What is diarrhea in a child?
Diarrhea (or diarrhea) is a disorder of the digestive system caused by a violation of the intestinal microflora, various types of infections, etc. The pathology is characterized by watery stools and is often accompanied by pain in the abdominal area. Diarrhea is defined as frequent bowel movements (more than 3 times a day). One way or another, parents should be wary if diarrhea continues for more than a day, as well as if there are traces of mucus or blood in the stool.
In third world countries, diarrhea is one of the causes of child mortality.
Diagnostics
With so many possible diseases, how can a correct diagnosis be made? To do this, the doctor will prescribe a series of tests and studies.
- To determine whether certain substances are well digested, a coprogram is prescribed
- To determine whether there are any disturbances in the intestinal microflora, a stool test is taken for dysbiosis
- To exclude the presence of parasites, the stool is checked for worm eggs.
- A general blood test will show whether there are foci of inflammation or allergies in the body
- Biochemistry will reveal whether indigestion is associated with problems with the liver and pancreas
- To assess the general condition of organs, an ultrasound examination is prescribed
Causes of diarrhea and fever in a child
Stool disorder can be caused by a number of provoking factors. Here are some of them:
- Infectious diseases (dysentery, intestinal rotavirus infection, salmonellosis, enterovirus, rubella, measles, scarlet fever, influenza, etc.).
- Food poisoning (for example, from stale or poor quality food).
- Helminthic infestations.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies (gastritis in the acute stage, colitis, dysbacteriosis, etc.).
- Drug poisoning (if medications have expired or as a result of an overdose: antibiotics, antihistamines, etc.).
- Teething, but in this case the temperature should not rise.
- Recent infectious diseases.
- Severe stress or severe psychological trauma.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules.
But symptoms such as persistently high temperature (around 40 degrees, in which antipyretic drugs either do not work or give a temporary effect), vomiting, acute abdominal pain, the presence of blood or mucus in the stool or vomit, rashes should cause particular danger on the body, enlarged lymph nodes, etc. All of the above symptoms are a serious reason to consult a doctor.
Causes of diarrhea with fever
Diarrhea with fever can be an alarming symptom. How dangerous this condition is depends on the factors that provoked its appearance.
The causes of diarrhea at fever can be divided into:
- Non-infectious.
- Infectious.
If high fever and loose stools are caused by a non-infectious pathogen, the problem can be solved quickly. This does not always require the help of a doctor. If the baby becomes infected with an infectious disease, qualified treatment is necessary.
Non-infectious factors of occurrence
Causes not related to infection, but which can cause fever and diarrhea:
- teething;
- drug intolerance;
- poisoning;
- overfeeding;
- diet of a nursing mother;
- introduction of complementary foods;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- stress.
To distinguish between dangerous signs of infection and a normal reaction to teeth, it’s worth taking a closer look.
Signs of teething
Fever and diarrhea in a child often develop during teething. This process affects absolutely everyone. For some, tooth growth begins at 5–8 months, for others closer to one year of age.

The peculiarity of dyspeptic symptoms when teeth appear in a child under one year old is that after a day or two the symptoms weaken, the diarrhea stops, and the temperature returns to normal.
Diarrhea due to medications
Although parents rarely give their children medications that are not prescribed by the attending physician, even they can provoke unpleasant phenomena. Because of this reason, the following symptoms may appear:
- rash;
- cough;
- itching;
- heat;
- diarrhea.
We recommend: Can the development of green diarrhea in infants be considered normal?
To reduce the negative effects of medications on the child’s body, it is necessary to stop using these drugs and consult a doctor for advice.
Food poisoning disorder
No matter how hard parents try to closely monitor the baby’s diet, sometimes low-quality food products cause problems in the digestive system.

In case of poisoning, body temperature can rise to 38–39 degrees. The child experiences a strong fever and weakness. Attacks of nausea and vomiting are possible.
With frequent bowel movements and vomiting, you should try to replenish the volume of lost fluid. For this purpose, it is important to provide the baby with plenty of fluids, and in case of vomiting, you can give several tablespoons of warm water every 2 minutes.
Problems due to overfeeding
Too large portions, even breast milk, can provoke the development of dyspeptic symptoms, accompanied by body temperature. To avoid this, a woman must follow a diet.
There should be approximately an equal amount of time between each meal. You should not often shift the baby from one breast to another so that he has time to draw milk from the posterior chamber, since it is more nutritious and more enriched with valuable enzymes for normal digestion.
Errors in the mother's diet
A woman’s menu directly affects the quality and chemical composition of milk. It is necessary to monitor not only the child’s diet, but also your own.
Eating spicy, salty, smoked foods can lead to intestinal upset in a child. Particular attention should be paid to medications taken by women. Sometimes medications penetrate into the milk and affect the baby’s well-being.
Abrupt introduction of complementary foods
Diarrhea accompanied by high fever often occurs due to improper introduction of complementary foods. You can give your baby new foods no earlier than 6 months. Before this, the enzymatic system is practically not formed, and the digestion of ordinary foods becomes impossible.
You should not start complementary feeding with fresh fruits and vegetables, even if they are pureed.
Gastrointestinal diseases
The reasons why some children develop a fever and diarrhea may lie in diseases of the digestive tract. Some pathologies are congenital.
We recommend: What to do if a baby has diarrhea?
For example, dysbiosis develops due to a violation of the intestinal microflora. Problems appear after a course of antibiotic therapy. To restore, the diet is adjusted and lacto- and bifidobacteria are prescribed.
Stress
No matter how old a child is, he is susceptible to emotional disruptions and experiences. Even a newborn baby may show signs of anxiety if for some reason he does not find his mother nearby.

Stressful situations cause intestinal spasms, and children begin to experience diarrhea. The condition is rarely accompanied by an increase in temperature, but when the problems are protracted, this phenomenon occurs.
Infectious factors causing diarrhea
However, green diarrhea with water and a rise in temperature to 37–39 degrees in a baby may indicate the development of an infectious disease. To understand what to do in this case, parents must be able to distinguish between the main symptoms of the disease and a common malfunction of the intestines.
A significant increase in temperature and dyspeptic symptoms can be caused by the following diseases:
- rotavirus;
- measles;
- enterovirus;
- rubella;
- scarlet fever;
- flu;
- otitis;
- angina;
- rhino-pharyngitis;
- salmonellosis;
- dysentery.
To prevent complications and receive quality medical treatment when the first signs of pathology appear, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Some features of infectious diseases
Sometimes an infection can be suspected based on certain symptoms that appear in children. With enterovirus and rotavirus infections, the following phenomena are present:
- frequent watery stools up to 20 times a day;
- greenish tint to stool;
- specific unpleasant odor.
When salmonella, E. coli or dysentery pathogens penetrate, the following signs appear:
- heat;
- the presence of mucus in the discharge;
- foul odor of stool;
- the stool becomes swamp-greenish.
With intestinal infections, diarrhea with blood may appear.
Features of acetonemic crisis
Some parents know firsthand what “acetone” is. At the time of an acetonemic crisis, children’s body temperature rises and diarrhea begins. This disease is diagnosed after reaching one year of age.

Children feel severe weakness, suffer from repeated vomiting and loss of strength. Medical attention required.
First aid
In order to avoid dehydration and in order to alleviate the child’s condition, it is necessary to take a number of effective measures, in particular:
- Call an ambulance (if diarrhea does not go away within 2-3 days and is accompanied by fever in the body).
- Do not give your baby antibiotics and antiviral drugs (until diagnosis).
- Isolate other family members until the cause of the eating disorder is determined.
- Give the child an antipyretic based on paracetamol (Panadol, Cefekon D, etc.). Aspirin is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age. Children under 2-3 years old can be given drugs exclusively in the form of syrup or rectal suppositories.
- To cleanse the gastrointestinal tract from harmful toxic substances, give the child an enterosorbent (activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel, etc.).
- Wait for the ambulance to arrive.
To prevent dehydration, you can give your baby one of the following solutions:
- Dissolve 1 tbsp in a glass of boiled water at room temperature. l. sugar, 1 tsp. salt and half a teaspoon of baking soda. Mix the mixture thoroughly.
- Dissolve 3-4 tbsp in 1 liter of clean drinking water. l. sugar, 1 tsp. salt and freshly squeezed orange juice (you will need 2 oranges for this).
The child should be given a couple of sips of one of the above solutions every 5-10 minutes.
For diarrhea with fever, it is recommended to follow a therapeutic diet (i.e., remove fatty, fried and meat dishes from the diet).
Types of diarrhea
First of all, the danger of accelerated fecal excretion in children is dehydration. Therefore, the primary task of parents is to replace fluid in the body by drinking plenty of fluids.
In medicine, the following types of diarrhea are distinguished: 1. Infectious, 2. Toxic, 3. Nutritional, 4. Neurogenic, 5. Medicinal, 6. Dyspeptic.
⇒Infectious diarrhea can be caused by toxicological food infection, dysentery, amoebiasis, viral diseases and salmonellosis. The main provocateurs of infectious diarrhea are enteroviruses and rotaviruses. Rotavirus diarrhea is most common in children under 2 years of age. Immediately after the first symptoms appear, a high temperature may jump, which is accompanied by headaches and muscle spasms.
It should be noted that this type of diarrhea can last up to a week, therefore, children endure this kind of disorder quite hard.
With diarrhea, there is always a risk of dehydration, so the main rule is to provide your baby with plenty of fluids. In addition, it is necessary to constantly monitor the color of the skin and mucous membranes, especially in children under one year old.
Diarrhea and fever in a child in this case are significant risk factors. ⇒Toxic diarrhea. This type of diarrhea can be caused by exposure to toxic substances or kidney failure.
⇒Alimentary diarrhea. Alimentary diarrhea can be caused by a lack of vitamins in the body, or the disorder can appear as a result of an allergic reaction to medications or food. In addition, nutritional diarrhea is caused by poor diet and monotonous food. Children under one year of age often experience this prominent diarrhea because their gastrointestinal tract is in the process of developing.
⇒Dyspeptic diarrhea. Dyspeptic diarrhea develops as a result of malfunction of the small intestine caused by a lack of enzymes. Improper digestion of food, poor functioning of the stomach, pancreas and liver - all these types of pathology can provoke dyspeptic diarrhea. This type of diarrhea is typical for children under one year old, however, at the age of 2-3 years and older you can encounter this phenomenon.
⇒Drug-induced diarrhea. In most cases, drug-induced diarrhea is caused by drugs that act to suppress bowel function. Such drugs are antibiotics. Therefore, the attending physician must take into account the possible consequences of taking medications, calculate doses based on the child’s age, and also prescribe medications that stop or mitigate the negative effects of medications. Before the age of one year, you need to especially carefully monitor what the doctor prescribes, because taking antibiotics incorrectly can lead to dire consequences.
⇒Neurological diarrhea. Stressful situations, strong emotions, worries and other similar cases can cause intestinal upset, which leads to frequent bowel movements. At the same time, the stool is always copious and liquid. This type of diarrhea is practically never observed in young children.
Most often, children over 7 years old experience such abdominal disorders. The so-called “bear sickness” can occur due to fear of an exam or test. A consultation with a neurologist and a child psychologist can help cope with this problem. If you don't solve this problem, it can really ruin your adult life.
Treatment
Various groups of medications and folk remedies are used as therapy. To speed up the healing process, you must follow a certain diet.
Drug therapy
The following drugs are used to combat diarrhea:
- Adsorbing agents (Enterosgel, Smecta, Polysorb, Laktofiltrum, etc.).
- Regidron solution (to replenish fluid in the body).
- Antipyretic drugs (Paracetamol, Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Panadol, Efferalgan, etc.). But these products are used only if the temperature exceeds 38 degrees.
- Antibiotics (if necessary and under medical supervision: Levomycetin, Metronidazole, Furazolidone, Intetrix, etc.).
The dosage and course of use of certain drugs should be prescribed by a doctor.
Among other things, it is necessary to observe the drinking regime, i.e. the child must drink at least 1.5 liters of clean boiled water per day (in small portions).
Folk remedies
The following remedies are recommended as folk therapy to normalize stool:
- Rice water - add 2 tsp to 0.5 liters of boiling water (without adding salt). washed rice (grains can be pre-soaked in cold boiled water for 1-1.5 hours). Stirring, bring the product to a boil and simmer over low heat for 50 minutes. Cool the finished broth and strain through cheesecloth. Single dose: 50 ml. Frequency of use: 3-4 times a day.
- Bird cherry decoction - rinse ripe bird cherry clusters under running water, fill the glass halfway with berries and pour into the container in which the potion will be prepared. Next, fresh fruits are poured with 2 cups of boiling water and kept in a water bath for 30 minutes. The finished product is infused under the lid for another half hour, after which it is filtered and topped up with an equal amount of natural blueberry juice. It is recommended to give the finished mixture to the child 1 tbsp. l. each hour. For children under 3 years of age, the dosage is 1 tsp. every 2 hours.
- Pomegranate decoction - dry pomegranate peels are ground in a coffee grinder, then 1 tsp. pour the resulting powder into a glass of boiling water and cook in a water bath for 15 minutes. The finished product is infused for about an hour and given to the child 1 tsp. 4 times a day (until stool normalizes).
If allergic reactions to a particular drug occur, treatment should be temporarily stopped and consult a pediatrician.
Diet
It is recommended that children over 1 year of age be given exclusively porridge (without milk), fruits (apples, bananas), carrots, boiled chicken, natural homemade yoghurts and slimy soups for several days. All food must be served pureed or pureed. Prohibited foods include: milk, sweets, salty and fried foods, fatty meat broths, fast food, ice cream, chocolate, candy, nuts, chips, coffee, sweet carbonated drinks and concentrated juices.
We recommend: Measles vaccinations for children
If the baby is less than 1 year old, there is no need to stop breastfeeding (except for moments of diarrhea or vomiting, including when the child has no appetite). In the case of artificial feeding, it is advisable to switch to soy formula until recovery.
Traditional methods of treatment
In order to help the baby, parents can turn to traditional medicine, but this should only be done after consulting a doctor.
Below you can see information about the safest folk remedies used for diarrhea and fever in children:

- Rosehip decoction. Lowers body temperature and helps restore digestion. Take 50 g of rose hips per liter of boiling water, let it brew for one hour. Give it to your child three times a day in small sips.
- Crackers with water. Soak 200 g of rye crackers, pour in 500 ml of boiled warm water, leave for half an hour. Give your baby 50 ml of the product every three hours.
- Chamomile tea with mint.
- Blueberry and bird cherry fruits. Take equal quantities of raw materials and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Let your child drink 100 ml of medicinal infusion in the morning and evening.
- Decoction of pomegranate peels.
- Rice broth.
- Decoction of oak bark.
- Dry starch diluted in water.
- Carrot puree.
When it comes to the health of a child, you cannot engage in amateur activities.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
Dr. Komarovsky gives parents the following recommendations:
- Do not overfeed your baby during and after illness.
- Maintain drinking regime.
- Pay attention to accompanying symptoms (vomiting, blood in the stool, etc.) and immediately consult a doctor.
- Do not self-medicate.
- If there is an intestinal infection, provide the child with separate dishes.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations.
This approach to treatment, according to the doctor, will prevent possible complications.
Symptoms
Although we strongly advise you to contact a professional to make a diagnosis, parents, after observing the clinical picture, can independently determine the approximate cause of the ailment. To do this, you need to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms.
- Bloody diarrhea (invasive diarrhea) . May be accompanied by weakness and fever, a symptom of an intestinal infection;
- Diarrhea with mucus. The cause is usually the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the child's body. For example, cryptosporidium, salmonella, lamblia, enterotoxigenic or enteropathogenic coli, enteroviruses, rotaviruses;
- Vomit . If a child has diarrhea, vomiting and high fever, as well as the smell of acetone from the mouth, then this is an acetonemic crisis. If he has cold hands and feet, he feels very weak, and his face turns pale, then this is most likely food poisoning;
- Rash. In this case, there is a high probability that the disease is scarlet fever, measles or rubella. It may also be a sign of an allergy or intolerance to certain medications;
- Abdominal pain indicates that indigestion or upset stomach has occurred. The reason can be found in the products consumed by the child;
- Swelling and inflammation of the gums. If the baby is under three years old and exhibits similar symptoms, this means that he is teething. This process can cause general ill health, diarrhea, and a slight fever;
- Cough, runny nose, sore throat. Together with high fever and diarrhea, these signs may indicate that the child is developing infectious diseases such as influenza, sore throat, otitis media or nasopharyngitis.
By carefully observing the child, you can identify the approximate causes of the baby’s illness. Be more sensitive to accompanying symptoms, but do not neglect medical help and seek it at the first opportunity.
Prevention
To avoid diarrhea with fever, it is necessary to follow a number of preventive rules:
- Monitor the quality of food products (expiration date, minimum preservatives and dyes, etc.).
- Feed the child according to age (limit the consumption of sausages, chocolate, mushrooms, etc.).
- Drink vitamin and mineral complexes (to strengthen the immune system).
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Maintain hygiene (wash your hands before eating and teach your child to do this).
- Wash fresh fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
- Drink only boiled water.
- Avoid swimming in suspicious bodies of water.
- Limit contact with sick people (especially during epidemic periods).
Diarrhea and fever in a child can occur for a variety of reasons. But in most cases, this condition is caused by infectious diseases, which often leads to complications. Therefore, it is strictly not recommended to self-medicate and at the first opportunity you should show the baby to a pediatrician (or call a doctor at home).
Causes
Diarrhea accompanied by fever is most likely caused by an intestinal infection. According to the type of pathogen, intestinal infections are divided into bacterial, viral and protozoal.
The most common bacterial intestinal infections include:
- Dysentery is an infection caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella, which affects the mucous membrane of the large intestine. The disease is characterized by repeated diarrhea mixed with blood, fever up to 38-39 ° C, vomiting and loss of appetite;
Salmonellosis is an intestinal infection caused by Salmonella. With this disease, diarrhea may be greenish in color, vomiting is observed, and the temperature rises to 38 ° C;
- Botulism is a disease that develops when botulinum toxin, a waste product of the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, enters the body. In addition to diarrhea, vomiting with fever, the disease is characterized by damage to the nervous system with impaired visual and other functions.
Diarrhea can also be caused by viral infections. The most common of them:
Adenoviral infection. With this disease, the virus affects the mucous membrane of the intestines, upper respiratory tract, and eyes. Against the background of elevated temperature, the symptoms of a cold (sore throat, cough, runny nose) are accompanied by abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Rotavirus infection or “intestinal flu” manifests itself in the form of fever up to 38-39 ° C, diarrhea, vomiting
Enterovirus infection also manifests itself in the form of symptoms characteristic of influenza, that is, sore throat, runny nose, cough, to which are added vomiting, diarrhea, and bloating.
Intestinal infections can also be caused by protozoa, for example, giardia (giardiasis), amoebas (amoebiasis), schistomatosis (develops as a result of the penetration of blood flukes - trematodes) into the body.
However, other reasons cannot be ruled out. Diarrhea with high fever can also occur with a number of other diseases, for example:
- Food poisoning from expired products;
Diseases requiring surgical intervention (acute appendicitis, intestinal obstruction);
Other infectious diseases (measles, chickenpox, etc.).
In children under one year of age, diarrhea with fever can be caused by teething. Usually after 2-3 days the temperature drops and a new tooth erupts in the mouth.
Therapeutic measures

If a child has a fever and diarrhea, then therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked the onset of the malaise. At the same time, therapy is used to relieve severe symptoms of the pathological process.
For this use:
- Adsorbents effective against diarrhea.
- Gastric lavage with soda solution or boiled water. It is advisable to carry out detoxification even in the absence of vomiting. It will help lower the temperature and remove toxic substances, which will significantly alleviate the child’s condition.
- Rehydration therapy, which replenishes fluid lost by the body. To do this, use non-carbonated mineral water, tea, herbal and berry decoctions. Pomegranate juice with lemon helps a lot. You can use a concentrated solution of Gastrolit, Normohydron, Regidron. Children under two years of age should be given Regidron (and similar drugs) in a dosage according to the instructions and age, in order to prevent disturbances in the water-salt balance.
- Antipyretics if diarrhea develops and the child’s temperature exceeds 38°C.
- Antibiotics if you need to treat an intestinal infection in which blood or mucous clots appear in the stool.
- Enveloping drugs that form a protective film in the gastrointestinal tract. Instead of medicine, you can give viscous porridge (for example, oatmeal, buckwheat), rice water, starch jelly.
- Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria are probiotics that restore intestinal microflora.
Important! If diarrhea begins and the temperature is very high, then a 1-2 year old child will respond well to antipyretic syrup or suspension. For children under one year of age, it is better to use rectal suppositories with paracetamol.
Diet food

In order for diarrhea to disappear and the child’s body temperature to normalize, it is necessary to adhere to a diet that allows normalization of the gastrointestinal tract:
- The diet for a one-year-old child and children under two years of age should be left to five meals a day, but the portions should be small.
- Children who have crossed the one and a half year age threshold should eat lightly salted boiled vegetables (they are ground to a puree) and cereals.
- When the patient’s condition has stabilized, they are allowed to give meat and fish meatballs, steamed cutlets, and crackers. Fermented milk products are also gradually introduced.
[adsp-pro-7]
At the beginning of treatment, older children are given a lean diet, including only healthy foods in the diet: cereals, vegetable soups, lean meat and fish, boiled apples, compotes. Be sure to eat rice water, boiled eggs, and bananas.
You must refrain from:
- Carbonated drinks.
- Dairy products.
- Packaged juices.
- Smoked and canned goods.
- Fatty, sweet, spicy foods, fast food.
There are opposing opinions from experts regarding feeding infants with diarrhea and fever. If previously it was believed that mother's milk could worsen the baby's condition, modern doctors categorically do not recommend giving up feeding. On the contrary, the child needs frequent feeding to the breast and supplemented with water. At the same time, a nursing mother must adhere to a strict diet, limiting harmful and allergenic foods in the menu.
How to react to temperature
Antipyretics should be used if the temperature reaches 38.5 degrees. It is important to take into account that with infectious diseases, indicators increase rapidly. Therefore they need to be kept under control.
Indicators in the range of 41-41.5 degrees pose a danger to the baby’s life. In addition, high fever can cause febrile seizures.
The condition is characterized by impaired breathing, severe muscle tension, blueness of the body and erratic twitching. If the child has a history of febrile convulsions, the temperature should be reduced already at 38 degrees.
Another dangerous condition for children is white fever. In this case, the child’s skin remains pale and dry, and the limbs remain cold. Then it is very difficult to reduce the temperature, so you need to immediately call a doctor.
Methods for normalizing temperature are divided into 2 categories - household and medicinal. To improve your child’s condition, you need to do the following:
- remove the baby’s diaper and excess clothing, covering him with a light blanket;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
- give the baby water often;
- wipe the skin with a damp towel - if the baby has symptoms of white fever, this is prohibited.
As for medications, the baby can be given children's ibuprofen or paracetamol. The dosage should be selected depending on the age category and body weight of the child. Before starting to use such products, it is best to consult your pediatrician.
The choice of dosage form is also important. If you have diarrhea, it is better to give the product in syrup form. If a child vomits, you should use suppositories. It is important to take into account that the effect of rectal suppositories begins only after 40 minutes, while the effect of the syrup is achieved after 20 minutes.
Summary
Humanity has accumulated vast experience in dealing with diarrhea and high fever in children. Modern medicine, the experience of pediatricians, and effective pharmacology guarantee a cure for unpleasant, often dangerous diseases. The main thing is not to let things take their course, not to waste time, and to consult a doctor.
Don't neglect simple prevention. Make sure your child maintains hygiene, wash fruits and vegetables, and drink clean water. Your child will be healthy, full of strength, develop normally, and show energy.
What can you do first?
In addition to calling a doctor, parents can take a number of other steps to help alleviate the symptoms of diarrhea:
- do not start treatment with antibiotics (they destroy all bacteria, including beneficial ones);
- place the child in a separate room and limit his contact with other people (to avoid infection);
- reduce the temperature yourself only as a last resort if it is more than 38.5-39 degrees;
- For children under one year old and one year old, administer the antipyretic in the form of a suppository; for children over two years old, give syrup;
- give the child sorbents (activated carbon, smecta, etc.).
Diarrhea and fever in a child cause dehydration. To cope with it, you can prepare several solutions
.
For example, dissolve a large spoon of sugar, a dessert spoon of salt and half a dessert spoon of soda in 1000 ml of clean water. The solutions should not be drunk in one gulp, but a little bit every five minutes
. Dehydration will stop and the child's condition will improve.
Complications
Both infectious and non-infectious causes have one thing in common: they are dangerous for the baby’s body. Much more dangerous than the same reasons - the same pathogens, the same prerequisites - would be dangerous for the body of an adult. They can cause:
- Dehydration. The most dangerous danger is prolonged diarrhea combined with fever. The child sweats and loses water. The child cries and loses water. The child gets rid of the intestinal contents - and also loses water. As a result, he almost never goes to the toilet, the mucous membranes dry out and become covered with a white coating, the eyes become red and inflamed, and the reaction to the environment becomes slow and indifferent. The worst thing is that it is very difficult to cope with dehydration in a baby at home, because there is no way to put him on an IV. And long-term dehydration leads to disruptions in organ function and can lead to death.
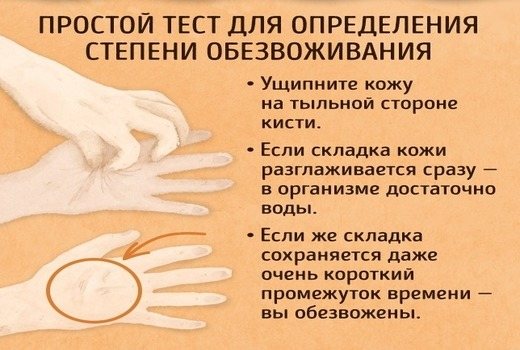
- Dysbacteriosis. It becomes the result of the use of antibiotics (and they will almost certainly be prescribed) and constant diarrhea. Because of it, weakness, lethargy occurs and lactose deficiency may develop and the baby will have to be transferred to complementary foods.
- Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. A prolonged increase in temperature negatively affects the functioning of the entire body as a whole and can lead to pathologies of the heart, kidneys, and liver. And, of course, to problems with the stomach and intestines.
To avoid complications, you need to consult a doctor in time and start treatment.
The importance of timely treatment
If you experience any symptoms of discomfort, you should consult a doctor. Otherwise there is a risk of dangerous consequences. These include the following:
- dehydration;
- fainting;
- convulsions;
- dysfunction of the intestines.
After rotavirus there is a risk of developing lactase deficiency. If diarrhea was infectious in nature, there is a possibility of dysbacteriosis.
The combination of diarrhea and high temperature indicates a variety of disorders. To eliminate this condition, it is imperative to establish the provoking factor. To do this, it is important to consult a doctor and undergo the necessary diagnostic tests.