Vascular spots on the skin of a child
Vascular spots on the skin of a child in most cases appear if disorders of the circulatory or vascular systems are diagnosed. They can have a variety of shapes and sizes depending on the reasons for their appearance.
The rashes can be single or multiple, convex and flat, homogeneous or differ in texture. Pigmentation can spread throughout the body or be localized in small areas.
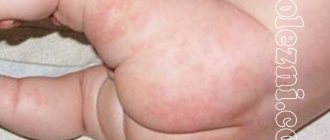
Most often, children have red spots; the pigments have a bright red tint, but dark purple is also considered the norm. There are many examples in the photo of what vascular spots look like in infants.
Reasons for appearance
The cause of the appearance of vascular formations is a violation of the blood supply. Therefore, the child has vascular spots on the body.
There are other factors that provoke the appearance of pigmentation. These include:
- infectious diseases in a woman at the beginning of pregnancy, when the circulatory system develops in the fetus;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in which the expectant mother lived;
- hereditary predisposition in the baby, if one of the parents has such a pathology.
If a vascular spot appears in a newborn, you need to visit a pediatrician to examine the baby.
Varieties
Rashes in children are divided into several types. Taking into account the type of pigmentation and the level of danger, the doctor selects adequate treatment.
Flat hemangiomas
Hemangiomas are superficial plaques of various shapes and sizes. Their color ranges from bluish to scarlet. They protrude slightly above areas of the skin. Pigmentation does not require removal. By the age of 7 it goes away on its own.
Capillary hemangiomas
These are flat-shaped formations, which in color resemble wine-purple spots due to the pronounced vasodilation in this place. They resemble several mature, slightly dilated blood capillaries, which are located asymmetrically to each other.
The spots are localized on the face, a red spot on the forehead of a newborn, on the eyelids. The formations slightly rise above healthy areas of the skin. They have clearly defined boundaries and a dense texture. They are hard to the touch.
Stellate hemangioma
The formation resembles a small nodule the size of a match head. Small blood vessels branch out from it in various directions in the form of peculiar rays.
The location is the ears, the surface of the face, the upper part of the body, and the inside of the hands. The disease is observed in the child from the first days of birth and goes away on its own within a year without therapy.
Tuberous-cavernous hemangioma
This hemangioma looks like a tumor that rises above healthy skin. Vascular spots in newborns are localized on the face, on the buttocks, and rarely in the oral cavity.
The plaques have a lumpy structure with blood-filled cavities. They are soft on palpation. They have brown or bluish tints.
Angiodysplasia
The disease is associated with a defect in the proper development of blood vessels. The pigments have a variety of shades from light pink to bluish.
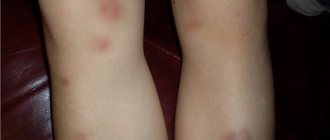
The surface of the formations is smooth and even. Vascular spots may appear on the legs, arms and other places on the skin.
Cavernous hemangioma
The appearance of formations is provoked by disturbances in the quality of the hematopoietic system. Nodules protruding above healthy skin acquire a light shade when lightly pressing on them.
When injured, they can transform into ulcers that must be urgently removed due to the risk of infection. Often in children, red vascular spots on the legs, arms and other parts of the body indicate the presence of cavernous hemangioma.
Their appearance is associated with malfunctions of internal organs due to lack of blood circulation. After diagnostic procedures, the doctor can determine the name of the disease. Only after this is the question of choosing a therapeutic treatment or method of removing plaques.
Treatment
Vascular lesions do not always require treatment. If a child has flat angiomas, they are monitored. If they do not change in size, removal is not necessary. By the age of 7-9 years, such rashes go away on their own. If the color, shape and size of the plaques change, the doctor prescribes removal, selecting an effective method.
Laser therapy is most often used. This is a safe method of therapy in which a beam of laser beams is applied to the plaque without damaging the structure of healthy areas of the skin.
This prevents the appearance of wounds, and prevents the occurrence of inflammatory processes and infection. Laser beams burn out the plaque and after a week it disappears.
After the procedure, scars and cicatrices do not appear. After removing the pigmentation, a wound remains, which heals on its own in 1-2 weeks.
Removal is possible using the coagulation method. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. An electric current is applied to the plaque, cutting out the root. After the procedure, a wound remains, which is treated with antiseptic drugs for 7-10 days. After removal there is a possibility of scarring.
If a newborn has a vascular spot on the leg or other areas of the skin, cryodestruction is resorted to. The removal method involves exposing the plaque to liquid nitrogen. The procedure lasts a maximum of 3 minutes.
The doctor treats the surface of the skin using a special apparatus with ultra-low temperature nitrogen. The rash itself and the intercellular fluid are frozen, which is why the vital activity of cells stops.
The plaque tissues are gradually destroyed and over time replaced by new, healthy ones. After the procedure, small scars remain, which will disappear on their own over time.
It does not matter what type of vascular rash the child has pigmentation. Parents independently constantly monitor the size and color of the hemangioma, so that in case of minor deviations or other changes, contact their pediatrician in a timely manner.
Do not forget that this type of pigmentation is a tumor, which will lead to negative consequences if injured and damaged.
Conclusion
Doctors warn! Shocking statistics - it has been established that more than 74% of skin diseases are a sign of parasite infection (Accarida, Giardia, Toxocara).
Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which should protect the body from various diseases.
The head of the Institute of Parasitology shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that it’s enough... Read more...
You should not resort to self-medication. Ointments and traditional medicine recipes will not help get rid of hemangiomas. By cauterizing them, there is a risk of causing injury and introducing infection into the wound. For this reason, the pigmented plaque is likely to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Therefore, treatment and removal are carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Source: https://kozhamed.com/sosudistyie-pyatna-na-kozhe-u-rebenka/
Treatment options
Note! Never start treatment
port-wine stains
before puberty
. These formations are prone to spontaneous disappearance, leaving no traces behind. The use of cryodestruction or, especially, surgical removal in childhood can lead to the formation of rough scars and facial asymmetry. Treatment should begin only after the start of puberty.
Methods for removing a flaming nevus include: Surgical removal
Recently
it has not been used
due to the leaving behind rather rough scars, which is unacceptable due to the peculiarities of the location of the nevus.
Photo 3. Laser removal is the most modern and least traumatic way to remove nevi.
Vascular spots in newborns or hemangiomas. Causes and methods of treatment
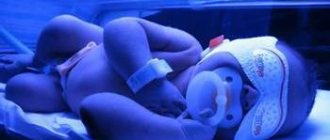
The appearance of vascular spots on the skin of a newborn, alas, is not uncommon. They can be of completely different shapes and different colors: from light pink to wine-burgundy. They can especially cause concern for parents because they develop very quickly and increase in volume, reaching 10 centimeters in diameter.
Causes of vascular spots
Good to know: vascular spots or hemangiomas arise as a result of inadequate blood supply to certain parts of the body, therefore the functioning and structure of the circulatory system is disrupted.
The exact causes of this childhood disease have not yet been determined. Pediatricians are still only making assumptions, putting forward certain theories:
- the disease develops in children whose mothers suffered from a cold or infectious infection in the first or second month of pregnancy. It is during this period that the baby’s circulatory system develops;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in the place where the mother lived during pregnancy;
- the disease is transmitted by heredity, so if the father or mother of a newborn suffered the disease in their childhood, then the baby cannot avoid this either.
Type of vascular spots
There are several types of spots that occur in newborns. Depending on this type, a decision is made about the level of danger of the disease and how to treat it.
Types of vascular spots:
- Flat angioma . The disease manifests itself in the form of crimson dots, which can be located on any part of the body. During childbirth they are invisible and appear during the first month of the child’s life. This type of hemangioma occurs quite often in children.
Good to know: Most often this disease appears as a single red dot in a specific location, but sometimes they can appear in several places at the same time.
Flat angioma can be located both on the skin and on the tissues of internal organs.
The likelihood of such spread increases with a large number of hemangiomas that are located on the face or upper body.
Please note that the hemangioma grows with the child, so during the first six months it increases significantly in size, which often frightens parents.
Important: if you find such red dots, be sure to contact your pediatrician. Most spots go away on their own by age 7, but sometimes they need to be treated. The doctor will help you understand your situation and explain how to treat this disease correctly.
- Capillary hemangiomas . The disease occurs as a result of deformation of the capillaries and is characterized by the appearance of a collection of them in one place, which thus form a spot. They appear on the surface of the skin even before birth and are immediately visible. Capillary hemangiomas themselves do not go away; they require treatment and consultation with a doctor. This type of disease most often has a purely cosmetic nature. Sometimes cases arise in which hemangiomas can cause more complex diseases that require further treatment. For example, the location of such a spot near the eyes can lead to the development of glaucoma. Therefore, it is imperative to visit a pediatrician to control this spot: its size, location and nature.
- Angiodysplasia . The disease is considered a malformation of blood vessels. The spots have a different color shade: from soft pink to cherry purple. They have a smooth surface, do not protrude on the skin, tend to darken and are a significant cosmetic drawback.
- Cavernous hemangioma . The disease occurs due to a disturbance in the structure of blood vessels . The structure is nodular, protrudes above the surface of the skin, and can lighten when pressed. The size of the spot can change both larger and smaller. Such hemangiomas can cause the development of infectious ulcers, so their removal or treatment is an urgent need, because such ulcers can directly interfere with the full functioning and development of internal organs.
Treatment of vascular spots
Initially, you must consult a doctor. You should not start treating such spots on your own. First of all, contact a specialist to examine and monitor the stain.
Depending on what type of disease is diagnosed, subsequent treatment decisions will be made.
Most often, the main reason for treatment is a cosmetic issue, since in most cases vascular spots are considered harmless.
Flat angiomas require only observation. If they do not increase beyond normal limits, then they are not removed. They disappear on their own after a few years: by the age of 7-9 they do not remain.
Capillary hemangiomas and angiodysplasias are also not treated until about two years of age, allowing them to disappear on their own.
Spots can be removed if they interfere with the development of facial muscles. So they can be removed using a vascular laser.
This method is also used if you want to remove this flaw due to the appearance not meeting cosmetic standards.
Cavernous hemangiomas are recommended to be removed immediately when they occur. To do this, several different ways to exclude the disease are used.
Good to know: if the hemangioma is small in size, it is removed by electrocoagulation or cryodestruction. For this, local anesthesia is used.
If the spot located on the body is large, then surgical intervention is used.
Modern technologies make it possible to carry out the procedure as painlessly as possible and leave minimal scars, which later become completely invisible.
Regardless of what type of hemangioma was discovered, it is worth treating the resulting spot very carefully. Remember to monitor the size and color of the hemangioma. If there are minimal changes or deviations, you should immediately consult a doctor. Don’t forget, hemangioma is a tumor and therefore requires attention.
Folk remedies cannot help in the treatment of hemangioma. The fact is that the only suitable remedy is celandine juice, which has significant cauterizing properties. Therefore, its use may cause ulceration of the tumor.
In addition, incorrect treatment of the disease can cause the situation to worsen: a hemangioma can become malignant, that is, a hemangioma, which is a benign tumor, turns into a malignant one.
That is why herbal decoctions or other medicinal substances can be used exclusively to disinfect the surface of a stain in case of injury.
vascular spots in newborns
0
Source: https://best-nyanya.ru/zdorove-rebenka/bolezni-u-detej/23-sosudistye-pyatna-u-novorozhdennyh.html
Signs of benign formations
The reasons for the development of nevus include a hereditary factor. Children with white skin, premature babies, and girls are more susceptible to this disease. There is also an opinion that the formation of a fiery nevus is facilitated by a lack of oxygen in the child during passage through the birth canal. The appearance of the spot is also associated with the pressure of the pelvic bones on the child’s scalp.
Strong pressure causes paralysis of blood vessels, due to which a spot is formed.
Signs of fiery nevus:
- The nevus is visible immediately after birth.
- The spot is most often located on the bridge of the nose, eyes, and the back of the head.
- The shape of the spot is most often irregular with a red or pale pink tint.
- The formation does not itch or hurt.
- When the child cries, the nevus becomes bright. The spot on the forehead is usually the most saturated. Sometimes it appears during the first months of life.
- It does not rise above the skin, does not grow, and after time some regression is visible.
- When you press on the spot, it turns pale.
- If the nevus is not located on the face, then there is a high probability that the spot will not disappear. In half of the cases it remains on the back of the head, but is invisible due to the hair.
Nevus of Unna may turn red and pale
Vascular, red spot on the forehead of a newborn – Website about osteochondrosis
Not all parents know why a red spot appears on the forehead of a newborn, what types it comes in and what should be done. This problem is very common, but in most cases it is not dangerous and does not require urgent intervention.
If this suddenly turns out to be the case, you should immediately consult a doctor and not make any independent decisions.
Is a birthmark fraught with danger? It is impossible to say for sure without studying the specific education. It is very important to examine the baby after birth to identify the problem. When making a diagnosis, it will be important whether the formation appeared immediately after birth or arose later.
What are the reasons
This problem can arise due to various circumstances. However, most often this is a consequence of a hormonal imbalance that was in the mother’s body, as well as the fact that she was in poor environmental conditions during pregnancy.
Here are other possible causes:
- lack of food in the mother, both in quantitative and qualitative terms;
- genetically determined tendency to such formations;
- hypoxia that occurs in the fetus;
- Rhesus conflict.
Also, postpartum spots can form due to pregnancy pathology, for example, due to the incorrect position of the fetus, which it assumed in the last weeks of the process. Because of this, the newborn develops areas with poor blood supply and dilated capillaries.
The latter leads to the fact that a person eventually develops small or large spots or even groups of them, which can go away quickly, over many years, and in rare cases, not go away at all. That's why you should definitely pay attention to the problem.
What are postpartum spots?
There are several variations of this problem. Each of them has its own characteristics of course and treatment.
Here are the main spots that a newborn may encounter:
- hemangiomas;
- nevi;
- telangiectasia.
There are other varieties that appear from birth, but they are much less common. Among them are hematomas. They may not be so quickly recognized by medical personnel, and therefore it is very important that the child is examined in a timely manner by experienced doctors. A good dermatologist will immediately determine what kind of formation it is and what measures need to be taken.
Not all of these problems require treatment. For example, a hematoma goes away on its own. However, if any of these phenomena are detected on the skin, it is necessary to diagnose it immediately, as this will avoid problems in the future.
A separate discussion is whether it is worth removing stains that do not pose a danger and will definitely go away on their own in a few years. It is better for parents to think about how a defect such as a spot between the eyebrows will affect the child’s fate in kindergarten and school. But here everything depends on the individual situation and the parents’ views on this issue.
Hemangiomas
This is the name given to formations of small vessels that have not developed to a normal state. The shade of hemangioma may vary.
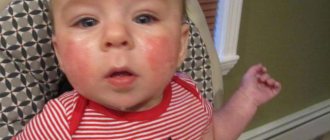
There are formations of bluish, purple, and pink colors. Some intermediate shades are possible, but a specialist can easily identify this problem. If a baby has purple spots on the forehead, it may be a hemangioma. The problem is quite common: out of a dozen children, one is a carrier.
Simple hemangioma
Represents convex areas. These places have a color that can be compared to the color of strawberries at the peak of ripeness. The red spot can be located on the forehead between the eyebrows, but is more common on the back of the head.
After more than three such formations have been detected, the specialist will refer you for an ultrasound of the internal organs. By the age of nine or ten, the formations will disappear on their own. So unless they're particularly noticeable, it probably won't cause your child any problems.
Nevi
These are pigmentation and moles, reddish or brown in color, essentially a lot of melanocytes that can appear at any age. However, most often they occur in children. Sometimes this phenomenon can also occur in newborns.
In this case, the dermatologist offers one or another monitoring of the problem, depending on its nature and dynamics of development. This will allow you to avoid complications in the future and accurately establish the diagnosis.
- A simple nevus is a redness in a newborn that can occur as a large red spot on the forehead or spots. Simple nevus is the scientific name, and the trivial one includes “stork’s kiss.” This problem occurs in a quarter of children. The disease goes away with difficulty, and sometimes it doesn’t go away at all.
- Flame nevus is an even more serious problem, because over time it retains its color and does not fade. This is a red formation of a purple hue and a convex shape. It causes almost no discomfort: it does not bleed, does not itch, or becomes inflamed. The appearance of such a nevus may indicate problems with brain activity. It can be easily removed with laser.
Telangiectasia
These are ordinary blood ducts that are just slightly dilated. There is nothing critical here. Such enlarged vessels are a remnant of embryonic vessels, a rudiment. Seventy percent of newborns have it. As a person grows up, these spots will gradually disappear.
Vascular spots in newborns or hemangiomas. Causes and methods of treatment
The appearance of vascular spots on the skin of a newborn, alas, is not uncommon. They can be of completely different shapes and different colors: from light pink to wine-burgundy. They can especially cause concern for parents because they develop very quickly and increase in volume, reaching 10 centimeters in diameter.
Diagnostics
A red, asymmetrical birthmark on a newborn’s forehead or back of the head can be easily detected by visual examination. Such a baby requires close attention of a neonatologist and geneticist. In isolated cases, the presence of Unna's nevus on the skin signals dangerous genetic disorders. To exclude them, the newborn needs a consultation with a neurologist, an ophthalmologist and the necessary tests. Spots on the back, arms and legs should be examined by a vascular surgeon to ensure that there is no defect in the blood supply to the affected area. During diagnosis, it is important to completely exclude hemangioma, a vascular tumor that tends to grow in size and bleed.
If no anomalies are detected, doctors advise parents to calm down and wait until the baby is 2 years old. A stain that has not resolved by this time can be removed for aesthetic reasons.
Vascular spots on the skin of a child and a newborn, photos and causes – About the skin
In newborns, vascular spots can be noticed immediately after birth. Their shape, color and texture vary. Most often, their appearance is caused by genetic reasons, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
What are port wine stains
This is a congenital pathology in which flat vascular formations with unclear boundaries appear on the skin. It occurs in both girls and boys. The origin of the disease has not yet been clarified, but experts say with confidence that the problem is not related to the use of medications while carrying a child.
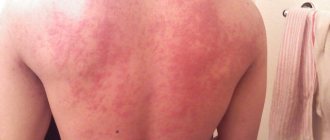
Flaming nevus - this is another name for the disease - can be localized in any part of the body. Typically, the disease affects the side of the head and the back of the head, located on the limbs or in the center of the face. As the child grows, the spots also grow. Because they are close to the surface of the skin, their color varies from pink to dark purple.
Nevus are often confused with birthmarks. But if the latter disappear on their own during the first year of life, then the former grows and becomes coarser over time. The rash is usually observed on the baby's face and neck.
Causes of the disease
Numerous studies have helped to establish the causes of the formation of port-wine stains; in particular, the disease develops in newborns in cases where the contact of the nerve roots with the capillary walls is disrupted. Because of this, the vessels spontaneously expand, fill with blood, which stagnates and forms a purple area on the skin.
Until recently, doctors believed that port-wine stains disappeared on their own. But most often they only increase in size, causing discomfort to the child. Today, nevus responds well to treatment. The main thing is to start it as early as possible. In addition, it is important to establish that these are port-wine stains and not birthmarks.
Statistics show that the most susceptible to developing the disease are:
- premature babies;
- fair-skinned children;
- girls.
There is also an opinion that the appearance of neoplasms is provoked by hypoxia, which develops during the movement of the child through the birth canal.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is the formation of red spots in newborns. On palpation they turn pale. It should be remembered that such rashes never itch, become inflamed or bleed, but do not disappear without treatment. As the baby grows, the nevus grows. With age, the tumors may become cyanotic.
In some cases, nevus signals genetic diseases that need to be constantly monitored and treated. These include:
- Sturge-Weber-Krabbe syndrome - a port-wine stain is considered a type of benign tumor. The pathology can manifest itself as paresis, movement disorders, seizures, and glaucoma.
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome - rashes accompanied by dwarfism and low mental development. The baby’s body grows disproportionately, and paired organs may be located asymmetrically.
- Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome - nevus is localized on the legs or one of the arms. As a rule, neoplasms are complemented by varicose veins. In some cases, pathologies develop in the development of blood vessels, as a result of which venous blood mixes with arterial blood, oxygen starvation and intoxication begin. The child has limb gigantism.
- Cobb syndrome - a port-wine stain in an infant is observed along the spine and causes damage to the vessels located in the spinal cord. A characteristic symptom of the disease is paralysis, in which the sensitivity of the legs suffers.
If your newborn has port-wine stains, you should talk to a geneticist. When the nevus affects the limbs, the help of a vascular surgeon will be required. Spots localized in the spine area may also indicate pathology. To prevent the development of Cobb syndrome, it is advisable to go to a pediatric neurologist.
How to cure nevus
As the child develops, the nevus may thicken, grow, and change color. If it is located on the legs, face and other parts of the body, the disease causes discomfort. Therefore, therapy is mandatory.
The following methods will help rid your child of unpleasant stains:
- Laser treatment is an effective procedure that can be performed at any age. After the session, the patient is sent home. The laser beam penetrates the skin and affects the dilated blood vessels, as a result of which the blood cells stick together and the problem disappears.
- Surgical treatment is performed in cases where laser therapy does not produce results. But it is prescribed very rarely - due to the long rehabilitation period.
- Cryotherapy – the spots are frozen using liquid nitrogen. It promotes the death of affected cells and skin restoration.
One of the methods of treating the disease is alternative medicine recipes. The most popular means are:
- Celandine juice - applied to the problem area and covered with a band-aid, the procedures are carried out for ten days, after which the stain lightens and becomes less pronounced.
- Juice of unripe figs – it is recommended to lubricate the skin once a day.
- Chalk and hemp oil provide a lasting whitening effect.
- Honey and castor oil - apply to the stain for three minutes twice a day.
Folk remedies will help reduce the brightness of the spots, but are not able to completely cure flaming nevus. Therapy should begin immediately after detection of the disease.
Parents should remember that the older the child, the more difficult it is to get rid of port wine stains.
Danger of disease
As the nevus develops, it causes many problems.
The spot can change its color, increase in size and even disrupt important functions.
The flat texture becomes embossed, and painful papules form on it. If they are damaged, they begin to bleed and heal slowly. The moral aspect plays an important role, especially in adolescence, when children are very vulnerable.
As a rule, port-wine stains do not cause dangerous complications, but they still need to be removed. This will help solve the aesthetic problem and prevent the risk of developing seborrhea and psoriasis.
Prevention
Flaming nevus has the ability to recur. To avoid its reappearance, you should follow simple rules:
- Follow a diet and exclude unhealthy and spicy foods from the child’s diet.
- Avoid any tanning – sun exposure increases the risk of relapse.
- Protect your baby from sudden temperature changes, as they can lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
- Do not use aggressive cosmetics.
By following these rules, you can not only cure the disease, but also prevent the possibility of its recurrence in the future.
Source:
Red spots on the skin of a newborn
Various marks on the skin of newborn babies are not uncommon. Doctors claim that almost every second baby is born with red spots on the skin.
Spots in newborns
Vascular spots on the skin of infants cause concern among parents, because doctors are not always able to clearly explain the features of such marks. And vascular spots in newborns on the face or open areas of the body, as well as formations of especially large sizes and rich colors, become a cause of serious anxiety.
In fact, a vascular spot on the skin of a newborn does not always require anxiety and panic. Sometimes such a phenomenon is considered completely natural and transitory. So, doctors distinguish several types of such marks:
- Reddish bundles of choroid plexuses that are visible through thin skin. Such meshes are especially often visible on the head, namely on the eyelid, in the middle part of the forehead, and also on the back of the neck. Such spots are considered completely safe; they disappear without a trace or become noticeably pale when the baby grows a little, and his skin naturally becomes thicker.
- Telangiectasia or spider veins. They are also called "stork bites" or birthmarks. They can be localized in different parts of the body, but most often on the back of the neck.
- Hemangiomas or benign tumors.
- Symptoms of angiodysplasia, which is a malformation of blood vessels.
Only a qualified doctor can accurately determine the cause of the appearance of red spots on the skin of a baby. Additional research techniques may be necessary.
Telangiectasia
The occurrence of such formations is explained by the prolonged presence of the fetus in the mother's womb in a forced position (embryonic position).
Shortly before birth, the baby is pressed tightly against the mother's muscular wall and the bones of her pelvis, and local ischemia (inadequate blood supply to tissues) may develop in areas of maximum pressure.
As a result of this, the baby is born with red spots on the skin - areas of expansion of superficial vessels:
- With the most common occipital presentation, marks appear in the hair growth area - on the top of the neck. A red spot on the back of a newborn’s head is most often a “stork bite.”
- In babies born facing forward (with a face presentation), such marks may be visible on the upper lip, bridge of the nose, tip of the nose and chin. Surprisingly, the eyelids are very often affected, which is most likely due to the particularly thin and vulnerable skin in these areas.
- Sometimes vascular spots in a newborn are located on the back, along the spinal column. In the lumbar region, such marks can merge, forming a large triangle or diamond.
- Much less often, the birthmark is visible on the buttocks or forehead.
As a rule, as the baby grows, telangiectasias begin to gradually fade, becoming more noticeable during periods of great anxiety and tension. Most often, they disappear without a trace by the age of five years of a child’s life. However, there is a risk that such marks will remain with the baby for life.
Doctors usually do not provide targeted treatment for telangiectasia. The areas of dilated vessels are completely safe for the child, cannot increase in size and gradually fade.
It is important to consider that red spots on the back of the baby’s head, as well as on other parts of the body, even with all their similarity to “stork bites,” can be caused by other factors, for example:
- Birth trauma.
- Various skin diseases.
- Allergic reactions.
- Heat rash, etc.
Only an experienced specialist can accurately determine the cause of the appearance of red spots.
Reasons for appearance
Experts do not have a consensus on what causes the defect.
- Many believe that most often port-wine stains are formed as a result of intrauterine developmental disorders of the superficial vessels of the skin.
- Sometimes the nerve endings responsible for capillary growth lose control of this process. The vessels stop contracting fully and change.
- The accumulation of dilated capillaries in the upper layer of the skin appears outwardly as reddish spots, the color of which becomes more saturated when the baby cries.
The second reason for the development of nevus of Unna is considered to be fetal hypoxia during childbirth. Powerful pressure during passage through the birth canal and lack of oxygen provoke changes in the blood vessels, which appear in the form of bright spots.
The hereditary factor plays a major role, so wine nevus is more often diagnosed in those children in whose families similar cases have been observed before. According to doctors, premature babies with fair skin and girls are more likely to develop the defect.