Normal stool standards for a child
Doctors consider it normal for a newborn baby to have a bowel movement after each feeding. By four months, the number of bowel movements decreases to three times a day. But this is not a dogma; in practice, things can happen completely differently. Each child has its own characteristic individual characteristics and the development of the child’s body depends on them. Therefore, if a breastfed baby’s bowel movements are less frequent than normal, but the baby is cheerful and gaining weight, there is no reason to worry.
Before the introduction of complementary foods, the stool of a small child is unformed and does not have an unpleasant odor.
Typically, a small child's stool has a lactic-sour smell.
Constipation problem
Constipation in a four-month-old baby will be considered a pathology if:
- there is no bowel movement for a long time;
- the child is restless;
- strains excessively, grunts, turns red when defecating;
- points his legs toward his stomach;
- the chair looks like balls.
If, with these symptoms, the baby has a normal temperature and gains weight, then the cause of constipation is a violation of the mother’s diet. Otherwise, you must urgently seek help from a pediatrician, since the pathological condition can be caused by severe diseases of the digestive system.
Stool retention may be a consequence of insufficient milk consumption. To avoid this, it is necessary to weigh the baby before and after each feeding.
Causes

Having discovered constipation in a child, it is necessary to correctly determine its cause. This is the first thing you should do. Without knowing the cause, you will not be able to provide full assistance in getting rid of this disease. The causes of constipation in children 2 years old are varied:
- The most common cause of constipation is a violation of the diet and its quality. The gastrointestinal tract is still developing at 2 years of age; for the coordinated functioning of its organs, adequate nutrition is required, received at a certain time. Sometimes the daily routine of children and parents is reflected in meals, they become uneven and go astray. Many snacks appear, and main meals decrease or disappear altogether. This causes great harm to the condition of the entire body, including affecting the frequency of bowel movements.

- Dehydration. We forget about the role of water in our lives. A child needs it just as much as an adult. Monitor the amount of water your baby drinks; if the child refuses clean water, offer unsweetened compotes and fruit drinks, diluted juices. A 2-year-old child should receive at least 2-3 glasses of liquid per day.
- Taking medications. Many medications have side effects that cause constipation. If medications prescribed by your doctor cause fecal retention, report this immediately. Your doctor will change this drug or stop it. Constipation often occurs during or after the use of antibiotics. They disrupt the intestinal microflora, in which case it is worth talking about dysbiosis. The pediatrician will prescribe an appropriate course of treatment to fill the intestines with beneficial bacteria.
- Psychological problems. Perhaps your baby is going through temporary difficulties, he was sent to kindergarten and the new environment scares him and makes him worry. Pay attention to relationships in the family - quarrels and a negative background in the house can cause a sharp deterioration in the functioning of the body. The age of two is the time to potty train a child; constipation can also occur due to the fear of not meeting the parent’s expectations, or the parents put too much pressure on the child to go to the potty.
- Intestinal obstruction. This pathology can be caused by several factors. For example, ingestion of a foreign body, improper transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding, congenital problems with intestinal motility. As a result, the feces create a kind of plug, which makes it difficult for the intestines to work, and the wall begins to stretch. In some cases, even surgical intervention may be required, so be careful, if constipation is accompanied by vomiting, fever, or malaise, immediately seek help from the hospital.
Often there can be several reasons.
Maternal malnutrition
If the main cause of constipation is breast milk, the nursing mother should avoid the following foods:
- Unripe fruits containing starch. It is difficult to digest by the gastrointestinal tract and consumes a lot of energy and time.
- Cottage cheese, which is consumed by a nursing mother due to the large amount of calcium in this product. An excess of this useful element also causes stool retention.
- Fried and fatty foods.
- Chocolate and cocoa are foods that slow down intestinal motility.
Among the recommended products are:
- ripe ripened fruits in moderation;
- various vegetables (especially beets);
- adding vegetable oil to the diet as an additive to salads;
- dried fruits (dried apricots, prunes).
Constipation in a child can also be caused by the mother taking certain medications (antibiotics, muscle relaxants).
Gastrointestinal diseases

Among the most dangerous pathologies leading to the development of constipation are:
- Hirschsprung's disease. A severe disease of the digestive tract in which there is no innervation of certain parts of the intestine. As a result, its function is disrupted and constipation occurs.
- Dolichosigma. Pathology of the sigmoid colon, characterized by its elongation. This leads to numerous bends and the formation of pockets where stool can get stuck.
- Lactase deficiency. The disease is characterized by the absence of an enzyme involved in the breakdown of milk sugar (lactose). The condition is accompanied by the development of constipation.
In addition to the above reasons, constipation in a child can be caused by:
Other pathologies
Constipation in a 4-month-old child can also occur due to other concomitant diseases:
- Dysbacteriosis is a disorder of the intestinal microflora. It can be caused by an infectious disease of the digestive tract in the mother and child or by taking antibacterial drugs.
- Violation of the nervous regulation of the intestines can be caused by a child's birth injury or cerebral palsy.
- Rickets is a lack of vitamin D in a baby and, as a result, a violation of the formation of bone and muscle tissue. This leads to improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the development of constipation.
- Incorrect drinking regime in a child.
- The presence of acute respiratory diseases in a child, accompanied by fever and dehydration.
- The presence of emotional stress in the child, which can be provoked by prolonged separation from the mother.
Constipation in children
What is constipation?
Constipation in a child is difficult or systematically insufficient bowel movement. Each born child has its own individual characteristics, which parents must take into account so as not to panic and not resort to various means of stimulating the act of defecation. Parents should remember: in breast-fed infants, the absence of stool for up to 3 days is considered normal, for bottle-fed children - up to 2 days - if the child’s behavior and condition are not disturbed. Such a child behaves as usual: he has a normal appetite, he is active, he passes gas, there is no fever or any other signs of illness. The mother of such a child should not resort to an enema or use other methods in order to achieve an inevitable bowel movement every day. At the same time, any violation of the baby’s general condition, when, along with stool retention, he develops vomiting, lethargy, drowsiness, lack of or decreased appetite, temperature, as well as delayed passage of gases, require immediate consultation with a doctor and assistance.
Constipation in children: norm and pathology
A feature of infancy is that the nature of feces and the number of bowel movements are determined by the nature of feeding.
When bottle-fed, the baby's stool is light yellow to light brown in color, its consistency is thicker, and the smell may be unpleasant. The number of bowel movements up to six months is 3-4 times a day, after 6 months - 1-2 times a day. However, you should know that artificial nutrition is a risk in terms of constipation in a child .
According to a number of physiologists, this is due to the fact that transferring a child to formula milk leads to premature maturation of the secretory apparatus of the gastrointestinal tract, and then to the depletion of its ability to digest and assimilate food, which, in turn, predisposes to constipation.
If a mother feeds her baby with her milk, the baby’s stool has a golden-yellow color, the appearance of runny sour cream, and a sour smell. The number of bowel movements in children, as a rule (but not always), is up to 5–7 times a day in the first six months, after six months – up to 2–3 times.
But we should not forget that constipation in a child is a common occurrence in infancy: according to pediatricians, it affects 10 to 25% of children. When should parents be wary and assume that the baby really has problems with bowel movements?
Indirect signs of constipation in a 3-month-old child are not so much rare bowel movements, but primarily a change in behavior associated with the passage of feces: increased anxiety before and during bowel movements, severe straining, severe crying. The nature of the stool also matters: in children under 6 months of age, a sign of constipation should be considered a dense, well-formed stool; sometimes such stool may have streaks of blood. Along with this, chronic constipation is characterized by the development of other manifestations in the form of anemia (decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood), decreased weight gain, allergic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, dry skin and mucous membranes.
Risk factors for constipation in a 3-month-old child are artificial feeding, prematurity, damage to the central nervous system (central nervous system) and dysbiosis (a condition in which the normal composition of bacteria inhabiting the intestines changes).
Types of constipation
Acute constipation in a child is the absence of bowel movements for several days. It develops with obstruction of the large intestine caused by various reasons (in infants, most often it is intussusception - the penetration of one part of the intestine into another, which causes clogging of the intestinal lumen and impaired circulation of the intestine itself). The causes of intussusception are intrauterine anomalies of intestinal development in a child, overfeeding the baby, early introduction of complementary foods (due to the immaturity of the enzymatic system that breaks down food), and intestinal infections. This condition develops more often in children from 3 months to 1 year, and it often affects well-fed children. Such a child, in the midst of complete well-being, suddenly suddenly becomes restless, cries, and refuses to eat. The attack of anxiety ends as suddenly as it begins, but after a short period of time (3-5 minutes) it repeats again. Vomiting appears once or twice with an admixture of green bile, feces may be excreted once or twice mixed with blood. Later, the stool stops, and bright bloody discharge is released from the rectum (they most often occur 5-6 hours after the onset of the first attacks of pain). At the same time, the baby’s stomach is soft. The temperature is most often normal. The child may lose consciousness. Naturally, when such symptoms appear, parents will be concerned not so much about the presence of stool, but rather about severe attacks of pain, vomiting and spotting in the child, and they will not hesitate to call an ambulance.
Chronic constipation in Rebecca develops gradually. This diagnosis is made when it is observed in a child for more than 3 months. It should be remembered that constipation in itself is not a disease. In most cases, this is only a manifestation of some condition or illness in the child, so it is necessary to treat not the constipation itself, but its cause. And this will require effort and attention, both from the doctor and from the parents.
Causes of constipation
in children
Constipation in children can be caused by the following reasons:
Nutritional – incorrect diet, insufficient amount of food or water in the child’s diet , as well as constant overheating of the baby. Such reasons lead to a decrease in the volume of feces in the intestines, loss of water (and feces also contain water), and a disruption in the composition of the intestinal microflora. In children of the first year of life who are on mixed or artificial feeding, such constipation occurs much more often than in children who receive only breast milk.
Abnormalities of intestinal development . Hirschsprung's disease is especially important for newborns. The basis of this disease is a violation of the innervation of the colon, its peristalsis (motor function of the intestine) is impaired, the colon becomes “switched off” from work. As a result, intestinal contents accumulate in the overlying parts of the intestine, which in advanced cases causes intestinal distension. If only a short part of the intestine is affected in a child, then constipation develops gradually and may not require surgical intervention for a long time. If a longer section of the large intestine is affected, then constipation in the child is accompanied by a serious condition and immediate surgical intervention is required.
Infectious diseases . Intestinal infections suffered in the first months of life can cause the death of nerve cells in the large intestine, which, in turn, leads to disruption of the motor (motor) function of the intestine. And this causes a delay in defecation, accumulation of feces in the intestines and the development of constipation.
Various inflammatory processes in the intestines or vascular diseases (vasculitis) . Such constipation also develops due to damage to the nerve plexuses and sensory cells in the intestinal wall.
Damage to the central nervous system . Constipation is common in children with cerebral palsy syndrome, as well as in babies whose birth was associated with various complications during childbirth. In addition to constipation, such children may experience various swallowing disorders, regurgitation, and vomiting.
Endocrine disorders (hypothyroidism - insufficiency of thyroid function, diabetes mellitus, etc.). With such diseases, constipation is not uncommon. For example, with hypothyroidism, the movement of contents through the intestines is slowed down. With dysfunction of the parathyroid glands, constipation occurs due to a violation of mineral metabolism. Constipation in a child with diabetes may be a consequence of damage to the nerve plexuses of the intestines or dehydration of the child's body.
Taking certain medications . Before giving your child any drug prescribed by a doctor, carefully read the instructions. For example, iron supplements, which are prescribed for anemia, can cause constipation. Strict adherence to the rules for taking the drug will help to avoid it. Drug-induced constipation in a child is a consequence of taking other drugs, among which nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipsychotics, and sorbents are of greatest importance. Constipation, which develops as a result of uncontrolled and/or prolonged use of antibiotics, deserves special attention. In this case, stool retention is a consequence of intestinal dysbiosis.
Thus, there are many reasons that can cause constipation in a child . Therefore, by only treating constipation, you can miss the cause that caused it. That is why constipation in a child is an indication to see a doctor.
If your child is constipated
If a child strains, blushes, or cries when you touch his stomach, this is a request for help. How can you help your baby with constipation?
Offer your child bottled water (unboiled, still). It is convenient to give your baby something to drink from a regular sterile syringe (without a needle), or you can give him water from a teaspoon. Even a small amount of liquid entering the intestines will help soften the stool and stimulate the exit of feces.
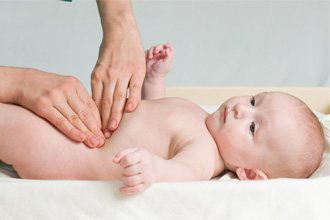
Give your child a tummy massage . Start doing massage immediately after drinking. Wash and dry your hands to keep them warm. To combat constipation, abdominal massage should be done regularly: immediately after waking up, and then several times during the day before feeding or no earlier than an hour after feeding. The massage is performed with the baby lying on his back. Any movements are made without strong pressure. Each exercise is performed for 1–2 minutes; in children after six months, the massage time can be extended. During the massage, talk to your baby and smile at him. Monitor the child’s condition: massage should not cause discomfort or pain.
Using the palm of your right hand, make circular movements clockwise. We start from the navel and gradually expand the circle from the lower right corner up to the right hypochondrium, pass across the abdomen to the left hypochondrium and go down to the lower left corner. We try to put the least amount of pressure on the right hypochondrium (where the liver is located) and the left hypochondrium (where the spleen is located).
Having clasped the child’s lower back with our hands on both sides, we move them towards each other through the lateral surfaces of the abdomen, meeting with our palms above the navel. We perform stroking for 1–2 minutes.
With our right palm we begin to stroke the area from the navel to the pubis. Massage from top to bottom for 1-2 minutes.
We massage the sigmoid colon (the lower part of the colon that goes into the rectum). Mentally divide your baby's belly into four squares. The lower left square is the location of the sigmoid colon, which diagonally crosses this square from top to bottom. The sigmoid colon, especially when it is filled, can be easily palpated in the form of a roller. Using two fingers, lightly press on the area of the sigmoid colon. Massage in a circular motion, without moving your fingers, for 2-3 minutes. After just 1–2 minutes of massage, the urge to defecate usually occurs.
Exercises for constipation . While lying on your back, alternately bend and unbend the child’s legs, pressing them to the stomach, 6–8 times. You can diversify gymnastics by simulating cycling. Then press both legs against your baby's belly, holding for a few seconds. Straighten your legs. The exercise is repeated up to 8 times.
To perform the exercises, you will need a large gymnastic ball with horns. Having placed the child with his tummy on the ball and letting him grab the horns, roll him on the ball for 1-2 minutes. Accompany the exercises with conversation and songs: the baby should enjoy them.
Abdominal massage and gymnastics often help the child empty his bowels and make the passage of gas less painful.
Bath for constipation . If massage does not help, you can immerse the baby in warm water, then remove him from the bath and wrap him up.
After this, we place the baby on our bare stomach with his bare tummy or hold him over a basin or diaper, pressing the baby’s legs to his tummy. It should be remembered that the most unfavorable position for a baby suffering from colic or constipation is the position on the back, since in the prone position the child’s intestines undergo self-massage and thereby improve the movement of gases and intestinal contents. Children's suppositories for constipation . If this does not help and the baby continues to cry, you can insert a suppository with glycerin into the rectum.
You should not use suppositories regularly as a cure for constipation: this is an emergency medicine. The suppositories are inserted with the baby lying on his back, with his legs bent to his stomach. Gas outlet pipe . To alleviate the condition of a baby suffering from bloating and gas, you can use a gas tube. It should be inserted into the rectum to a length of no more than 3 cm (you can purchase a rectal catheter at the pharmacy, the inserted part of which does not exceed 2.5 cm). A catheter or gas tube is inserted with the baby lying on his back or side with his legs bent to his stomach. The tip of the inserted catheter or tube must be generously lubricated with baby cream or petroleum jelly.
As for the enema, this is not as harmless an event for the baby as is commonly believed. Regarding the appropriateness and method of its use, you should consult with your pediatrician.
If the above measures do not help, you should consult a pediatrician who can prescribe medications for your child. The drug of choice for treating constipation in children is lactulose syrup (for example, DUPHALAC), which your doctor will recommend. Remember that any medications are only good if they affect the cause of constipation. For bloating and intestinal colic, the baby is additionally given ESPUMIZAN, SAB SIMPLEX, PLANTEX before each feeding.
Remember that constipation in infants is not a disease. It only serves as a signal that something is wrong in the body. And the doctor must look for the cause, as well as deal with the symptoms (in this case, constipation).
You may be interested in the articles “Vaccinations for children: right or obligation?” and “Vaccinations according to the calendar” on the website mamaexpert.ru
Treatment
Treatment of constipation in a small child is usually prescribed for a long period of time, especially if stool retention was caused by congenital abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to specify the types of assistance that any parent can provide to the baby when the first signs of constipation are detected:
- Non-drug treatment methods. They include abdominal massage, the use of thermal procedures, gymnastics for infants, and normalization of the drinking regime.
- Drug treatment methods. Use of various types of enemas, rectal suppositories and oral laxatives.
Thus, following the above recommendations can help get rid of the problem of stool retention.
Medication methods

In cases where the above recommendations were ineffective, it is necessary to resort to the use of medications.
If constipation lasts more than a day in a 4-month-old child, the following remedies can be used:
- rectal suppositories;
- enemas;
- oral laxatives.
Please note that independent use of medications in infants is unacceptable. Any medications are prescribed by a doctor after an objective examination of the child, laboratory and instrumental studies, and the exclusion of all contraindications to their use.
Laxatives
Oral laxatives (“Dufalak”, “Normaze”, “Portalak”) contain lactulose; when it enters the intestines, it absorbs water and swells. This helps soften stool and remove it more quickly from the body.
Any drugs with a laxative effect should not be used frequently due to the risk of developing addiction to the drugs.
Suppositories
Glycerin suppositories are an effective treatment method even for prolonged constipation. There are suppositories for children, but adults can also be used, but do the following:
- Take the medicine from the refrigerator, keep it at room temperature for a while and divide into 4 servings.
- Take ¼ of the candle in your hands. It has already reached body temperature and can be sculpted. Form a sharp edge with your fingers for ease of insertion into the anus.
- Lay the baby on his side and, with his knees bent, lubricate the anus with baby cream. Now insert the prepared piece, returning the legs to their original position and moving the buttocks to prevent the suppository from coming out back, as the baby may try to push against a foreign body in the rectum.
Enemas
Microclysters are also approved remedies for infants. Microlax is a safe drug because it is not absorbed through the intestinal wall, and therefore does not enter the child’s bloodstream. The laxative effect is observed within half an hour after use. The drug should be administered in the same way as rectal suppositories.
In addition to ready-made medications, cleansing enemas can be used in children of this age. For this procedure, 40-60 ml of boiled water is used, which is administered rectally using a syringe with a rubber tip.
It is not recommended to carry out this procedure at home, since administering an enema to a 4-month-old child requires a medical education.
Non-drug methods
Non-drug treatment methods are a priority for the treatment of constipation in a four-month-old child. Since any medications in young children can harm the body.
Among the methods available to every parent at home, the child can use:
- performing abdominal massage;
- gymnastics;
- applying heat to the abdominal area;
- restoration of the correct drinking regime in the child.
The advantage of non-drug methods is their ease of use, they are easy to learn and will not be difficult to perform on an infant every day.
Massage
Abdominal massage is an effective procedure for the treatment and prevention of stool retention in infants. It can be done 2-3 times a day, preferably after meals.
There are several rules for performing the procedure:
- All movements should be performed only clockwise. Other directions may cause intussusception in the child.
- You should not use force when stroking your belly. The procedure should be tolerated comfortably by the baby.
- The hands of the person performing the massage should be warm. This will make the procedure more effective and comfortable for the child.
- For a massage, it is enough to stroke the child’s abdomen in a clockwise direction for a couple of minutes.
Gymnastics
Among the gymnastic exercises for infants with constipation, the following will be useful:
- “Bicycle” exercise: the mother bends the child’s legs one by one, simulating riding.
- Pressing the baby's legs against the tummy for a couple of seconds and then straightening them.
- Place it on the baby's tummy more often before feeding.
- Exercise with a child on a fitball (this will not only help cope with constipation, but also stimulate the physical development of the baby).
Heat on the abdominal area
Blood flow to the intestines often solves the problem of constipation by increasing the peristalsis of the organ. An ordinary heating pad, preheated to 39-40 degrees, will help create this effect. It is enough to perform this procedure once a day for 5-7 minutes.
An alternative to using a heating pad can be a regular warm bath at a temperature of 36-37 degrees.
Normalization of drinking regime
Regular boiled water can solve the problem of constipation. This is especially true during the hot summer months. The daily norm for a 4-month-old baby is approximately 50-70 ml. A lack of fluid in the baby's body leads to increased absorption from the large intestine and, as a consequence, hardening of the stool and the occurrence of stool retention.
What to avoid
Inexperienced mothers often tend to resort to various unconventional methods of treatment and folk recipes. However, before using these medications on a baby, you should consult with your doctor to assess their possible harm.
Here are some examples:
- One of the folk methods for treating constipation is laundry soap, which is used instead of rectal suppositories. Such a remedy can cause inflammation of the rectal mucosa, allergic reactions in the child, and also lead to bleeding.
- Another folk remedy for constipation is a decoction of dried fruits or beet juice. These drinks effectively cope with stool retention, however, they are not recommended to be given to a child before complementary feeding is introduced, as this can cause the development of food allergies.
Drug treatment of constipation in children

Drug treatment of constipation in a child is prescribed by a pediatrician in the absence of positive results from massage and diet and includes a number of the following measures (carried out selectively):
- Taking medications containing lactulose is one of the most effective ways to treat constipation (often prescribed when taking antibiotics), but requires careful dosage calculation.
- Introduction of glycerin suppositories into the rectum (children's dosage).
- Use of a gas outlet tube. The effect is achieved by irritating the rectum, which promotes bowel movements.
- The use of enemas as a last resort if previous methods are ineffective. Should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the pediatrician.
Important: self-prescribing laxatives to young children is strictly prohibited (including the period of introducing complementary foods to children 4–5 and 6–8 months of age)! An illiterate approach to choosing a drug can aggravate existing problems. As for traditional methods of combating constipation, you should consult a specialist before using them. As an example: such a widespread popular recommendation for introducing soap into the rectum in some cases can lead to serious damage to its mucous membrane, including burns.