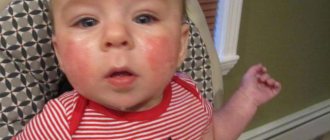
Jaundice in newborns - In the past, elevated bilirubin in infants was much less common than it is now.
Today, such a deviation is diagnosed in 70% of newborns. Although jaundice is a very unpleasant diagnosis, there is no need to panic. It is enough just to listen to the doctor’s recommendations and do everything to make the baby recover faster. Moreover, after just 5-7 days of therapeutic procedures, the condition will stabilize and the pathological symptoms of the newborn baby will completely disappear. [Hide]
Content
- Bilirubin: General information about the pigment
- Why do bilirubin levels increase in a newborn?
- Diagnosing elevated bilirubin
- Standard indicators of bilirubin
- Physiological jaundice in newborns: Symptoms
- Can jaundice occur from breast milk?
- Symptoms of pathological jaundice in newborns
- Why is pathological jaundice dangerous in newborns?
- Treatment of jaundice in newborns
- Conclusion
Treatment and consequences
Treatment tactics and possible consequences are determined after diagnosing the pathological condition and assessing the general threat to the child’s body.
This is how phototherapy is performed on a newborn baby in the maternity hospital.
Common destination options are:
- phototherapy for jaundice in newborns (treatment with a special lamp, the light of which helps accelerate the breakdown of bilirubin;
- fresh air and sunlight to produce certain substances that can accelerate the process of decay and release of a specific pigment;
- the use of glucose, which optimizes liver functionality and promotes the breakdown and elimination of harmful bases;
- activated carbon, Hofitol or Smecta for jaundice in newborns are used only on the recommendation of a doctor, if there is an urgent need for it.
In discussing such a seemingly harmless problem as jaundice, it is believed that the main thing is to distinguish between both processes . The pathology requires careful therapy, and sometimes even surgery, but if its cause is a simple process of adaptation, no medications are needed.
Bilirubin: General information about the pigment
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is a byproduct of the breakdown of red blood cells.
Red blood cells circulate through the bloodstream and are responsible for normal gas exchange rates in the body. They consist of the protein compound hemoglobin, which supplies all cellular structures with the oxygen molecules they need for normal functioning. After delivery is completed, hemoglobin picks up the carbon dioxide produced by the cells on the way back.
The breakdown of red blood cells is normal. Red blood cells that have spent their time are disposed of, and they are replaced by new red blood cells. The blood of an unborn baby contains fetal hemoglobin cells, which are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body of the fetus in the womb until it is born and the lungs take over this function. When the baby is born and breathes, fetal hemoglobin will be replaced by normal hemoglobin. Hemoglobin found outside red blood cells is toxic. To neutralize it, a series of transformations occur in the body, as a result of which bilirubin is formed.

Which children are prone to jaundice?
Jaundice in the maternity hospital is common in newborns, but not in all. When is physiological jaundice most likely to appear:
- in case of multiple pregnancy,
- in case of prematurity,
- if your mother has bad habits,
- with a lack of iodine in a woman’s body during pregnancy,
- during traumatic births,
- when using labor stimulants,
- with mother's diabetes.
If signs of jaundice persist in children older than 1 month, this may indicate the development of pathological processes:
- genetic diseases,
- complications of postpartum injuries,
- infection of the baby during or after childbirth,
- diseases of the bile ducts,
- severe liver diseases.
To establish the true cause of jaundice in a child, you must consult a doctor . There may be no cause for concern and the yellowing of the skin is caused by breastfeeding jaundice. Pregnane jaundice occurs due to increased levels of the hormone prenandinol in the mother’s body. During lactation, it passes into breast milk, and during feeding - into the baby’s body. Such prolonged jaundice in a newborn is easy to treat; it is enough to wean him from the breast for 2-3 days. Pregnane jaundice can also occur in older babies, when they are already 2 months old, but this type of jaundice no longer occurs in three-month-old children.
Jaundice in a one-year-old child usually has the same signs and causes as in adults and requires mandatory treatment.
Why do bilirubin levels increase in a newborn?
Bilirubin is divided into direct and indirect. During breakdown, hemoglobin is synthesized into indirect hemoglobin, which does not dissolve in liquid and is not excreted from the body. It combines with albumin and, together with the blood, enters the liver, where it is transformed into direct hemoglobin, which is excreted from the body along with urine.
In a newborn, the liver's enzymatic system only works halfway, so it is unable to quickly remove unnecessary fetal hemoglobin from the body. Therefore, indirect hemoglobin remains in the child’s body for some time. It is for this reason that the normative indicators of the bilirubin index in the blood of a newborn baby are much higher than a month after birth. If the child’s liver is not functioning properly, bilirubin turns the skin and mucous membranes yellow. This condition is called physiological jaundice in a newborn.

Mechanism of development of jaundice
Why does a newborn baby hiccup and spit up after feeding?
Elevated bilirubin levels in newborns are associated with the destruction of fetal hemoglobin. It is released in large quantities into the bloodstream as the baby passes through the birth canal. The launch of the bilirubin conjugation system normally occurs within a period of several hours to several days after the baby is born.
Jaundice syndrome in newborns can occur with infections or hemolytic disease. If we talk about physiological jaundice, then, from a medical point of view, this situation is considered not as a syndrome or an independent disease, but as a period of adaptation of the child to new conditions.
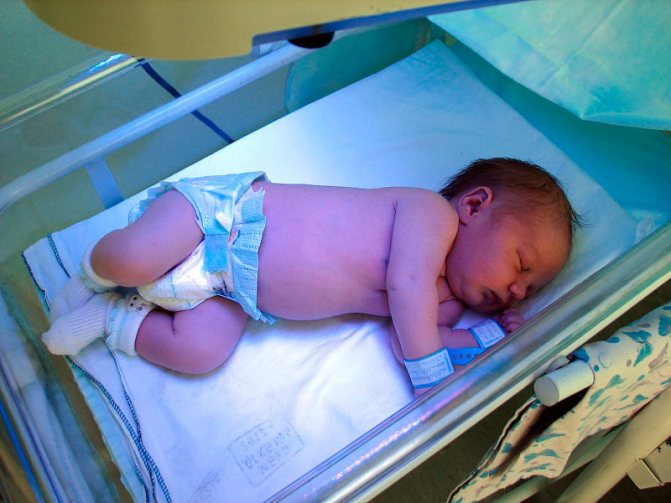
Treatment of jaundice in newborns using a lamp
Diagnosing elevated bilirubin
After the baby is born, umbilical cord blood is immediately taken and tested for bilirubin levels. If the baby is full-term, after two days blood is taken from a vein and the test is repeated. In premature babies, repeated bilirubin screening is carried out every other day. Further monitoring of this pigment is carried out every twelve hours. Since premature babies have too fragile and fragile blood vessels, blood is drawn from the parietal-temporal vein, located on the baby’s head.
Parents should not be afraid of this procedure, since the vein is quite large and the skin in this area is thin. In addition, the procedure is absolutely safe and brings much less discomfort if blood was taken from a vein in the arm or leg. It is also worth considering that the diagnosis is carried out by experienced staff trained in working with newborns.
However, there is also a bloodless test for bilirubin. For this purpose, special equipment is used, which is applied to the baby’s forehead and, based on the color of its skin, determines the quantitative indicators of bilirubin in the bloodstream. This technique is mainly used in those children who do not have pronounced signs of jaundice. The advantages of this test are its non-invasiveness, painlessness, safety and instant results. During the treatment of a baby with jaundice, pediatricians regularly monitor the bilirubin index until it returns to normal.
The disadvantage of the bili test is the ability to determine only total bilirubin without dividing it into indirect and direct, which is extremely important when diagnosing jaundice in a newborn. After the baby is discharged from the hospital, bilirubin will continue to be measured for another month to ensure that the baby’s condition has normalized.
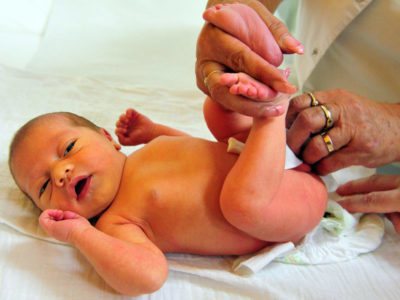
Diagnosis of physiological jaundice in newborns
Jaundice is detected while the child is in the maternity hospital by a neonatologist or pediatrician when visiting a newborn shortly after discharge.

The Cramer scale is used to visually assess the degree of jaundice in newborns.
- I degree – jaundice of the face and neck (bilirubin 80 µmol/l)
- II degree – jaundice extends to the level of the navel (bilirubin 150 µmol/l)
- III degree – jaundice extends to the level of the knees (bilirubin 200 µmol/l)
- IV degree – jaundice extends to the face, torso, extremities, with the exception of the palms and soles (bilirubin 300 µmol/l)
- V – total jaundice (bilirubin 400 µmol/l)
The necessary laboratory tests for the primary diagnosis of jaundice in newborns are: bilirubin and its fractions, complete blood count, blood group of the child and mother, Coombs test, IPT, general urine test, liver tests.
If hypothyroidism is suspected, it is necessary to determine the thyroid hormones T3, T4, and TSH in the blood. Detection of intrauterine infections is carried out by ELISA and PCR.

As part of the diagnosis of obstructive jaundice, newborns undergo ultrasound of the liver and bile ducts, MR cholangiography, FGDS, plain radiography of the abdominal cavity, consultation with a pediatric surgeon and pediatric gastroenterologist.
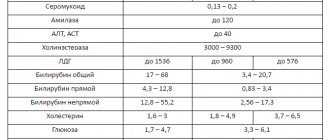
Standard indicators of bilirubin
After the baby is born, bilirubin levels constantly change depending on the baby’s age. In full-term and premature babies, bilirubin levels will be different. The table below will help you understand them.
| Age category of the baby | Standard indicators of the bilirubin index for full-term infants | Standard indicators of the bilirubin index for premature infants |
| day | up to 85 µmol/l | up to 97 µmol/l |
| 36 hours | up to 150 µmol/l | up to 120 µmol/l |
| two days | up to 180 µmol/l | up to 150 µmol/l |
| from the third to the fifth day | up to 256 µmol/l | up to 171 µmol/l |
| from the sixth to the seventh day | up to 145 µmol/l | up to 145 µmol/l |
| eighth - ninth day | up to 110 µmol/l | up to 97 µmol/l |
| from the tenth to the eleventh day | up to 80 µmol/l | up to 50 µmol/l |
| twelfth - thirteenth day | up to 45 µmol/l | up to 35 µmol/l |
| over fourteen days | up to 20.5 µmol/l | up to 18 µmol/l |
Pediatricians use these indicators to determine the normal bilirubin index in newborns.

Features of the development of jaundice in babies
With physiological jaundice, the baby’s stools do not change color, the baby sucks milk well, and steadily gains weight.
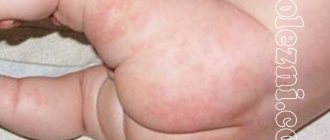
Pathological types are immediately determined by the special symptoms of jaundice in newborns:
- bright orange skin color;
- loss of appetite or complete refusal of breastfeeding;
- eye rolling;
- monotonous scream;
- compaction of the tummy in the liver area;
- arching of the body;
- increased drowsiness
- convulsions,
- frequent regurgitation;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- lightening of stool;
- darkening of urine;
- enlarged spleen.
Pathological types require immediate treatment. The condition is assessed according to the severity of neonatal jaundice using the Cramer scale. There has been a relationship between the concentration of pigment and changes in the color of the skin of babies
Cramer scale
| Degree | Bilirubin concentration µmol/l | Newborn jaundice zone |
| I | 80 | face, neck |
| II | 150 | upper body to navel |
| III | 200 | upper body to knees |
| IV | 300 | Only the palms and soles of the feet do not turn yellow |
| V | 400 | total pigmentation |
Physiological jaundice in newborns: Symptoms
Signs of jaundice appear in the baby on the fourth day after birth. If there are no serious problems with the liver, then the symptoms disappear on their own after three weeks. The skin with increased bilirubin has a slight yellowish tint, but this does not affect the baby’s health at all, he has a normal appetite, he is not lethargic, he does not have drowsiness and he does not refuse the breast.
Jaundice may develop in newborns if:
- During pregnancy, the mother was diagnosed with pathologies that required taking various medications;
- The woman had a multiple pregnancy;
- During pregnancy, the expectant mother drank alcohol or smoked;
- The baby was born premature;
- During childbirth or during pregnancy, fetal hypoxia was diagnosed.
Physiological jaundice is not classified as a pathological condition. However, when its symptoms appear, the newborn is carefully monitored to prevent the transition of the physiological type of jaundice to pathological.
Jaundice in newborns: Epilogue
Despite the fact that the child is entirely yours, it is not you who should decide what to do with him if he turns yellow. And the health workers. And deal with it.
Find out whether your baby’s jaundice is dangerous (that is, is it a symptom of a serious illness?) or completely harmless, treat it or be patient and just wait, and if treated, then in what way - only a pediatrician can decide all these questions. Your task is to present your newborn to him for examination and tests.
Because in the case of jaundice in newborns, the probability of making a mistake is very high: a completely normal physiological state can be mistaken for a symptom of a serious illness, and vice versa. Are you really ready to guess if the health of your beloved, “golden” in every sense of the word, baby is at stake?
Can jaundice occur from breast milk?
In some cases, yellowing of the skin appears only a week after birth. Often, such manifestations are characteristic of those children who experience rapid weight gain. Mothers of such babies produce a lot of milk, which contains a large amount of the female hormone estrogen due to the physiological characteristics of the female body after childbirth.
Estrogen in milk interferes with the natural excretion of fetal bilirubin from the baby's body. If the bilirubin index does not drop, then the mother will need to express her milk, warm it up to 70 degrees, cool it, and only then give it to the little one.
During heating, the hormone is destroyed, but the composition and nutritional value do not change. By heating the milk, you can eliminate the negative effect of maternal hormones on the baby’s body without interrupting breastfeeding. Young mothers should take into account that often in the maternity hospital they do not bother with expressing and warming milk, recommending that they immediately switch the baby to infant formula.
This is fundamentally wrong. Since hormonal changes in the female body will end in a couple of weeks, but maintaining the possibility of breastfeeding after such a break is unlikely to be possible. Therefore, a woman should monitor this herself and not give up breastfeeding to please doctors, depriving her child of a useful product that will help maintain health and support immunity.

Types of Jaundice
- Physiological jaundice of newborns (neonatal jaundice or hyperbilirubinemia)
This is a natural condition that appears at birth and goes away in infants without medical intervention. You need to trust your doctor to distinguish physiological jaundice from pathological jaundice. The first symptoms of jaundice are usually observed on days 1-3 of the baby’s life (maybe later). Transient (temporary) jaundice develops in 50-70% of newborns, while an increase in the level of indirect bilirubin is found in all. Anemia and enlargement of internal organs are not diagnosed.
The skin may turn lemon-colored.
With neonatal jaundice, quite often there is an increased level of estrogen in mother's milk, which is passed on to the baby during breastfeeding. In this case, estrogen is excreted first, and then bilirubin.
How long does jaundice last in newborns? If jaundice in a baby has only physiological causes, then it lasts 7-10 days, but if it is caused by hormonal disorders in the child’s mother, then this condition is longer and can persist even in one-month-old children. The condition can last up to three months.
It is not recommended to stop breastfeeding if the general condition of the newborn is not disturbed - he has excellent sleep, the sucking reflex is active, and weight gain is not below normal.

- Pathological jaundice
This is a critical condition characterized by damage to body cells and loss of reflexes.
- Mechanical - caused by blockage of the bile ducts.
- Hemolytic - this congenital jaundice is less common and is diagnosed in the first hours of life. It occurs for various reasons, except mechanical ones - liver dysfunction, Rh conflict, viruses, bacteria, etc.
After recovery, children must be observed over the next year by an ophthalmologist, neurologist and orthopedist. You must follow the doctor's recommendation - not to vaccinate for 1 year.
Symptoms of pathological jaundice in newborns
Pathological jaundice, unlike physiological jaundice, is a dangerous condition for a newborn. It is diagnosed when the bilirubin index exceeds the established norm.
Pathological jaundice in newborns can develop due to:
- Viral hepatitis or other infectious pathologies of the liver;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Rhesus conflict between mother and baby;
- Intestinal obstruction in a newborn;
- Genetic failures that lead to the destruction of red blood cells;
- Mechanical jaundice, developed due to impaired outflow of bile;
- Dysfunctional processes in the liver;
- Cephalohematomas in an infant.
Symptoms of pathological jaundice appear in a newborn on the first day after birth and are presented by:
- Increased bilirubin index, which exceeds standard values or reaches critical values;
- Intensely yellow colored skin, including the palms and soles of the feet;
- Dark urine and colorless feces;
- The presence of a confirmed Rh conflict between the newborn and his mother;
- Protracted or wavy jaundice.
An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a pediatrician after analyzing the medical history of the baby’s mother, the symptoms of the newborn’s illness and the diagnostic results.

Physiological jaundice in newborns is within normal limits
But jaundice in newborns is most often a physiological norm. The bottom line is that a child, barely born, has a very high level of hemoglobin, which begins to decline sharply in the new conditions of the baby’s life. In addition, a newborn baby has a not yet fully formed “army” of liver enzymes. In other words, in the first days of life, the newly born baby is simply physically unable to cope with the high level of bilirubin in her blood. That is why the baby is rapidly turning yellow.
At least 60% of absolutely healthy full-term newborn babies turn yellow on the second or third day of life. This is normal and does not threaten the child with any harm. In medicine there is even a term - physiological jaundice of newborns. Physiological means natural, normal, without pathology.
So, even if you are in this 60%, there is no reason to be afraid. And if it happens that the child was born premature (which means that he has even fewer capable liver enzymes than a healthy toddler), then you have an even greater chance of admiring his yellow color - 80-90% of all babies born prematurely , experience physiological jaundice of newborns.
]premature babies[/anchor] at risk for jaundice in newborns are babies whose mothers have diabetes, as well as twins (twins, triplets, etc.)
Normally, jaundice in a newborn baby should go away within two to three weeks. But what to do in cases where the child turns yellow naturally, but doesn’t seem to be going back to pink, even after three weeks?
Why is pathological jaundice dangerous in newborns?
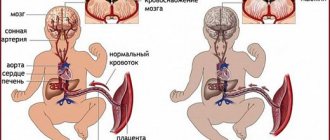
In newborns, the blood-brain barrier works only at half its capacity, so it cannot fully retain toxic and other dangerous substances, preventing them from entering the brain. It is for this reason that increased bilirubin is not filtered, but passes through this barrier and enters the child’s central nervous system and brain through the bloodstream. It has a toxic effect on the nervous system, which is called bilirubin encephalopathy or kernicterus.
Already from the first day after birth, a baby with kernicterus appears the following symptoms, presented:
- Enlarged spleen and liver;
- Decreased sucking reflex or its complete absence;
- Low body weight;
- Decreased blood pressure levels;
- Excessive activity or, conversely, drowsiness and apathy;
- Convulsive syndrome.
Pathological jaundice in newborns requires properly selected and timely therapy. This pathology is extremely dangerous for the entire body, and especially for the brain. If help is not provided to the baby, then by the age of six months he will show signs of delayed mental and physical development. Hearing problems and possible paralysis will also be diagnosed.
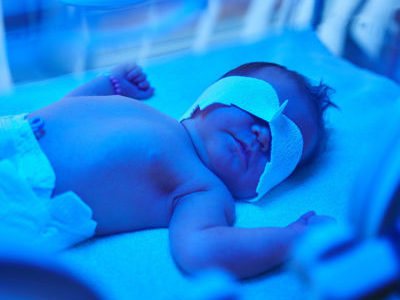
Treatment methods for jaundice in newborns
It is not entirely correct to talk about the treatment of jaundice itself in the context of newborns - since this, as has already been said fifty times, is not a disease, but only a symptom.
If jaundice is a symptom (indicator or consequence) of some serious disease, then, naturally, it is not jaundice that is treated, but this very disease. But no disease can be cured overnight, and there are situations when, simultaneously with therapy, it is necessary to reduce the level of bilirubin in the blood, which is dangerously “creeping” to a critical level.
Even 15-20 years ago, in a situation where the level of bilirubin became alarmingly dangerous and could cause irreparable damage to the baby’s central nervous system, the child was given an exchange blood transfusion.
Today, this method of treating jaundice in newborns is also used, but only in extreme cases. And in less severe situations, over the last decades they have been practicing another effective method of combating increased bilirubin - a bright lamp!
Treatment of jaundice in newborns
The selection of therapy and its implementation should only be performed by a doctor in a hospital setting. The prescribed treatment will depend on the reasons that led to the increase in bilirubin index.
To relieve the manifestations of jaundice, the following methods are often prescribed:
Phototherapy is the main and most effective therapeutic technique used to relieve jaundice in newborns. The baby is placed under a special lamp, the light of which allows the bilirubin to be transformed into lumirubin, which is non-toxic and is excreted from the body within twelve hours.
During the procedure, a special bandage is put on the baby's eyes to protect them from light. After the procedure, you may experience dryness and flaking of the skin, drowsiness and loose stools. Therapy is carried out in several approaches with breaks of three hours. Typically, light therapy takes two days, after which the child experiences a decrease in the bilirubin index to normal levels.
Intravenous infusions of detoxifying drugs or glucose to promote the removal of bilirubin . This measure is considered emergency. The administered drugs improve the fluidity of bile, which promotes its accelerated excretion and improves the condition of the toddler.
Early and frequent breastfeeding of the newborn . This technique helps loosen the baby's stool due to the consumption of colostrum. Thus, meconium with a high content of bilirubin will quickly leave the baby’s intestines and reduce the bilirubin index to normal. However, it is important to do everything in a timely manner.
The doctor will decide which of the above methods to eliminate jaundice, taking into account the symptoms, complexity and type of jaundice in the newborn.

What is neonatal jaundice?
In the womb, instead of bilirubin, fetal hemoglobin circulates through the blood of the baby. When he begins to breathe on his own, a restructuring of the body occurs. About 1% of red blood cells are renewed daily, and when they break down, bilirubin is released. When it reacts with an enzyme produced by the liver, it becomes water-soluble and is excreted from the body through the bile ducts.
If for some reason bilirubin does not pass from indirect to direct form, it begins to accumulate in adipose connective tissue, and skin pigmentation occurs. What is newborn jaundice: this is a symptom that indicates the immaturity of the baby’s liver or pathology.
Physiological disturbances disappear within a month. When enzyme production is normalized, pigmentation disappears without medical intervention. But in pathologies, when too many red blood cells die or fermentation does not normalize in any way, jaundice persists for a long period.
The child becomes bright orange and capricious. In this case, he urgently needs treatment. Bilirubin is poisonous, dangerous in high concentrations, and affects the brain. Disorders of the central nervous system are irreversible.
Bilirubin norms by age
Bilirubin is a bile pigment formed as a result of the destruction of proteins - hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochrome. The process occurs in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Exceeding threshold values may indicate increased destruction of red blood cells, or failure of excretion from the body as a result of pathology. In a newborn, a test for bilirubin levels is taken from the umbilical cord immediately after birth.
The bilirubin levels of a newborn and an adult are different. The table presents age characteristics.
| Age | Norm, micromoles per liter |
| Days from birth | 34 or less |
| Two days | 24-149 |
| From three to five days | 26-205 |
| From five days to sixty years | 5-21 |
The indicator can increase to 256 micromoles, 324 is considered an alarming signal. For premature infants, the norm is lower. Doctors become concerned at levels of 150-250 micromoles.
This is interesting: Jaundice in newborns: what is it, causes, timing of the disease and consequences