Author's rating
Author of the article
Green Elena Stanislavovna
Otolaryngologist of the second category
Articles written
665
about the author
Laryngitis in a one-year-old child is a fairly common occurrence. This is an inflammation of the larynx caused by viruses, pathogenic fungi, bacteria, even dust. The trachea and bronchial tree are involved in the process. The vulnerability of a child's body to pathogenic pathogens is associated with an insufficient level of development of immune defense. Intrauterine immunity (antibodies received from the mother) is exhausted by the age of three months. The greatest risk is the threat of narrowing of the airways, leading to respiratory failure and obstruction.
The first signs and how laryngitis manifests itself in children
Children aged six months to three years are most often susceptible to laryngitis. The unformed state of the child’s immunity is important in pathogenesis. Laryngitis occurs in the presence of provoking factors:
- diathesis;
- significant hypothermia;
- passive smoking;
- impaired breathing through the nose;
- tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- severe stress on the vocal cords (nodular laryngitis);
- vitamin deficiencies;
- eating food and liquids in a cold state.
There are cases of allergic laryngitis. It can be caused by animal hair, pollen, medications and food components. This type of laryngitis in a child is most often fraught with an attack of stenosis. Children's laryngitis is divided into simple acute, subglottic laryngitis (false croup), chronic (rare).
Laryngitis in a child initially manifests itself as a lack of appetite, increased sweating, and behavioral reactions in the form of tearfulness, drowsiness, and moodiness. A “barking” cough can develop into a silent, hoarse voice. The postauricular lymph nodes are enlarged, the temperature is elevated, and the throat is red. The addition of rhinitis contributes to difficulty in nasal breathing, and the oropharynx is sore.
The process is complicated by a dry cough and hoarseness. By night, the situation may be aggravated by difficulty breathing as a result of edema, air is drawn in with a specific whistle. As the disease progresses, the cough becomes “barking”, temperature readings can reach 40.
How to treat laryngitis in a one-year-old child depends on the factors that caused it. Most often these are herpes viruses, measles, parainfluenza, and adenovirus infection. In case of untimely treatment, bacterial accumulation of streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococcus, and hemophilus influenzae occurs.
Lack of nasal breathing.
How to recognize an attack?

An attack of laryngitis or false croup occurs most often at night, and they are sudden. Mostly in the evening you can see the first alarm bells. These include slight wheezing when breathing, apathy in the evening and frequent tossing and turning during sleep at night. But such symptoms rarely cause concern to parents if the child is healthy. What baby doesn’t get tired in the evening and doesn’t toss and turn at night? But then the baby begins to choke at night and develops a “barking” cough, and often the parents do not know what to do.
The disease begins with a dry, “barking” cough, since swelling of the larynx has already begun and it becomes difficult for the child to breathe. He breathes more and more quickly. So at the age of 2-5, with a norm of 25-30 breaths per minute, the child takes 50. The cough becomes more and more severe. The baby begins to worry, the wings of the nose swell. The skin turns pale and the nasolabial triangle becomes bluish. Such symptoms accompany the child in his sleep. In this case, the baby must be raised to an upright position and first aid begun. Otherwise, he may fall into unconsciousness, suffocation may occur, and death may occur.
How to properly treat laryngitis in a one-year-old child
The structural features of the nasopharynx in a one-year-old child allow pathogenic microorganisms to enter the larynx almost unhindered. In an adult, the size of the nasopharynx is significantly larger. Laryngitis for a baby is a serious problem, while for an adult it is characterized by unpleasant sensations.
At the first symptoms, treatment for laryngitis in a one-year-old child should be prescribed by a doctor. Accordingly, treatment is rather symptomatic. Drink plenty of warm milk, water with soda dissolved in it to moisturize the inflamed ligaments. Cool humidified air. Bed rest. Limitation of voice loads.
Laryngitis in a one-year-old baby is more difficult to treat than in an older child. This is due to the peculiarities of perception of a small patient.
How to properly treat laryngitis in a one-year-old child.
Treatment of recurrent laryngitis in children
The disease progresses at a high speed, so therapy must be provided promptly and professionally. After your child receives the necessary medical care, it is important to follow the treatment plan that the doctor creates.
First of all, you need to pay attention to the amount of water consumed and diet. You need to drink a lot. Eliminate unhealthy foods from your diet: sweets, fried foods, fatty foods, sweet carbonated drinks. To prevent your child from drinking only water, you can replace it with herbal tea, decoctions, fruit drinks, juices, and milk.
You also need to monitor conversational activity. It needs to be minimized. This can be done through games. For example, a silent person wins, the one who is silent the longest. Or read more to your child, talk about interesting things, and capture his attention.
The air in the room where the child is located must be humidified and the air temperature must be comfortable. Drafts are not allowed. Regular cleaning promotes rapid recovery. It is important to carry it out as often as possible, since dust and dirt entering the respiratory tract aggravates the situation. In especially severe cases, they suggest placing the baby in a hospital; under no circumstances should this be refused. Under the supervision of medical personnel, the child will be safe.
Effective drug treatment
Antiviral suppositories: “Viferon”, “Laferobion”, “Alfarekin”. With correctly prescribed treatment, on the third or fourth day, a small amount of sputum begins to be released, for example, taking the cough suppressant “Bromhexine”. Remedies for bronchospasm - "Eufillin".
It is unacceptable to use aerosol sprays on a one-year-old child, which can provoke laryngospasm. To relieve edema, antihistamine drugs with cetirizine and desloratadine are used. Nazivin drops can be used in the nose for rhinitis.
Among antipyretics, preparations with ibuprofen and paracetamol are acceptable, but preparations of acetylsalicylic acid are contraindicated due to the threat of life-threatening Reye's syndrome. Bacterial laryngitis requires the use of antibiotics, mainly the penicillin group.
Drug treatment
Treatment of laryngitis in children with medications
After the otolaryngologist has made an accurate diagnosis that the child has laryngitis, he will prescribe special treatment, which may vary slightly depending on the severity of the disease.
The difference will be that in one case he can prescribe antibiotics, and in the other he cannot.
The main medications used to treat laryngitis include:
- antihistamines, which can help relieve swelling
- cough suppressants or expectorants to help clear phlegm
- throat aerosols
- lozenges and lozenges
- antipyretics
- antibiotics
Each doctor has his own approach to the treatment of laryngitis, since there are adherents of using one group of drugs, and there are adherents of using another.
More information about laryngitis can be found in the video.
The best nasal drops for children for runny nose
Antihistamines
When treating laryngitis, doctors always prescribe antihistamines that help relieve swelling of the larynx. True, they do not have a 100% effect after the first dose, but after a few days you can notice the result. In addition, in the presence of a runny nose, they play an important role.
The most common drugs that can help with laryngitis include Zyrtec (or Zodak, its analogue), Cetrin, Claritin, Clarisens. For example, Zyrtec or Zodak are available in the form of drops that are convenient to give to a child.
It is best to give the drug at night, since all antihistamines cause drowsiness.
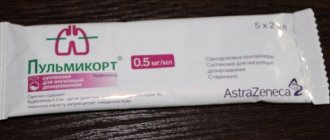
Sometimes, with severe swelling, doctors, in parallel with the use of antihistamines, also prescribe steroid hormones, for example, Pulmicort. You need to inhale it once or twice a day, since only it can quickly reduce swelling and improve breathing.
Antitussives and expectorants
In the first two days, the child’s cough will be dry, and if he talks a lot, it will be strong and debilitating. To reduce the number of attacks, you need to take antitussive drugs that will suppress this reflex:
- The most commonly prescribed medications are Stoptussin, which must be taken three times a day, Sinekod, and Gerbion.
- If the cough is wet, that is, even a small amount of sputum is released, then it is necessary to take expectorants that dilute it and improve the process of elimination from the body. These include Lazolvan, Bronchosan, etc.
After the child begins to cough, and the cough seems to come from his throat, his voice will begin to recover. Sputum settles on the mucous membrane and vocal cords, and therefore it is so important to make efforts to remove it.
You may notice that at the very beginning the sputum will be yellowish in color, this indicates an inflammatory process. As treatment progresses, the sputum will change color and become clear. At this stage, the main thing is not to stop treatment so that the disease does not develop again.
Gargling
Recipes for gargling
For laryngitis, gargling helps well, especially with herbs and alkaline solutions, which not only relieve inflammation, but also help mucus clear better.
The best ways to gargle include:
- Soda, salt and iodine. You need to take a teaspoon of salt, a teaspoon of soda, add warm water and mix well. After this, add a couple of drops of iodine. You need to rinse three times a day
- Beet. You need to take one beet, grate it, squeeze out the juice. And dilute this juice with a little water and rinse, preferably 5 or 6 times a day.
- An apple bite that is found in almost every home. To do this, take a teaspoon of vinegar and a glass of water.
- A decoction of chamomile or sage, which will help not only relieve inflammation, but also carry out antimicrobial treatment
- Weak solution of Iodinol
The only disadvantage of this method of treatment is that a child under 5 or 6 years old simply will not be able to gargle. That is why such methods of treating laryngitis are suitable for older children.
Sprays and lozenges
Many doctors prescribe throat sprays when treating laryngitis.
Today there are a lot of them, but Tantum Verde is most often used. Many children perceive it normally, as it has a sweetish taste. Also, Lugol or Hexoral are often prescribed.
Lately, fewer and fewer people are using Hexoral, as it causes an allergic reaction and also tastes unpleasant to children.
As for the use of lollipops and lozenges, it must be said right away that they can only be given to children over 5 years of age.
Among the tablets and lozenges for resorption, the following drugs are distinguished:
- Grammidin. This drug contains not only an anesthetic that reduces pain, but also a local antibiotic, which should completely kill all germs and viruses
- Faringosept. This drug belongs to a group of antiseptics that help reduce inflammation and swelling. The main thing is not to miss appointments
- Stopangin. Most people know that this drug is sold in pharmacies in the form of a spray.
Sometimes lozenges are much more effective than sprays. And all because with slow resorption in the mouth there will always be an active substance. But not all children can suck candy.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics for laryngitis: indications and types
Separately, it should be said about the use of antibiotics during laryngitis.
Most doctors prescribe antibiotics only when the body temperature lasts 3 days and does not decrease and is difficult to bring down with antipyretic drugs, as well as when the larynx is narrowed. It is very important to understand in time whether it is necessary to use antibiotics.
There are a number of indications when this becomes inevitable:
- it is discovered that laryngitis is caused by bacteria, that is, a focus of bacterial infection is found at the site of inflammation
- The child’s temperature lasts for several days, and at the same time all the symptoms of intoxication of the body appear - weakness, complete loss of appetite, headache
- breathing became difficult
The following drugs are mainly prescribed:
- Cephalosporins, which are available in the form of syrups. For example, Suprax, Ceftriaxone
- Penicillin series. These include Augmentin, Flemoklav, etc.
- Macrolides and Azithromycin, but only if the patient's condition is quite severe.
If laryngitis is discovered in a small child, he and his mother can be immediately taken to an infectious diseases hospital in order to relieve all symptoms as soon as possible.
Only a doctor can prescribe medications for laryngitis for children.
Under no circumstances should you purchase this or that drug on your own without a preliminary examination, especially when it comes to children. Properly selected medications guarantee a speedy recovery and restoration of the baby’s voice.
The best way to rinse a baby’s nose and how to properly rinse it
Chronic stage
Chronic laryngitis in a child develops according to the principle of catarrhal inflammation, atrophy or hypertrophy of tissues. Age category: children over ten to twelve years old. Characterized by symptoms such as:
- low-grade fever;
- slight cough;
- rough voice;
- sore throat;
- vocal cords get tired quickly.
These signs in a child increase significantly with exacerbation of laryngitis. There is a high probability of a night attack of false croup occurring in a child under five years of age. A choking child with blue lips makes wheezing sounds, his skin is covered with sweat. Tachycardia is observed - accelerated heartbeat.
An emergency call is required. The doctor will decide on the treatment.
Laryngitis in children: symptoms
As a rule, laryngitis in children is well recognized - any parent is able to suspect the disease based on the following signs:
- The child has a fever (and this is a sure sign of infection);
- The baby has a barking cough;
- There is a change in voice (or the voice disappears for a while);
In addition to high fever, the baby may have one or another of the “classic” signs of an infectious disease: runny nose, general weakness, etc.
Treatment of false croup
In the treatment of false croup, it is important to remember the causes of its occurrence. As a result of inflammation, the lumen of the airways narrows, swelling of the mucous membranes, hypersecretion (mucosal secretions). Also, fear due to difficulty breathing and neurosis on this basis cause spasm of the larynx. This is especially important for children with a narrow larynx, prone to obesity and allergic reactions. So, let’s treat it at home competently:
- Calm the child, eliminate any irritants;
- The room temperature should be maintained at about 18 degrees, humidity maintained at least 40;
- Voice rest (to lure the child with quiet games).
In a hospital setting, the child receives anti-inflammatory therapy and antibiotics. If necessary, resuscitation measures are taken. If there is a threat to life, surgical intervention is permissible.
Treatment of false croup.
Inhalations for laryngitis in children
Modern medicine offers experienced parents to purchase special nebulizer devices if their child suffers from frequent laryngitis. With the help of inhalation, drugs are able to penetrate deep into the larynx, each affected area receives the required amount of medicine.
Solutions for inhalation can be purchased at the pharmacy. It is advised to carry out the procedure using traditional medicine, which each parent can prepare on their own.
Most often, inhalations are performed with alkaline waters, saline solutions, and decoctions of medicinal herbs. For spasms, Eufillin and Prednisolone are prescribed. The procedure should last no longer than 3-5 minutes. Manipulative agents are used at room temperature. Before and after inhalation, it is recommended to keep the baby from eating and drinking for 30 minutes to an hour. Sessions are allowed if the patient’s body temperature does not exceed 38 degrees.
Thermal inhalations for laryngotracheitis are carried out with special devices or improvised means in the form of a kettle or pan. Towels. It is important to know that such procedures are prohibited even with a slight increase in temperature. The manipulation should be carried out carefully so that the baby does not get burns during inhalation.
If the child does not experience allergic reactions to essential oils, it is recommended to do aromatherapy, which will speed up the healing process, eliminate pain, cough and relieve inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx. Children over 2 years of age are allowed to breathe essential vapors.
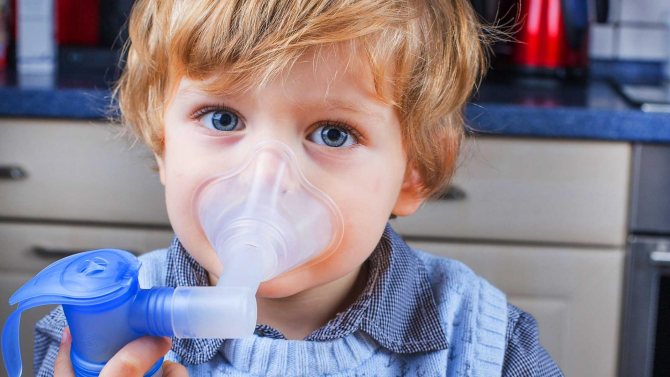
Inhalation of the pharynx in children to cure laryngitis.
Diagnosis and first aid for false croup
According to the famous doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky, croup is caused by the parainfluenza virus. The most risky period is the winter as a result of heating devices drying out indoor air. When it occurs later, it is especially difficult. You can determine the diagnosis yourself based on three noticeable signs and immediately consult a doctor:
- difficulty breathing when inhaling;
- change in voice (hoarse, disappears altogether);
- barking cough.
Against the background of the symptoms described above, the acute onset of the disease, sore throat, and high temperature are taken into account. The child turns pale and has a laryngitis-like dry cough. There can be no talk of any self-medication. Before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to provide first aid:
- sits you on your lap, unbuttoning your clothes on your chest;
- calm the child;
- provide access to cool fresh air (open the windows, hang wet sheets and towels around the room);
- drink plenty of soda water and milk;
- for hyperthermia above 38 degrees, use antipyretics;
- if the temperature is not high, it is possible to apply a mustard plaster to the calf muscles;
- relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa with vasoconstrictor drops.
If the room is hot, take the child, dressed, out to the balcony in winter, and into the bathroom in summer, turning on cool water to increase the humidity level. In no case should you give expectorants or use hot steam inhalations! Such actions will worsen suffocation and guarantee subsequent hospitalization. Let's say an ultrasonic humidifier.

How to help a child with false croup.
How to treat laryngitis in children
Laryngitis in children in 99% of cases is a manifestation of a viral infection (and in rare cases, an allergic reaction). Therefore, it is understandable that in the vast majority of cases it is not treated with antibiotics or antiallergic drugs. Antiviral drugs also have little effect on the course of laryngitis, although partly with their help they can relieve a child’s sore throat and reduce coughing. But what really helps effectively is clean, fresh and cool air in the room and drinking plenty of fluids.
With laryngitis, it is many times more beneficial for a sick baby to breathe frosty air while sitting at home in a fur hat than to breathe dry and hot air while walking around the apartment in only a diaper. For a child with laryngitis, who really has difficulty breathing, the optimal microclimate in the room is: temperature no higher than 18 ° C, humidity - 55-70%.
Drinking plenty of fluids is also of great importance for recovery. The fact is that excess fluid in a child’s body thins not only his blood, but also his mucus. Becoming more liquid, it does not accumulate in the inflamed larynx, but on the contrary, it is easier to expectorate.
For infection, symptomatic treatment :
- If a child’s temperature rises above 38°C, it must be brought down by giving the child antipyretic drugs, such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
- To alleviate the condition of the larynx, it is necessary to maintain nasal breathing “in working order” - this means that if the nose is “clogged” and cannot breathe freely, you need to instill a vasoconstrictor.
Nebulizer and steam inhalations
Treatment at home involves the use of inhalations. It is convenient to carry out dosed administration directly into the lesion using a device - a nebulizer. Solutions of Lazolvan, Ambrohexal, physiological sodium chloride solution, Borjomi, drugs for bronchospasm (Berodual, Ventolin), glucocorticosteroids for stenosis (Pulmircort) are used for their intended purpose.
In cases where a nebulizer is not available, steam inhalations over boiled potatoes and chamomile infusion are possible. With false croup, hot inhalations are unacceptable!
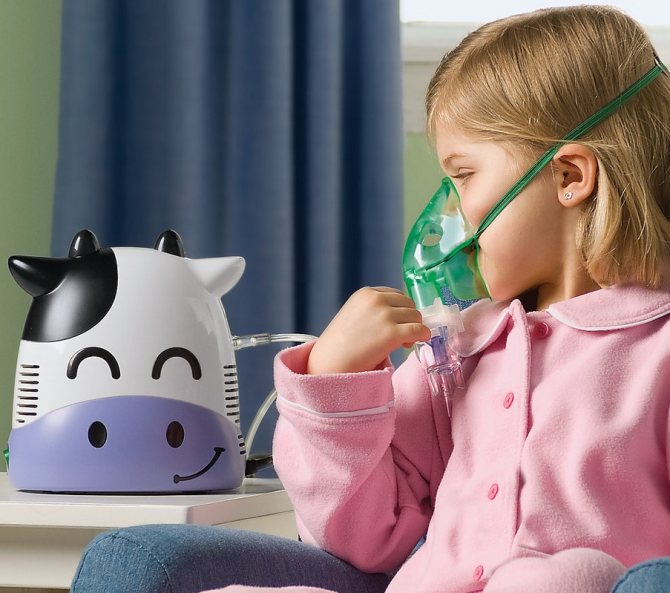

Nebulizer and steam inhalations.
Types and symptoms of laryngitis in children 3-4 years old
In children 3-4 years old, laryngitis can be diagnosed in one of the following forms and varieties:
- Catarrhal. The most common and easiest to treat. It is extremely rarely fraught with complications and is usually treated with standard therapeutic methods.
- Hypertrophic and atrophic forms. In contrast to catarrhal, these forms almost never occur in children under 4 years of age.
- Diphtheria (fibrinous laryngitis). In these cases, the laryngeal mucosa is affected by the diphtheria bacillus.
- Hemorrhagic. The peculiarity of this form is the formation of hemorrhages both on the larynx itself and on its mucous membrane.
- Subglottic laryngitis. Characterized by local damage to certain areas of the trachea.
- Phlegmonous. Not the most common form in children 3-4 years old, it develops with a decrease in the level of immunity, which is typical for past infectious diseases.
Any form of laryngitis can be acute or chronic.
Reference! Acute laryngitis always develops against the background of the activity of pathogenic microflora, while chronic types are a consequence of the development of the disease itself, during the development of which the body’s defense mechanisms are weakened.
Each type of disease has its own differences in terms of symptoms, but all forms are characterized by some common symptoms :
- hoarse weakened voice;
- general malaise;
- irritation and dry throat;
- cough; noisy inhalations and exhalations;
- possible manifestation of fever;
- sometimes – an increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes.
Complications of the disease
The main complication of laryngitis in a child is false croup. The soft, short, narrow vestibule of the larynx, its funnel-shaped shape, as well as excessive excitability of the muscles of the glottis, the prevalence of the tone of the sympathetic nerves contribute to it.
Asphyxia is typical when timely assistance is not provided. Hypothermia, convulsions, low heart sounds, complete cessation of breathing up to coma and death.
Laryngotracheitis (cough more often than with laryngitis), pneumonia, bronchitis often occur as complications of laryngitis. They require long-term, sometimes intensive treatment.
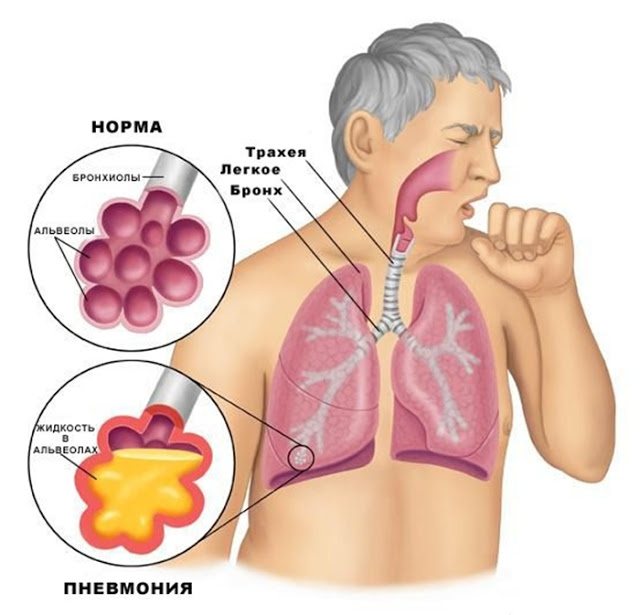
Pneumonia.
Danger for babies
False croup or stenosing laryngitis is a disease defined as inflammation in the trachea and larynx caused by scarlet fever, measles, whooping cough viruses, adenoviruses and rhinoviruses. It is diagnosed mainly in children starting from six months. In babies under 6 months of age, such a disease as false croup does not occur.

The development of the disease is due to the structural features of the respiratory tract in children. Their larynx has a small diameter, and the muscles around the vocal cords are quickly excited, which leads to closure of the glottis. The mucous membrane of the larynx contains a lot of lymphatic tissue and a large amount of loose fiber, which contributes to the appearance of swelling.
With laryngitis, viruses attack the surface of the larynx and provoke inflammation. The area of the glottis spasms reflexively and its lumen narrows. In a child under three years of age, the respiratory system has not yet fully formed and therefore it does not cope with some functions in full. When viruses or allergens enter the nasopharynx, some of them can penetrate further to the larynx, causing swelling of its mucous membrane. The lumen of the larynx becomes narrower, the child wheezes and suffocates. This scares him, he begins to scream and cry, which further provokes the development of edema. The presence of a “barking” cough, wheezing and whistling, retraction of the intercostal spaces when inhaling, and blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle indicate the severity of the child’s condition.
Children with allergies are mainly at risk of developing the disease, as they react sharply to toxins released by the virus, and this leads to swelling of the larynx. Stenosing laryngitis is considered the most severe form of the disease for a child.
Non-drug therapy at home

Treatment of acute laryngitis depends on the age of the child. This may include:
- compliance with bed rest;
- limiting vocal load (during the week it is better for the baby to speak as little as possible);
- maintaining the optimal temperature (+18...+20°C) and air humidity (50–70%) in the room where the sick baby is located;
- drink plenty of fortified drinks (the liquid should be warm and unsweetened);
- following a hypoallergenic diet - if there are symptoms of laryngitis, it is strictly not recommended for a child to give sour, spicy, too hot or cold foods, or carbonated drinks.
Types and forms
Laryngitis is a disease with a complex structure, in which the following forms are distinguished:
- catarrhal - the least dangerous, occurring in a mild form and accompanied by symptoms characteristic of any ARVI: cough and slightly elevated temperature;
- hypertrophic – dangerous due to laryngeal edema;
- hemorrhagic - characterized by the release of sputum streaked with blood during coughing. This occurs because during illness, hemorrhage occurs in the mucous membranes of the larynx. This form of the disease is rare and only in the presence of predisposing factors: liver disease or cardiovascular disease;
- diphtheria - differs in that the inflammation affects not only the larynx, but also the tonsils;
- laryngotracheitis - in this form the disease also affects the trachea;
- phlegmonous - the most severe form of the disease, complicated by damage to the perichondrium, muscular layer of the larynx, and lymph nodes; accompanied by severe pain and high fever;
- atrophic – characterized by thinning of the larynx; it is extremely rare in children.

Symptoms of laryngitis in adults can be found here.
Most often in children, the catarrhal form of laryngitis occurs, which can be easily treated at home and, if all the doctor’s instructions are followed, does not leave behind complications. Diagnosed by a pediatrician after examination.