22647
The appearance of any skin changes or rashes on a child’s body may indicate the development of various diseases. Sometimes the rash may be localized to only one place, such as on a child's neck or head. Before treating this condition, you need to find out the cause that triggered it.
Chickenpox, or chickenpox
Pathogen: Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV).
Method of transmission: airborne. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Immunity to chickenpox: lifelong. Produced either as a result of illness or after vaccination. In children whose mothers had chickenpox or were vaccinated against it, immunity to chickenpox is transmitted from the mother in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 10 to 23 days.
Infectious period: the entire period of the rash is 5 days after the last rash.
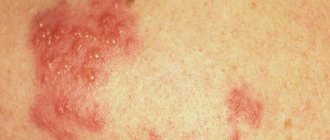
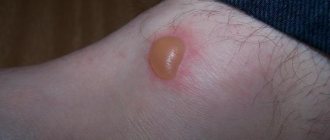
Manifestations: red dots appear simultaneously with a rise in temperature. However, sometimes the temperature may remain normal or rise slightly. The spots very quickly turn into single vesicles filled with a clear yellowish liquid. Soon they dry out and become crusty. A distinctive feature of chickenpox is a rash on the head under the hair and on the mucous membranes (in the mouth, on the eyelid, etc.). Very often this rash itches.
Treatment: chicken pox goes away on its own, so treatment can only be symptomatic: lower the temperature, treat the itchy rash with brilliant green (so that by scratching the blisters, the child does not introduce additional infection there), give an antihistamine to make itching less. You can swim if you have chickenpox! But at the same time, you should not rub the affected areas; instead, you need to gently blot them with a towel.
Important: you need to use brilliant green or other dyes (fucorcin, etc.) in order not to miss the next rash, because only old spots will be smeared. It is also easier to track the appearance of the last outbreak of the rash.
Rashes due to microclimate
A rash on the face and head of a month-old baby often appears not because of any special bacteria or fungi, but because parents do not maintain cool and humid air. The baby's head, especially covered with thick hair from birth, sweats intensely if the room where the baby sleeps is hot and dry.
Additional Information! You can observe an exacerbation of rashes on the face or back of the head immediately after sleep. When a child sleeps in a hot and unventilated room, the sweat glands work actively, the skin rubs against the bedding, which causes irritation.
Differential diagnosis of rash of infectious origin
Skin lesions due to infectious diseases are usually accompanied by fever and severe itching. There are a lot of pathologies in this group. Let's highlight the most common ones:
| Disease | Nature of the rash | Other symptoms | Consequences of the rash | Localization location |
| Scarlet fever | Small red dots. |
| Peeling. | The most pronounced rash is on the child’s neck, on the face (except for the nasolabial triangle), and in the folds of the skin. It does not spread as intensely throughout the body. |
| Rubella | Small pink spots. |
| No. | On the first day, the rash appears on the face, on the second and third it spreads throughout the body. |
| Measles | Bright pink tubercles. |
| Peeling, darkening. | On the first day, the rash appears along the hairline, behind the ears. In three days it covers the entire body. |
| Chicken pox | Bubbles with clear liquid. |
| If you make sure that the child does not scratch the pimples, there will be no marks left. Otherwise, scarring is possible. | First, a rash appears in the child’s hair and does not itch much, then it spreads throughout the body. |
| Meningitis | Bruises of different sizes. |
| Traces in the form of scars may remain. | The rash spreads over the torso and legs. |
The baby may have a fungal infection, which is caused by severe sweating of the feet and hands. Red spots appear between the fingers, and small pimples appear along the extremities. It is necessary to diagnose the disease and begin treatment immediately, otherwise the fungus will later become chronic if the parents realize what’s going on too late.
In what places does it most often occur?
The distribution of this disease throughout the body can be very heterogeneous. The rash can appear almost all over the body, or it can be located locally in one of the areas most susceptible to its occurrence. It is not uncommon for prickly heat to appear in the groin, which causes additional discomfort to the child. As a result, disturbed sleep and capricious behavior.
Where do rashes most often occur?
As mentioned earlier, heat rash is the result of high activity of the sweat glands when the baby overheats. The most vulnerable areas for her are the neck, back and face. At the same time, there is a lot of controversy regarding the appearance of prickly heat on the face. Each of these places is at risk for certain reasons that you should know.
Prickly heat on the neck of a baby
Since the newborn’s neck is quite short, it is at risk. Miliaria can form on it if the swaddling is too tight and due to the accumulation of saliva on the chin. Typically, the catalysts are high room temperature and improper child care.
Prickly heat on the back
In addition to overheating, risk factors include poor hygiene, too much diaper wear without resting the skin, and incorrectly selected biocreams. If you add sleeping linen and clothing made of synthetic materials to this, then the active spread of prickly heat is guaranteed.
Prickly heat on the face
The face is the most controversial area for the manifestation of heat rash, according to pediatricians. Some of them are of the opinion that there is no heat rash on the face and all redness and changes in the skin indicate the presence of an allergy.
The other part talks about the possibility of heat rash spreading to the face from the neck or ears if the child is too often wearing an overly warm and uncomfortable headdress. It is best to fight prickly heat on the face by wiping it with a decoction of string and chamomile or a weak solution of soda (no more than 1 teaspoon per 1 cup of water).
Doctor Komarovsky about spots on the back of the head
Doctor of the highest category, E.O. Komarovsky claims that children do not need hats indoors. Putting a cap on an infant greatly increases the likelihood of prickly heat. In addition, the mother may not always notice that after the baby burps, some of the milk flows down the cheek to the back of the head and remains under the cap. This situation can lead not only to irritation and heat rash, but also to the proliferation of pathogens on the baby’s skin.
Evgeniy Olegovich also warns against mistaking any other dangerous neoplasm for a harmless hemangioma. It is important to know the following distinctive features about hemangioma:
- it never appears in children older than one year, most often the child is already born with it or acquires it in the first weeks, maximum 3 months of life;
- hemangioma has three phases of development: the active growth phase, the fading phase and the reverse development phase;
- any hemangioma should be photographed regularly to provide the attending physician with reliable information about the progress of its growth and development.
These benign formations should be removed or treated, that is, their growth should be slowed down, in the following cases:
- the hemangioma is located in an area of the body that regularly comes into contact with elastic bands of clothing or shoes, which causes constant injury;
- the spot appears near the eye, on the mucous membranes, near the anus or in the ear area and grows inward;
- pigmentation caused a cosmetic defect on the face.
Important! Hemangioma is not inherited, most often occurs in girls, and is localized on the face, head and neck. It develops in newborns from multiple pregnancies; children with hemangiomas are also born to mothers whose age exceeds 40 years.
Any obvious changes in the color of the child's skin should be shown to a specialist. If pigmentation was noticed immediately after birth on the baby’s head, you should consult a neonatologist about its nature and safety for the baby. The vast majority of redness at the back of the head is generic and disappears on its own after a short period of time. Some obstetricians joke, reassuring young and confused mothers, that their child was accidentally pecked by a stork while rushing to deliver the baby.
Why might a child develop a rash on his face?
There are a lot of diseases that are accompanied by a rash. In order to distinguish them, you need to take into account the nature of the rash: color, size, dynamics of manifestation. The accompanying symptoms cannot be ignored. All rashes can be classified into 2 groups:
- primary - affecting healthy skin;
- secondary - appear as the primary develops.
The table shows the most common primary rashes:
| Appearance of the rash | Cause | Associated symptoms |
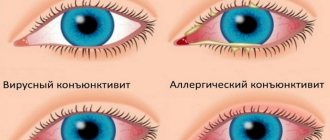
| Small red pimples. The boundaries are unclear, the rash appears in the form of clusters that can merge into one spot. | Allergy | Itching, drowsiness, bad mood, slight fluctuations in body temperature. Sometimes - redness of the eyes, runny nose. |
| “Mosquito bites” are pinkish or red pimples. They have a pronounced center surrounded by a border. The boundaries are clear, the number is gradually increasing. | Infectious diseases (measles, rubella, scarlet fever, etc.) | Severe increase in body temperature, chills, itching. |
| Rashes in the form of blisters filled with cloudy or white liquid. | Herpes | Severe pain in the area of the rash, increased body temperature (from 37.3 to 38°C). ARVI symptoms are often associated. |
| Watery pimples with a blackhead in the center. At first they appear in the form of compactions, but gradually become softer. | Molluscum contagiosum (we recommend reading: what molluscum contagiosum looks like in children: photo) | None. Rarely - itching. |
| Pink spots with purulent accumulations in the center. | Streptoderma (more in the article: effective treatment of streptoderma in a child) | Febrile fever, general intoxication of the body, enlarged lymph nodes. |
| White pimples on the mucous membrane of the mouth or around the lips (we recommend reading: why do rashes appear around a child’s mouth?). Accompanied by a cheesy coating. | Candidiasis | Burning in the affected areas, loss of appetite. |
| Small red pimples that appear after overheating. | Prickly heat | None. |
READ ALSO: 27 remedies for acne on the face: effective and inexpensive ointment, cream, pharmaceutical preparations and tablets for the treatment of acne and post-acne
Doctor Komarovsky about rashes in babies
There is a special type of rash characteristic of children from 6 months to 2 years. First, the child develops an elevated body temperature, the range of which varies from 37.5˚C to 38.5˚C. It persists for 3-4 days and is not accompanied by other symptoms characteristic of ARVI: there is no cough, runny nose or weakness.
Evgeniy Komarovsky, sharing his experience, reports that, despite the obviousness of the detection, this diagnosis is rarely made to children. The reason for the phenomenon lies in the parents - the average mother cannot simply look at a child with a fever and not use antipyretic medications. Therefore, according to the mother, the following picture emerges: the baby’s temperature rose, from which the mother gave antipyretic syrup, after which a rash appeared on the body. There is an allergic reaction to the components of the drug. It is this entry that is most often found in children's medical records.
Erytherma infectiosum, or fifth disease
Pathogen: parvovirus B19
Method of transmission: airborne. Most often, the infection occurs in children in organized children's groups - nurseries, kindergartens and schools.
Immunity: after illness - lifelong.
Incubation period: 6-14 days.
Infectious period: the incubation period is the entire period of the disease.
Manifestations: it all starts like a normal ARVI. Within 7-10 days, the child feels some discomfort (sore throat, slight runny nose, headache), but as soon as he “gets better,” a red, confluent rash appears on the cheeks, most reminiscent of mark from a slap.
At the same time or after a few days, rashes appear on the torso and limbs, which form “garlands” on the skin, but do not itch. The red color of the rash quickly changes to bluish-red. Over the next two to three weeks, the temperature remains low, and the rash appears and disappears, depending on physical activity, air temperature, contact with water, etc.
Treatment: there is no specific treatment, only symptomatic therapy. The disease goes away on its own, complications are extremely rare.
Types of rashes on the face in children of different ages
As already noted, the rash can be primary or secondary. Primary rashes are of greatest interest because they are the most common. It is with their diagnosis that difficulties arise. Based on shape and appearance, the following varieties are distinguished:
- Tubercles are non-hollow lumps on the skin.
- Blisters are dense areas that rise above the level of healthy skin. Blisters are an allergic reaction to poison from plants and insects.
- Papules, or nodules, are non-hollow elements that differ in height and color from healthy skin. They usually go away on their own.
- Bubbles are small pimples. They have a pronounced center filled with cloudy liquid.
- Bubbles are large formations (from 0.5 cm).
- Pustules are pimples filled with pus.
- Spots are changes in the color of the skin.
- Roseola are small pink or red spots that disappear when you apply pressure to the affected area.
Roseola nursery
Red rash
Acne can also appear in a child due to poor hygiene. If the baby is covered with bright pimples, then this is a skin reaction to pollution, to which children are especially susceptible in the first 6 years of life. To prevent your child from becoming covered with a painful crust on delicate areas of the skin, carefully monitor the baby’s cleanliness and accustom him to water procedures.
A consequence of unfavorable thermal effects is hyperhidrosis, or prickly heat. It manifests itself most clearly in infants, starting at one month of age. The baby’s body has not learned to adapt to the ambient temperature, so spots appear on his head and shoulders from sweat. All treatment comes down to frequent exposure of the little patient to the fresh air and regular ventilation of the premises.
Red spots on the forehead, cheeks and shoulders are often a sign of allergies. During lactation, this means that the mother should adjust her diet and also abandon aggressive household chemicals.
Allergic rashes
Red pimples in a child are also observed with toxic erythema. The rash occurs in the facial area: on the head, forehead, cheeks, nose. Newborns and babies under one year of age are most susceptible to it. This type of rash does not require specific treatment and disappears on its own within 7-8 days. At a later age, erythema is rare and, as a rule, is a consequence of uncomfortable living conditions: humidity, ambient temperature.
READ ALSO: Red bumps on a child’s tongue: finding out the causes and treating them
As mentioned above, red rashes can be infectious in nature and observed in the following diseases:
- measles;
- rubella;
- scarlet fever;
- chickenpox.
Chicken pox rash
The most dangerous possible cause of skin changes is meningitis. The disease is severe and in some cases is fatal. A characteristic feature of the infection is a rapid increase in body temperature and the gradual spread of an itchy rash throughout the body. If you have the slightest suspicion of meningococcal infection, you should immediately consult a doctor.
White pimples
Milia, or white pimples, are a type of acne that occurs in adolescents during hormonal changes. They are a small cyst formed as a result of excess sebum. Appear on the cheeks, nose, forehead. The causes of milia are varied: poor diet, poor-quality cosmetics, hormonal imbalance. As a rule, rashes disappear on their own with age (at 15-16 years of age). If not, you should visit a dermatologist or endocrinologist.
The predominant localization of milia is the area around the eyes, cheekbones, and T-zone (forehead-nose-chin). It is impossible to squeeze out such a tubercle - the source is deep under the skin. To get rid of white pimples on the face, you need to adjust your diet and provide quality skin care by choosing products that correct the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Similar rashes also occur in newborns and go away on their own within 1-2 months of life.
Milia in a newborn
Colorless rashes
Small colorless rashes that resemble nodules are called neonatal acne. Neonatal cephalic pustulosis appears on the face of children during the first month of life. This is how the baby’s skin reacts to the remnants of maternal hormones. No specific treatment is required - the baby will soon adapt to new living conditions. Acne usually goes away on its own within a few days, weeks or 1 year.
Colorless or flesh-colored watery pimples on the cheeks in later life may indicate a malfunction in the immune system: this is how a food allergy or reaction to emotional stress manifests itself. This phenomenon is called dyshidrosis. In emotionally stable children, it goes away on its own; otherwise, therapy is required, including the use of weak sedatives.
READ ALSO: Rash on the elbows of a child: photos with explanations, causes of rashes on the knees
Minor rash
If the fever is accompanied by low-grade body temperature (from 37.0 to 37.5 °C), allergic hyperemia, a systemic disorder or a sluggish infection occurs. In the presence of dermatological diseases (pyoderma, erythema, urticaria), body temperature may not increase.
Large purulent blisters
The appearance of purulent blisters can be caused by various factors:
- hormonal disorders;
- compaction of the apex of the epidermis - hyperkeratosis;
- improper skin care;
- abuse of low-quality decorative cosmetics;
- frequent stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Other types of rashes
Almost every person is familiar with acne on the face firsthand. They can appear at any age and significantly spoil plans. Children with immature immunity and during the period of hormonal changes are most prone to the appearance of acne and rashes (see also: photos of rashes and other manifestations of measles in children). In most cases, acne on a child’s face is normal, but sometimes a rash is a sign of dangerous pathologies.
Skin rashes in adolescents are a normal variant during the period of hormonal changes in the body
If the symptoms are not similar to any of the cases described above, you should pay attention to the table with explanations of other types of rashes.
| Type of rash | Description | Possible diagnoses |
| Ulcer | A deep defect of the skin and mucous membranes with the obligatory formation of a scar. | Diabetes, anemia, cancer, aerobic infections. |
| Crust | The dried contents of pustules, blisters or ulcers. | Herpes, eczema, diathesis. |
| Flake | Loosened horn cells. The skin is severely peeling at the affected area. Often localized on the head. | Ichthyosis, fungal infection, tinea versicolor. |
| Lichenization | Thickening, compaction, dry skin, pigmentation. The skin pattern is clearly visible. | Lichenification. |
Rubella
Pathogen: rubella virus
Method of transmission: airborne. The virus is transmitted through communication, coughing, and talking.
Immunity: lifelong. It is produced either after an illness or after vaccination. For children whose mothers had rubella or were vaccinated against it, immunity to rubella is transmitted in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 11 to 24 days.
Infectious period: from the 7th day from infection until the complete disappearance of the rash, another 4 days.
Manifestations: temperature rises. A small, pale pink, non-itchy rash appears on the face, limbs, and torso, and at the same time the posterior cervical lymph nodes enlarge. The temperature lasts no more than 2-3 days, and the rash goes away on the 2-7th day from its onset.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy only: drinking plenty of fluids, lowering the temperature if necessary, etc. Children tolerate the disease easily, but adults often experience complications. Rubella is especially dangerous in the first trimester of pregnancy: the virus crosses the placenta and causes congenital rubella in the baby, which can result in deafness, cataracts or heart defects in the newborn. Therefore, everyone, especially girls, is strongly recommended to undergo vaccination against this disease.
Dangerous consequences
Advanced cases of skin inflammation in infants can lead to scars that will last a lifetime. A rash similar to urticaria, significantly worsening after each meal and accompanied by itching, may indicate fermentopathy. This phenomenon occurs when the liver and pancreas do not produce enough enzymes, causing any food to cause rashes because it cannot be digested.
The most dangerous rash is the one that does not look like pimples, but like small hemorrhages. If you press on such redness with your finger, it will not lighten. This is a sign of meningococcal infection, which is very dangerous due to its consequences for the brain and life of the child. As soon as such a rash appears, you need to rush to the hospital, the hours are counting.
Causes of rash on the face and head of a baby
Among the huge number of possible prerequisites, pediatricians identify several of the most common:
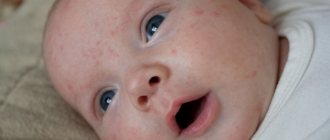
- Newborn acne is red or white bumps with a raised center. They are similar to acne that appears in humans during puberty. It is noteworthy that such a rash does not itch and does not bother the baby in any way. Acne is not contagious and goes away without special procedures (many parents mistakenly start treatment with fucorcin and brilliant green). The main thing is to keep your skin clean until maternal hormones are cleared from the body.
- A rash from irritation is the result of excessive drooling and poor hygiene. When saliva constantly comes into contact with the skin, small reddish rashes appear that can itch or hurt. Therefore, during the period of active eruption of the child’s first teeth, it is necessary to wash his face more often than on ordinary days.
- Milia (bloom) is not a disease, but rather a symptom of clogged sebaceous pores. This happens due to the immaturity of the excretory and hormonal systems of the newborn. Milia is a small rash on the face and head of a newborn that only takes time to disappear.
- Erythema toxicum is a common phenomenon that occurs in infants after direct contact with allergens. These are hyperemic hot red spots. They can be located on the face, sometimes occupy areas of the skin around the joints, and are found on the chest. The pathology most often occurs in full-term infants against the background of an allergic reaction; it can have a severe form, in which manifestations return a couple of weeks after therapy. For treatment, a nursing mother should exclude the possible allergen from her menu. Pediatricians prescribe antihistamines and diuretics.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a rash in the form of light yellow or brownish scales that occurs most often on the scalp. There may be several reasons for the pathology, ranging from hormonal imbalances to the spread of yeast-like fungi on the skin.
Causes of rashes in an infant (photo and description)
During infancy, from 1 month to 1 year, the skin of infants is susceptible to many pathologies.
READ ALSO: Diet for acne: which foods are ok and which are not?
This is caused by the following reasons:
- allergies;
- violation of hygiene rules;
- influence of maternal hormones;
- infections.
Hormonal rash – neonatal pustulosis
A small, red rash may appear in newborns in the first days and weeks after birth. This is the so-called hormonal rash.
The child’s hormonal system is rebuilt, begins to function independently and rejects the mother’s hormones.
Remnants of maternal hormones are released through the skin in the form of neonatal pustules. They look like papules with a white tip.
Usually located on the upper half of the body:
- head;
- forehead;
- cheeks;
- neck;
- back.
If proper skin care is not taken care of, a child may develop a fungal infection.
Separately, a rash is distinguished on the face and on the head (cephalic) in infants. They will be caused by the still imperfect functioning of the sebaceous glands or follicles and the simultaneous rapid proliferation of lipophilic yeast-like fungi such as Malassezia on the child’s face. Sometimes they are detected by light palpation.
The concern is that you may miss the signs and rashes caused by meningitis.
Signs of allergies
The appearance of a red rash on the cheeks of a baby primarily indicates the presence of an irritant.
- food products, drinks, mixtures;
- household items, clothing, toys;
- baby care products;
- environment, heat, cold, tobacco smoke.
After feeding, the mother will always notice the baby’s painfully pink cheeks and can guess what foods this happened after: those that she consumed herself or gave to the baby in complementary foods.
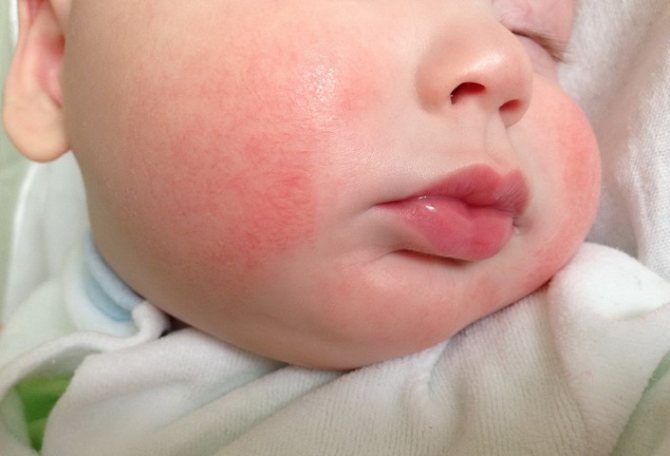
If a small red rash in a newborn does not disappear, merges, gets wet, crusts and peeling appear - you need to look for and identify the allergen.
Until the allergen is identified, the nurse herself must adjust her diet.
Avoid obviously allergenic foods:
- chocolate;
- citrus;
- honey;
- canned food;
- smoked meats
If the red rash and peeling on the face and body of the baby do not go away, you need to change the mixtures and carefully study their composition.
Additions to feedings should be done carefully, step by step. Start juices with drops, gradually increasing each day.
It is necessary to review the composition of creams, ointments, sprays, and powders that are used to treat the skin of babies.
Understand the toys, find out what material they are made of, who the manufacturer is.
Buy from natural fabrics:
- bed sheets;
- towels;
- blanket;
- diapers;
- baby vests;
- sliders;
- booties.
We need to find out if there are any smokers nearby. Maintain a constant indoor temperature.
Diaper dermatitis
Very often, children suffer from diaper dermatitis. It usually occurs on the body in places of contact with wet diapers, diapers, and diapers.
If you do nothing, the process progresses. Redness gives way to irritation, bright red diaper rash appears, and painful cracks form on it. Ulcers appear in their weeping gaps.
READ ALSO: Rash on the body of a child without fever: what the rash looks like and what causes it
The result depends only on proper care of the child. It is within the power of any mother to prevent such irritations.
If such a disaster has happened, it is necessary to more strictly control the hygienic care of the baby’s skin - wash it after each diaper change, bathe the child in string or chamomile, use baby creams and powders with zinc oxide.
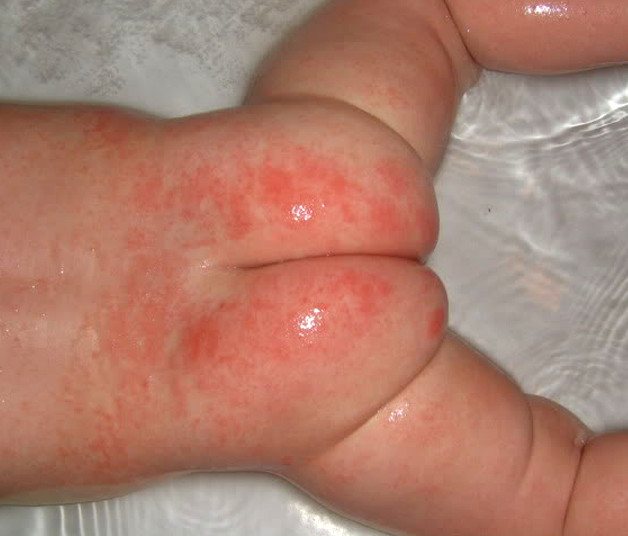
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis develops in children with a hereditary predisposition.
It will be provoked by food products entering the child’s body and the mother’s body during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
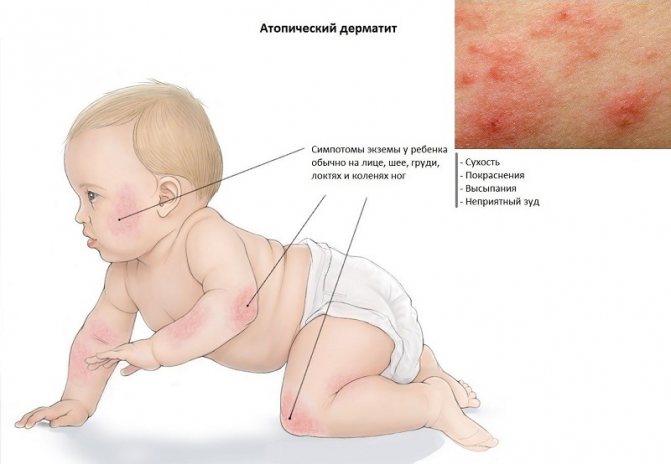
Scientists have found that the main allergen is whole milk protein. In second place are the proteins of soybeans, eggs, cereals, and fish.
The leading role in the development of dermatitis is given to the state of the digestive organs of the baby, the selection of food products of the mother during feeding and during pregnancy.
The child should not be overfed. Pasty children are more likely to suffer from atopic dermatitis.
The disease is dangerous because, starting with redness, peeling and itching of the cheeks and buttocks, the process expands and spreads, capturing the deeper parts of the skin on the body.
The resulting blisters become ulcers, the itching intensifies, greatly disturbing the baby.
Timely identification and elimination of the allergen will help to get rid of the disease faster.
Video from Dr. Komarovsky about atopic dermatitis:
Infectious rashes
Infectious rashes are caused by viruses, bacteria and fungi.
Fungal rashes are easily distinguished by the clear boundaries of clusters of small rashes. They quickly dry out, become covered with a white or yellowish coating, which is very flaky.
Among bacteria, a rash on a child’s body is most often caused by staphylococci and streptococci.
Infection with staphylococci manifests itself as pustular diseases.
Streptococcal infection is recognized by the appearance of a small red rash or blisters on the legs, arms, and face of a newborn. Blisters filled with exudate burst and the wounds dry out into crusts.
Viruses cause severe infectious diseases:
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- chicken pox;
- rubella;
- Infectious mononucleosis.
The main signs of these diseases will be:
- heat;
- cough;
- a sore throat;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache;
- abdominal pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The rash will be a characteristic sign for each of them and distinguish them from each other.
Usually, rashes start from the scalp in the scalp, behind the ears, then appear on the face, cheeks, neck, and then go down to the body. They are found on the stomach, back, and buttocks. Then they cover the limbs up to the feet.
To make it easier to identify which infectious disease, here is a rash recognition table:
READ ALSO: Boil in the nose, boil: treatment at home, boil inside the nose in adults and children, autopsy
| Disease | Type of rash | Color | Place and time of appearance |
| Infectious mononucleosis | Various in shape and size | Red | On the 5th – 6th day. On the face, less pronounced on the body. |
| Measles | Large spots, papules | Bright red | For 3 – 5 days. Appears behind the ears, along the hair, down to the feet. Step by step: face – torso – limbs. |
| Rubella | Small spots | Pale pink | Right from day 1. On the face, all over the body. |
| Scarlet fever | Small dots | Bright red on congested skin. Pale nasolabial triangle. | For 1 – 2 days. All over the body, worse in the folds. |
| Chicken pox | Spots, papules, blisters with liquid. Crusts. They develop gradually. Coexist at the same time. | Red | On the 2nd day. On the head, face, torso, mucous membranes. |
Symptoms and types of rashes
In order to figure out why a rash appeared on the head or body of a baby, you should remember all the events that preceded it, which may include:
- using a new detergent;
- buying new synthetic clothing;
- walking with a child in the hot season using a synthetic carrier;
- the mother of a breastfeeding child happily ate three oranges;
- Grandmother made delicious tea with condensed milk for the baby.
These are all common causes of rashes in children. In addition, if the rash has clear boundaries, each pimple contains a white head that becomes larger every day and then dries, it is most likely a bacterial infection.
Important! Pediatricians distinguish a bacterial infection from an allergic reaction by the appearance of the rash. As a rule, the presence of a white head on pimples indicates the presence of pus under the skin, which most often occurs as a result of the development of a staphylococcal infection.
A rash behind the ears in a child, spreading over the scalp, which is accompanied by severe peeling, may be seborrheic dermatitis. This condition is similar to dandruff in adults. By analyzing the fallen off crusts, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Rash in children for the first time days and weeks of life
Between 1 and 6 weeks of age, residual exposure to maternal hormones causes increased sebum production. The ducts of the sebaceous glands become clogged, as happens later in adolescence and young adulthood. When a rash appears on the head of an infant, it is advisable to take the baby to the doctor to determine the exact cause. The fact is that hormonal factors, allergies, and infections can initially give the same clinical picture.
Neonatal pustular eruption, or acne of newborns, is a rash on the scalp that almost always disappears within the first year of life. In dermatology, pustules are skin formations, inside of which there is a cavity filled with pus. There is a natural physiological process of formation of a rash in a child under the influence of mother’s hormones. Red spots and papules (lumps without cavities) appear on the scalp and face. In addition, pustules with white and yellow tips appear.
Newborn acne does not cause discomfort, is not dangerous, and does not leave scars.
Acne usually appears during the first four weeks, but may be present at birth. In addition to the rash on the forehead, the formation of nodules and pustules on the cheeks and upper chest is observed. Inflammation begins in children with a hereditary predisposition to such a reaction of the body to hormones. Hot and humid conditions in the children's room and improper care of the child's skin contribute to suppuration.
Apply a solution of 1% methylene blue to the pimples 3 or 4 times a day. If a yeast infection is involved in the inflammatory process, then creams with antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects are used. Pediatricians prescribe oral medication in severe cases.
Miliaria in the form of red dots and blisters occurs in the folds of the body. The affected areas are washed daily with a solution of potassium permanganate, a decoction of oak bark, and infusions of herbs (chamomile or chamomile). Cosmetic creams and ointments clog pores and increase inflammation.
Rash in infants
In newborns, rashes on the scalp appear for the following reasons:
- Formation of hormonal levels. The so-called neonatal rash appears immediately after the baby is born and lasts for several weeks or months. If the pimples do not spread to other parts of the body and cause discomfort to the child, then there is no reason to worry.
- Diathesis. If the child is breastfed, then the rash occurs in response to food allergens in the mother's diet - chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs. Redness of the skin can also be caused by an incorrectly selected formula if the child is transferred to artificial feeding.
- Diaper rash. Failure to comply with the temperature regime and too warm clothes cause prickly heat. It looks like a small rash that spreads throughout the body.
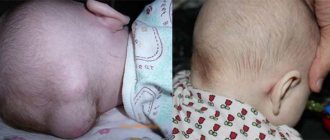
Rash on the back of the head in a baby
Childhood is the most memorable age for parents, and any illness during this period causes increased concern. The occurrence of a rash can have a different nature and course. To find out the cause, first of all, determine the appearance of the rash.
Types of skin rashes:
- Papules are small nodules that are easily felt when touched. They are usually uniform in color;
- The spots can be isolated on the skin, or they can be grouped. Their color is very different: from light gray or pink to burgundy;
- Blistering rashes are usually filled with serous fluid, which can be multivariate. Sometimes they may contain pus and are called pustules;
- Erosion usually severely damages the skin and always produces discharge. Quite often, infections are associated with erosions.
The factors that provoke these rashes are very diverse. A rash on the body can be a consequence of a change in temperature, underwear, or as a manifestation of a viral disease.
Rash in a child
There can be many causes of a rash in a child, but the main ones are:
- Improper nutrition of a mother who is feeding her baby with her own milk and a child who is feeding on his own. Often women do not know what can be consumed and what should be avoided when eating foods that cause allergies in children. For example, citrus fruits are strictly prohibited; berries, fruits, red vegetables; chocolate; cow's milk; nuts, especially peanuts; legumes In addition, they are very difficult for digestion even by an adult organism, and even more so for the digestive tract of an infant. This can cause colic, spasms, and indigestion in a child, resulting in dysbacteriosis, which also causes skin rashes. Children under three years of age should limit allergic foods, as well as fried, fatty, spicy, smoked foods - the right food is the key to health.
- The next reason is improper hygiene. So, bathing a child too rarely leads to the fact that he may develop heat rash, which first appears in the form of small pimples on the rash on the head and behind the ears. Later, red spots begin to appear around them. This is more typical for the age of the baby, especially if he is constantly in a room with high air temperatures or is wearing a hat all the time. Too frequent bathing can also cause various kinds of reactions to excessive drying of the skin, which at the same time loses its protective abilities against harmful microorganisms. This is especially evident when the hair care product is incorrectly selected. For infants and children under three years old, it is best to buy shampoo intended for newborns. It contains a minimum of chemical additives that cause irritation. You should wash your hair with it no more than once a week. On other days, it is better to use water with the addition of herbal decoctions: chamomile, calendula, burdock. They act as antiseptics, while soothing and not drying out the skin.
- Damage by pathogenic microorganisms. These could be bacteria, fungi, mites. They easily multiply on the delicate skin of a child if it is not properly cared for or the immune system is weakened. To identify the pathogen and begin treatment (otherwise you won’t get rid of it), you need to submit a scraping of skin tissue and a few hairs for laboratory testing.
- Viral diseases are very common among children. The most common include: measles, chicken pox, rubella. In addition to the rash, which most often appears on the scalp, abdomen, face, and neck, the child may have a fever, runny nose, diarrhea, and vomiting. To protect your baby and yourself from such diseases, you need to be vaccinated against them. Although many doctors recommend specifically placing the child in a social circle with infected children, so that he can survive the disease in childhood, since in adulthood it threatens with serious consequences. But it is worth remembering that it is better to protect the baby from the disease, since the body is still developing until the age of three and exposure to various types of viruses can cause serious deviations. At the first suspicion of these diseases, you should take your child to a dermatologist.
- Lice are the most common parasite found in hair. He lies in wait for a child in a kindergarten or school, where there is a large concentration of children. In order to identify and destroy parasites in time, you need to check the baby’s head twice a week under good daylight. The lice themselves are hard to see, but their eggs can be seen. They have a yellowish iridescent color with a black dot inside, and are well attached to the hairs. Lice lay their eggs mainly on the back of the head, so this is the part of the head that needs to be examined especially carefully. As you can see, there are quite a few reasons for the appearance of a rash on the scalp in infants and older children, but they all affect his health in one way or another. Therefore, at its first manifestations, you must go to the hospital to receive timely treatment.
Causes of the disease
The main factor causing heat rash in infants is excessive wrapping. As a result, thermoregulation of the skin is disrupted and a rash appears, accompanied by burning and itching. The baby becomes restless, sleeps poorly, and breaks out of his usual daily routine. Pediatricians warn caring parents not to dress their child like an “onion,” but to create comfortable conditions in the room (temperature from 19 to 22 °C, at which he does not even need a hat).
Miliaria may appear due to parents’ failure to follow the rules for caring for a newborn. Until the age of six months, it is recommended to bathe him daily, preferably before bed. You can use decoctions of calendula, thyme, yarrow, oak bark or special herbs to provide a calming effect. They are prepared at the rate of 3 tbsp. l. vegetable raw materials per 1 liter of boiling water. However, you need to know that the series dries out the skin. Before bathing, it is advisable to treat the reddened areas with chamomile decoction, but again remember that in some it can provoke allergies. A baby's heat rash will probably go away if he is given baths with walnuts, which contain a lot of iodine.
After water procedures, the baby’s body must be thoroughly blotted, and powder should be applied to the folds with a cotton swab. Some of its types contain panthenol for the regeneration of scratched wounds, as well as anesthesin for a cooling effect. Only after the doctor’s approval can you use Drapolen, Desitin, Bepanten ointments, which accelerate skin healing. We must not forget about air baths in the form of short “walks” naked, which strengthen the child, strengthen his health, and serve as a preventive measure for prickly heat.
A rash is only a consequence, not a cause, of prickly heat . The condition is provoked by:
- Diathesis.
- Atypical reaction to blood clotting.
- Mechanical impact on the baby's delicate skin.
- Infections.
- Allergy.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends:
- Wipe the affected areas with a solution prepared from 250 ml of water and 1 tsp. baking soda.
- Every day, give your baby the opportunity to feel the cool air without tight diapers.
- In summer, bathe up to 4 times a day. To harden, add sea salt to the water, which will kill germs and also saturate the skin with useful microelements.
But if there is vomiting or bleeding on the rash, seek medical help immediately.