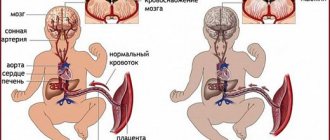
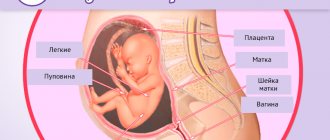
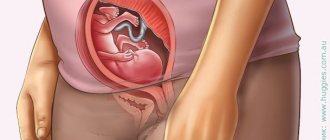
An embryo develops in the uterus in early pregnancy. It is protected by a thin film of the fertilized egg - the chorion, which during normal development is transformed into the placenta.
If during this period there is a failure in the development of the embryo, the embryonic egg is separated from its chorion film. The detachment site fills with blood. This pathology is called retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy. It can cause fetal development to stop and be lost.
What is retrochorial hematoma
Ultrasound can detect hematoma during pregnancy. In the photo taken by an ultrasound diagnostic device, the characteristic darkening, as well as the deformation of the fertilized egg, is clearly visible.
A retrochorial hematoma develops during a singleton pregnancy at 5-7 weeks and in cases where a woman is pregnant with twins. Pathology can be suspected by the appearance of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, brownish or scarlet discharge. If a woman discovers these symptoms, she should immediately consult a doctor.
In addition to retrochorionic pathology, there are:
- subchorionic - it poses a serious threat to the fetus, surrounding the placenta;
- retroamniotic - timely detected formation, subject to adequate therapy, does not pose a threat to the developing baby;
- retroplacental - it is formed after the formation of the placenta, after 16 weeks of pregnancy;
- subamniotic - its presence is not dangerous for the baby, but requires regular monitoring;
- intrauterine - the presence of such a hematoma carries a serious risk to the fetus and requires urgent treatment.
Symptoms that can help determine the onset of a dangerous problem

Retrochorial hematoma during early pregnancy signals its presence by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, the pain is nagging in nature. Sometimes the lower back may hurt, but this is an apparent sensation; in fact, the pain radiates to the back.
The second sign is that more often spotting, less often moderate, bloody discharge appears. By the appearance of the discharge one can judge the size of the problem and the degree of its danger:
- A bright red discharge indicates that the cavity filled with blood is growing and has reached a size that threatens the detachment of the amniotic sac. Such discharge is accompanied by cutting pain and a sharp decrease in blood pressure. The situation is extremely dangerous and requires immediate hospitalization of the woman.
- Dark-colored smears, almost burgundy, indicate that the blood clot is dissolving. If the phase of bright discharge passed by and dark discharge immediately formed, this is a favorable sign, which means that the danger of losing the child is negated.
A large percentage of pregnant women generally do not observe traces of biological fluid on their underwear. However, pain as during menstruation and/or in the lumbar back should alert you and force you to urgently consult a doctor.
The course of a retrochorial hematoma can occur, in general, without the manifestation of minor symptoms. A woman can only learn about the danger during a routine ultrasound or from the results of a blood test: the doctor must be wary and prescribe an additional examination if the level of protein responsible for blood clotting is elevated in the blood.
We also recommend reading: Taste in the mouth during pregnancy
What determines the presence or absence of discharge?
If a retrochorial hematoma during early pregnancy is not accompanied by discharge, this means that the detachment occurred in the upper part of the uterus, and it can only be determined by ultrasound.
Bruising (a smear on your underwear is enough) indicates an early stage. Blood may continue to accumulate in the cavity, which will increase in size, and then there will be more discharge.
Danger for the expectant mother and baby
If a dangerous condition is detected on time, the woman has a great chance of recovering and saving the baby. With the normal further course of pregnancy and adequate therapy, the blood clot that has collected behind the membrane resolves within a month and is not detected on a subsequent ultrasound. This applies to pathologies whose blood clot volume does not exceed twenty milliliters.
The greatest danger comes from retroamniotic hematoma, or retroamniotic hematoma, as it is called. This is hemorrhage between the amniotic sac and the wall of the uterus. It is dangerous because it is accompanied by bleeding and threatens the mother with blood loss.
Any unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen or spotting during pregnancy require attention from the woman and specialists. They may be a sign of retrothecal hematoma. To diagnose the condition, a blood test is ordered and one or more ultrasound examinations are performed.
If the hemorrhage occupies about half the surface of the separation of the uterine wall and the chorion, and the volume of blood accumulated in it exceeds twenty milliliters, there is a high probability of a frozen pregnancy.
Even if the disease was stopped at an early stage and the blood clot has resolved, the risk to the fetus still remains. The subsequent formation of placental insufficiency, its premature “aging”, a reduction in the amount of nutrients supplied to the baby, the development of hypoxia, as well as the birth of a low-weight baby are possible.
Discharge from hematoma
Very often on women's forums you can read a story that a woman has some strange brownish discharge due to a hematoma, but she does not want to go to the doctor and asks for advice from all friends and strangers. We will not analyze the reasonableness of this approach. It is very difficult even for the most experienced doctor to identify a disease without appropriate tests and additional examination and questioning of the patient. These symptoms may be caused by a banal infection, but at the same time it may be discharge that is characteristic of a hematoma. But this is no longer a joke!
Discharge from hematoma - causes
This type of hematoma occurs in pregnant women when the fertilized egg is rejected from the chorion or, more simply, from the uterus. The cavity that appears is filled with blood, which coagulates - this is where the so-called retrochorial hematoma occurs. The reasons why discharge occurs during a hematoma are very diverse: inflammation of the genitourinary system caused by infection, severe toxicosis in the last months of pregnancy, and high blood pressure. There is also an opinion that injuries, even minor ones, received by the expectant mother are to blame.
But, in any case, the process of discharge during a hematoma is quite dangerous for the life of the unborn baby, because the hematoma impairs the supply of nutrients to the baby and can cause premature birth.
Symptoms of hematoma
Discharge from a hematoma indicates the severity of the disease. With a mild form, which the expectant mother practically does not notice, no discharge is observed. With a moderate hematoma, bleeding and discharge may occur. During examination in the hospital, irregularities in the child’s heartbeat rhythm are determined. Severe forms of the disease are necessarily accompanied by bleeding. In this case, the woman experiences severe pain in the lower abdomen, and loss of consciousness is possible.
Treatment of discharge from hematoma
If you observe discharge during a hematoma, you should in any case go to the hospital. In case of moderate or severe form of the disease, drug treatment of hematoma during pregnancy is carried out, which is not dangerous for the baby. You also need to follow some simple tips:
1.
Eliminate legumes and all kinds of foods that cause gas. This will reduce pressure on the uterus.
Why does the disease occur?
Causes of retrograde hematoma:
- a change in hormonal levels in a woman’s body, provoked by bearing a baby;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- severe toxicosis of pregnant women;
- blood pressure surges, hypertension;
- severe nervous stress;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- the presence of pathologies in the uterine cavity;
- addiction to nicotine and alcohol;
- increased physical activity;
- the presence of a benign or malignant tumor in the expectant mother;
- autoimmune diseases;
- blood clotting disorder;
- overweight.
Why can a hematoma form in the uterus during pregnancy?
As a rule, such a problem appears under the influence of some unfavorable factor. It causes separation of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterus and the formation of a hematoma at the site of separation. Such an unfavorable factor in the early stages may include:
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Malfunctions of the nervous system (especially during stress, neuroses and similar conditions).
- Sudden changes in blood pressure.
- Strong physical activity.
- Injuries received.
- Infectious diseases.
- Having sex.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages.
How to identify a hematoma - symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease depend on the severity of the disease, its nature and stage. If the pathological changes are mild, the expectant mother may not be aware of their presence. They are detected only with the help of ultrasound diagnostics. Bloody discharge does not appear because blood cells are retained by the chorionic villi. This pathological condition passes without threatening either the pregnant woman or her baby.
The average degree of the disease is manifested by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, as well as brown discharge. If the color of the discharge is brown, the woman’s condition does not worsen, and the discharge does not change its color to scarlet, specialists are in no hurry to resort to treatment. This condition indicates that the retrochorial formation is in the stage of resorption, that is, it comes out on its own.
The severe form of retrocapsular hematoma is characterized by nagging pain in the lower abdomen with cramping attacks. The condition is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, bleeding begins. Loss of consciousness is possible. Emergency medical care and immediate hospitalization are required.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease directly depend on the type of hematoma, its size and location. For example, a hematoma on the fundus of the uterus practically does not manifest itself at all, and this is the danger of certain types and locations of hematomas.

If symptoms are present, they may manifest themselves as:
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of pain during menstruation;
- Abnormal red, brown, or bloody discharge;
- Lower back pain;
- General weakness and malaise.
With a severe form of hematoma, the condition of a pregnant woman can be critical:
- severe paroxysmal pain occurs,
- blood pressure drops sharply,
- there is a risk of fainting.
How a woman should behave if she is at risk of miscarriage is described in the video:
Tumor treatment
Treatment of retrotracheal hematoma is carried out under the strict supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist. His tactics come down to two directions: stopping bleeding, blocking tumor growth and its gradual resorption. At all stages of treatment of the disease, the use of magnesium drugs, antispasmodics (Nosh-Pa), which relieve uterine tone, as well as hemostatic agents, if necessary, is indicated (Ascorutin, Dicynon).
Often, the doctor prescribes mild sedatives (tincture of valerian) to stabilize the emotional state of the expectant mother. Patients are prescribed medications that improve uteroplacental permeability, as well as some homeopathic remedies. The form and dosage of all drugs is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease.

Mild forms of the tumor can be treated at home, but under the supervision of a doctor, without missing scheduled specialist appointments and mandatory tests. Inpatient treatment is preferable, since at home it is more difficult for a woman to comply with all instructions, especially adherence to bed rest.
The expectant mother must do a blood test throughout the entire period of bearing the baby to monitor fibrinogen levels. The severe course of the disease requires mandatory hospitalization.
During treatment, a woman must remain in bed, avoid physical activity, stress, and adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Working women are entitled to sick leave during treatment. The duration of therapy is determined by the severity of the condition. On average it ranges from one to three weeks.
Will a caesarean section be required?
The indication for delivery by cesarean section is a retroplacental formation that occurs in the later stages. If the diagnostic results indicate that the fetus is suffering from its presence, the operation is scheduled a little earlier than the expected date of natural birth.
How does a hematoma heal?
The fact that the hemorrhage is resolving is indicated by spotting or moderate brown discharge from the vagina. How long it takes for a retrochorial formation to emerge depends on the timing of its appearance and the size of the blood clot. On average, discharge lasts from 15 to 35 days. It is important to make sure that the appearance of discharge does not mean a missed pregnancy. The gynecologist who monitors the pregnancy and an ultrasound diagnostic specialist will tell you exactly how long the tumor will resolve.
Can a hematoma not come out?
The structure of the female pelvic organs in some cases does not allow the tumor to come out in the form of brown discharge. This is impossible when it is located high at the fundus of the uterus. In such cases, it slowly resolves without the threat of termination of pregnancy. You can read about this on pregnancy forums and read numerous reviews from those who had such a hematoma.
Hematoma during pregnancy
Causes of hematoma during pregnancy
Such a hematoma occurs if changes have occurred in the uterus, such as changes in the placenta, or damage to blood vessels. Such a change can appear after a variety of diseases of the reproductive system. Hematoma in pregnant women can also appear due to toxicosis in the later stages, various infections in the reproductive system, inflammation in the urinary system, inflammation of the uterus, ovaries and appendages. High blood pressure can cause blood to pool in the uterus. If such inflammation is not detected in time and treatment of a hematoma during pregnancy is not started, it can grow to enormous sizes. A hematoma in pregnant women causes terrible harm to the health of the unborn baby; it deforms the uterus and interferes with the nutrition of the fetus.
Forms of hematoma
Hematoma during pregnancy comes in three forms:
1.
A mild form of hematoma in pregnant women - a woman may not feel any discomfort at all; such a hematoma will not cause much harm if it does not begin to grow. It often happens that it is discovered after childbirth; a blood trail from such damage remains on the placenta.
2.
Moderate form of hematoma in pregnant women - this hematoma will definitely make itself known. A pregnant woman feels pain in the lower abdomen, and there may be bleeding. If you experience similar symptoms of a hematoma, you should not hesitate and consult a doctor. This hematoma significantly affects the baby's heartbeat.
3.
Severe form of hematoma in pregnant women - such a hematoma can be accompanied by severe pain and loss of consciousness, bleeding and a drop in pressure.
Childbirth in pregnant women with hematoma
If a woman develops a mild hematoma during pregnancy, the birth will take place naturally and without complications. The only thing that is recommended is that the doctor open the amniotic sac himself, and not wait until it bursts. If there is a suspicion that the baby is receiving poor oxygen or no oxygen at all, you cannot wait for a natural birth; this process must be accelerated. In some cases, the baby is removed from the womb by an obstetrician using special obstetric forceps. If it so happens that a moderate or severe hematoma has formed, the pregnant woman is prescribed a cesarean section ahead of schedule.
Consequences of the disease
From the moment a blood clot appears until delivery, the woman is under close medical supervision. If she strictly follows all the recommendations, the prognosis is positive. In most cases, with adequate and timely treatment, the blood clot comes out on its own or resolves without harming the growing baby.
Without timely medical assistance, a retrothecal hematoma during pregnancy leads to:
- intrauterine fetal death;
- uterine bleeding;
- miscarriage;
- abnormalities in child development;
- placental abruption at 8-9 months.

If no measures are taken, the bleeding will not stop, which means the tumor will increase in size, threatening the safety and normal course of the gestation period.
How to prevent hematoma - preventive measures
The appearance of this unpleasant complication can be avoided if the expectant mother leads a healthy lifestyle and is attentive to her new condition.
Main preventive measures:
- Rejection of bad habits. If a woman smoked before conception, then during the period of bearing the baby and feeding him, you should forget about smoking.
- Timely treatment of infectious viral diseases. Gestation is not the time to experiment with your health.
- Maximum compliance with the doctor’s instructions if there is a risk of developing retrochorial pathology. In this case, you need to stay in bed and avoid physical and emotional stress. It is recommended to lie with a bolster or pillow under the pelvic area to drain the blood.
- Avoid bruises, injuries and falls.
- Do not lift or carry heavy objects.
- Monitor your diet. It is necessary to consume foods rich in vitamins that stabilize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system. It is advisable to exclude foods that cause constipation and gas formation in the intestines.
- Do not delay registration. The earlier the pathology is identified, the easier it will be to overcome it without consequences.
Watch an informative video on the topic of miscarriage: