What is a fontanel in a baby?
A fontanelle is a section of the skull that has not completely fused. A newborn has 6 such areas - they are necessary for the skull to pass through the birth canal without injury. The four small holes close quickly - within the first few days after birth. Parents often do not notice them, paying attention to two located on the back of the head and on the crown.
The fontanel is responsible for thermoregulation of the body, preventing the brain from overheating.
The occipital fontanel closes after 3 months, but the large one closes completely only by 1-2 years of age. It is this that is an important indicator of the baby’s health; its condition determines the course of child development and the presence of certain diseases. Read more about the timing of fontanelle closure here.
Despite the external fragility, the gap between the bones of the skull is well protected by a membrane located under the skin. It protects the newborn's brain and mitigates the effects of head impacts. If you gently touch the area with your fingers, you may feel a pulsation . Normally, the bones on the crown of the head grow together gradually, but in boys this process occurs faster.
Types of fontanelles and timing of their closure
Immediately after birth, a child should have 6 windows:
- frontal,
- occipital,
- 2 wedge-shaped,
- 2 mastoid.
The large fontanel is located at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones.
Small - at the junction of the parietal bones with the occipital bone. The anterior window is the largest, has a diamond shape . It is formed by the frontal and parietal bones. The average size from birth is 2-3 cm. Education closes by the year in 40% of children, by 2 years - in 55%, and 1% falls on those who do not have a large window by 3 months. During the first months, it may increase slightly in size due to intensive growth of the brain.
In the next video, Dr. Komarovsky will talk about the timing of the closure of a large fontanel and explain whether you need to worry about this.
The occipital window is formed from 2 parietal and 1 occipital bone and has the shape of a triangle. It closes no later than 2 months from birth. Sphenoid fontanelles are located at the junction of the sphenoid, squamosal, parietal and frontal parts of the skull. Visually, they are practically invisible and cannot be felt. They close either during gestation or a few days after birth. The mastoid formations are located behind the ears and close within a few days; they are not noticeable.
Follow the link to learn more about when fontanelles in newborns become overgrown and in what cases there is cause for concern.
Large fontanel is normal
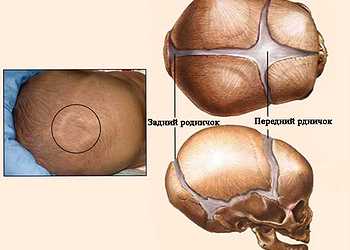
The large fontanel is located on the crown of the head and has a clear diamond-shaped shape.
Normal sizes vary from 0.5x0.5 to 3x3 cm.
The dimensions of this area are influenced by several factors:
- genetic characteristics;
- amount of calcium;
- speed of development of the baby.
At hand, the membrane covering the crown is soft, but not always smooth. Normally, both a slightly protruding and slightly sunken fontanelle . Uniform pulsation is a sign of good blood circulation.
Functions of the anterior fontanel
The intrauterine norm for fontanelles in a child is 6 pieces. After birth, in most children, only the “soft crown” remains uncovered. Before its final overgrowth, the anterior fontanelle performs important functions for the body.

Assistance in the passage of the birth canal (flexible cranial bones that have not completely fused together seem to “layer” on top of each other, temporarily reducing the diameter of the infant’s head and thereby making it easier for the child to be born).
Participation in the correct and harmonious formation of rapidly growing cranial bones in the early years of life.

Cushioning of the skull in case of an accidental impact or fall.

Possibility of conducting high-precision ultrasound of the baby’s brain in the area of the open anterior fontanel.

Deviation options
The most common deviation is the slow fusion of cranial sutures. This occurs due to a lack of calcium and nutrients during the mother's pregnancy or in the infant's diet.
Pathological causes of a slowly overgrowing area include:
- rickets;
- impaired growth of bone tissue;
- congenital bone diseases;
- genetic developmental abnormalities.
Sizes larger than normal indicate Down syndrome and other abnormalities. Early closure (about 4 months), on the contrary, indicates an excess of calcium. Less commonly, the cause of this deviation is craniostenosis, in which all cranial joints heal too quickly, whereas normally this process is completely completed only at 20 years of age.
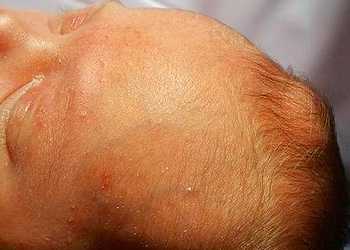
Protruding fontanelle in a baby
A strongly protruding membrane is a sign of increased intracranial pressure or cerebral hemorrhage.
If this symptom is accompanied by vomiting, high fever, convulsions or fainting, or sleep disturbances, you should urgently call a doctor.
Protrusion also occurs with head injuries.
A sunken fontanel in a baby often indicates dehydration. This symptom also occurs after severe vomiting or diarrhea, when a lot of fluid comes out along with toxins. The child should be given more water and taken to see a doctor, who will help determine the cause of the lack of fluid in the body and prescribe appropriate treatment. In some cases, a slight retraction indicates that the baby was born a little later than the due date. No treatment is required.
Why does it sink?
The reasons for the retraction of the fontanelle are varied. Most often this is due to a lack of fluid in the body. This is usually an acute process, after which the baby recovers quickly. There are also physiological reasons. They do not require special treatment.
Mild dehydration
Dehydration is a lack of fluid in the body. The fontanelle drains due to the infant’s improper drinking regimen. This often happens when feeding with artificial milk formulas. They have a thicker texture than breast milk. For each month and weight of the baby there are norms for drinking water. The pediatrician talks about this at monthly checkups.
Children under one year old are given special water or boiled water to drink. The norm is calculated according to weight and age.
Significant dehydration
With severe dehydration, a deep confluence of the fontanel is observed. This can be easily checked by pulsation. If the number of beats exceeds 130 per minute, then the baby needs additional fluids. Such conditions are usually accompanied by additional symptoms.
The baby behaves restlessly, sleeps poorly, and has problems with stool and nutrition.
Severe overheating
The optimal air temperature for a baby is 20-22 °C. As this indicator increases, the child will begin to sweat frequently, which causes increased loss of moisture. If the room where the child lives is too hot, he needs to be dressed accordingly. In the first weeks of life, thermoregulation is not yet fully established in children. If they have cold hands and feet, this does not mean that they are cold. They dress the kids according to their own feelings. If mom or dad wears a T-shirt, then the baby is put on 1 more layer of clothing.

Digestive problems
A retracted fontanel indicates indigestion. Formula or breast milk is not suitable for the baby and causes frequent diarrhea. Dehydration occurs. It is necessary to consult a doctor to prescribe treatment and receive nutritional recommendations.
Infection or viruses
The immune system of newborns is weak, so infection is possible. This condition affects not only the fontanelle, but also general well-being. Associated symptoms are observed:
- heat;
- vomiting and diarrhea;
- refusal to eat;
- poor sleep;
- capriciousness.
It is necessary to call a doctor at home and undergo a course of treatment. Usually children recover on the 3-5th day from the onset of the disease.

Nervous diseases
The most common causes are the development of meningitis or influenza. Accompanied by symptoms:
- severe headaches;
- elevated temperature;
- convulsions;
- vomit;
- capriciousness.
Urgent examination by a pediatrician and drug therapy are required. In serious cases, they are redirected for examination to highly specialized doctors.
Important! Lack of treatment leads to complications: perinatal disorders.
Perinatal disorders
Children born with cerebral palsy often experience retraction of the fontanel. In advanced forms, neurotoxicosis and seizures occur.
Requires intensive monitoring and complex treatment.

Heat
Children should be dressed according to the weather. During the hot season, children are provided with adequate drinking conditions, shelter from the scorching sun, and go for walks in the evening. Heat causes the body to overheat and dehydrate.
Physiological reasons
A sunken fontanel has physiological causes. It occurs within normal limits in post-term infants, in an upright position and while crying.
Post-term
Children born later than expected have a depression in place of the fontanel. This is normal and does not require treatment. The condition returns to normal by 6 months.
Vertical position
Newborns are constantly in a horizontal position. When the baby is suddenly picked up and the head is positioned vertically, a temporary confluence of the fontanel can be observed. It returns to its normal position on its own.

While crying
When a child screams loudly, the intracranial pressure changes. Because of this, the depression in the place of the fontanel becomes deeper. You need to calm the child down and everything will return to normal.
The condition of the fontanelle is checked only in a horizontal position at rest.
Causes and signs of retraction
The main reasons include:
- Dehydration of the body (this is possible not only due to illness, but also due to high temperature in the house).
- Infections or disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Genetic abnormalities.
Sometimes the fontanel also sinks in a healthy baby under severe stress or during a hysteria . In a calm state, this defect disappears, but if the retraction is too obvious, it is worth visiting a doctor.
You can understand that the membrane is sunken by several signs:
- the depression is noticeable visually;
- high pulsation (above 130 beats/min.). More information about heart rate norms in children can be found in this publication;
- the fontanel collapses even in a calm state.
In addition to external signs, it is important to pay attention to the color of the child’s urine . When the fontanelle membrane retracts, it becomes darker and a specific unpleasant odor appears. This indicates dehydration. Normally, a baby should urinate at least 10 times in 24 hours; this is not difficult to calculate from diapers.
If the retraction is caused by dehydration, the baby behaves lethargically and capriciously, and becomes drowsy. If he cries, there are no tears at that moment, because the mucous membranes are dry. The skin is dry and hot, with a distinct red tint. Dehydration is life-threatening for the baby and requires immediate medical attention.
When to sound the alarm?
The way the fontanel pulsates in a newborn is an indicator of his general health, so it is recommended to know about possible deviations and what they may be associated with.
- High vibration frequency. Remember that babies have a much higher heart rate than adults. The heart rate will decrease as the baby grows. The rate also increases during prolonged crying. If the baby is more than 6 months old, and the pulsation is constantly high, then increased intracranial pressure is possible.
- Intermittent pulsation, frequent changes in tempo and low oscillation speed are a cause for concern; you need to see a cardiologist to rule out pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- If the pulsating fontanel on the baby’s head is not visible at all, you need to consult a pediatrician.
- A dangerous phenomenon is protrusion of the fontanelle; we can talk about a tumor, meningitis, or high intracranial pressure. The appearance of seizures against the background of symptoms indicates the need to urgently call an ambulance.
- If it is difficult for you to see the pulsation due to the retraction of the fontanelle, then serious deviations from the norm are possible. Recession of the area below the level of the bones indicates dehydration of the child’s body.
To summarize, the baby’s fontanel should pulsate, as nature intended. For parents, such fluctuations are a way to notice pathologies at an early stage. Consult your doctor, he will tell you how to properly monitor the phenomenon. Don’t be alarmed ahead of time; tell your local pediatrician about your observations. This information will be very valuable.
Who to contact and how to treat
If you find a sunken fontanel in a baby, you need to show it to your local pediatrician, who, after examination, will write out referrals for the necessary tests and to other specialists (neurologist and endocrinologist). If the pathology is caused by genetic characteristics, the help of a geneticist will be required.
To determine the exact cause of pathology in an infant, an ultrasound of the brain is used. It is advisable for all premature babies and victims of birth trauma to undergo this examination (read the link about the development of premature babies by month to one year).
In case of illness, any self-medication is prohibited; all drugs and their dosage should be prescribed only by a doctor in accordance with the diagnosis. On your own, you can help with the retraction of the fontanel if it is caused by dehydration.

A sunken fontanelle in a baby may indicate a lack of fluid in the body
Water balance must be restored if:
- the child is in the heat or in a very warm room;
- the body overheated;
- the air in the nursery is not humid enough;
- heat;
- The baby is on artificial feeding.
If the fontanel has sunk due to infectious diseases, in addition to supplementary fluids, medical assistance is necessary. Before visiting a doctor, who will establish a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medications, you can give your baby Regidron to drink. This drug restores the balance of salts and fluids in the body. Give Regidron a teaspoon every 15 minutes.
Whether to give water to newborns during breastfeeding and in what cases - find out here.
In order not to worsen the situation, it is necessary to provide the baby with normal conditions:
- room temperature not higher than 25°C;
- humidity – not lower than 60%. An air humidifier can help you control this parameter, which you can select using the information from this review of devices;
- cleanliness of the room.
To prevent your baby from overheating, you need to dress him according to the weather, and do not bundle him up in the heat. The stroller should not be left in the open sun; direct rays will cause not only overheating, but also sunstroke.
Causes of pulsation
To understand whether the fontanelle should pulsate in an infant, why this happens and what the nature of the phenomenon is, you need to consider the anatomy of the brain. A distinctive feature of the structure of the skull in newborns is the presence of elastic connective tissue at the junction of three or more bones - the fontanelles.
A noticeable pulsation in the area of the largest of them is due to the work of the heart muscle. At the moment of its contraction, blood flows through the vessels into various systems of the body. The vibrations cause the cerebrospinal fluid, which is located in the space of the brain, to sway.
These processes ensure metabolism and maintain normal intracranial pressure. The membrane of the soft crown is very thin, so in the first months of life it is clearly noticeable how the fontanel in an infant pulsates. This physiological property of the soft crown is a normal phenomenon, therefore, if the oscillation rhythm corresponds to the norm, there is nothing to worry about.
This is interesting. In European countries, the fontanelle is called fontanelle, fonticulus, fontanela, which means “fountain”.
How to care
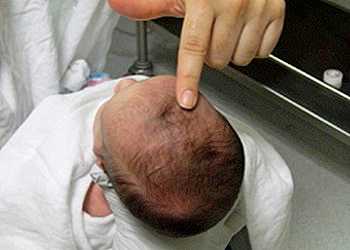
Despite the fact that the crown of the head seems fragile and vulnerable, ordinary washing of the hair or combing will not harm it.
There is no need to particularly protect this place; the membrane is quite dense.
The baby’s head should be protected during active games; it is important to ensure that there is no strong pressure on this area, and especially no direct blows.
The baby’s skull is still soft, so for its normal formation it is necessary to periodically turn the baby from one side to the other. This will prevent the head from becoming deformed and the fontanelle from “caking.”
If crusts appear on the crown, they must be carefully removed. How to do it:
- An hour and a half before bathing, before going to bed, apply a little baby or regular olive oil to the crusts with careful, light movements.
- You can wear a cap made of light natural fabric.
- Before washing your hair, you need to gently massage your skin with a special brush with soft bristles. In this case, the baby does not experience any discomfort.
- Bathe the baby while gently holding the head.
- After washing, the crust will finally soften and come off the skin when scratched.
To reduce the load on the parietal part, it is recommended to carry the baby in a kangaroo or more often carry it in your arms so that the head is in a vertical position. Periodically turning the baby onto his tummy serves the same purpose.
If, despite all the care and following the rules, the fontanelle area on the crown of the head is still a little sunken, you should pay attention to the baby himself. With normal slight retraction, a healthy child is active and cheerful, eats well, sleeps, and is not capricious for no reason.
Causes
Often, a vigilant (and sometimes overly suspicious) parent sounds the alarm when he notices the fontanelle on his child’s head. First of all, in such cases, the degree of retraction should be determined: a slight retraction of the fontanel membrane is a completely normal phenomenon.
If the hole noticeably sinks in comparison with what it was before, this indicates that some unfavorable factors are affecting the baby.
- First on the list of causes of retraction is a lack of fluid in the baby’s diet. Simply put, mild dehydration can manifest itself in this way. Most often this happens when a mother breastfeeds her baby and does not give him enough to drink. Meanwhile, during the hot season, breast milk is often unable to fully satisfy the baby’s body’s need for fluid. Children who are bottle-fed need to be supplemented even more so.
- Dehydration of the body and retraction of the fontanelle can also occur for a more serious reason: if the baby has diarrhea or vomiting. In this case, it is necessary to find out the root cause of the digestive disorder, eliminate it and be sure to replenish the fluid balance in the baby’s body.
- Noticeable retraction of the fontanel can occur in post-term infants. In this case, this is considered as a variant of the norm and passes over time.
- If the fontanel pulsates strongly and the difference between its retraction and bulging is clearly noticeable, you should consult a doctor about this. This is a normal phenomenon when the baby is screaming and crying, but if in a calm state a strong pulsation is visible to the naked eye, this may be the first sign of health problems in the baby.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=TIoNVhE16to
Overgrows for a long time or too quickly

The condition of the fontanel is checked by a doctor during regular examinations of the baby. A change in the timing of overgrowth can be the norm if you feel well and there are no visible deviations in development. The cause in most cases is metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances.
More common is slow overgrowth associated with hereditary factors, lack of calcium and vitamins during intrauterine development and in the nutrition of the newborn. The cause may be rickets, congenital diseases of the skeletal system, disorders in the formation of bone tissue, and genetic abnormalities.
Early closure (up to 4 months) occurs for individual reasons not related to an excess of calcium and vitamin D. In rare cases, it is caused by the development of craniostenosis - a pathological rapid connection of cranial sutures that normally heal completely by the age of 20. To accurately determine the causes, the pediatrician examines possible external signs and prescribes additional studies.
What is a fontanel for?
The fontanelle is an unhardened area of the cranial bone. Necessary for the child to pass through the birth canal: allows the head to take an elongated shape. In the first days, the shape of the skull remains changed, then gradually becomes rounded.
At birth, the baby has 4 small fontanelles on his head, which disappear in the first days of life; more often than not, parents are not aware of their existence. There are also 2 large ones: on the back of the head, which closes by the age of three months, and on the crown, which disappears in most children by the age of two. In a third of babies it hardens at the age of one. In rare cases, it does not close in children over 2 years of age.
The anterior parietal fontanel may enlarge slightly in the first months of a child's life due to rapid brain growth. Then it begins to overgrow; the exact period cannot be determined, since it depends on individual characteristics. In most boys it disappears faster than in girls.
Parents try not to touch the soft part for fear of damaging it, but it is quite reliably protected. Under the skin at the site of the fontanel there is an elastic membrane that performs a protective function; it helps to absorb head impacts, reducing possible complications and concussions. It ossifies at the edges, ensuring gradual closure.
The fontanel is used to determine possible deviations in the development of the child, depending on changes in shape: swelling, sinking, bulging, rapid or slow overgrowth can be a sign of disease or discomfort.
In a healthy child, the fontanel pulsates slightly, which can be felt by gently touching it with your fingers. This is a normal sign of blood moving through the vessels. The shape is not perfectly even - it sticks out a little or is sunken.
Why can there be a sunken fontanel?
A sunken fontanel in a baby is not an independent disease, but a symptom of other health problems. In most cases, the confluence of the crown can be a sign of dehydration in the baby. Dehydration is caused by:
- insufficient fluid intake, especially when formula feeding or regular breastfeeding;
- high temperature with significant sweating, this leads to loss of moisture;
- digestive problems accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, impaired fluid absorption;
- the presence of an infection or virus in the body;
- nervous diseases;
- perinatal disorders;
- hot time of year.
Important! Dehydration can be prevented by maintaining proper nutrition and care for your infant.
Sometimes sinking is a normal physiological process. If a baby's fontanel has sunk in, the reasons may be as follows:
- The baby is post-term. In this case, this is normal and does not require treatment. By six months everything will be back to normal.
- From time to time, the fontanel may sink a little if you hold the child in an upright position.
- During crying, the crown can retract or protrude.
Let's find out how to find out how serious the problem is, what it is connected with and what to do to help the child.
Here's what Dr. Komarovsky says about this.











