an infection caused by the candida fungus. A baby can become infected from a mother who is sick at birth, because he passes through the birth canal. Babies also often become infected with candidiasis from unclean pacifiers and bottles. A white, cheesy coating forms on the tongue, with bleeding ulcers underneath. Saliva with this disease is cloudy, profuse and smells unpleasant.
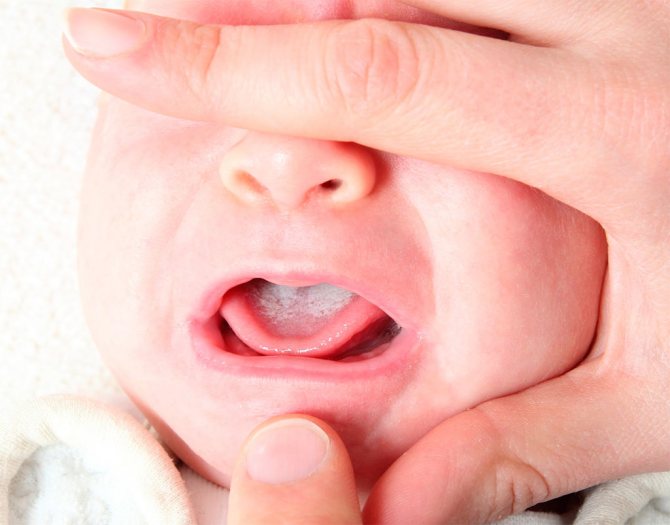
Candidiasis in a newborn
- Central nervous system disorders and cerebral palsy. A child with such a disease is susceptible to convulsions, partial or complete paralysis, and the coordination of muscle contractions is impaired. The child cannot keep drool in his mouth.
- Colds, ARVI, respiratory diseases (bronchitis, asthma, sore throat, pneumonia). In addition to hypersalivation, cough, runny nose, and fever are observed.
- Malfunction of the digestive system. At the same time, drool smells unpleasant and has a thick consistency.
- Endocrine system disorders. Added to hypersalivation are a constantly open mouth, a thickened tongue that does not fit in the oral cavity, and other signs of developmental delay.
- Neuralgia problems. In addition, the fontanel pulsates strongly, the baby screams and starts crying, and cannot hold the head up and lying on the tummy.
Additional Information. A change in the amount of saliva can be caused by stress or nervous tension.
Your doctor will help you identify the cause of hypersalivation. First of all, you should take the baby to a pediatrician; he may refer you to other specialists: a gastroenterologist, neurologist, dentist or endocrinologist.
To summarize: when should you see a doctor?
A trip to the pediatrician is inevitable if, in addition to increased salivation, the child has the following symptoms: high fever, unpleasant odor from the mouth, hyperemic (reddened) and swollen gums, rashes, white plaque, wounds or pustules in the oral cavity. Parents should also sound the alarm when their baby has severe diarrhea (diarrhea); if it is difficult to breathe through the nose, and the mouth is open almost all the time; if saliva flows more abundantly at night; if “jams” have formed in the corners of the mouth and began to fester.
What should healthy saliva look like?
Healthy saliva of an adult and a baby should be:
- Transparent;
- Liquid;
- Should not foam;
- It cannot be viscous or viscous.
Functions performed by oral fluid:
- Maintaining pH levels in the body within normal limits;
- Preventing the development of caries and tartar;
- Reducing the number of harmful microbes, and therefore preventing the appearance of bad breath;
- Of course, the process of processing and digesting food, because carbohydrates are broken down in the oral cavity;
- In newborns, it also protects the delicate mucous membrane from damage and irritation;
- Cleansing the oral cavity from food debris;
- It is the lipase found in the oral cavity that helps in infancy to better absorb milk, which is why salivation is so abundant;
- She also actively participates in the formation of taste sensations.

It's better to consult
It is recommended to go to the clinic if the child is teething, and in this place the gums are moderately hyperemic and swollen;
Subfebrile (37-37.5) temperature lasts for 2-3 days; mild diarrhea for several days; if “jams” in the corners of the mouth do not heal for a long time. This article will help young parents determine what physiological processes are normal when their child is 3 months old. Are you drooling and have no other symptoms to worry about? So everything is fine. Stock up on napkins and bibs. But if you have noted other causes of salivation listed in the article, try to get an appointment with a doctor. An experienced pediatrician will examine the child, advise the parents and, possibly, prescribe the correct treatment. After all, you shouldn’t self-medicate, even when it comes to the health of an adult. And our children are too dear to us, so at the first suspicion of any disease (and even just if there are any doubts), you must immediately contact a specialist.
When should you contact specialists?
Typically, a dysarthric child sees a speech therapist at 4-5 years of age. This is quite late, but with proper correction and regular classes, the violation can be minimized by the time he enters first grade. The sooner you contact specialists, the higher the chances of success.
A simple test will help determine whether a child has problems with the mobility of the speech apparatus. Stand in front of the mirror, complete the tasks yourself first, then ask your child to repeat them:
- smile, and then stretch out your lips. Only the lips work, the teeth are closed, the chin does not move;
- stick out your tongue and then remove it;
- open your mouth slightly and spread your tongue on your lower lip, hold it in this position for 5 seconds;
- open and close your mouth wide, slapping your lips;
- open and close your mouth, make a tube with your lips, repeat several times;
- open your mouth, touch the corners of your mouth with the tip, move your tongue back and forth, imitating the pendulum of a clock.
Keep in mind that any conclusions can be drawn only after the child has made several unsuccessful attempts, because the first time he may not understand what is required of him. The following signs are reasons to contact a neurologist or speech therapist:
- the child cannot immediately find the right position for the speech organs;
- has difficulty holding them in a given position;
- the smile and protruding tongue seem to move to the side;
- he cannot perform individual movements;
- involuntary synchronous movements of the speech organs.
Dysarthria is also indicated by undeveloped fine motor skills, awkwardness, difficulty maintaining balance, excessive tension or relaxation of the muscles of the face and neck, and nasal pronunciation. If you notice at least two or three of the listed signs, immediately show your baby to a speech therapist and neurologist.
Excessive drooling in a newborn
Just yesterday your little one was a cute baby, but today he suddenly started blowing bubbles. What happened, why is your mouth watering so much that you don’t have time to wipe it off? What should I do: call a doctor or is it not dangerous and will they go away on their own?
With the birth of a child, a mother has new questions every day. Before, there were no tears when I cried. Then you need to wipe your mouth, clean your ears, but it’s scary to get hurt. Now suddenly my mouth is watering, and for some reason so much... There are a lot of questions, let's consult a pediatrician.
How to help your baby
Parents will have to come to terms with and go through the period of slobbering toddler. It is unpleasant for the baby to be slobbery, so parents take special care and care for the baby at this time.
It’s not in vain, apparently, that our great-grandmothers invented bibs for babies. Bibs will help now: the fabric absorbs liquid, blouses remain dry, the skin on the neck and chest is also dry.
Sometimes a baby drools so much when lying down that he chokes and simply choke on it. He may experience a cough, even wheezing. To prevent your child from getting into trouble, place him on his side or tummy, or you can put him on a low pillow. So, the drool will flow down and will not harm the baby.
If a baby sucks on a pacifier, he is able to swallow his saliva. When going for a walk, give your baby a pacifier. Using a pacifier is another way to cope with the problem.
Soon the time for teething comes, the baby's gums itch and itch, he constantly chews something to relieve the itching. Help him, massage his gums with your finger. And in the places where the first teeth appear, press lightly. On the doctor's recommendation, buy a special product and lightly lubricate the gums with it, this will calm the baby.
A pacifier will help minimize the problem of drooling. If a baby sucks on a pacifier, he will swallow saliva
Baby care
Excessive salivation requires increased care from parents. Mothers stock up on handkerchiefs or soft napkins to wipe the newborn's mouth and chin.
Even with constant wetting of the chin, dripping drool causes redness, peeling, and a rash on the skin around the mouth and on the chin. Knowledgeable mothers advise using baby cream and lubricating irritated areas several times a day until the skin is restored.
Your doctor will tell you which creams and ointments to relieve irritation on your child’s skin. You need to lubricate delicate skin with the prescribed products very carefully, in a thin layer, so as not to cause even more irritation.
If the abundance of saliva scares you
Usually, a 2-3 month old baby begins to produce copious amounts of saliva as the salivary glands begin to function. The second stage, which decorates the little one with bubbles, is the period of teething.
During colds and other diseases of the ENT organs, with allergic reactions to house dust or animals, when the nose does not breathe, the baby has to open his mouth. In such cases, the amount of saliva that can drain from the mouth increases. Consult a doctor, eliminate the cause, and the amount of saliva will return to normal.
The most common cause of excessive drooling is teething.
The causes of excessive leakage may be gastrointestinal diseases. And also if the baby does not know how to close his mouth tightly. It must be said that when affected by an oral disease such as thrush, saliva partially loses its functions.
In particular, the digestion of starch into glucose stops. The absence or insufficiency of sugars in the body of infants will negatively affect their development.
Therefore, during your daily morning toilet, look into your baby’s mouth, and if you have any suspicions, contact your pediatrician.
But if there is too much saliva, it is of a different color, type or consistency, if the abundance of discharge scares you, be sure to consult a pediatrician. If necessary, after a thorough examination and tests, the pediatrician will refer you to another specialist. An ENT specialist, a neurologist, a dentist, and a surgeon can help.
Using saliva analysis, the doctor will make the correct diagnosis. If the baby has problems of an endocrine nature or in the adrenal cortex, a saliva test will show the disease. To obtain accurate data, saliva is tested several times during the day. It is not difficult, painless, and will show the right result.
If the baby is healthy, the period of drooling will soon stop, the baby's mouth and chin will be dry.
Source: https://floragaz.ru/obshee/obilnye-slyuni-novorozhdennogo