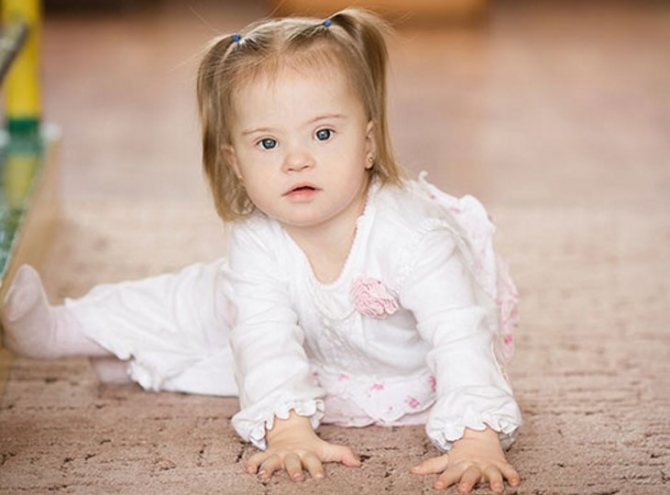
If a person has difficulties or problems, it is advisable to start dealing with them immediately. This is especially true for health. A child in the house is not only joy and excitement, but also worries. When children are sick, the main thing for parents is not to get confused, but to boldly begin treatment and, if necessary, rehabilitation of the child. This is especially true for Down syndrome, a disease that occurs in one case in a thousand. This genetic defect is characterized by developmental delays. And the sooner you begin to purposefully engage in the education and development of a newborn child with Down syndrome, the more he will be able to achieve in adulthood. Therefore, early diagnosis is important, which begins not with tests, but with identifying external signs that are not the basis for making a diagnosis, but are still characteristic enough for the doctor to determine the likelihood of the disease.
Head
The main symptom of Down syndrome in a newborn is a chromosomal malfunction, in which a person has 47 rather than 46 chromosomes. To determine the disease at the genetic level, complex tests are needed. But genetic characteristics often manifest themselves in appearance, body structure, and behavior.
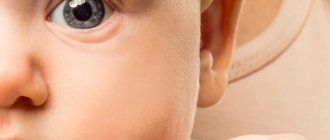
Signs of Down syndrome in newborns - eyes:
- the inner corner of the eye has the so-called epicanthus (third eyelid, Mongolian fold), covers the lacrimal tubercle, because of this feature Down syndrome was called Mongolian syndrome for a long time;
- the eyes look slanted, with raised corners;
- possible squint;
- the presence of pigment spots along the edges of the iris of the pupils, the so-called “Brushfield spots”;
- clouding of the eye lens;
- visual impairment occurs in two thirds of children with the syndrome - there may be clouding of the cornea, increased intraocular pressure, uncontrolled movements of the eyeballs, which can be rhythmic (so-called nystagmus), the eyes may have other pathologies, a tendency to inflammatory processes, vision hygiene and regular consultations are needed ophthalmologist
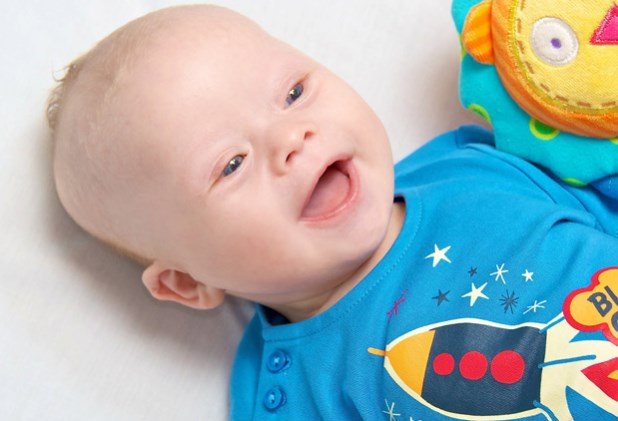

External signs of Down syndrome - face and head shape:
- the face as a whole is sculpted, but looks a little flattened;
- visually the bridge of the nose looks flat and wide, due to this the nose may appear insufficiently prominent and shortened;
- brachycephaly or short-headedness - large transverse and small longitudinal diameter of the cerebral part of the skull;
- the neck can be short and wide, have a leather fold;
- the shells of the ears may appear deformed, the auditory openings are narrowed, the ear lobes are small;
- Infants may have small ears;
- visually reduced chin;
- the back of the head may be flat, as if flattened;
- the baby may have an extra fontanel on the head; this maternity feature soon goes away, although in some cases the fontanel, both additional and in the usual place, may not close for a long time.

Mouth:
- the mouth is relatively small, the jaw is also small,
- the mouth may be open for a long time (this is not a very characteristic sign, it can also occur in healthy children);
- the palate in the mouth of a newborn with Down syndrome is narrow, similar to an arch;
- the tongue appears large (due to a relatively small mouth) and may stick out of the mouth (due to weakened muscle tone);
- The tongue may have small folds in the form of grooves, which tend to increase with age.

Methods for diagnosing an abnormality in an infant
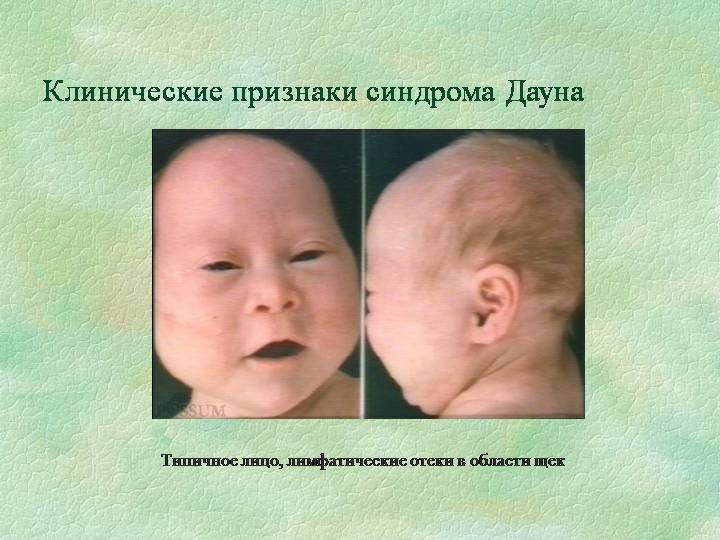
Common signs of Down syndrome in newborns are determined by the shape of the skull
The development of a pathology characterized by an incorrect number of chromosomes can be determined in the early stages of pregnancy (12-14 weeks), then the woman can terminate it. Using ultrasound diagnostics, the presence of a cervical fold and the size of the nasal bone are determined.
A more reliable way to determine Down syndrome in an infant is through a special blood test. If necessary, amniotic fluid is monitored, and if risks to the fetus are identified, additional studies are prescribed.
Children say! Timokha (4 years old) is going to the store with his grandmother, put on a backpack and says: “Grandma, I’ll walk harder.”
Limbs
Down syndrome - features of the appearance of hands and feet in newborns.
- decreased muscle tone;
- joints have strong mobility, which can lead to dysplasia (partial or complete dislocation of joints);
- legs and arms may be shorter than those of peers;
- the fingers may have underdeveloped middle phalanges, while the fingers may look short, the palm visually appears flat and wide;
- the little finger has a slight curvature towards the ring finger;
- there may be a fold on the palms that runs horizontally;
- a so-called sandal-shaped gap is formed on the toes - the big toe is somewhat distant from the others;
- There may be a crease on the foot under the big toe.

Less common signs
Down syndrome (signs in newborns very often appear already in infancy) can be diagnosed based on other indicators. Among them:
- Small mouth and arched narrow palate.
- Weak tone of the tongue: it constantly protrudes from the mouth. Over time, wrinkles may form on it.
- A small chin, as well as a short nose and a wide bridge of the nose.
- Short neck.
- A horizontal crease may form on the palms.
- The big toe is located at a great distance from the others. And on the foot underneath there is a fold.
These signs of Down syndrome in a newborn may not appear immediately, but as they grow older. By the way, with age, a child often begins to develop problems with the cardiovascular system.
Organism
The body of a newborn with Down syndrome:
- the baby’s height and weight are lower than those of other newborn children; in the future there may be a tendency to become overweight;
- children with Down syndrome are often diagnosed with heart defects (about a third of children), but in most cases this can be solved with a simple operation; the main thing is not to overlook heart problems;
- the chest may have a special structure, which consists of both possible protrusion (the so-called keeled) and possible recession (funnel-shaped);
- epilepsy attacks are possible;
- defects of the digestive system, for example the duodenum, which may suffer from stenosis (reduction of the lumen of the initial part of the small intestine) or atresia (a developmental abnormality that occurs in the first trimester of development in the mother’s tummy and is characterized by complete internal closure of the lumen of the duodenum);
- intestinal obstruction is possible, which can manifest itself in the first days after birth and is manifested by vomiting after eating, in which case examination is necessary, and, if necessary, surgical intervention;
- food mixed with digestive juices can return to the esophagus (the so-called food reflux), to avoid this, you need to feed the child in small portions, but often, so that the baby does not feel hungry;
- organs of the genitourinary system may have malformations;
- perhaps one of the most severe consequences of Down syndrome is leukemia (blood cancer), manifested by severe hemorrhages in the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs, blood is possible during vomiting or in the stool, treated with chemotherapy;
- weakened immunity - children are prone to bronchitis and pneumonia;
- reduced resistance to disease leads to possible frequent infections of the pharynx and tonsils; children can often suffer from sore throats, which cause complications for the entire body; if necessary, treatment is carried out with antibiotics; hardening of the body is also necessary;
- there may be an episyndrome - seizures, which are similar in symptoms to epileptic seizures, can occur after stressful situations and infectious diseases;
- the thyroid gland may not secrete the required amount of hormones, which may cause sluggishness and a tendency to obesity;
- possible apnea - cessation of breathing during sleep, to prevent this from happening, you need to try to have the child sleep on his side, at least for a while, when the muscles of the pharynx and tongue are stronger;
- There may be hearing impairment associated with improper development of the auditory ossicles or due to inflammatory diseases.

In order for a child to develop normally, consultations are needed with a local pediatrician (identifying pathologies), a neurologist (prescribing physical therapy, massages, physiotherapeutic procedures), an ophthalmologist (identifying early vision problems), an ENT specialist (audimetric examination of hearing power), an endocrinologist (checking the functioning of the thyroid gland). and other glands), a speech therapist (eliminates speech difficulties), a psychologist (an experienced specialist will know how best to act so that the child develops quickly), there are also various rehabilitation centers for children with Down syndrome.
Features of development
Children with the syndrome develop well; they need to work harder than their peers to achieve the same result. A child has its own advantages that need to be used in upbringing:
- They perceive objects well visually, and they are especially good at analyzing details. If you teach a child from the first days, even when he seems to understand nothing, for example, show cards with images, numbers, letters, he will study them quite successfully. And in the future, in studies, the emphasis should be on clarity - teaching with the help of pictures, gestures, and signs.
- Surprisingly, they quickly master reading. They can also understand the text well, learn passages by heart, and practically use useful information from the book.
- They are observant - they adopt skills if they have a clear example from their peers, so you need to communicate more with kind and talented children, take them to concerts.
- Children have different talents; in the future they should be enrolled in creative clubs for dancing, singing, and handicrafts. Moreover, they are quite capable of working with ordinary children. Due to perseverance, they can do much better than their peers. In the future, such activities may develop into a profession and become the basis for independent income, which can sometimes be quite significant.
- Children can develop well physically and be much stronger than their peers - swimmers, fighters, gymnasts, bodybuilders - this is not a complete list of sports that people with Down syndrome engage in. Many athletes receive medals at the Paralympic Games, and along with them, substantial prize money.
- Children are very observant, they understand people’s feelings well, and are ready to emotionally support another person. They are prone to empathy - strong emotional experiences that allow them to feel the psychological state of another person, sympathize with him and even have compassion with their neighbor.
- A very important advantage is that children with the syndrome master computers well. Combined with perseverance and, possibly, a large reserve of time, computer knowledge can become the basis of an Internet profession, remote earnings. You just need to be careful, because children with Down syndrome may have vision problems.
Symptoms of Down syndrome can manifest themselves in behavior, but the features can be minimized, since children study well and master information, you just need to make an effort.

Down syndrome: signs in newborns
The term “syndrome” in medicine means a set of symptoms that appear in a certain human condition. In 1866, scientist and physician John Down grouped a complex of symptoms in a certain group of people with this disease. The syndrome is named after this man.
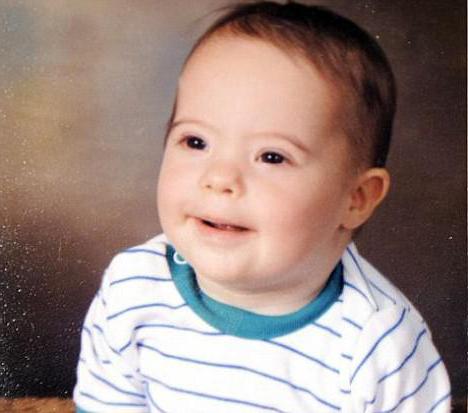
Most often, signs of Down syndrome in a newborn are noticeable immediately after birth. Such children, unfortunately, are born quite often. For every seven hundred newborns, there is one child with Down syndrome. However, most babies show the same signs:
- The face is slightly flattened and flat. The back of the head has the same shape.
- A skin fold can be seen on the neck.
- There is decreased muscle tone.
- The baby has an oblique cut, and their corners are raised. A “Mongolian fold” or the so-called third eyelid is formed.
- The child's limbs are short when compared with other children.
- His joints are very mobile.
- The fingers are the same length, so the palm appears wide and flat.
- The child is small. Most often, excess weight appears with age.
These features characterize Down syndrome. Almost all signs are associated with deformation of the skull and facial features, as well as with disorders of bone and muscle tissue. However, there are other signs. They don't happen that often.

Studies
Features of children with the syndrome:
- They give preference to the study of small details; they do not study the holistic image so carefully. They master the features of shapes, colors, and love to watch their peers. They quickly learn to identify the characteristics of objects and can sort them.
- Children may have subtle vision problems. Even if everything is fine with the eyes, you need to watch TV carefully, and children can also study on the computer for a short time.
- When children with the syndrome learn to read, they can expand their horizons with the help of useful texts. They love to write, and sometimes it is easier for them to give a written explanation than to talk about an event in detail.
- Children have underdeveloped short-term auditory memory. Because children's speech is slow, their memory for sentences is structured in such a way that it is difficult for them to perceive speech that is too long or too fast. This leads to the fact that, if they are instructed, they have difficulty following complex instructions, and it is also difficult for them to understand a long text read, or to count in their head. But this insufficiently developed short-term auditory memory is easy to train - teach the child phrases, first for a few words, then for a few sentences.
- Down syndrome in a child does not affect all areas of development. Spatial and visual memory is the same as in healthy people. When learning new words, educational material should be accompanied by a picture of an object or a demonstration of an action. You can do something and comment on everything that happens - “I pick up a pencil,” “I draw a red line,” “I make the bed,” and so on.
- Children may have problems concentrating, short-term memory, and analyzing material. These characteristics of the child lead to difficulty in mastering mathematical theoretical material. In order to teach a child to count orally, you need counting material - matches, sticks, pencils, cubes.
Children can be very diligent in learning, but they think more slowly, and they learn better when they are clearly shown what exactly needs to be done. After long training, theoretical perception of knowledge can improve significantly.